Abstract
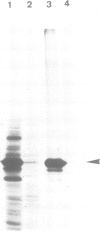
Two distinct phenotypic groups of inbred strains of mice, with different amounts of submaxillary gland (SMG) renin have been described. We have previously shown that strains with high levels of SMG renin, such as Swiss or AKR mice, have two renin genes, Rn1 and Rn2, per haploid genome, while strains with low levels of SMG, such as BALB/c or C57Bl/6, have only one renin gene. We now report the molecular cloning of cDNA copies of Swiss mouse kidney renin mRNA and present nucleotide sequence data of the recombinant clones. Comparison of these sequences with the sequence of Swiss mouse SMG renin mRNA we have previously reported, demonstrates that Swiss mice express the two non-allelic genes, Rn1 and Rn2.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auffray C., Nageotte R., Chambraud B., Rougeon F. Mouse immunoglobulin genes: a bacterial plasmid containing the entire coding sequence for a pre-gamma 2a heavy chain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 25;8(6):1231–1241. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.6.1231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bing J., Poulsen K. Cause of the disproportion between the vast increase in plasma renin and the only small (if any) increase in blood pressure after manipulation of the submaxillary gland. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A. 1977 Sep;85(5):691–698. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1977.tb00460.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bing J., Poulsen K. Differences in renal and submaxillary renin release after stimulation with isoprenaline and noradrenaline. Acta Physiol Scand. 1979 Jan;105(1):58–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1979.tb06314.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bing J., Poulsen K. Different effects on renal and submaxillary renin release after blockade of the renin system in mice. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A. 1975 Nov;83(6):733–736. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1975.tb01404.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOULD A. B., SKEGGS L. T., Jr, KAHN J. R. THE PRESENCE OF RENIN ACTIVITY IN BLOOD VESSEL WALLS. J Exp Med. 1964 Mar 1;119:389–399. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.3.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganten D., Minnich J. L., Granger P., Hayduk K., Brecht H. M., Barbeau A., Boucher R., Genest J. Angiotensin-forming enzyme in brain tissue. Science. 1971 Jul 2;173(3991):64–65. doi: 10.1126/science.173.3991.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose S., Workman R. J., Inagami T. Specific antibody to hog renal renin and its application to the direct radioimmunoassay of renin in various organs. Circ Res. 1979 Aug;45(2):275–281. doi: 10.1161/01.res.45.2.275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malling C., Poulsen K. Direct measurement of high molecular weight forms of renin in plasma. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Apr 25;491(2):542–550. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90299-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D. K., Kempter A., Boll H., Eisenreich M., Hertting G. alpha-Adrenoceptor-mediated inhibitory effect of the sympathetic nervous system on the isoprenaline-induced increase in plasma renin concentration. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1977 Aug;299(1):77–82. doi: 10.1007/BF00508641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelakis A. M., Yoshida H., Menzie J., Murakami K., Inagami T. A radioimmunoassay for the direct measurement of renin in mice and its application to submaxillary gland and kidney studies. Endocrinology. 1974 Apr;94(4):1101–1105. doi: 10.1210/endo-94-4-1101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins J. J., Burt D. W., Windass J. D., McTurk P., George H., Brammar W. J. Molecular cloning of two distinct renin genes from the DBA/2 mouse. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1461–1466. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01338.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver W. J., Gross F. Effect of testosterone and duct ligation on submaxillary renin-like principle. Am J Physiol. 1967 Aug;213(2):341–346. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.213.2.341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panthier J. J., Foote S., Chambraud B., Strosberg A. D., Corvol P., Rougeon F. Complete amino acid sequence and maturation of the mouse submaxillary gland renin precursor. Nature. 1982 Jul 1;298(5869):90–92. doi: 10.1038/298090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panthier J. J., Holm I., Rougeon F. The mouse Rn locus: S allele of the renin regulator gene results from a single structural gene duplication. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1417–1421. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01332.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rougeon F., Chambraud B., Foote S., Panthier J. J., Nageotte R., Corvol P. Molecular cloning of a mouse submaxillary gland renin cDNA fragment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6367–6371. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner S. L., Lumbers E. R., Symonds E. M. Renin concentration in human fetal and maternal tissues. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1968 Jun 15;101(4):529–533. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(68)90564-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WERLE E., BAUMEISTER K., SCHMAL A. [On the renin-like enzyme in the submaxillary gland of the white mouse]. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1962;244:21–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. M., Erdös E. G., Dunn J. F., Wilson J. D. Genetic control of renin activity in the submaxillary gland of the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1185–1189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. M., Erdös E. G., Wilson J. D., Taylor B. A. Location on chromosome 1 of Rnr, a gene that regulates renin in the submaxillary gland of the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5623–5626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. M., Taylor B. A. Genetic regulation of thermostability of mouse submaxillary gland renin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 10;257(1):217–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]