Abstract
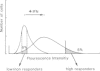
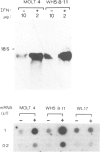
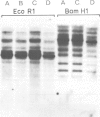
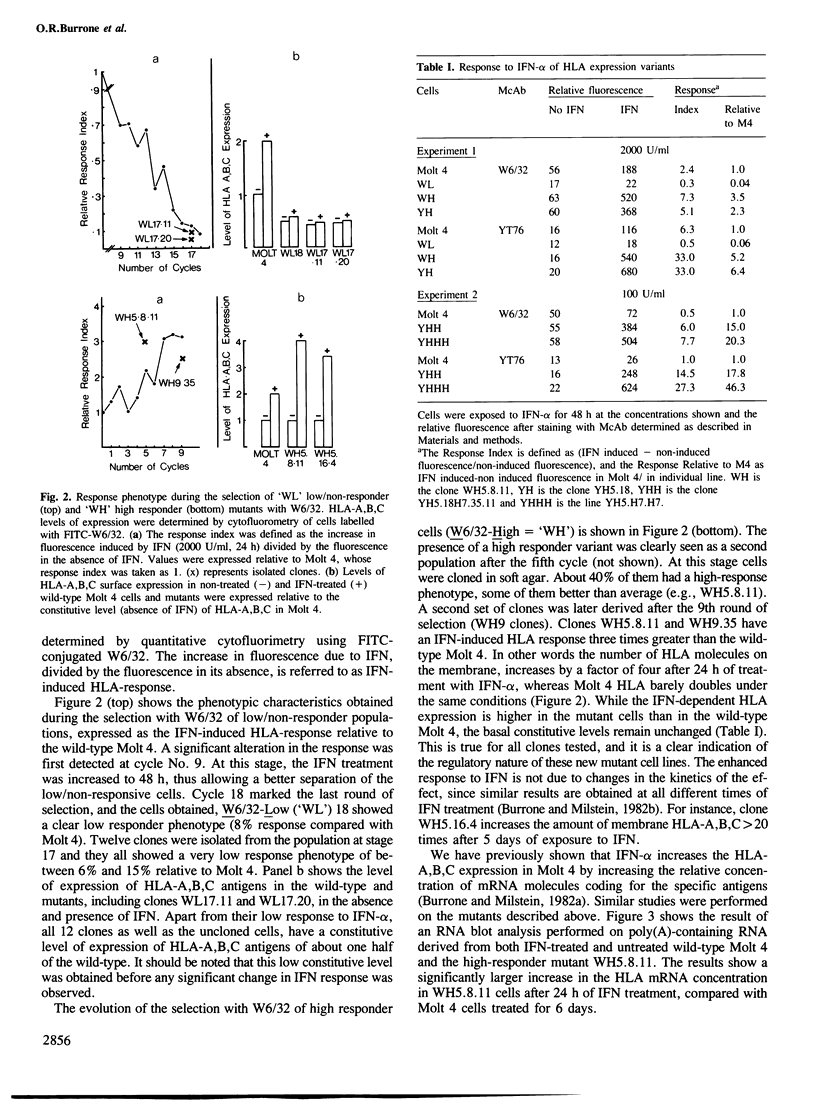
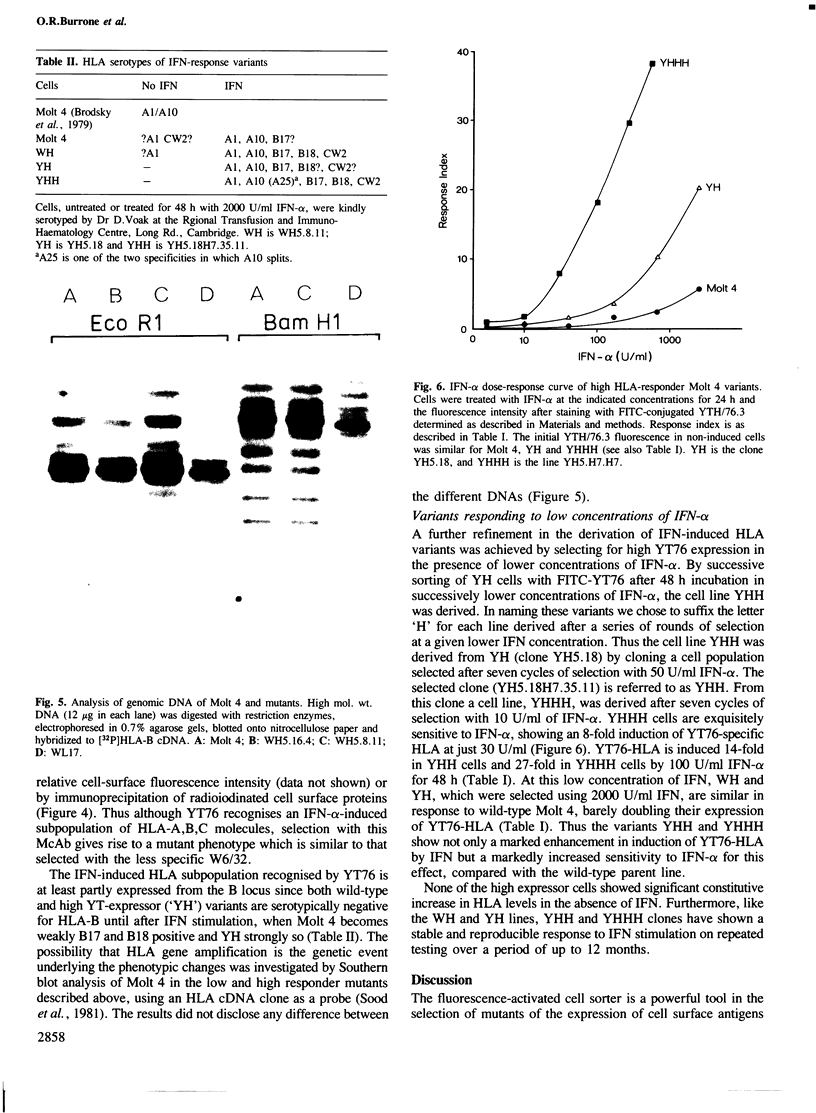
Spontaneous mutants with altered HLA-A,B,C response to interferon-alpha (IFN-alpha) were isolated from the human thymus leukemia cell line Molt 4. Using fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-conjugated W6/32 (a monoclonal antibody to HLA-A,B,C) and the fluorescence-activated cell sorter, the cells with highest and lowest fluorescence after 24-48 h of IFN-alpha treatment were selected and expanded. After several cycles of selection, mutant clones with low (greater than 10% of wild-type) and high (three times better) response were obtained. A similar protocol was employed to derive high responder mutants with the monoclonal antibody YT76, which recognises a subset of HLA strongly induced by IFN-alpha. Stable clones were derived for which YT-HLA induction was 7-fold that of Molt 4 cells and for which HLA induction occurred at 100-fold lower concentrations of IFN-alpha. The high response phenotype of the mutants was not accompanied by a significant increase in the constitutive level of expression of HLA-A,B,C (in the absence of IFN). The increase in the level of HLA-A,B,C expression after IFN-alpha treatment is mostly accounted for by the increase in the expression of a subset of HLA molecules, detected by the monoclonal antibody YT76 including HLA-B molecules.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguet M. High-affinity binding of 125I-labelled mouse interferon to a specific cell surface receptor. Nature. 1980 Apr 3;284(5755):459–461. doi: 10.1038/284459a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnstable C. J., Bodmer W. F., Brown G., Galfre G., Milstein C., Williams A. F., Ziegler A. Production of monoclonal antibodies to group A erythrocytes, HLA and other human cell surface antigens-new tools for genetic analysis. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basham T. Y., Bourgeade M. F., Creasey A. A., Merigan T. C. Interferon increases HLA synthesis in melanoma cells: interferon-resistant and -sensitive cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3265–3269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branca A. A., Baglioni C. Evidence that types I and II interferons have different receptors. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):768–770. doi: 10.1038/294768a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky F. M., Parham P., Barnstable C. J., Crumpton M. J., Bodmer W. F. Monoclonal antibodies for analysis of the HLA system. Immunol Rev. 1979;47:3–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00288.