Abstract
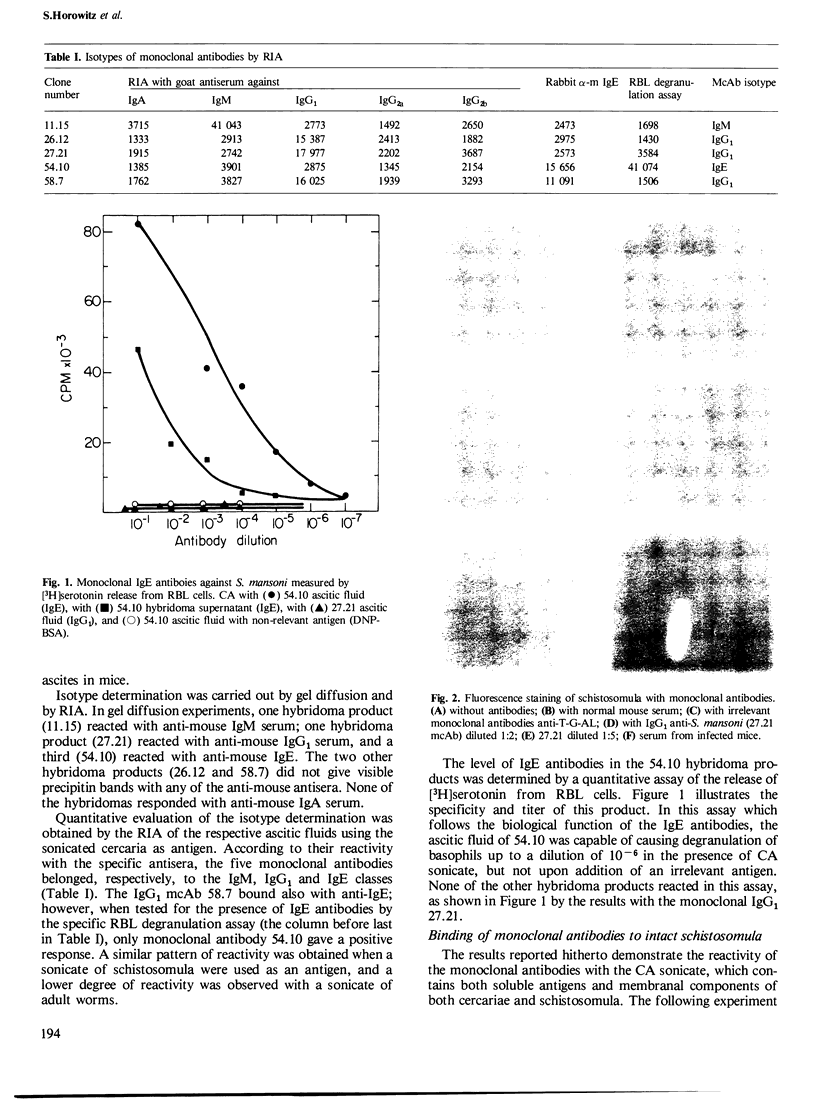
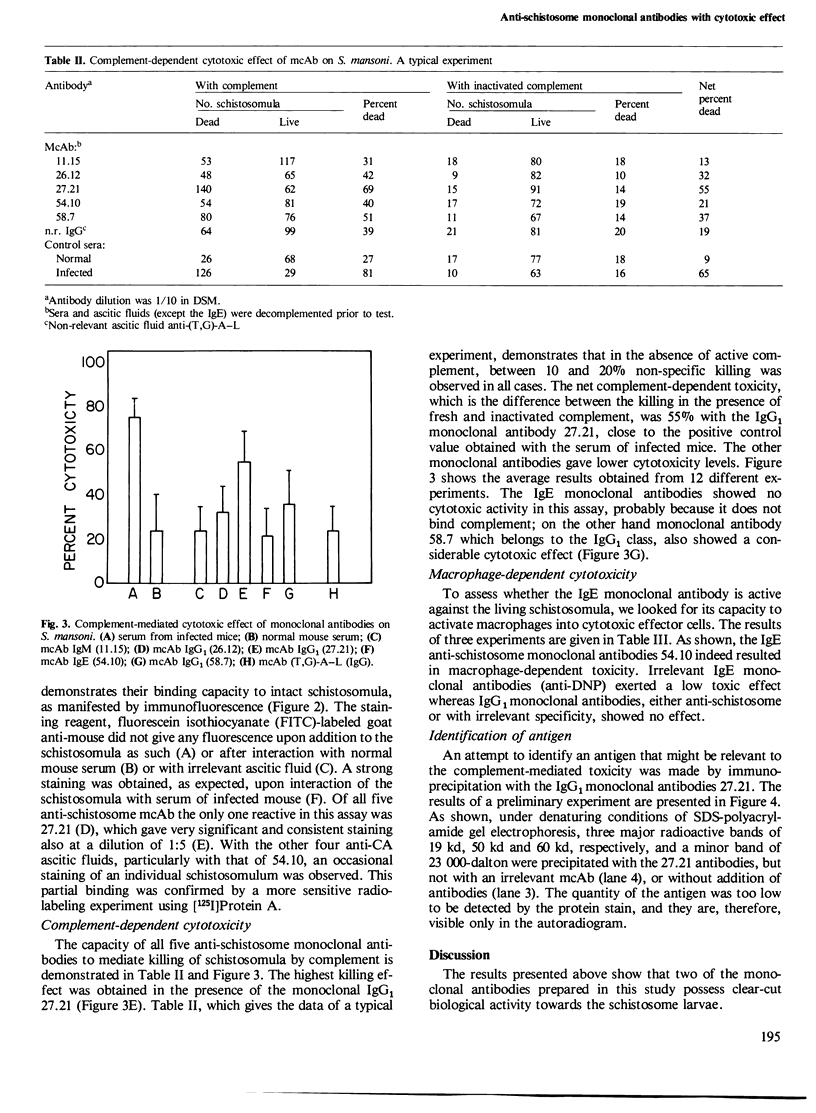
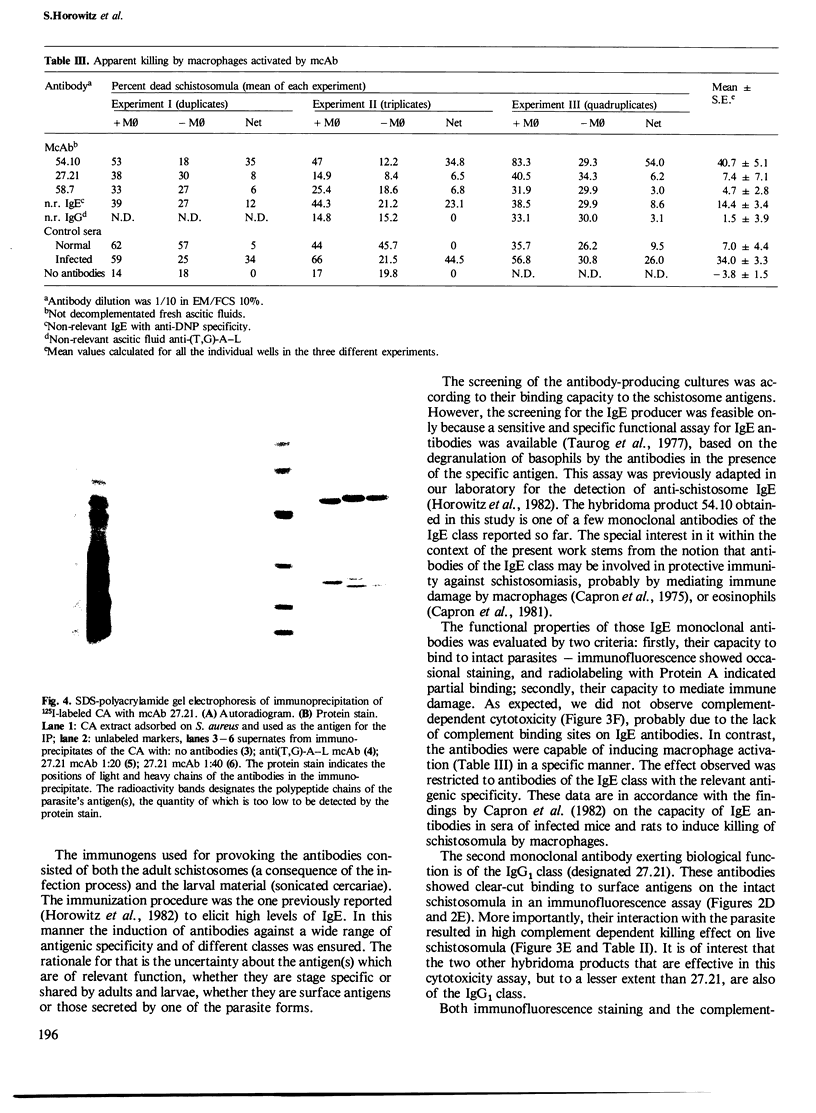
Five monoclonal antibodies specific towards Schistosoma mansoni antigens were prepared by fusion of spleen cells of infected and immunized mouse with the murine myeloma NS-1 cells. Three of the five antibodies belonged to the IgG1 class, one was an IgM and the fifth one was an IgE. The IgE monoclonal antibody designated 54.10, induced antigen-specific degranulation of rat basophilic cell line, a property which served as the basis for the screening assay. Its biological function was demonstrated by a specific macrophage activation that led to killing of schistosomula; no such killing was obtained with anti-schistosome antibodies of other classes or with IgE of different antigenic specificity. The second monoclonal antibody of biological significance was an IgG1, designated 27.21 which is reactive in the immunofluorescence staining of surface antigens on intact schistosomula. All three monoclonal antibodies that belonged to the IgG1 class were effective in mediating killing of schistosomula by complement, with the highest effect exerted by 27.21. It is thus apparent that the 27.21 monoclonal antibody is directed against a densely distributed surface antigen on the schistosomula membrane which is possibly involved in the protective immunity. Preliminary data showed that immunoprecipitation with the 27.21 antibodies results in the isolation of three major protein bands, of 60 kd, 50 kd, 19 kd, respectively.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Butterworth A. E., Taylor D. W., Veith M. C., Vadas M. A., Dessein A., Sturrock R. F., Wells E. Studies on the mechanisms of immunity in human schistosomiasis. Immunol Rev. 1982;61:5–39. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00372.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capron A., Dessaint J. P., Capron M., Bazin H. Specific IgE antibodies in immune adherence of normal macrophages to Schistosoma mansoni schistosomules. Nature. 1975 Feb 6;253(5491):474–475. doi: 10.1038/253474a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capron A., Dessaint J. P., Capron M., Joseph M., Torpier G. Effector mechanisms of immunity to schistosomes and their regulation. Immunol Rev. 1982;61:41–66. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00373.