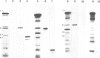Abstract
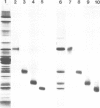
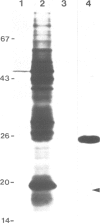
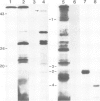
Cytochrome b6/f complex was prepared from washed thylakoid membranes by a procedure involving detergent treatment and centrifugation in sucrose gradients. The complex is composed of at least four polypeptide species, cytochrome f which occurs in two variant forms (mol. wt. 34/33 kd), cytochrome b6 (23 kd), the high-potential Rieske iron-sulfur protein (19 kd) and a fourth subunit (17 kd) of unknown function. Transcripts for the cytochromes f, b6 and subunit 4 were found in plastid RNA, those for the Rieske iron-sulfur protein in cytosolic poly(A)+ RNA. Transcripts for cytochrome b6 and subunit 4 are translated in rabbit reticulocyte lysates into products of correct length. The Rieske iron-sulfur protein and the cytochrome f apoprotein appear to be made as precursors with excess sequences of 7 and 4 kd, respectively. Cytochrome f, cytochrome b6 and subunit 4 are encoded by uninterrupted plastid genes that are located in the large single-copy region of the circular DNA molecule. Each of these genes is present once per chromosome. Their location and direction of transcription have been determined by hybrid-selection mapping and by cell-free transcription/translation of various recombinant DNAs. The genes for cytochrome b6 and for subunit 4 lie near each other, but do not overlap. They are transcribed into a single message. The gene for cytochrome f maps 15 kbp away from this cluster, close to the 3' end of the gene for the large subunit of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase, and is transcribed into a separate 4 kb long RNA. All these genes have the same polarities with respect to each other.
Keywords: cytochrome genes, thylakoid membrane, plastid DNA, transcripts, spinach
Full text
PDF

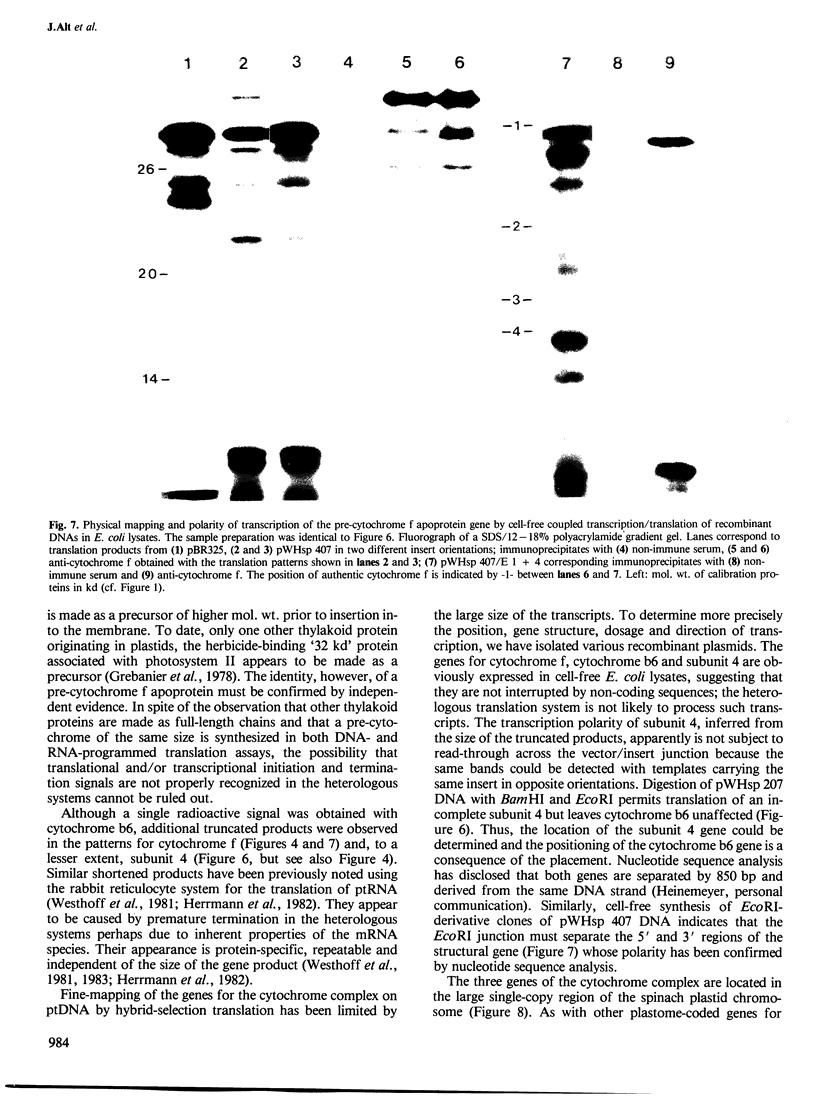
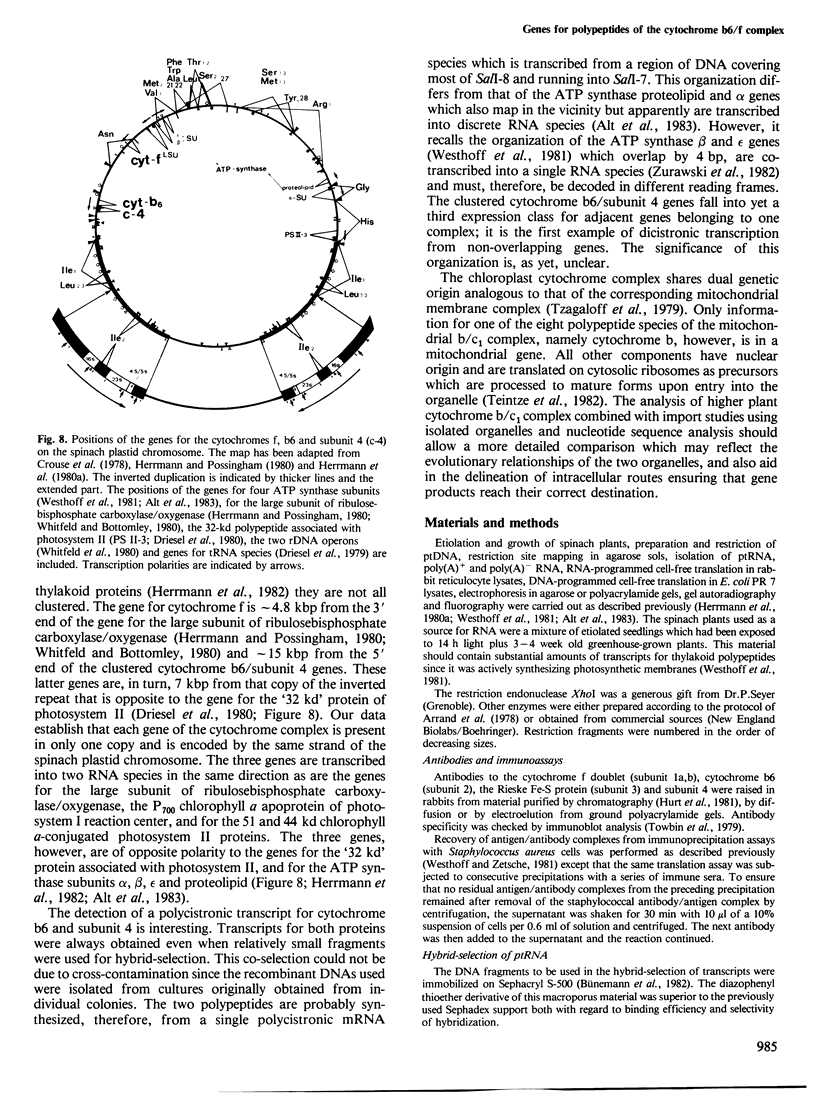

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arrand J. R., Myers P. A., Roberts R. J. A new restriction endonuclease from Streptomyces albus G. J Mol Biol. 1978 Jan 5;118(1):127–135. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90249-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bünemann H., Westhoff P., Herrmann R. G. Immobilization of denatured DNA to macroporous supports: I. Efficiency of different coupling procedures. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7163–7180. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chua N. H., Schmidt G. W. Transport of proteins into mitochondria and chloroplasts. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jun;81(3):461–483. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.3.