Abstract
We have characterized the binding of lambda phage replication initiation protein O to the phage origin of replication. The minimal DNA segment required for O binding is the single iteron, a 19-bp sequence of hyphenated dyad symmetry that is repeated with variations four times in the origin. The isolated amino terminus of O protein is also sufficient to bind DNA. Electrophoretic studies show that the amino terminus of O protein induces bending of a single iteron. The DNA-protein interaction was characterized by ethylation interference, dimethyl sulfate protection and neocarzinostatin footprinting. Points of DNA-protein contact are largely concentrated in two areas symmetrically disposed with respect to the dyad symmetry of the iteron. This suggests the protein interacts as a dimer with half sites in the DNA. However, a few non-symmetrical contacts are found, indicating that O protein may distort the helix. This may correlate with the bending effects demonstrated electrophoretically. Cylindrical DNA projections were used to model O protein binding to the lambda origin and compare it with the lambda repressor-operator interaction. Whereas bound repressor nearly encircles the DNA in the major groove, O protein leaves the major groove on the opposite side exposed.
Full text
PDF

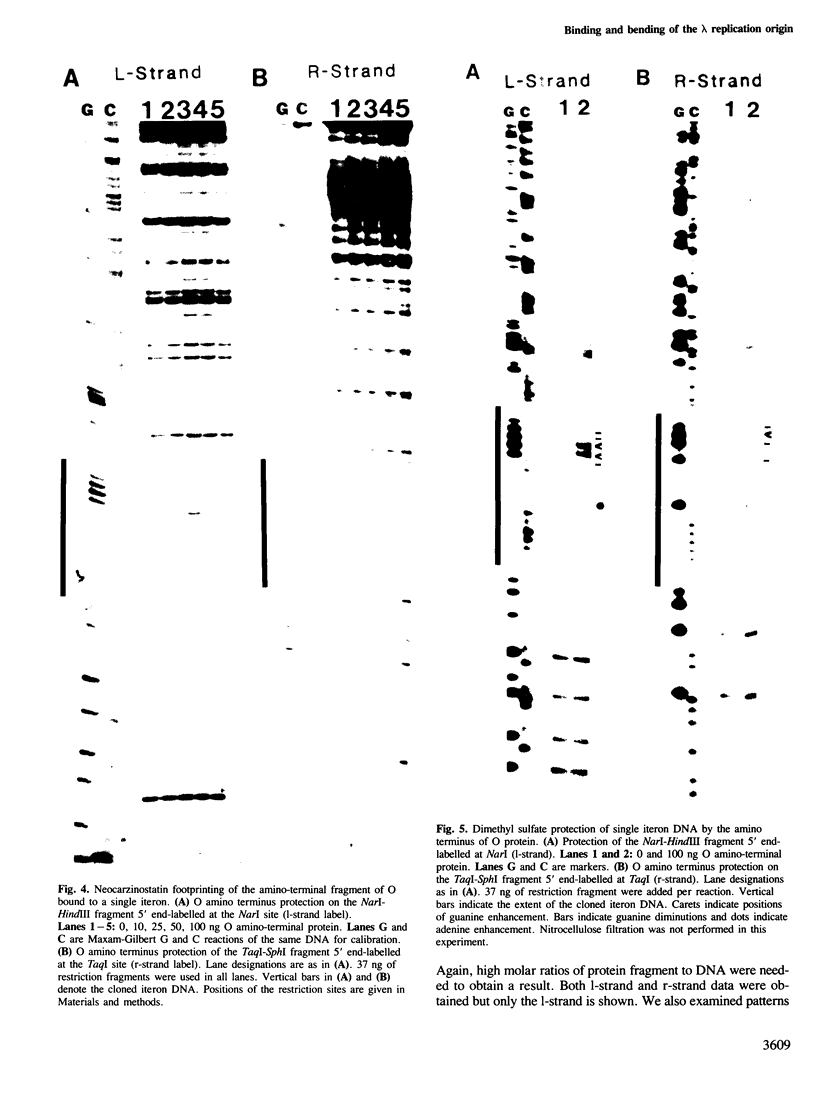


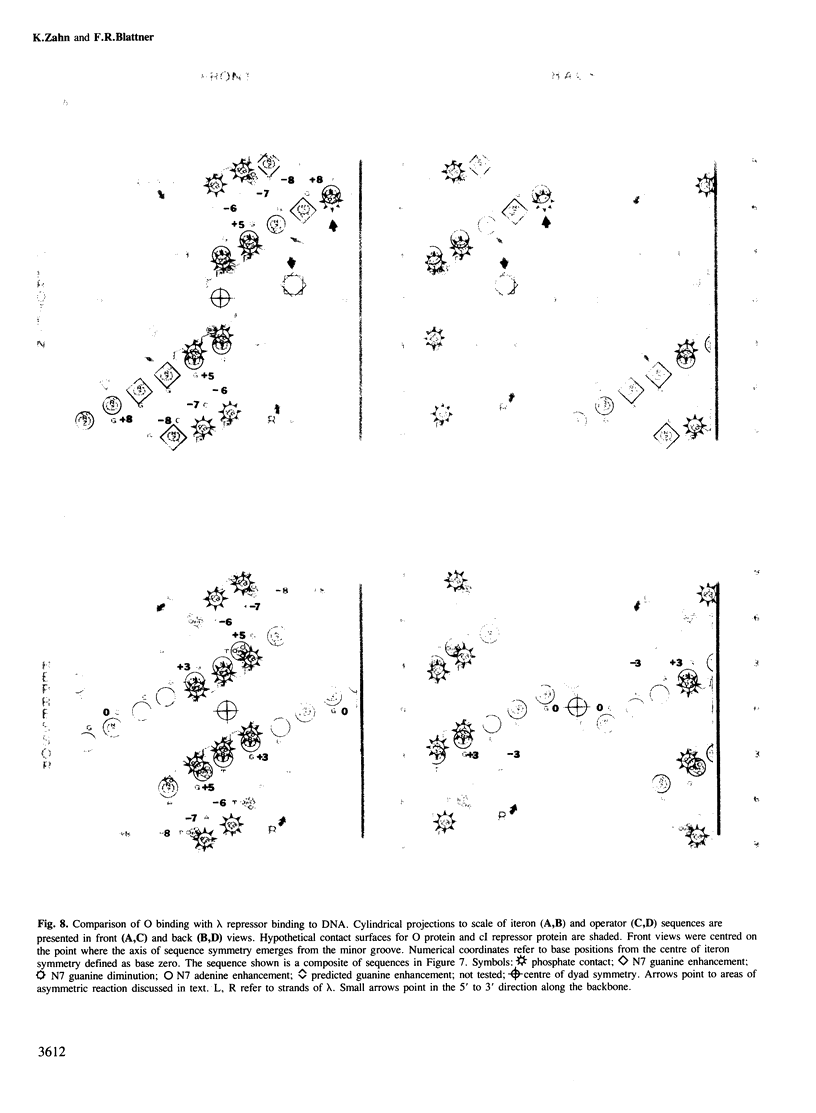
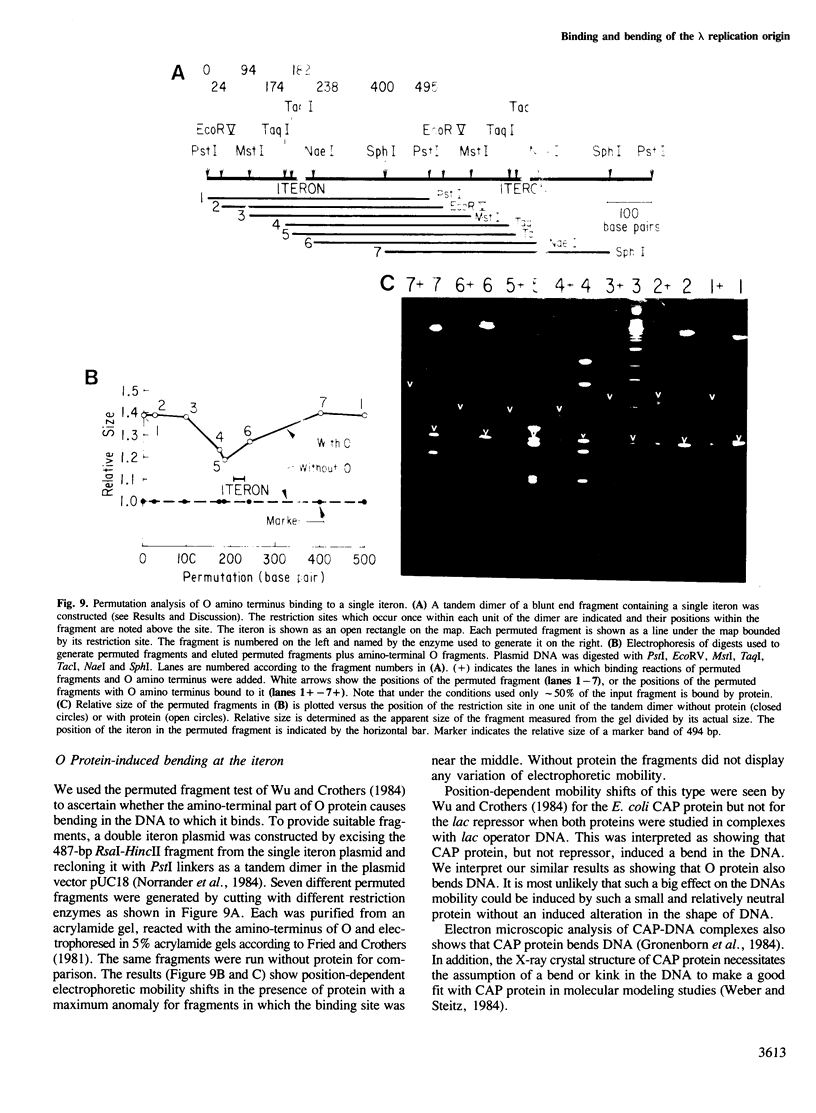



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of protein conformation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):222–245. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denniston-Thompson K., Moore D. D., Kruger K. E., Furth M. E., Blattner F. R. Physical structure of the replication origin of bacteriophage lambda. Science. 1977 Dec 9;198(4321):1051–1056. doi: 10.1126/science.929187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echols H., Dodson M., Better M., Roberts J. D., McMacken R. The role of specialized nucleoprotein structures in site-specific recombination and initiation of DNA replication. