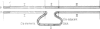Abstract
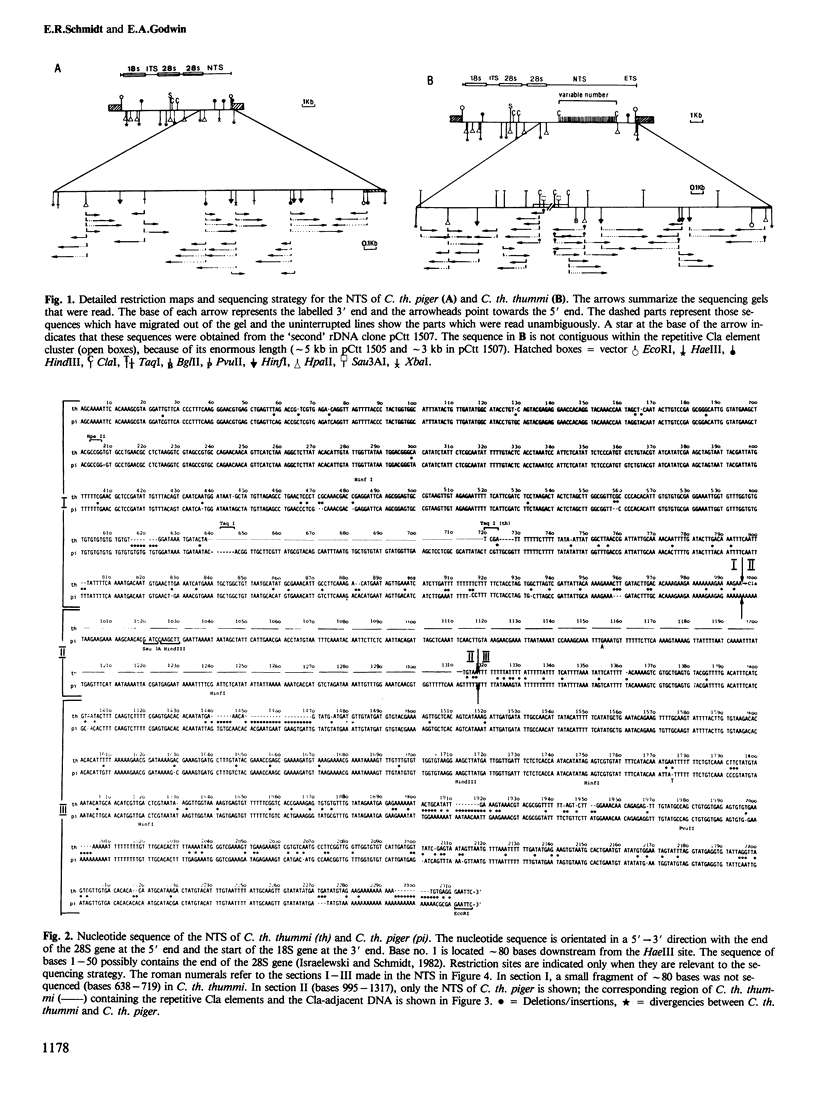
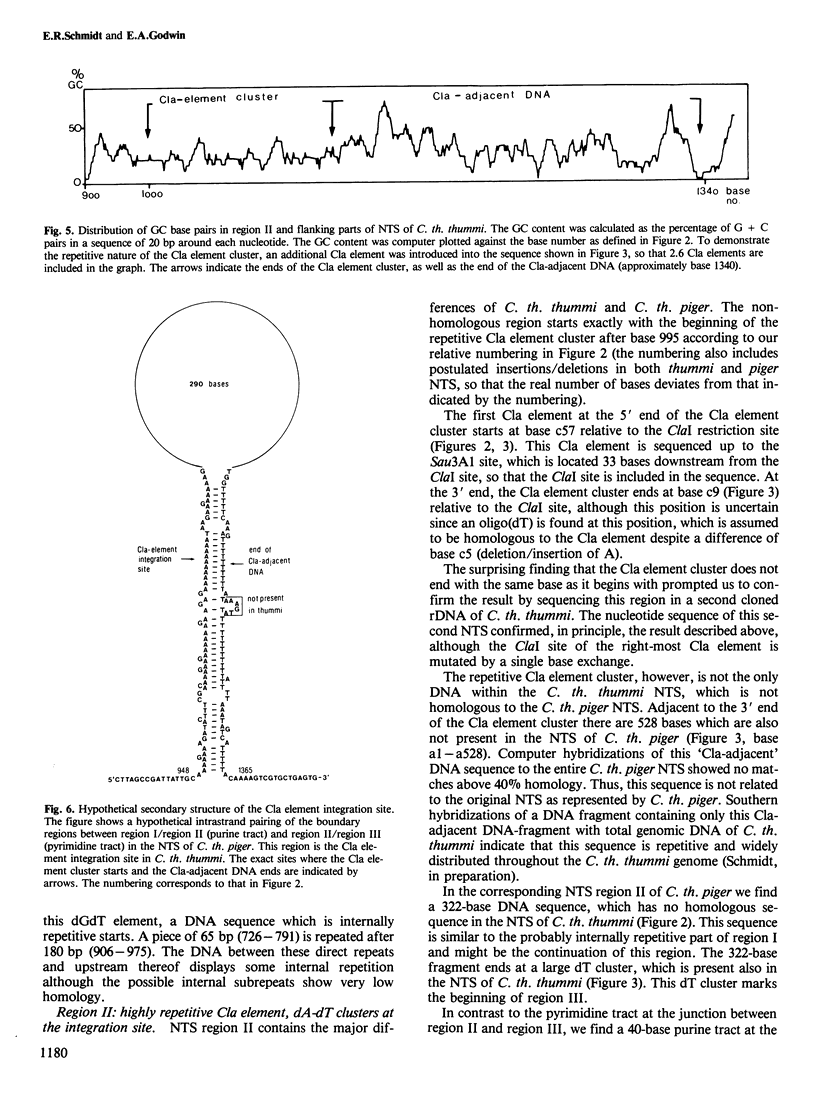
The nucleotide sequence of the non-transcribed spacer (NTS) in the ribosomal DNA (rDNA) of Chironomus thummi thummi and Chironomus thummi piger, including major parts of the external transcribed spacer, is described. The NTS of the two subspecies are very different in length, (thummi, 7 kb, piger, 2 kb); this is due to the insertion into the NTS of C.th. thummi of a large cluster of highly repetitive DNA sequences which are not present in the NTS of C. th. piger. The repetitive sequences, called Cla elements, are present in high copy number elsewhere in the genome of C. th. thummi and, in lower copy number, in the genome of C. th. piger in which they are mainly in the centromeric regions. Sequencing of the NTS of thummi and piger yielded information on the junctions between the Cla element cluster and the original NTS sequence, as well as on the sequence of the integration site before the transposition has occurred. The integration site is characterized by a dA cluster at the one end and a dT cluster at the other.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnheim N., Kuehn M. The genetic behaviour of a cloned mouse ribosomal DNA segment mimics mouse ribosomal gene evolution. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 15;134(4):743–763. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90483-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnheim N., Seperack P., Banerji J., Lang R. B., Miesfeld R., Marcu K. B. Mouse rDNA nontranscribed spacer sequences are found flanking immunoglobulin CH genes and elsewhere throughout the genome. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):179–185. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90166-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach R., Allet B., Crippa M. Sequence organization of the spacer in the ribosomal genes of Xenopus clivii and Xenopus borealis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5311–5330. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boseley P., Moss T., Mächler M., Portmann R., Birnstiel M. Sequence organization of the spacer DNA in a ribosomal gene unit of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):19–31. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90291-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen E. S., Dover G. A. Multiple Pol I initiation sequences in rDNA spacers of Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):7017–7026. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.7017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen E. S., Thoday J. M., Dover G. Rate of turnover of structural variants in the rDNA gene family of Drosophila melanogaster. Nature. 1982 Feb 18;295(5850):564–568. doi: 10.1038/295564a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortadas J., Pavon M. C. The organization of ribosomal genes in vertebrates. EMBO J. 1982;1(9):1075–1080. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01299.