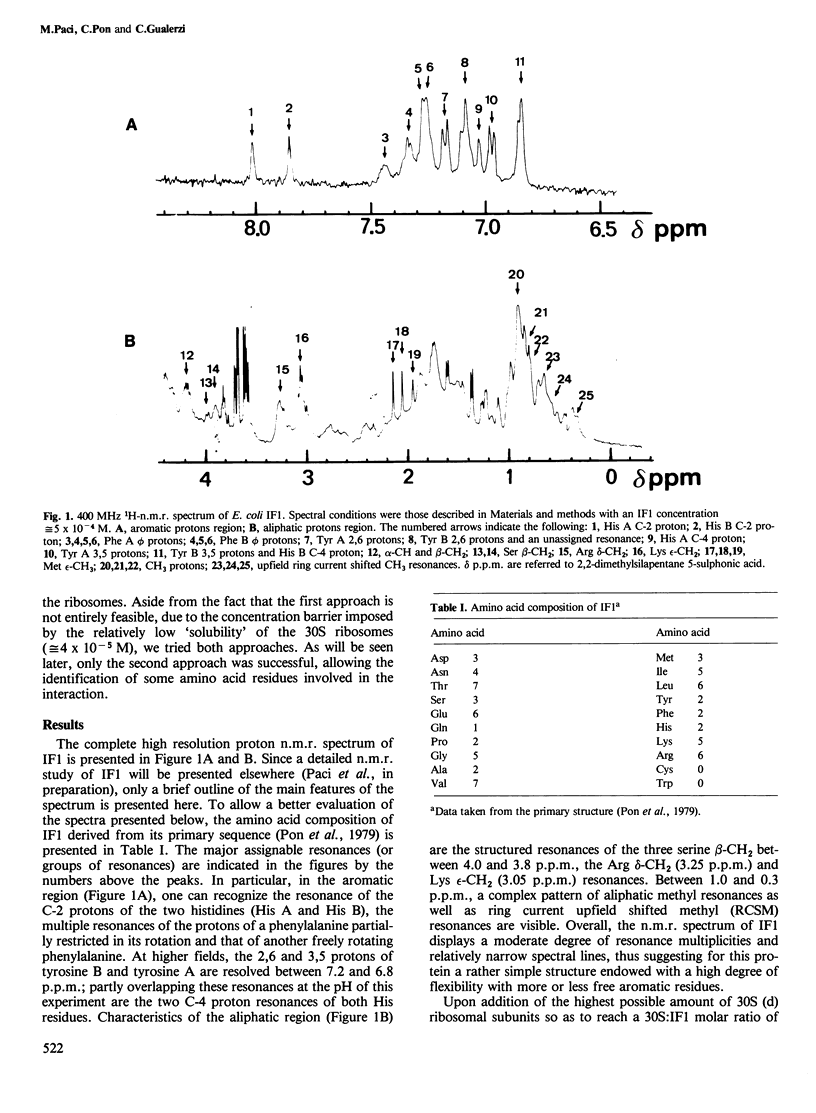
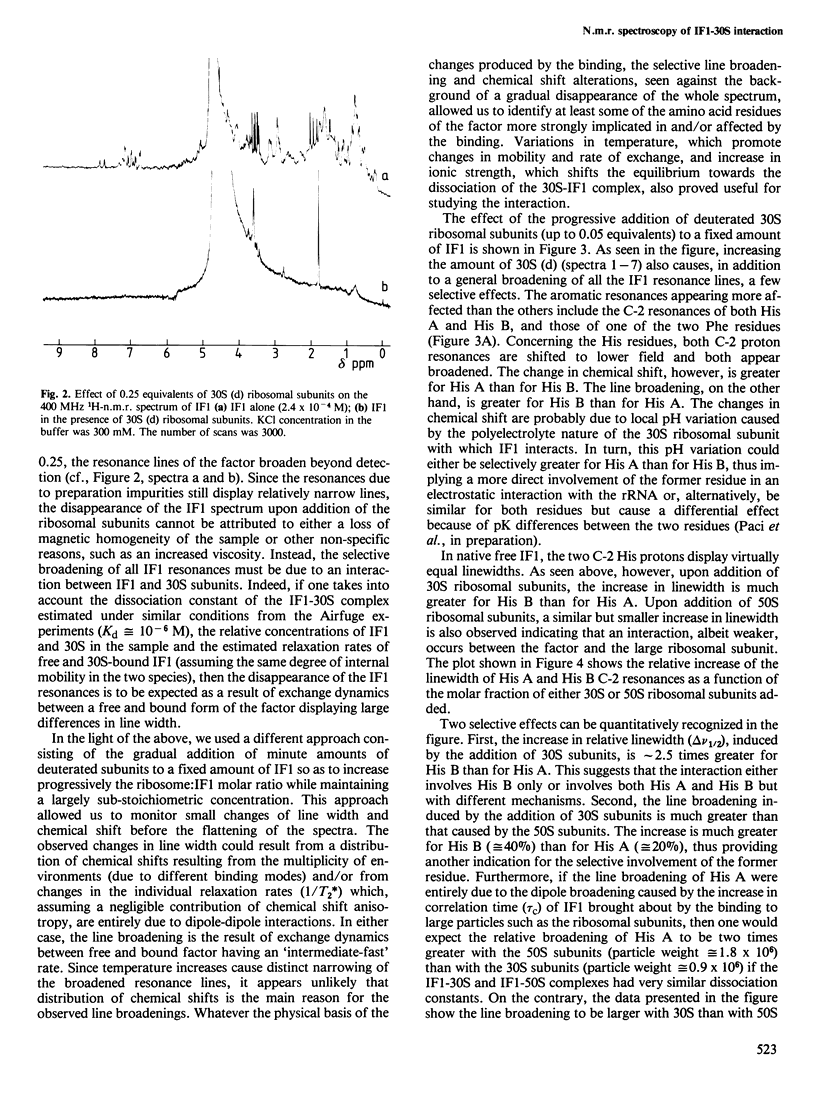
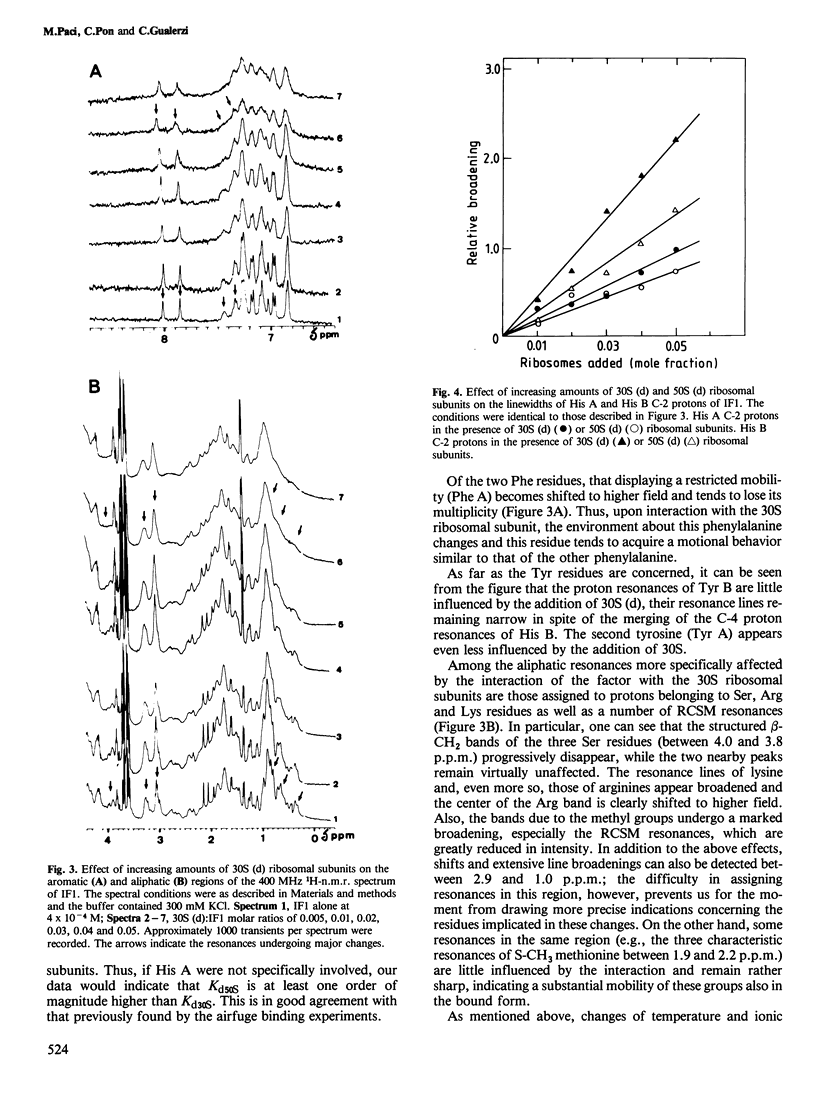
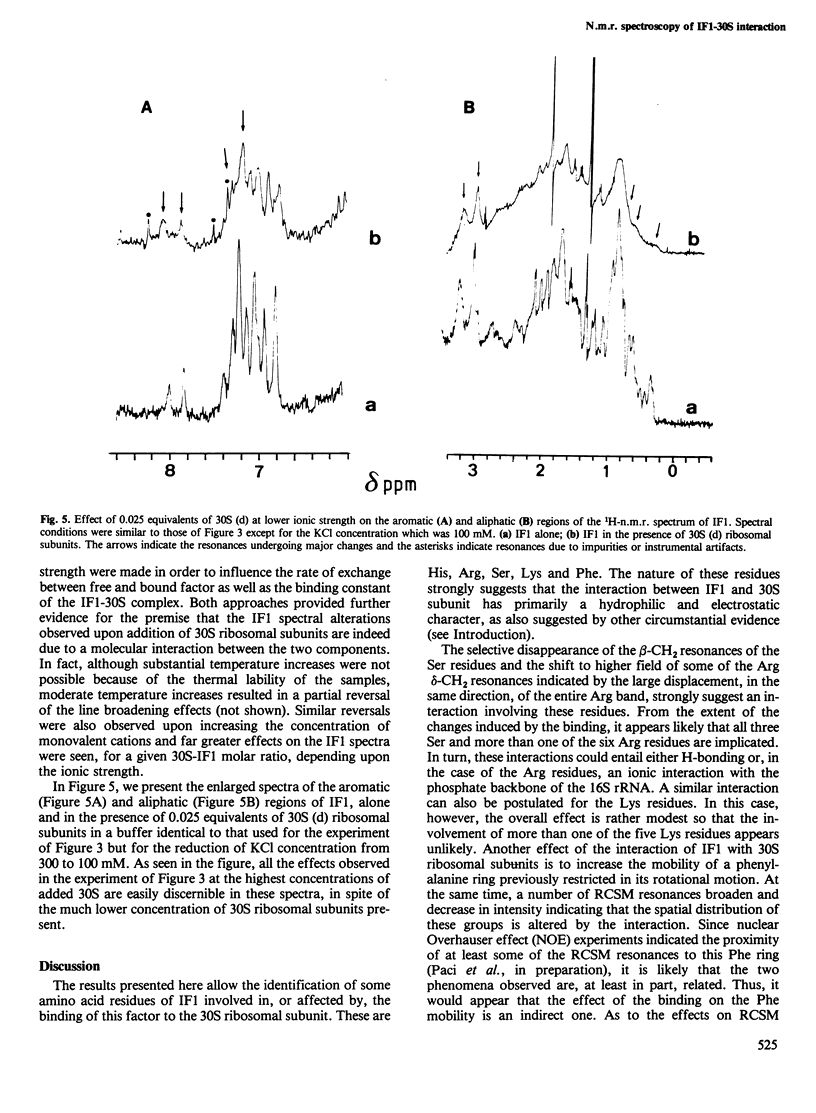
Abstract
Interaction between Escherichia coli translational initiation factor IF1 (mol. wt. 8119) and 30S ribosomal subunits was followed by high resolution 1H-n.m.r. spectroscopy. Upon gradual addition of increasing yet largely sub-stoichiometric amounts of biologically active deuterated 30S ribosomal subunits, selective line broadenings and chemical shift changes were observed against the background of the gradual disappearance of the whole spectrum. At the highest 30S:IF1 ratio attained (0.25), all the resonance lines were broadened beyond meaningful detection. This behaviour, which can be partly reversed by increasing the ionic strength and/or the temperature, is due to the interaction between IF1 and the 30S ribosomal subunits, and can be explained by the existence of a medium-fast exchange dynamics between free and bound factor. The selective effects