Abstract
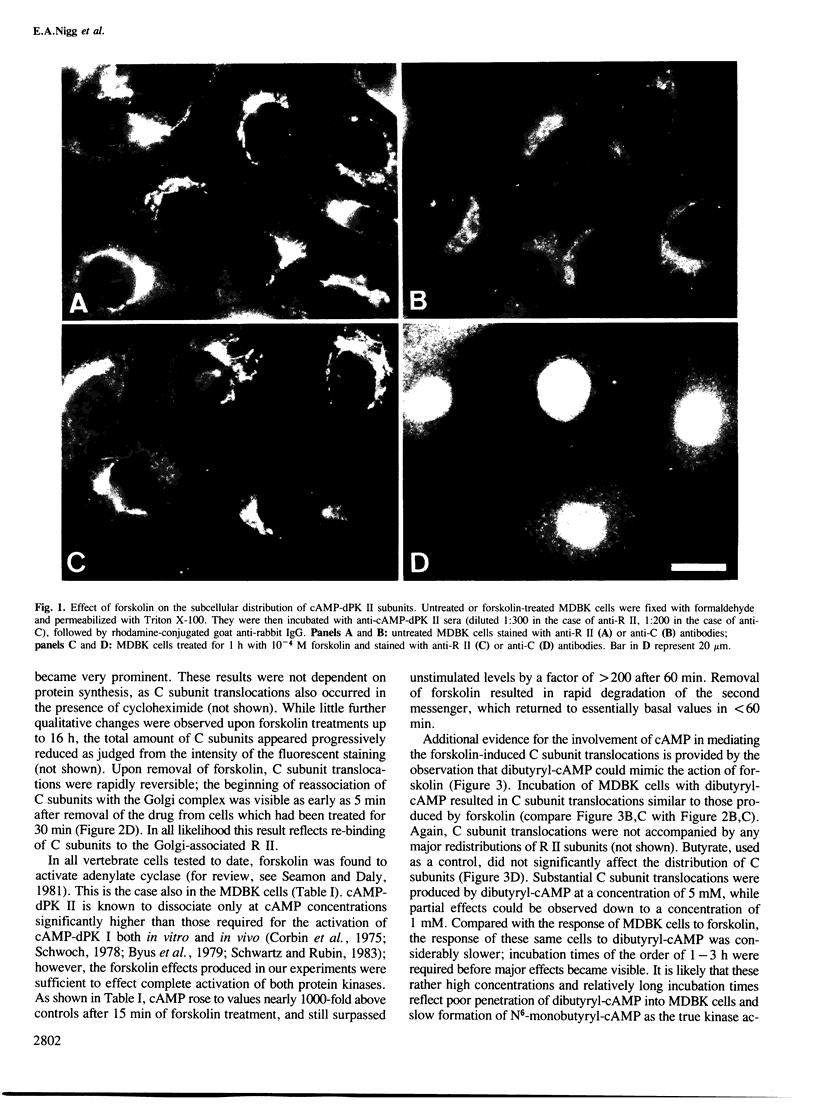
In unstimulated interphase bovine epithelial (MDBK) cells, both regulatory (R II) and catalytic (C) subunits of the type II enzyme of cAMP-dependent protein kinase (cAMP-dPK II) are associated with the Golgi complex. However, as demonstrated by indirect immunofluorescence microscopy, within 5 min after stimulation of adenylate cyclase by forskolin, the C subunit dissociates from the Golgi-associated R II and becomes diffusely distributed. With increasing time of forskolin treatment, C subunits accumulate in the nucleus, while R II subunits remain associated with the Golgi complex. The effect of forskolin is rapidly reversible in that C subunits begin to reassociate with the Golgi complex within a few minutes after drug removal. C subunit translocations similar to those produced by forskolin also occur after treatment of MDBK cells with dibutyryl-cAMP, confirming that the observed effects are most likely mediated by elevation of intracellular cAMP levels. These results suggest that nuclear translocation of activated protein kinase subunits may represent an important link between hormonal stimuli and physiological responses.
