Abstract
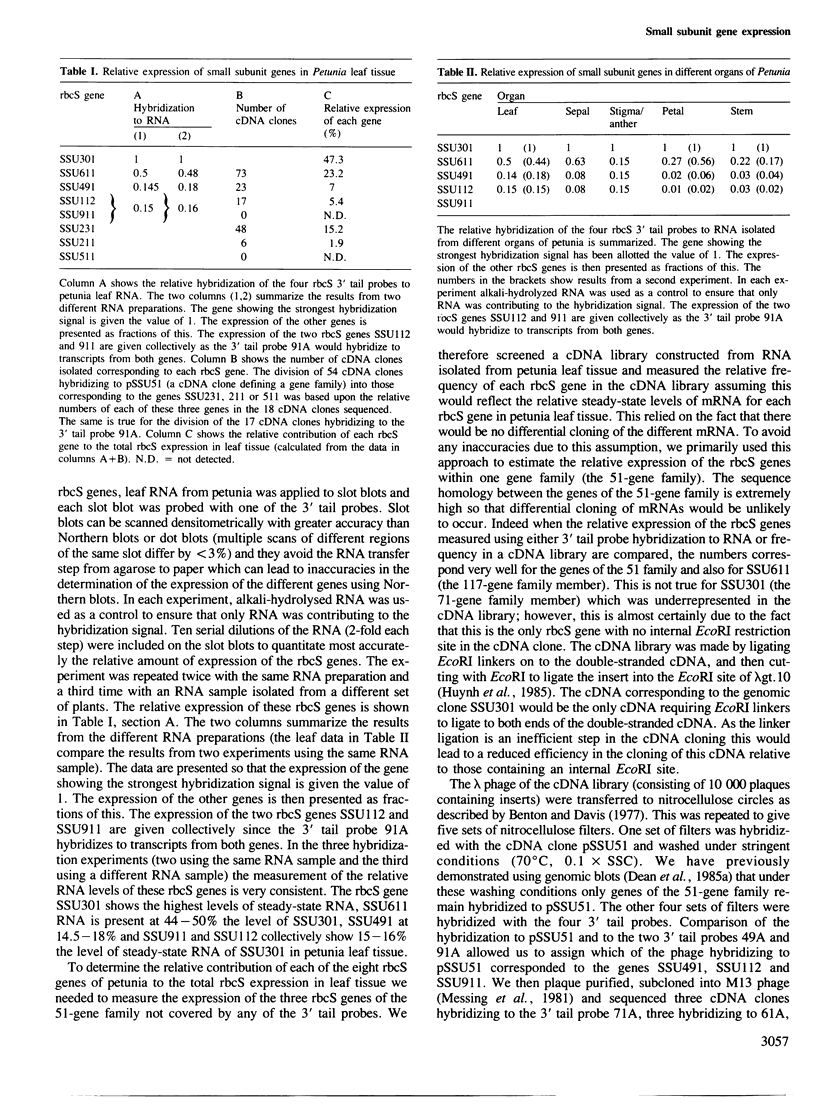
Of the eight nuclear genes in the plant multi-gene family which encodes the small subunit (rbcS) of Petunia (Mitchell) ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase, one rbcS gene accounts for 47% of the total rbcS gene expression in petunia leaf tissue. Expression of each of five other rbcS genes is detected at levels between 2 and 23% of the total rbcS expression in leaf tissue, while expression of the remaining two rbcS genes is not detected. There is considerable variation (500-fold) in the levels of total rbcS mRNA in six organs of petunia (leaves, sepals, petals, stems, roots and stigmas/anthers). One gene, SSU301, showed the highest levels of steady-state mRNA in each of the organs examined. We discuss the differences in the steady-state mRNA levels of the individual rbcS genes in relation to their gene structure, nucleotide sequence and genomic linkage.
Keywords: small subunit, ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase, gene expression, multi-gene family, nucleotide sequence
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry-Lowe S. L., Mc Knight T. D., Shah D. M., Meagher R. B. The nucleotide sequence, expression, and evolution of one member of a multigene family encoding the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase in soybean. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(6):483–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chua N. H., Schmidt G. W. Post-translational transport into intact chloroplasts of a precursor to the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6110–6114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen D. M., Bedbrook J. R., Bogorad L., Rich A. Maize chloroplast DNA fragment encoding the large subunit of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5487–5491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coruzzi G., Broglie R., Edwards C., Chua N. H. Tissue-specific and light-regulated expression of a pea nuclear gene encoding the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1671–1679. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02031.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean C., Leech R. M. Genome Expression during Normal Leaf Development : I. CELLULAR AND CHLOROPLAST NUMBERS AND DNA, RNA, AND PROTEIN LEVELS IN TISSUES OF DIFFERENT AGES WITHIN A SEVEN-DAY-OLD WHEAT LEAF. Plant Physiol. 1982 Apr;69(4):904–910. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.4.904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean C., van den Elzen P., Tamaki S., Dunsmuir P., Bedbrook J. Linkage and homology analysis divides the eight genes for the small subunit of petunia ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase into three gene families. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4964–4968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunsmuir P., Smith S., Bedbrook J. A number of different nuclear genes for the small subunit of RuBPCase are transcribed in petunia. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 25;11(12):4177–4183. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.12.4177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunsmuir P. The petunia chlorophyll a/b binding protein genes: a comparison of Cab genes from different gene families. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2503–2518. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyrberg E. A., Mahaffey J. W., Bond B. J., Davidson N. Transcripts of the six Drosophila actin genes accumulate in a stage- and tissue-specific manner. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):115–123. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90340-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher T. F., Ellis R. J. Light-stimulated transcription of genes for two chloroplast polypeptides in isolated pea leaf nuclei. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1493–1498. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01345.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hightower R. C., Meagher R. B. Divergence and differential expression of soybean actin genes. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):1–8. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02309.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawashima N., Wildman S. G. Studies on fraction I protein. IV. Mode of inheritance of primary structure in relation to whether chloroplast or nuclear DNA contains the code for a chloroplast protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 23;262(1):42–49. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90217-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations close to the AUG initiator codon affect the efficiency of translation of rat preproinsulin in vivo. Nature. 1984 Mar 15;308(5956):241–246. doi: 10.1038/308241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Possible role of flanking nucleotides in recognition of the AUG initiator codon by eukaryotic ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5233–5252. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazur B. J., Chui C. F. Sequence of a genomic DNA clone for the small subunit of ribulose bis-phosphate carboxylase-oxygenase from tobacco. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2373–2386. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. The end of the message. Nature. 1982 Aug 5;298(5874):516–517. doi: 10.1038/298516a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverthorne J., Tobin E. M. Demonstration of transcriptional regulation of specific genes by phytochrome action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1112–1116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. M., Ellis R. J. Light-stimulated accumulation of transcripts of nuclear and chloroplast genes for ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase. J Mol Appl Genet. 1981;1(2):127–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin E. M. Light regulation of specific mRNA species in Lemna gibba L. G-3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4749–4753. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiher H., König M., Gruss P. Multiple point mutations affecting the simian virus 40 enhancer. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):626–631. doi: 10.1126/science.6297005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