observed during titration with 30S ribosomal subunits shed some light on the mode of interaction of IF1 with 30S ribosomal subunits. At least one of the two His residues of the factor appears to be involved in the binding, since it undergoes a low-field change of chemical shift and becomes totally immobilized in the IF1-30S complex. Also strongly implicated in the interaction with 30S are more than one Ser and Arg residue and probably one lysine. Additional effects of the interaction of IF1 with ribosomes are a drastic reduction in the intensity of the ring current upfield shifted methyl resonances and mobilization of a previously rotationally hindered phenylalanine ring.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Pon C. L., Wittmann-Liebold B., Gualerzi C. Structure--function relationships in Escherichia coli initiation factors. II. Elucidation of the primary structure of initiation factor IF-1. FEBS Lett. 1979 May 1;101(1):157–160. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81316-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risuleo G., Gualerzi C., Pon C. Specificity and properties of the destabilization, induced by initiation factor IF-3, of ternary complexes of the 30-S ribosomal subunit, aminoacyl-tRNA and polynucleotides. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 16;67(2):603–613. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10726.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleich T., Verwolf G. L., Twombly K. A circular dichroism study of Escherichia coli Initiation Factor-1 binding to polynucleotides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Sep 19;609(2):313–320. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90243-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintermeyer W., Gualerzi C. Effect of Escherichia coli initiation factors on the kinetics of N-Acphe-tRNAPhe binding to 30S ribosomal subunits. A fluorescence stopped-flow study. Biochemistry. 1983 Feb 1;22(3):690–694. doi: 10.1021/bi00272a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