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capron M., Bazin H., Joseph M., Capron A. Evidence for IgE-dependent cytotoxicity by rat eosinophils. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):1764–1768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eshhar Z., Ofarim M., Waks T. Generation of hybridomas secreting murine reaginic antibodies of anti-DNP specificity. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):775–780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfre G., Howe S. C., Milstein C., Butcher G. W., Howard J. C. Antibodies to major histocompatibility antigens produced by hybrid cell lines. Nature. 1977 Apr 7;266(5602):550–552. doi: 10.1038/266550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz S., Smolarsky M., Arnon R. Protection against Schistosoma mansoni achieved by immunization with sonicated parasite. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Apr;12(4):327–332. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Urban J. F., Jr, Ishizaka K. IgE formation in the rat following infection with Nippostrongylus brasiliensis. I. Proliferation and differentiation of IgE-bearing cells. Cell Immunol. 1976 Mar 15;22(2):248–261. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90027-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett E., Bazin H. Elevation of total serum IgE in rats following helminth parasite infection. Nature. 1974 Oct 18;251(5476):613–614. doi: 10.1038/251613a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Schaffer F., Smolarsky M. Schistosoma mansoni: effect of insulin and a low-molecular-weight fraction of serum on schistosomula in chemically defined media. Exp Parasitol. 1981 Dec;52(3):378–385. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(81)90096-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell G. F., Cruise K. M., Garcia E. G., Anders R. F. Hybridoma-derived antibody with immunodiagnostic potential for schistosomiasis japonica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3165–3169. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musoke A. J., Williams J. F., Leid R. W. Immunological response of the rat to infection with Taenia taeniaeformis. VI. The role of immediate hypersensitivity in resistance to reinfection. Immunology. 1978 Mar;34(3):565–570. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogilvie B. M., Jones V. E. Immunity in the parasitic relationship between helminths and hosts. Prog Allergy. 