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrone O. R., Calabi F., Kefford R. F., Milstein C. Somatic variants of the level of expression of a cell surface antigen. EMBO J. 1983;2(9):1591–1595. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01629.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrone O. R., Milstein C. Control of HLA-A,B,C synthesis and expression in interferon-treated cells. EMBO J. 1982;1(3):345–349. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01172.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrone O. R., Milstein C. The effect of interferon on the expression of human cell-surface antigens. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Sep 24;299(1094):133–135. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1982.0116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chebath J., Merlin G., Metz R., Benech P., Revel M. Interferon-induced 56,000 Mr protein and its mRNA in human cells: molecular cloning and partial sequence of the cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1213–1226. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellous M., Bono R., Hyafil F., Gresser I. Interferon enhances the amount of membrane-bound beta2-microglobulin and its release from human Burkitt cells. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Jun;11(6):524–526. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellous M., Kamoun M., Gresser I., Bono R. Enhanced expression of HLA antigens and beta 2-microglobulin on interferon-treated human lymphoid cells. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Jun;9(6):446–449. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellous M., Nir U., Wallach D., Merlin G., Rubinstein M., Revel M. Interferon-dependent induction of mRNA for the major histocompatibility antigens in human fibroblasts and lymphoblastoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3082–3086. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfrè G., Milstein C. Preparation of monoclonal antibodies: strategies and procedures. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):3–46. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtkamp B., Cramer M., Lemke H., Rajewsky K. Isolation of a cloned cell line expressing variant H-2Kk using fluorescence-activated cell sorting. Nature. 1981 Jan 1;289(5793):66–68. doi: 10.1038/289066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamarck M. E., Barbosa J. A., Ruddle F. H. Somatic cell genetic analysis of HLA-A, B, C and human beta 2-microglobulin expression. Somatic Cell Genet. 1982 May;8(3):385–402. doi: 10.1007/BF01538895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengyel P. Biochemistry of interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:251–282. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMichael A. J., Pilch J. R., Galfré G., Mason D. Y., Fabre J. W., Milstein C. A human thymocyte antigen defined by a hybrid myeloma monoclonal antibody. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Mar;9(3):205–210. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabholz M., MacDonald H. R. Cytolytic T lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:273–306. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.001421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuberger M. S., Rajewsky K. Switch from hapten-specific immunoglobulin M to immunoglobulin D secretion in a hybrid mouse cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1138–1142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T. Gene amplification in cultured animal cells. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):705–713. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90406-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Secher D. S., Burke D. C. A monoclonal antibody for large-scale purification of human leukocyte interferon. Nature. 1980 Jun 12;285(5765):446–450. doi: 10.1038/285446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sood A. K., Pereira D., Weissman S. M. Isolation and partial nucleotide sequence of a cDNA clone for human histocompatibility antigen HLA-B by use of an oligodeoxynucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):616–620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svasti J., Milstein C. The disulphide bridges of a mouse immunoglobulin G1 protein. Biochem J. 1972 Feb;126(4):837–850. doi: 10.1042/bj1260837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan Y. H. Chromosome 21 and the cell growth inhibitory effect of human interferon preparations. Nature. 1976 Mar 11;260(5547):141–143. doi: 10.1038/260141a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan Y. H., Greene A. E. Subregional localization of the gene(s) governing the human interferon induced antiviral state in man. J Gen Virol. 1976 Jul;32(1):153–155. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-32-1-153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallach D. The HLA proteins and a related protein of 28 kDa are preferentially induced by interferon-gamma in human WISH cells. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Oct;13(10):794–798. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830131003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. A., Bancroft F. C. Cytoplasmic dot hybridization. Simple analysis of relative mRNA levels in multiple small cell or tissue samples. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8569–8572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]