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. P., Andersson B. Lateral and transverse organisation of cytochromes in the chloroplast thylakoid membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Dec 31;103(4):1336–1342. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90269-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty A., Gray J. C. Synthesis of cytochrome f by isolated pea chloroplasts. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jul;98(1):87–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13164.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driesel A. J., Crouse E. J., Gordon K., Bohnert H. J., Herrmann R. G., Steinmetz A., Mubumbila M., Keller M., Burkard G., Weil J. H. Fractionation and identification of spinach chloroplast transfer RNAs and mapping of their genes on the restriction map of chloroplast DNA. Gene. 1979 Aug;6(4):285–306. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90070-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driesel A. J., Speirs J., Bohnert H. J. Spinach chloroplast mRNA for a 32 000 dalton polypeptide: size and localization on the physical map of the chloroplast DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Dec 11;610(2):297–310. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grebanier A. E., Coen D. M., Rich A., Bogorad L. Membrane proteins synthesized but not processed by isolated maize chloroplasts. J Cell Biol. 1978 Sep;78(3):734–746. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.3.734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Wallis J. Colony hybridization. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:379–389. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann R. G., Possingham J. V. Plastid DNA-the plastome. Results Probl Cell Differ. 1980;10:45–96. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-38255-3_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann R. G., Whitfeld P. R., Bottomley W. Construction of a SalI/PstI restriction map of spinach chloroplast DNA using low-gelling-temperature-agarose electrophoresis. Gene. 1980 Jan;8(2):179–191. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90036-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurt E., Hauska G. A cytochrome f/b6 complex of five polypeptides with plastoquinol-plastocyanin-oxidoreductase activity from spinach chloroplasts. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jul;117(3):591–595. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06379.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurt E., Hauska G. Identification of the polypeptides in the cytochrome b6/f complex from spinach chloroplasts with redox-center-carrying subunits. