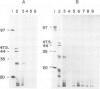
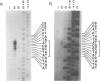
Abstract
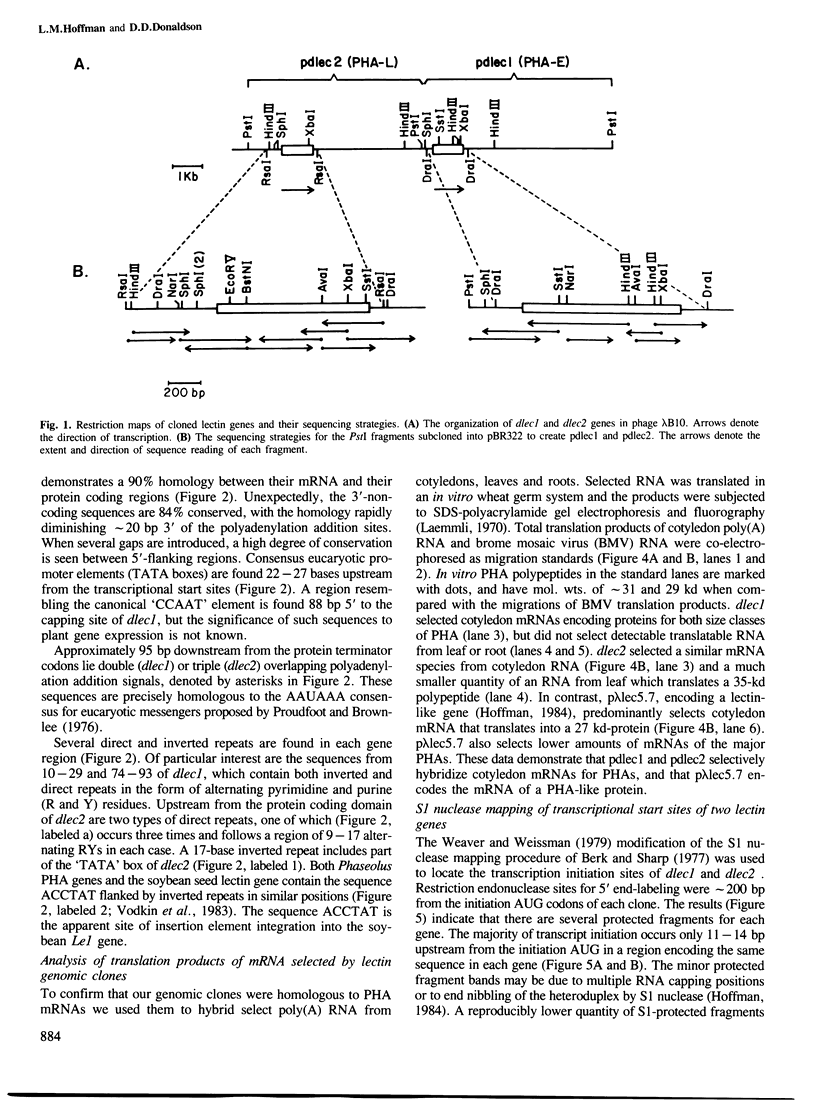
A lambda 1059 library of Phaseolus vulgaris cv. 'Tendergreen' DNA was screened with a cloned lectin-like cDNA. Among the phages selected was clone lambda B10 containing two complete lectin genes in the same orientation approximately 4 kb apart. The DNA sequences of the lectin genes and their flanking regions have been determined and their transcriptional initiation sites were located by S1 nuclease mapping. On the basis of the deduced amino acid sequences and compositions and the mol. wts. of their encoded glycoproteins, the genes, dlec1 and dlec2, are predicted to encode erythro- and leucoagglutinating phytohemagglutinins (PHA-E and PHA-L), respectively. The mRNA coding regions of dlec1 and dlec2 are 90% homologous, suggesting an origin involving duplication of an ancestral gene. Both lectin genes are intronless and have at least two ATG codons in a short (11-14 bp) 5'-untranslated region. Most of their 5'-untranslated regions consist of alternating pyrimidines and purines (RY repeats). Upstream sequences are also highly conserved between dlec1 and dlec2, including stretches of nine or more alternating R and Y residues. RY repeats of such length are not found within the protein coding portion of dlec1, dlec2 or a Phaseolus lectinlike gene previously described. Overlapping double (dlec1) or triple (dlec2) polyadenylation addition signals are found and there is an unusually high degree of homology (84%) between their 3'-untranslated regions.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brisson N., Verma D. P. Soybean leghemoglobin gene family: normal, pseudo, and truncated genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4055–4059. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coruzzi G., Broglie R., Cashmore A., Chua N. H. Nucleotide sequences of two pea cDNA clones encoding the small subunit of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase and the major chlorophyll a/b-binding thylakoid polypeptide. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1399–1402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coruzzi G., Broglie R., Edwards C., Chua N. H. Tissue-specific and light-regulated expression of a pea nuclear gene encoding the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1671–1679. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02031.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. A., Wang J. L., Waxdal M. J., Edelman G. M. The covalent and three-dimensional structure of concanavalin A. II. Amino acid sequence of cyanogen bromide fragment F3. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1503–1512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. W., Kaesberg P. Translation of virus mRNA: synthesis of bacteriophage Q beta proteins in a cell-free extract from wheat embryo. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1434–1441. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1434-1441.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foriers A., Lebrun E., Van Rapenbusch R., de Neve R., Strosberg A. D. The structure of the lentil (Lens culinaris) lectin. Amino acid sequence determination and prediction of the secondary structure. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5550–5560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halling S. M., Kleckner N. A symmetrical six-base-pair target site sequence determines Tn10 insertion specificity. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):155–163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90385-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins T. J., Chandler P. M., Zurawski G., Button S. C., Spencer D. The biosynthesis and primary structure of pea seed lectin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9544–9549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman L. M., Fritsch M. K., Gorski J. Probable nuclear precursors of preprolactin mRNA in rat pituitary cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):2597–2600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman L. M., Ma Y., Barker R. F. Molecular cloning of Phaseolus vulgaris lectin mRNA and use of cDNA as a probe to estimate lectin transcript levels in various tissues. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7819–7828. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman L. M. Structure of a chromosomal Phaseolus vulgaris lectin gene and its transcript. J Mol Appl Genet. 1984;2(5):447–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Hemperly J. J., Cunningham B. A. Amino acid sequence and variant forms of favin, a lectin from Vicia faba. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4473–4483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley D. E., Coleclough C., Perry R. P. Functional significance and evolutionary development of the 5'-terminal regions of immunoglobulin variable-region genes. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):681–689. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90184-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick M. W., Klysik J., Singleton C. K., Zarling D. A., Jovin T. M., Hanau L. H., Erlanger B. F., Wells R. D. Intervening sequences in human fetal globin genes adopt left-handed Z helices. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7268–7274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Comparison of initiation of protein synthesis in procaryotes, eucaryotes, and organelles. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):1–45. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.1-45.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Possible role of flanking nucleotides in recognition of the AUG initiator codon by eukaryotic ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5233–5252. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. B., Hsu R., Heinrikson R., Yachnin S. Extensive homology between the subunits of the phytohemagglutinin mitogenic proteins derived from Phaseolus vulgaris. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1388–1391. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordheim A., Rich A. The sequence (dC-dA)n X (dG-dT)n forms left-handed Z-DNA in negatively supercoiled plasmids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1821–1825. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnes J. R., Velan B., Felsenfeld A., Ramanathan L., Ferrini U., Appella E., Seidman J. G. Mouse beta 2-microglobulin cDNA clones: a screening procedure for cDNA clones corresponding to rare mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2253–2257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen K., Devereux J., Wilson D. R., Sheldon E., Larkins B. A. Cloning and sequence analysis reveal structural variation among related zein genes in maize. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):1015–1026. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90465-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah D. M., Hightower R. C., Meagher R. B. Genes encoding actin in higher plants: intron positions are highly conserved but the coding sequences are not. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(1):111–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slightom J. L., Sun S. M., Hall T. C. Complete nucleotide sequence of a French bean storage protein gene: Phaseolin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1897–1901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot C. F., Etzler M. E. Isolation and characterization of a protein from leaves and stems of Dolichos biflorus that cross reacts with antibodies to the seed lectin. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 18;17(8):1474–1479. doi: 10.1021/bi00601a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vodkin L. O., Rhodes P. R., Goldberg R. B. cA lectin gene insertion has the structural features of a transposable element. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):1023–1031. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90560-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiher H., König M., Gruss P. Multiple point mutations affecting the simian virus 40 enhancer. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):626–631. doi: 10.1126/science.6297005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiborg O., Hyldig-Nielsen J. J., Jensen E. O., Paludan K., Marcker K. A. The structure of an unusual leghemoglobin gene from soybean. EMBO J. 1983;2(3):449–452. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01443.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]