1973;17:93–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkhouse R. M., Philipp M., Ogilvie B. M. Characterization of surface antigens of Trichinella spiralis infective larvae. Parasite Immunol. 1981 Winter;3(4):339–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1981.tb00412.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potocnjak P., Yoshida N., Nussenzweig R. S., Nussenzweig V. Monovalent fragments (Fab) of monoclonal antibodies to a sporozoite surface antigen (Pb44) protect mice against malarial infection. J Exp Med. 1980 Jun 1;151(6):1504–1513. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.6.1504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potocnjak P., Zavala F., Nussenzweig R., Nussenzweig V. Inhibition of idiotype--anti-idiotype interaction for detection of a parasite antigen: a new immunoassay. Science. 1982 Mar 26;215(4540):1637–1639. doi: 10.1126/science.6122269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseaux-Prevost R., Capron M., Bazin H., Capron A. IgE in experimental schistosomiasis. II. Quantitative determination of specific IgE antibodies against S. mansoni: a follow-up study of two strains of infected rats. Correlation with protective immunity. Immunology. 1978 Jul;35(1):33–39. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadun E. H., Gore R. W. Schistosoma mansoni and S. haematobium: homocytotropic reagin-like antibodies in infections of man and experimental animals. Exp Parasitol. 1970 Dec;28(3):435–449. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(70)90112-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taurog J. D., Mendoza G. R., Hook W. A., Siraganian R. P., Metzger H. Noncytotoxic IgE-mediated release of histamine and serotonin from murine mastocytoma cells. J Immunol. 1977 Nov;119(5):1757–1761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzehoval E., Segal S., Stabinsky Y., Fridkin M., Spirer Z., Feldman M. Tuftsin (an Ig-associated tetrapeptide) triggers the immunogenic function of macrophages: implications for activation of programmed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3400–3404. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verwaerde C., Grzych J. M., Bazin H., Capron M., Capron A. Production d'anticorps monoclonaux anti Schistosoma mansoni. Etude préliminaire de leurs activités biologiques. C R Seances Acad Sci D. 1979 Oct 29;289(10):725–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]