Abstract
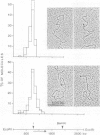
Stable ternary transcription complexes assembled in vitro, using a HeLa whole-cell extract, have been isolated and visualized by electron microscopy. The formation of these stable complexes on the DNA fragment used as template, the 5' end region of the Xenopus laevis vitellogenin gene B2, depends on factors present in the whole-cell extract, RNA polymerase II and at least two nucleotides. Interestingly, bending in the DNA fragment was frequently observed at the binding site of RNA polymerase II. Dinucleotides that can prime initiation within a short sequence of approximately 10 contiguous nucleotides centered around the initiation site used in vivo, also favour the formation of stable complexes. In addition, pre-initiation complexes were isolated and it was shown that factors in the extract involved in their formation are more abundant than the RNA polymerase II molecules available for binding. The possible implication of this observation relative to the in vivo situation is discussed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman S., Bunick D., Zandomeni R., Weinmann R. RNA polymerase II ternary transcription complexes generated in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 10;11(17):6041–6064. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.17.6041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C., Dubochet J. Electron microscopic localization of the binding sites of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase in the early promoter region of T7 DNA. Eur J Biochem. 1974 May 15;44(2):617–624. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03519.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brack C., Pirrotta V. Electron microscopic study of the repressor of bacteriophage lambda and its interaction with operator DNA. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jul 25;96(1):139–152. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90187-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunick D., Zandomeni R., Ackerman S., Weinmann R. Mechanism of RNA polymerase II--specific initiation of transcription in vitro: ATP requirement and uncapped runoff transcripts. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):877–886. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90449-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppola J. A., Luse D. S. Purification and characterization of ternary complexes containing accurately initiated RNA polymerase II and less than 20 nucleotides of RNA. J Mol Biol. 1984 Sep 15;178(2):415–437. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90151-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison B. L., Egly J. M., Mulvihill E. R., Chambon P. Formation of stable preinitiation complexes between eukaryotic class B transcription factors and promoter sequences. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):680–686. doi: 10.1038/301680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubochet J., Ducommun M., Zollinger M., Kellenberger E. A new preparation method for dark-field electron microscopy of biomacromolecules. J Ultrastruct Res. 1971 Apr;35(1):147–167. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(71)80148-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Isolation of transcription factors that discriminate between different promoters recognized by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):669–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fire A., Samuels M., Sharp P. A. Interactions between RNA polymerase II, factors, and template leading to accurate transcription. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2509–2516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germond J. E., ten Heggeler B., Schubiger J. L., Walker P., Westley B., Wahli W. Vitellogenin B2 gene in Xenopus laevis: isolation, in vitro transcription and relation to other vitellogenin genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 25;11(10):2979–2997. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.10.2979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronenborn A. M., Nermut M. V., Eason P., Clore G. M. Visualization of cAMP receptor protein-induced DNA kinking by electron microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 15;179(4):751–757. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90166-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Learned R. M., Tjian R. In vitro transcription of human ribosomal RNA genes by RNA polymerase I. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(6):575–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui T., Segall J., Weil P. A., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors required for accurate initiation of transcription by purified RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11992–11996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safer B., Yang L., Tolunay H. E., Anderson W. F. Isolation of stable preinitiation, initiation, and elongation complexes from RNA polymerase II-directed transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2632–2636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels M., Fire A., Sharp P. A. Dinucleotide priming of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2517–2525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels M., Fire A., Sharp P. A. Separation and characterization of factors mediating accurate transcription by RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14419–14427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stüber D., Bujard H. Organization of transcriptional signals in plasmids pBR322 and pACYC184. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):167–171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolunay H. E., Yang L., Anderson W. F., Safer B. Isolation of an active transcription initiation complex from HeLa cell-free extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):5916–5920. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.5916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vollenweider H. J., Szybalski W. Electron microscopic mapping of RNA polymerase binding to coliphage lambda DNA. J Mol Biol. 1978 Aug 15;123(3):485–498. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90092-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahli W., Germond J. E., ten Heggeler B., May F. E. Vitellogenin genes A1 and B1 are linked in the Xenopus laevis genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6832–6836. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P., Brown-Luedi M., Germond J. E., Wahli W., Meijlink F. C., van het Schip A. D., Roelink H., Gruber M., Ab G. Sequence homologies within the 5' end region of the estrogen-controlled vitellogenin gene in Xenopus and chicken. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2271–2279. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01734.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P., Germond J. E., Brown-Luedi M., Givel F., Wahli W. Sequence homologies in the region preceding the transcription initiation site of the liver estrogen-responsive vitellogenin and apo-VLDLII genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8611–8626. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil P. A., Segall J., Harris B., Ng S. Y., Roeder R. G. Faithful transcription of eukaryotic genes by RNA polymerase III in systems reconstituted with purified DNA templates. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):6163–6173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson J. K., Sollner-Webb B. Transcription of Xenopus ribosomal RNA genes by RNA polymerase I in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14375–14383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. The locus of sequence-directed and protein-induced DNA bending. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):509–513. doi: 10.1038/308509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Crombrugghe B., Busby S., Buc H. Cyclic AMP receptor protein: role in transcription activation. Science. 1984 May 25;224(4651):831–838. doi: 10.1126/science.6372090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Hippel P. H., Bear D. G., Morgan W. D., McSwiggen J. A. Protein-nucleic acid interactions in transcription: a molecular analysis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:389–446. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.002133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]