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:727–733. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen H., Pereira da Silva L., Jacob F. The regulation and mechanism of DNA synthesis in bacteriophage lambda. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:755–764. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. I., Olson E. R., Georgopoulos C., Tilly K., Herskowitz I., Banuett F. Interactions of bacteriophage and host macromolecules in the growth of bacteriophage lambda. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Dec;48(4):299–325. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.4.299-325.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
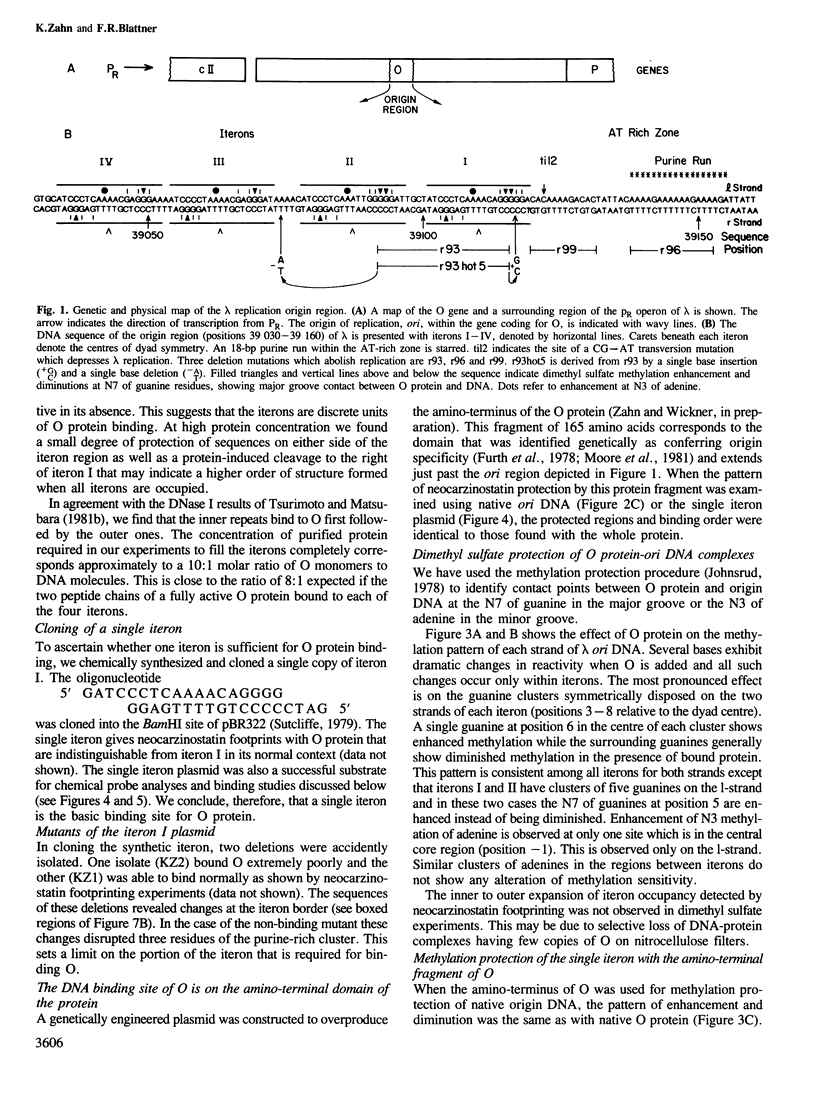
- Furth M. E., Blattner F. R., McLeester C., Dove W. F. Genetic structure of the replication origin of bacteriophage lambda. Science. 1977 Dec 9;198(4321):1046–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.929186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth M. E., McLeester C., Dove W. F. Specificity determinants for bacteriophage lambda DNA replication. I. A chain of interactions that controls the initiation of replication. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 5;126(2):195–225. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90359-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronenborn A. M., Nermut M. V., Eason P., Clore G. M. Visualization of cAMP receptor protein-induced DNA kinking by electron microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 15;179(4):751–757. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90166-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Hobom G. DNA sequences and structural homologies of the replication origins of lambdoid bacteriophages. Nature. 