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz M. O., Barsacchi-Pilone G., Mahon K. A., Gall J. G. Transcripts from both strands of a satellite DNA occur on lampbrush chromosome loops of the newt Notophthalmus. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):649–659. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90091-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dover G. Molecular drive: a cohesive mode of species evolution. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):111–117. doi: 10.1038/299111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall J. G., Stephenson E. C., Erba H. P., Diaz M. O., Barsacchi-Pilone G. Histone genes are located at the sphere loci of newt lampbrush chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1981;84(2):159–171. doi: 10.1007/BF00399128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada H., Petrino M. G., Kakunaga T. A novel repeated element with Z-DNA-forming potential is widely found in evolutionarily diverse eukaryotic genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6465–6469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israelewski N., Schmidt E. R. Spacer size heterogeneity in ribosomal DNA of Chironomus thummi is due to a 120 bp repeat homologous to a predominantly centromeric repeated sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7689–7700. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keyl H. G. Duplikationen von Untereinheiten der Chromosomalen DNS während der Evolution von Chironomus thummi. Chromosoma. 1965;17(2):139–180. doi: 10.1007/BF00330079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemenz R., Geiduschek E. P. The 5' terminus of the precursor ribosomal RNA of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jun 25;8(12):2679–2689. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.12.2679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohorn B. D., Rae P. M. Accurate transcription of truncated ribosomal DNA templates in a Drosophila cell-free system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1501–1505. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohorn B. D., Rae P. M. Nontranscribed spacer sequences promote in vitro transcription of Drosophila ribosomal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6879–6886. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunz W., Petersen G., Renkawitz-Pohl R., Glätzer K. H., Schäfer M. Distribution of spacer length classes and the intervening sequence among different nucleolus organizers in Drosophila hydei. Chromosoma. 1981;83(2):145–158. doi: 10.1007/BF00286785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long E. O., Dawid I. B. Repeated genes in eukaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:727–764. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long E. O., Rebbert M. L., Dawid I. B. Nucleotide sequence of the initiation site for ribosomal RNA transcription in Drosophila melanogaster: comparison of genes with and without insertions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1513–1517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maden B. E., Moss M., Salim M. Nucleotide sequence of an external transcribed spacer in Xenopus laevis rDNA: sequences flanking the 5' and 3' ends of 18S rRNA are non-complementary. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 10;10(7):2387–2398. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.7.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter S., Truett M., Phillips M., Maher A. Eucaryotic transposable genetic elements with inverted terminal repeats. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):639–647. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90310-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rae P. M., Barnett T., Murtif V. L. Nontranscribed spacers in Drosophila ribosomal DNA. Chromosoma. 1981;82(5):637–655. doi: 10.1007/BF00285773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. The use of thin acrylamide gels for DNA sequencing. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 1;87(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer J., Schmidt E. R. Different repetition frequencies of a 120 base-pair DNA-element and its arrangement in Chironomus thummi thummi and Chironomus thummi piger. Chromosoma. 1981;84(1):61–66. doi: 10.1007/BF00293363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt E. R., Godwin E. A., Keyl H. G., Israelewski N. Cloning and analysis of ribosomal DNA of Chironomus thummi piger and Chironomus thummi thummi. The nontranscribed spacer of Ch. th. thummi contains a highly repetitive DNA sequence. Chromosoma. 1982;87(4):389–407. doi: 10.1007/BF00327181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer M., Wyman A. R., White R. Length variation in the non-transcribed spacer of Calliphora erythrocephala ribosomal DNA is due to a 350 base-pair repeat. J Mol Biol. 1981 Feb 25;146(2):179–199. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90431-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. P. Evolution of repeated DNA sequences by unequal crossover. Science. 1976 Feb 13;191(4227):528–535. doi: 10.1126/science.1251186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Reeder R. H. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation and termination sites for ribosomal RNA transcription in X. laevis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. A new computer method for the storage and manipulation of DNA gel reading data. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 25;8(16):3673–3694. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.16.3673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson E. C., Erba H. P., Gall J. G. Histone gene clusters of the newt notophthalmus are separated by long tracts of satellite DNA. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):639–647. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90090-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szalay A. A., Grohmann K., Sinsheimer R. L. Separation of the complementary strands of DNA fragments on polyacrylamide gels. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1569–1578. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]