Full text
PDF
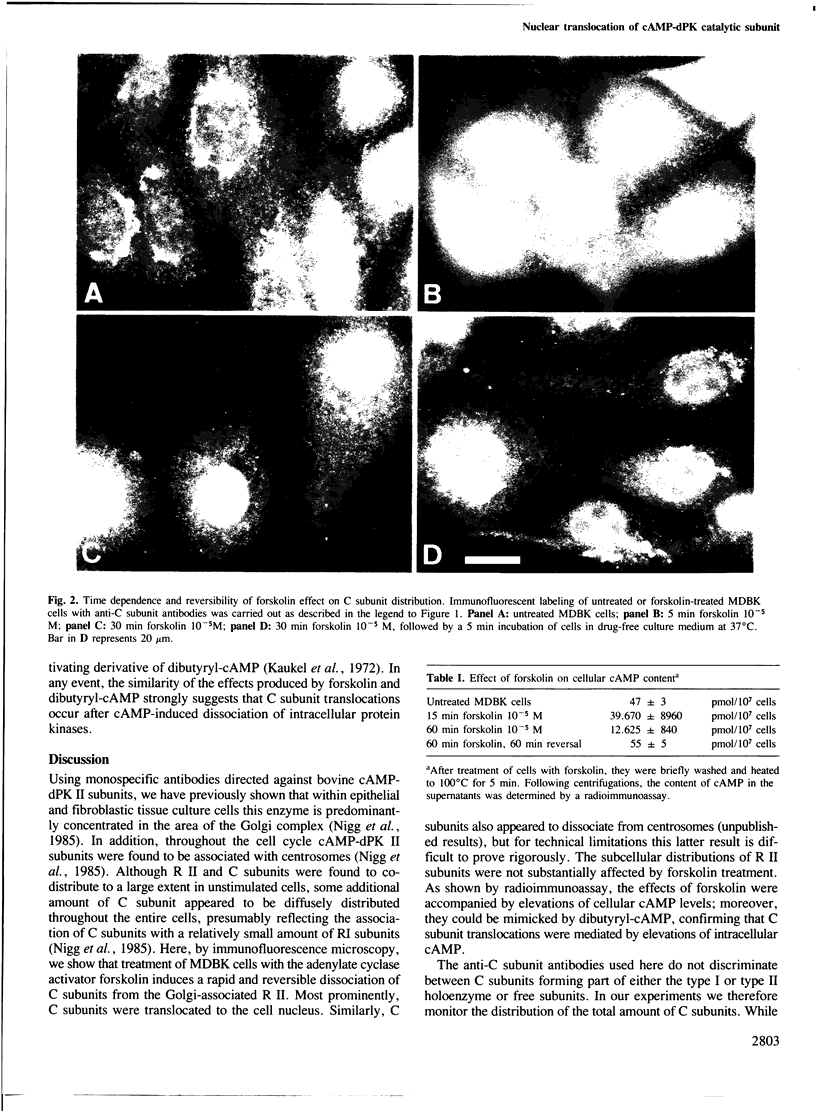
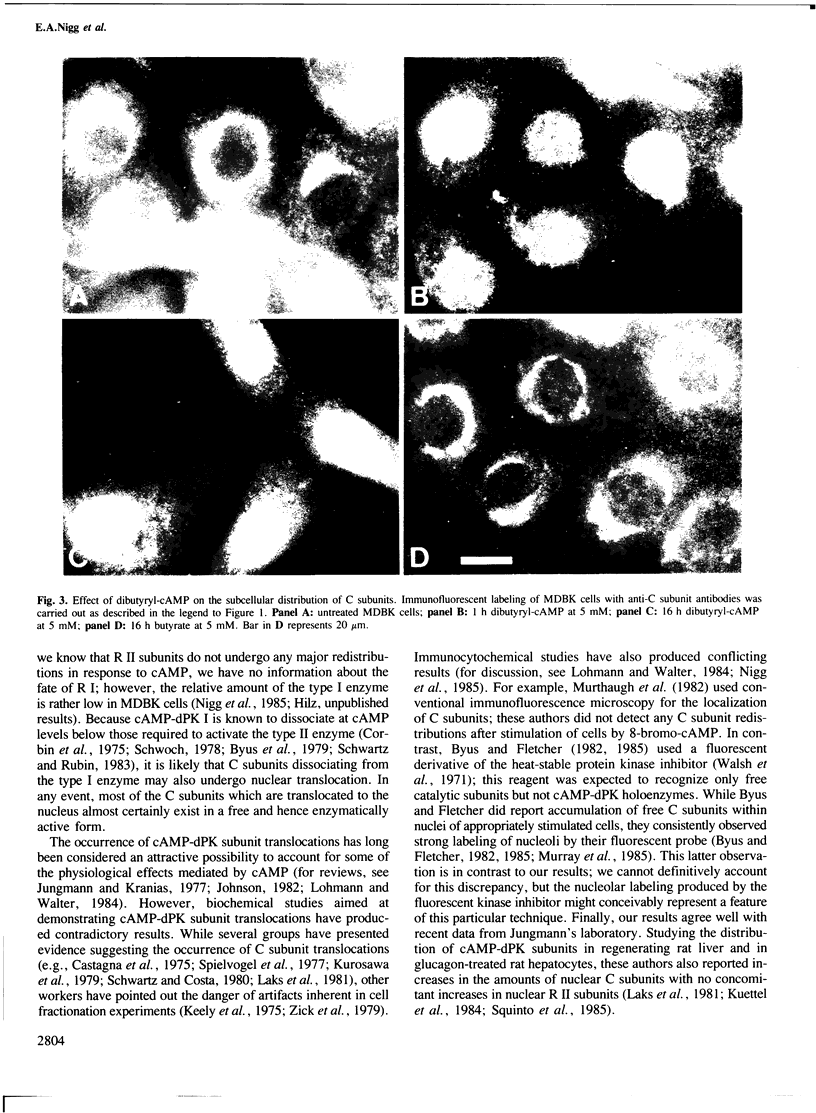


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alhanaty E., Shaltiel S. Limited proteolysis of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase--a membranal regulatory device? Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jul 27;89(2):323–332. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90633-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byus C. V., Fletcher W. H. Intracellular localization of the catalytic subunit from cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase in mutant Chinese hamster ovary cells deficient in this enzyme. J Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphor Res. 1985;10(1):9–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byus C. V., Hayes J. S., Brendel K., Russell D. H. Regulation of glycogenolysis in isolated rat hepatocytes by the specific activation of type I cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Nov;16(3):941–949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Palmer W. K., Walsh D. A. Nuclear protein-kinase activity in perfused rat liver stimulated with dibutyryl-adenosine cyclic 3':5'-monophosphate. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun 16;55(1):193–199. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02151.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The role of protein phosphorylation in neural and hormonal control of cellular activity. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):613–620. doi: 10.1038/296613a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. D., Keely S. L., Park C. R. The distribution and dissociation of cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases in adipose, cardiac, and other tissues. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 10;250(1):218–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. D., Sugden P. H., West L., Flockhart D. A., Lincoln T. M., McCarthy D. Studies on the properties and mode of action of the purified regulatory subunit of bovine heart adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):3997–4003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flockhart D. A., Corbin J. D. Regulatory mechanisms in the control of protein kinases. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1982 Feb;12(2):133–186. doi: 10.3109/10409238209108705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengard P. Phosphorylated proteins as physiological effectors. Science. 1978 Jan 13;199(4325):146–152. doi: 10.1126/science.22932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungmann R. A., Kelley D. C., Miles M. F., Milkowski D. M. Cyclic AMP regulation of lactate dehydrogenase. Isoproterenol and N6,O2-dibutyryl cyclic amp increase the rate of transcription and change the stability of lactate dehydrogenase a subunit messenger RNA in rat C6 glioma cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):5312–5318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaukel E., Mundhenk K., Hilz H. N 6 -monobutyryladenosine 3':5'-mono phosphate as the biologically active derivative of dibutyryladenosine 3':5'-monophosphate in HeLa S3 cells. Eur J Biochem. 1972 May;27(1):197–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01826.