1979 Feb 22;277(5698):621–627. doi: 10.1038/277621a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobom G., Grosschedl R., Lusky M., Scherer G., Schwarz E., Kössel H. Functional analysis of the replicator structure of lambdoid bacteriophage DNAs. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):165–178. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. D., Meyer B. J., Ptashne M. Interactions between DNA-bound repressors govern regulation by the lambda phage repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5061–5065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnsrud L. Contacts between Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and a lac operon promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5314–5318. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein A., Lanka E., Schuster H. Isolation of a complex between the P protein of phage lambda and the dnaB protein of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Mar;105(1):1–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04467.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levene S. D., Crothers D. M. A computer graphics study of sequence-directed bending in DNA. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1983 Oct;1(2):429–435. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1983.10507452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis M., Jeffrey A., Wang J., Ladner R., Ptashne M., Pabo C. O. Structure of the operator-binding domain of bacteriophage lambda repressor: implications for DNA recognition and gene regulation. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):435–440. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore D. D., Denniston-Thompson K., Kruger K. E., Furth M. E., Williams B. G., Daniels D. L., Blattner F. R. Dissection and comparative anatomy of the origins of replication of lambdoid phages. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):155–163. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore D. D., Denniston K. J., Blattner F. R. Sequence organization of the origins of DNA replication in lambdoid coliphages. Gene. 1981 Jun-Jul;14(1-2):91–101. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90151-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa T., Tomizawa J. Replication of bacteriophage DNA. I. Replication of DNA of lambda phage defective in early functions. J Mol Biol. 1968 Dec 14;38(2):217–225. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90407-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:293–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Povirk L. F., Goldberg I. H. Covalent adducts of DNA and the nonprotein chromophore of neocarzinostatin contain a modified deoxyribose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):369–373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rambach A. Replicator mutants of bacteriophage lambda: characterization of two subclasses. Virology. 1973 Jul;54(1):270–277. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90136-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Landy A., Kikuchi Y., Nash H. Interaction of int protein with specific sites on lambda att DNA. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):297–307. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90049-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer G. Nucleotide sequence of the O gene and of the origin of replication in bacteriophage lambda DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3141–3156. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnös M., Inman R. B. Position of branch points in replicating lambda DNA. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jul 14;51(1):61–73. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90270-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Gilbert W. Contacts between Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and an early promoter of phage T7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):122–126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):77–90. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Ohlendorf D. H., Anderson W. F., Matthews B. W. DNA-binding proteins. Science. 1983 Sep 9;221(4615):1020–1026. doi: 10.1126/science.6308768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
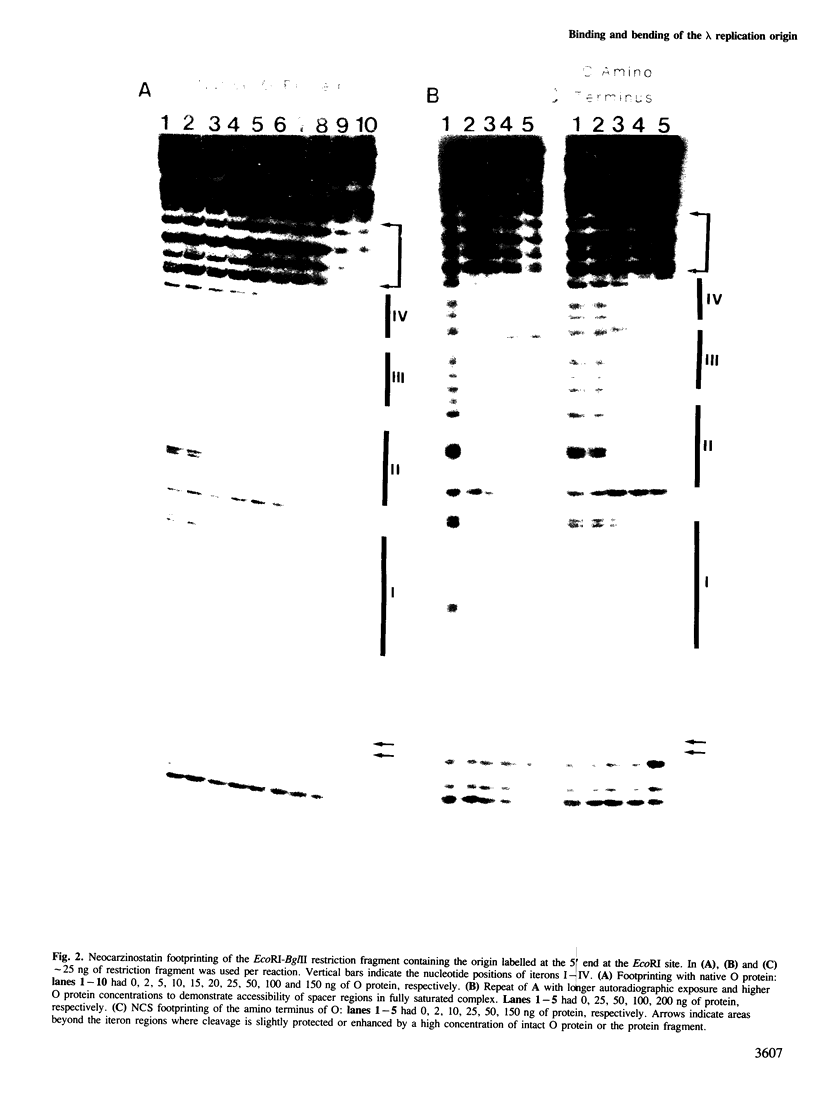
- Tsurimoto T., Matsubara K. Purification of bacteriophage lambda O protein that specifically binds to the origin of replication. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;181(3):325–331. doi: 10.1007/BF00425606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurimoto T., Matsubara K. Purified bacteriophage lambda O protein binds to four repeating sequences at the lambda replication origin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 24;9(8):1789–1799. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.8.1789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber I. T., Steitz T. A. Model of specific complex between catabolite gene activator protein and B-DNA suggested by electrostatic complementarity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):3973–3977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.3973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner S. H. DNA replication proteins of Escherichia coli and phage lambda. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):303–310. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. The locus of sequence-directed and protein-induced DNA bending. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):509–513. doi: 10.1038/308509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahn K., Blattner F. R. Sequence-induced DNA curvature at the bacteriophage lambda origin of replication. Nature. 1985 Oct 3;317(6036):451–453. doi: 10.1038/317451a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]