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1982 Dec;14(5-6):405–424. doi: 10.1007/BF00743067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurt E., Hauska G., Malkin R. Isolation of the Rieske iron-sulfur protein from the cytochrome b6/f complex of spinach chloroplasts. FEBS Lett. 1981 Nov 2;134(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80537-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz L., Kingsbury D. T., Helinski D. R. Stimulation by cyclic adenosine monophosphate of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid replication and catabolite repression of the plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid-protein relaxation complex. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):577–591. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.577-591.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teintze M., Slaughter M., Weiss H., Neupert W. Biogenesis of mitochondrial ubiquinol:cytochrome c reductase (cytochrome bc1 complex). Precursor proteins and their transfer into mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10364–10371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. E., Ryan D., Levin W. An improved staining procedure for the detection of the peroxidase activity of cytochrome P-450 on sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1976 Sep;75(1):168–176. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90067-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzagoloff A., Macino G., Sebald W. Mitochondrial genes and translation products. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:419–441. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.002223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westhoff P., Zetsche K. Regulation of the synthesis of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase and its subunits in the flagellate Chlorogonium elongatum. Different levels of translatable messenger RNAs for the large and the small subunits in autotrophic and heterotrophic cells as determined by immunological techniques. Eur J Biochem. 1981 May 15;116(2):261–267. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05328.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitfeld P. R., Herrmann R. G., Bottomley W. Mapping of the ribosomal RNA genes on spinach chloroplast DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jun;5(6):1741–1751. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.6.1741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurawski G., Bohnert H. J., Whitfeld P. R., Bottomley W. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for the M(r) 32,000 thylakoid membrane protein from Spinacia oleracea and Nicotiana debneyi predicts a totally conserved primary translation product of M(r) 38,950. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7699–7703. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]