Abstract
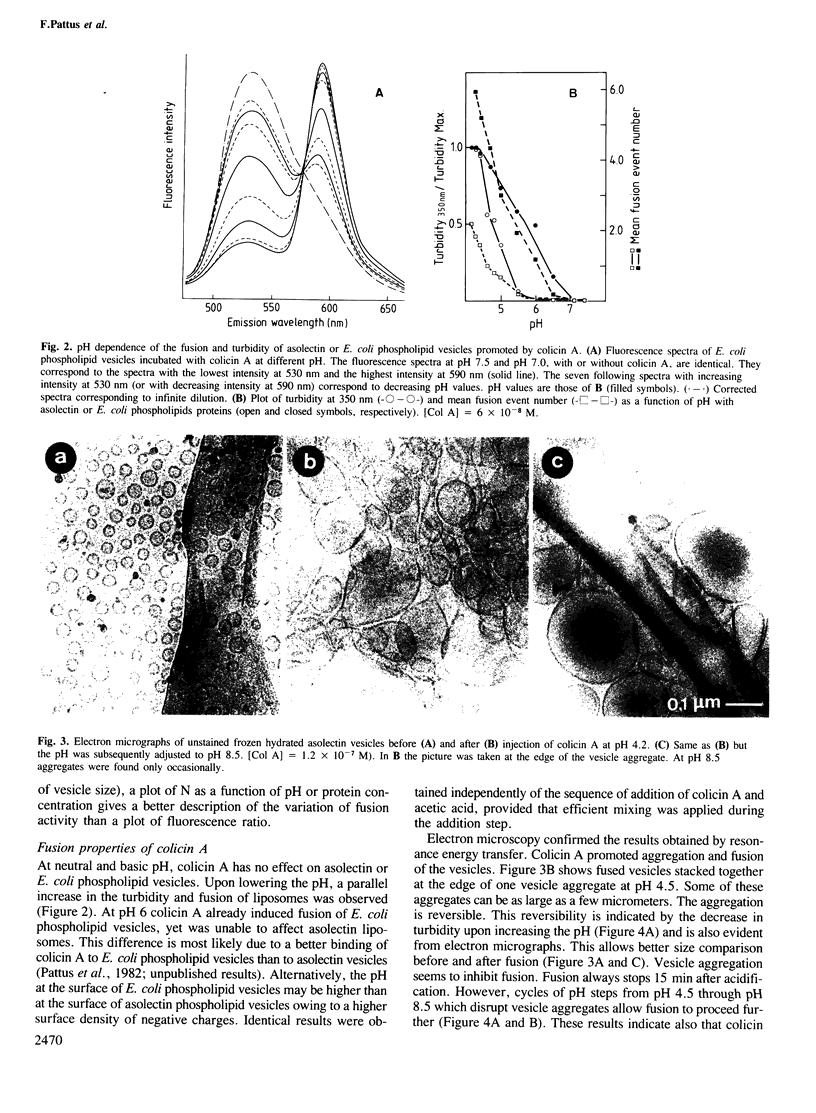
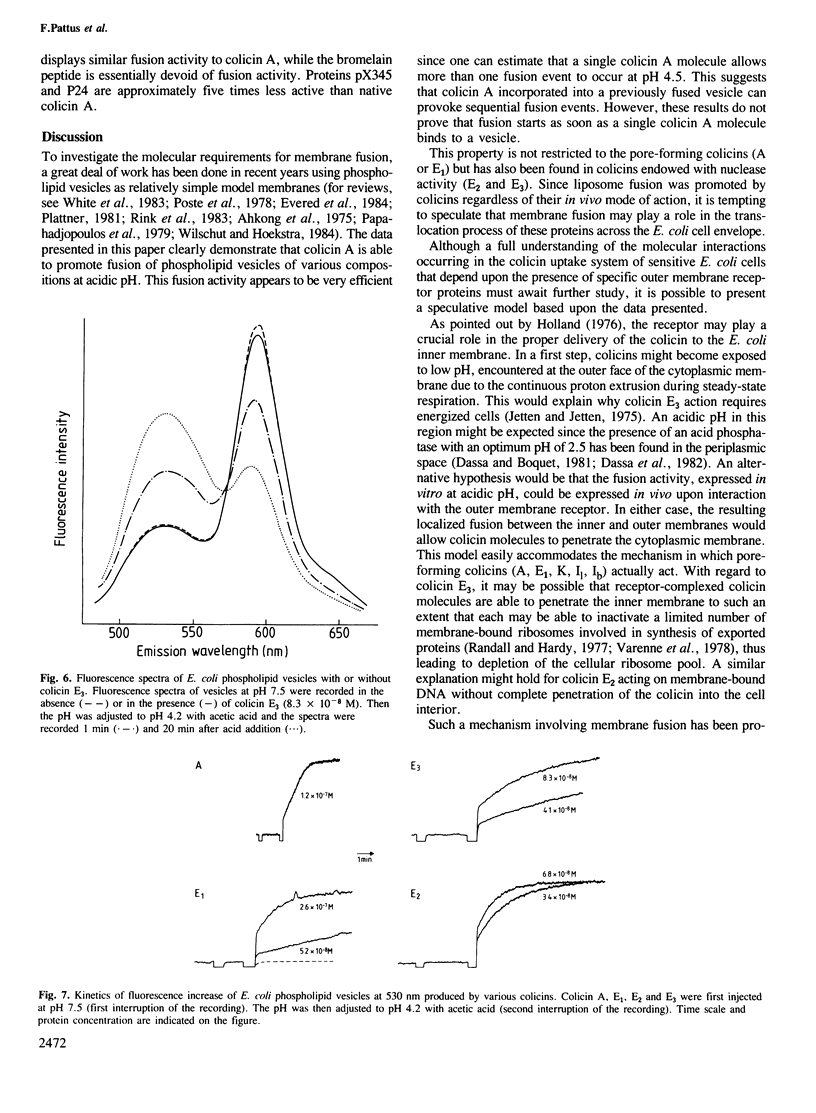
The ability of colicin A, a bacteriocin produced by some Enterobacteriaceae, to fuse phospholipid vesicles at acidic pH, was demonstrated by electron microscopy and resonance energy transfer. The fusion depends on protein concentration and on the nature of the phospholipids. Vesicles, prepared from Escherichia coli phospholipids, fused one or more rounds at pH 4.5 upon addition of stoichiometric amounts of colicin A. Fusion was not only induced by pore-forming colicins (E1, K) but also by colicins that contain nuclease activities (E2, E3). By recombinant DNA technology it is shown that the first glycine-rich 70 NH2-terminal amino acids and, most probably, the extreme COOH-terminal end of colicin A are involved in the fusion activity of the protein. The physiological relevance of this property of colicins is discussed.
Full text
PDF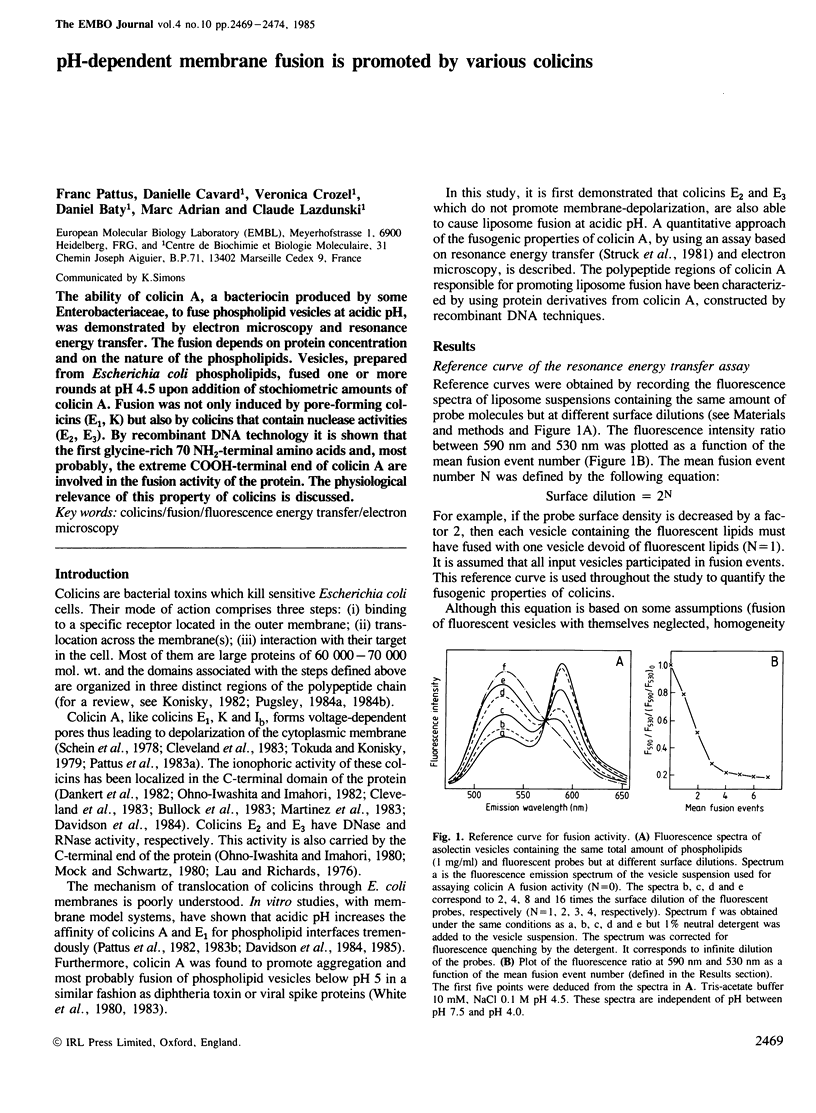



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian M., Dubochet J., Lepault J., McDowall A. W. Cryo-electron microscopy of viruses. Nature. 1984 Mar 1;308(5954):32–36. doi: 10.1038/308032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahkong Q. F., Fisher D., Tampion W., Lucy J. A. Mechanisms of cell fusion. Nature. 1975 Jan 17;253(5488):194–195. doi: 10.1038/253194a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavard D., Lazdunski C. J. Purification and molecular properties of a new colicin. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jun 1;96(3):519–524. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13065.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dassa E., Boquet P. L. Is the acid phosphatase of Escherichia coli with pH optimum of 2.5 A polyphosphate depolymerase? FEBS Lett. 1981 Nov 30;135(1):148–150. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80964-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dassa E., Cahu M., Desjoyaux-Cherel B., Boquet P. L. The acid phosphatase with optimum pH of 2.5 of Escherichia coli. Physiological and Biochemical study. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):6669–6676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dassa E., Tetu C., Boquet P. L. Identification of the acid phosphatase (optimum pH 2.5) of Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1980 May 5;113(2):275–278. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80608-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson V. L., Brunden K. R., Cramer W. A. Acidic pH requirement for insertion of colicin E1 into artificial membrane vesicles: relevance to the mechanism of action of colicins and certain toxins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1386–1390. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson V. L., Brunden K. R., Cramer W. A., Cohen F. S. Studies on the mechanism of action of channel-forming colicins using artificial membranes. J Membr Biol. 1984;79(2):105–118. doi: 10.1007/BF01872115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaastra W., Oudega B., de Graaf F. K. The use of mutants in the study of structure-function relationships in cloacin DF13. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 May 3;540(2):301–312. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90143-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jetten A. M., Jetten M. E. Energy requirement for the initiation of colicin action in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 14;387(1):12–22. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(75)90048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konisky J. Colicins and other bacteriocins with established modes of action. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:125–144. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.001013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau C., Richards F. M. Behavior of colicins E1, E2, and E3 attached to sephadex beads. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):666–671. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez M. C., Lazdunski C., Pattus F. Isolation, molecular and functional properties of the C-terminal domain of colicin A. EMBO J. 1983;2(9):1501–1507. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01614.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mock M., Schwartz M. Mutations which affect the structure and activity of colicin E3. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):384–390. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.384-390.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno-Iwashita Y., Imahori K. Assignment of the functional loci in colicin E2 and E3 molecules by the characterization of their proteolytic fragments. Biochemistry. 1980 Feb 19;19(4):652–659. doi: 10.1021/bi00545a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno-Iwashita Y., Imahori K. Assignment of the functional loci in the colicin E1 molecule by characterization of its proteolytic fragments. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6446–6451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plattner H. Membrane behaviour during exocytosis. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1981 May;5(5):435–459. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(81)90165-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P. The ins and outs of colicins. Part I: Production, and translocation across membranes. Microbiol Sci. 1984 Oct;1(7):168–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P. The ins and outs of colicins. Part II. Lethal action, immunity and ecological implications. Microbiol Sci. 1984 Nov;1(8):203–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall L. L., Hardy S. J. Synthesis of exported proteins by membrane-bound polysomes from Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1977 May 2;75(1):43–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11502.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T. J., Sanchez A., Hallam T. J. Diacylglycerol and phorbol ester stimulate secretion without raising cytoplasmic free calcium in human platelets. Nature. 1983 Sep 22;305(5932):317–319. doi: 10.1038/305317a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Rapid entry of nicked diphtheria toxin into cells at low pH. Characterization of the entry process and effects of low pH on the toxin molecule. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9068–9076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schein S. J., Kagan B. L., Finkelstein A. Colicin K acts by forming voltage-dependent channels in phospholipid bilayer membranes. Nature. 1978 Nov 9;276(5684):159–163. doi: 10.1038/276159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struck D. K., Hoekstra D., Pagano R. E. Use of resonance energy transfer to monitor membrane fusion. Biochemistry. 1981 Jul 7;20(14):4093–4099. doi: 10.1021/bi00517a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuda H., Konisky J. Effect of colicins Ia and E1 on ion permeability of liposomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6167–6171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varenne S., Piovant M., Pagès J. M., Lazdunski C. Evidence for synthesis of alkaline phosphatase on membrane-bound polysomes in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1978 May 16;86(2):603–606. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12344.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Helenius A. pH-dependent fusion between the Semliki Forest virus membrane and liposomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3273–3277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Kielian M., Helenius A. Membrane fusion proteins of enveloped animal viruses. Q Rev Biophys. 1983 May;16(2):151–195. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



