Abstract
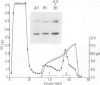
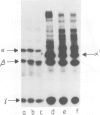
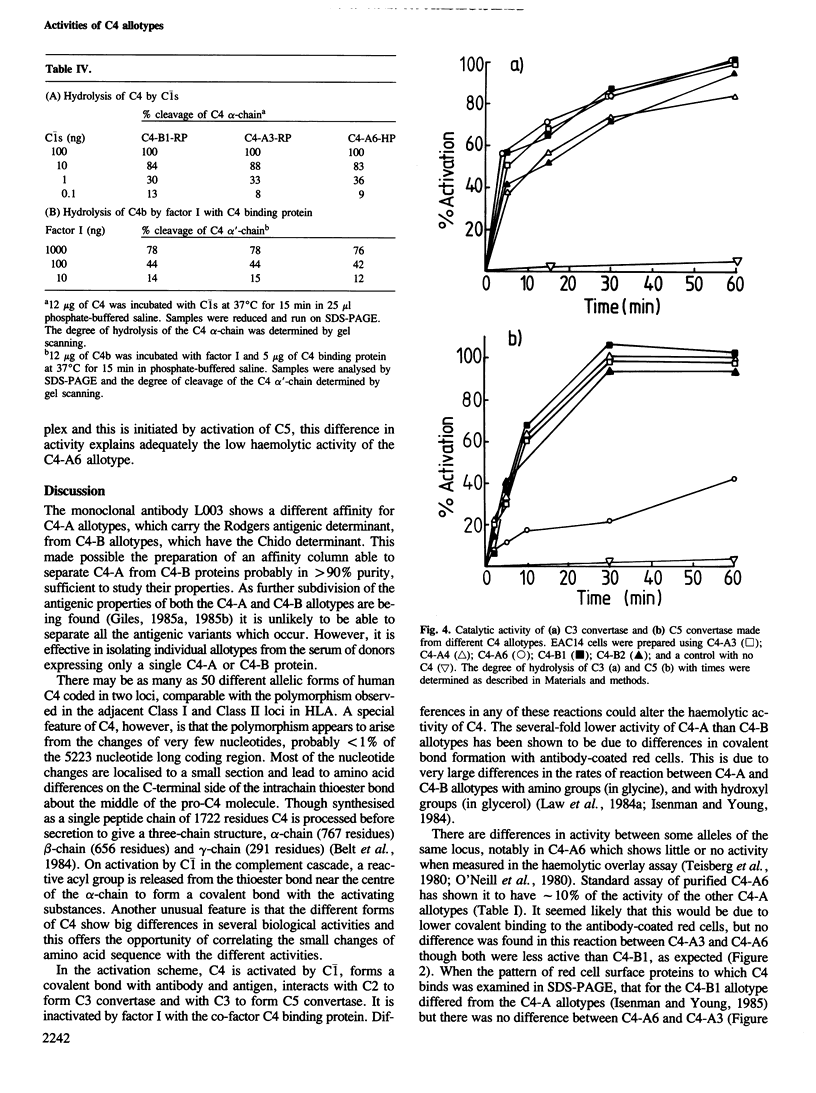
The human complement component C4 occurs in many different forms which show big differences in their haemolytic activities. This phenomenon seems likely to be of considerable importance both physiologically and pathologically. C4 is coded by duplicated genes between HLA-D and HLA-B loci in the major histocompatibility complex in man. Several fold differences in haemolytic activity between products of the two loci C4-A and C4-B have been correlated with changes of six amino acid residues in this large protein of 1722 residues and with differences of several fold in the covalent binding of C4 to antibody-antigen aggregates. Some allotypes of one locus also differ markedly, notably C4-A6 which has 1/10th the haemolytic activity of other C4-A allotypes. A monoclonal antibody affinity column has been prepared which is able to separate C4-A from C4-B proteins and, using serum from an individual expressing only the C4-A6 allele at the C4-A locus, C4-A6 protein has been prepared. Investigation has shown C4-A6 to have the same reactivity as other C4-A allotypes except in the formation of the complex protease, C5 convertase. This protease is formed from C4, C2 and C3 and if C4-A6 is used it has approximately 1/5th the catalytic activity compared with other C4-A allotype. Allelic differences in sequence identified in C4 proteins so far are few and it is probable that the big difference in catalytic activity of C5 convertase is caused by very small changes in structure.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belt K. T., Carroll M. C., Porter R. R. The structural basis of the multiple forms of human complement component C4. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):907–914. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90040-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belt K. T., Yu C. Y., Carroll M. C., Porter R. R. Polymorphism of human complement component C4. Immunogenetics. 1985;21(2):173–180. doi: 10.1007/BF00364869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsos T., Rapp H. J. Immune hemolysis: a simplified method for the preparation of EAC'4 with guinea pig or with human complement. J Immunol. 1967 Aug;99(2):263–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigli I., Porter R. R., Sim R. B. The unactivated form of the first component of human complement, C1. Biochem J. 1976 Sep 1;157(3):541–548. doi: 10.1042/bj1570541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigli I., von Zabern I., Porter R. R. The isolation and structure of C4, the fourth component of human complement. Biochem J. 1977 Sep 1;165(3):439–446. doi: 10.1042/bj1650439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giles C. M. 'Partial inhibition' of anti-Rg and anti-Ch reagents. I. Assessment for Rg/Ch typing by inhibition. Vox Sang. 1985;48(3):160–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1985.tb00164.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giles C. M. 'Partial inhibition' of anti-Rg and anti-Ch reagents. II. Demonstration of separable antibodies for different determinants. Vox Sang. 1985;48(3):167–173. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1985.tb00165.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer C. H., Wirtz G. H., Renfer L., Gresham H. D., Tack B. F. Large scale isolation of functionally active components of the human complement system. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3995–4006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiung L., Barclay A. N., Brandon M. R., Sim E., Porter R. R. Purification of human C3b inactivator by monoclonal-antibody affinity chromatography. Biochem J. 1982 Apr 1;203(1):293–298. doi: 10.1042/bj2030293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenman D. E., Young J. R. The molecular basis for the difference in immune hemolysis activity of the Chido and Rodgers isotypes of human complement component C4. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):3019–3027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. K., Dodds A. W., Porter R. R. A comparison of the properties of two classes, C4A and C4B, of the human complement component C4. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1819–1823. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02052.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. K., Levine R. P. Interaction between the third complement protein and cell surface macromolecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2701–2705. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. K., Lichtenberg N. A., Levine R. P. Covalent binding and hemolytic activity of complement proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7194–7198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. K., Minich T. M., Levine R. P. Covalent binding efficiency of the third and fourth complement proteins in relation to pH, nucleophilicity, and availability of hydroxyl groups. Biochemistry. 1984 Jul 3;23(14):3267–3272. doi: 10.1021/bi00309a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauff G., Alper C. A., Awdeh Z., Batchelor J. R., Bertrams J., Bruun-Petersen G., Dawkins R. L., Démant P., Edwards J., Grosse-Wilde H. Statement on the nomenclature of human C4 allotypes. Immunobiology. 1983 Mar;164(2):184–191. doi: 10.1016/s0171-2985(83)80009-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill G. J., Miniter P., Pollack M. S., Dupont B. Different HLA antigen associations for the functionally active and inactive products of the complement C4F1 allele. Hum Immunol. 1980 Jul;1(1):23–30. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(80)90006-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter R. R. Complement polymorphism, the major histocompatibility complex and associated diseases: a speculation. Mol Biol Med. 1983 Jul;1(1):161–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter R. R. The complement components of the major histocompatibility locus. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1984;16(1):1–19. doi: 10.3109/10409238409102804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B., Gagnon J. Human C4-binding protein: N-terminal amino acid sequence analysis and limited proteolysis by trypsin. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jan 11;137(1):75–79. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80318-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B., Porter R. R. The proteolytic activation systems of complement. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:433–464. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos M. H., Mollenhauer E., Démant P., Rittner C. A molecular basis for the two locus model of human complement component C4. Nature. 1982 Aug 26;298(5877):854–856. doi: 10.1038/298854a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teisberg P., Olaisen B., Nordhagen R., Thorsby E., Geddedahl T., Jr A haemolytically non-active C4 gene product. Immunobiology. 1980;158(1-2):91–95. doi: 10.1016/s0171-2985(80)80046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead A. S., Woods D. E., Fleischnick E., Chin J. E., Yunis E. J., Katz A. J., Gerald P. S., Alper C. A., Colten H. R. DNA polymorphism of the C4 genes. A new marker for analysis of the major histocompatibility complex. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jan 12;310(2):88–91. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198401123100204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson J. M. Variation in the N-terminal sequence of heavy chains of immunoglobulin G from rabbits of different allotype. Biochem J. 1969 Apr;112(2):173–185. doi: 10.1042/bj1120173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]