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keely S. L., Jr, Corbin J. D., Park C. R. On the question of translocation of heart cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1501–1504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs E. G., Beavo J. A. Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation of enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:923–959. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuettel M. R., Schwoch G., Jungmann R. A. Localization of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase subunits in rat hepatocyte nuclei by immunogold electron microscopy. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1984 Nov;8(11):949–957. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(84)90193-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurosawa A., Guidotti A., Costa E. Nuclear translocation of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase subunits during the transsynaptic activation of gene expression in rat adrenal medulla. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Jan;15(1):115–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laks M. S., Harrison J. J., Schwoch G., Jungmann R. A. Modulation of nuclear protein kinase activity and phosphorylation of histone H1 subspecies during the prereplicative phase of rat liver regeneration. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8775–8785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmann S. M., Walter U. Regulation of the cellular and subcellular concentrations and distribution of cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphorylation Res. 1984;18:63–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murdoch G. H., Rosenfeld M. G. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulation and chromatin-associated protein phosphorylation by cyclic AMP. Science. 1982 Dec 24;218(4579):1315–1317. doi: 10.1126/science.6293056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray S. A., Byus C. V., Fletcher W. H. Intracellular kinetics of free catalytic units dissociated from adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase in adrenocortical tumor cells (Y-1). Endocrinology. 1985 Jan;116(1):364–374. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-1-364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murtaugh M. P., Steiner A. L., Davies P. J. Localization of the catalytic subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent. Protein kinase in cultured cells using a specific antibody. J Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;95(1):64–72. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.1.64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigg E. A., Schäfer G., Hilz H., Eppenberger H. M. Cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinase type II is associated with the Golgi complex and with centrosomes. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):1039–1051. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nimmo H. G., Cohen P. Hormonal control of protein phosphorylation. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1977;8:145–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. S., Rosen O. M. Protein phosphorylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:831–887. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.004151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher M., Hilz H. Protein-bound cAMP, total cAMP, and protein kinase activation in isolated bovine thyrocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 14;80(3):511–518. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91598-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. A., Rubin C. S. Regulation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase subunit levels in Friend erythroleukemic cells. Effects of differentiation and treatment with 8-Br-cAMP and methylisobutyl xanthine. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):777–784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. P., Costa E. Protein kinase translocation following beta-adrenergic receptor activation in C6 glioma cells. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):2943–2948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwoch G., Hamann A., Hilz H. Antiserum against the catalytic subunit of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Reactivity towards various protein kinases. Biochem J. 1980 Oct 15;192(1):223–230. doi: 10.1042/bj1920223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seamon K. B., Daly J. W. Forskolin: a unique diterpene activator of cyclic AMP-generating systems. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1981;7(4):201–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seamon K. B., Padgett W., Daly J. W. Forskolin: unique diterpene activator of adenylate cyclase in membranes and in intact cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3363–3367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spielvogel A. M., Mednieks M. I., Eppenberger U., Jungmann R. A. Evidence for the identity of nuclear and cytoplasmic adenosine-3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase from porcine ovaries and nuclear translocation of the cytoplasmic enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Feb 15;73(1):199–212. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11308.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squinto S. P., Kelley-Geraghty D. C., Kuettel M. R., Jungmann R. A. Ultrastructural localization of cAMP-dependent protein kinase subunits in regenerating rat hepatocytes using immunogold electron microscopy. J Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphor Res. 1985;10(1):65–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh D. A., Ashby C. D., Gonzalez C., Calkins D., Fischer E. H. Krebs EG: Purification and characterization of a protein inhibitor of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):1977–1985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber W., Hilz H. Stoichiometry of cAMP binding and limited proteolysis of protein kinase regulatory subunits R I and R II. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Oct 12;90(3):1074–1081. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91935-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber W., Schröder H., Hilz H. Quantitation of heterologous protein kinase subunits R I and R II with the aid of type specific antibodies. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Mar 31;99(2):475–483. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91769-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zick Y., Cesla R., Shaltiel S. cAMP-dependent protein kinase from mouse thymocytes. Localization, characterization, and evaluation of the physiological relevance of a massive cytosol to nucleus translocation. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 10;254(3):879–887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]