Abstract
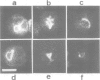
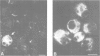
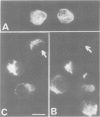
We describe the alterations of vimentin intermediate filament (IF) expression in human hemopoietic committed precursors as they differentiate into mature cells of the erythroid, granulomonocytic, megacaryocytic and lymphoid lineages. A double labelling fluorescence procedure was used to identify hemopoietic cells expressing lineage-specific antigens and to decorate the vimentin IF network. Whereas very early progenitors from each lineage expressed vimentin, the density and organization of the network differed strikingly as the cells matured on a given pathway. T lymphocytes, monocytes and granulocytes retained vimentin expression at all stages of maturation. In contrast, megakaryoblasts lose vimentin expression at a very early stage of differentiation, erythroblasts at variable steps between the committed erythroid cell and the red cell. Finally, B lymphocytes tend to lose vimentin expression later when they mature into plasma cells.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altmannsberger M., Weber K., Hölscher A., Schauer A., Osborn M. Antibodies to intermediate filaments as diagnostic tools: human gastrointestinal carcinomas express prekeratin. Lab Invest. 1982 May;46(5):520–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aye M. T., Seguin J. A., McBurney J. P. Erythroid and granulocytic colony growth in cultures supplemented with human serum lipoproteins. J Cell Physiol. 1979 May;99(2):233–238. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040990210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannasch P., Zerban H., Schmid E., Franke W. W. Liver tumors distinguished by immunofluorescence microscopy with antibodies to proteins of intermediate-sized filaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4948–4952. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branton D., Cohen C. M., Tyler J. Interaction of cytoskeletal proteins on the human erythrocyte membrane. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):24–32. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90497-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl D., Bignami A., Weber K., Osborn M. Filament proteins in rat optic nerves undergoing Wallerian degeneration: localization of vimentin, the fibroblastic 100-A filament protein, in normal and reactive astrocytes. Exp Neurol. 1981 Aug;73(2):496–506. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(81)90283-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dellagi K., Brouet J. C., Perreau J., Paulin D. Human monoclonal IgM with autoantibody activity against intermediate filaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):446–450. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dellagi K., Brouet J. C. Redistribution of intermediate filaments during capping of lymphocyte surface molecules. Nature. 1982 Jul 15;298(5871):284–286. doi: 10.1038/298284a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards P. A. Monoclonal antibodies that bind to the human erythrocyte-membrane glycoproteins glycophorin A and Band 3 [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1980 Jun;8(3):334–335. doi: 10.1042/bst0080334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golde D. W., Quan S. G., Cline M. J. Human T lymphocyte cell line producing colony-stimulating activity. Blood. 1978 Nov;52(5):1068–1072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger B. L., Repasky E. A., Lazarides E. Synemin and vimentin are components of intermediate filaments in avian erythrocytes. J Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;92(2):299–312. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iscove N. N., Guilbert L. J., Weyman C. Complete replacement of serum in primary cultures of erythropoietin-dependent red cell precursors (CFU-E) by albumin, transferrin, iron, unsaturated fatty acid, lecithin and cholesterol. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Mar;126(1):121–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90476-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson B. W., Grund C., Schmid E., Bürki K., Franke W. W., Illmensee K. Formation of cytoskeletal elements during mouse embryogenesis. Intermediate filaments of the cytokeratin type and desmosomes in preimplantation embryos. Differentiation. 1980;17(3):161–179. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1980.tb01093.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E. Intermediate filaments: a chemically heterogeneous, developmentally regulated class of proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:219–250. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.001251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehto V. P., Hovi T., Vartio T., Badley R. A., Virtanen I. Reorganization of cytoskeletal and contractile elements during transition of human monocytes into adherent macrophages. Lab Invest. 1982 Oct;47(4):391–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. J. Monoclonal antibodies against myofibrillar components of rat skeletal muscle decorate the intermediate filaments of cultured cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2335–2339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulin D., Babinet C., Weber K., Osborn M. Antibodies as probes of cellular differentiation and cytoskeletal organization in the mouse blastocyst. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Dec;130(2):297–304. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90006-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preud'homme J. L., Labaume S. Immunofluorescent staining of human lymphocytes for the detection of surface immunoglobulins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 30;254:254–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb29175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochiantz A., Delacourte A., Daguet M. C., Paulin D. Intermediate filament proteins in mouse brain cells cultured in the presence or absence of fetal calf serum. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Jun;139(2):404–410. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90267-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quesenberry P., Levitt L. Hematopoietic stem cells (third of three parts). N Engl J Med. 1979 Oct 18;301(16):868–872. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197910183011605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramaekers F. C., Puts J. J., Kant A., Moesker O., Jap P. H., Vooijs G. P. Use of antibodies to intermediate filaments in the characterization of human tumors. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1982;46(Pt 1):331–339. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1982.046.01.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnitzer J., Franke W. W., Schachner M. Immunocytochemical demonstration of vimentin in astrocytes and ependymal cells of developing and adult mouse nervous system. J Cell Biol. 1981 Aug;90(2):435–447. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.2.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelman B. M., Farmer S. R. Decreases in tubulin and actin gene expression prior to morphological differentiation of 3T3 adipocytes. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):53–60. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90089-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelman B. M., Farmer S. R. Decreases in tubulin and actin gene expression prior to morphological differentiation of 3T3 adipocytes. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):53–60. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90089-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staufenbiel M., Deppert W. Intermediate filament systems are collapsed onto the nuclear surface after isolation of nuclei from tissue culture cells. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Mar;138(1):207–214. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90107-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapscott S. J., Bennett G. S., Holtzer H. Neuronal precursor cells in the chick neural tube express neurofilament proteins. Nature. 1981 Aug 27;292(5826):836–838. doi: 10.1038/292836a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vainchenker W., Chapman J., Deschamps J. F., Vinci G., Bouguet J., Titeux M., Breton-Gorius J. Normal human serum contains a factor(s) capable of inhibiting megakaryocyte colony formation. Exp Hematol. 1982 Sep;10(8):650–660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vainchenker W., Deschamps J. F., Bastin J. M., Guichard J., Titeux M., Breton-Gorius J., McMichael A. J. Two monoclonal antiplatelet antibodies as markers of human megakaryocyte maturation: immunofluorescent staining and platelet peroxidase detection in megakaryocyte colonies and in in vivo cells from normal and leukemic patients. Blood. 1982 Mar;59(3):514–521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen S. H., Fields K. L. Antibodies to neurofilament, glial filament, and fibroblast intermediate filament proteins bind to different cell types of the nervous system. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jan;88(1):115–126. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.1.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]