Abstract
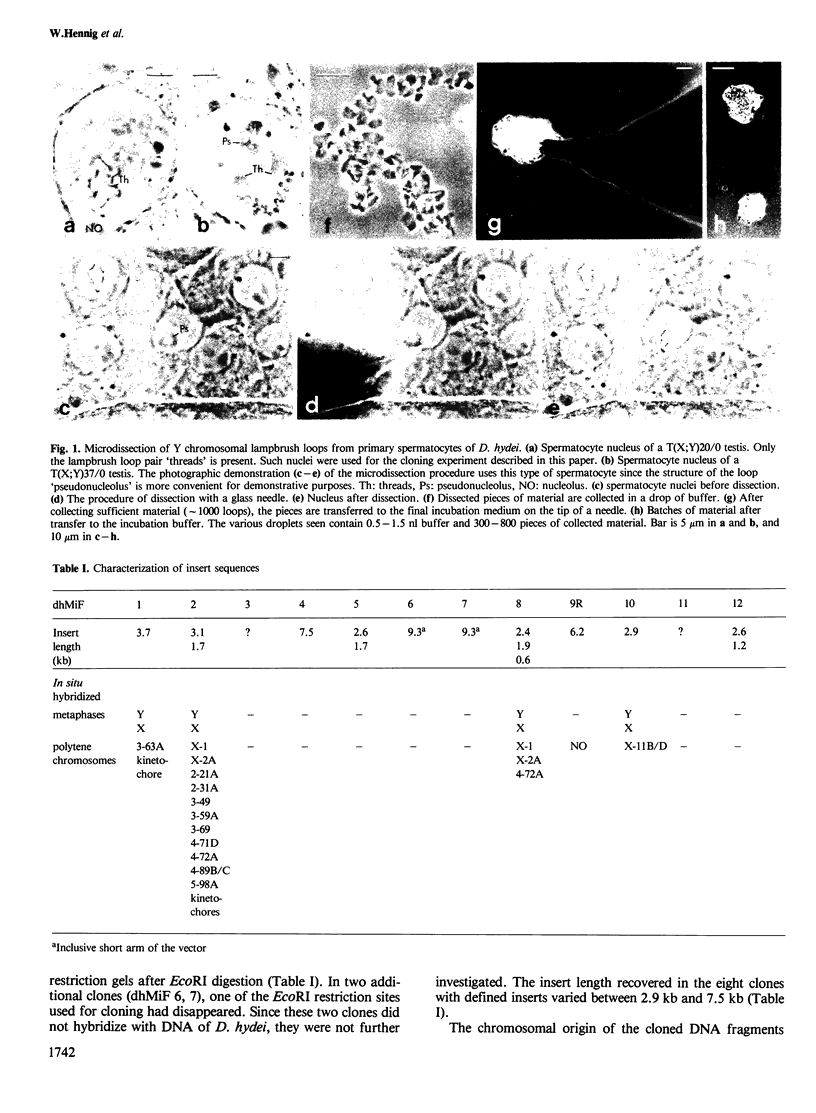
We microdissected a Y chromosomal lampbrush loop pair from primary spermatocyte nuclei of Drosophila hydei and cloned the DNA directly at the microscale. Four of the 12 recombinant DNA clones recovered display in situ hybridization to mitotic metaphase Y chromosomes, preferentially in the chromosomal region identified as the origin of the lampbrush loop pair. All clones, however, also hybridize to autosomal and X chromosomal loci in polytene chromosomes. Y chromosomal DNA sequences of D. hydei again prove to be members of different families of repeated sequences distributed throughout the genome. These microcloning experiments, which were carried out under very unfavourable experimental conditions (low DNA content of the lampbrush loops in the presence of large amounts of RNA) prove that almost any chromosomal structure detected by light microscopy is directly accessible to molecular cloning experiments by micromethods.
Keywords: Drosophila, Y chromosome, microcloning, repetitive DNA, genome structure
Full text
PDF


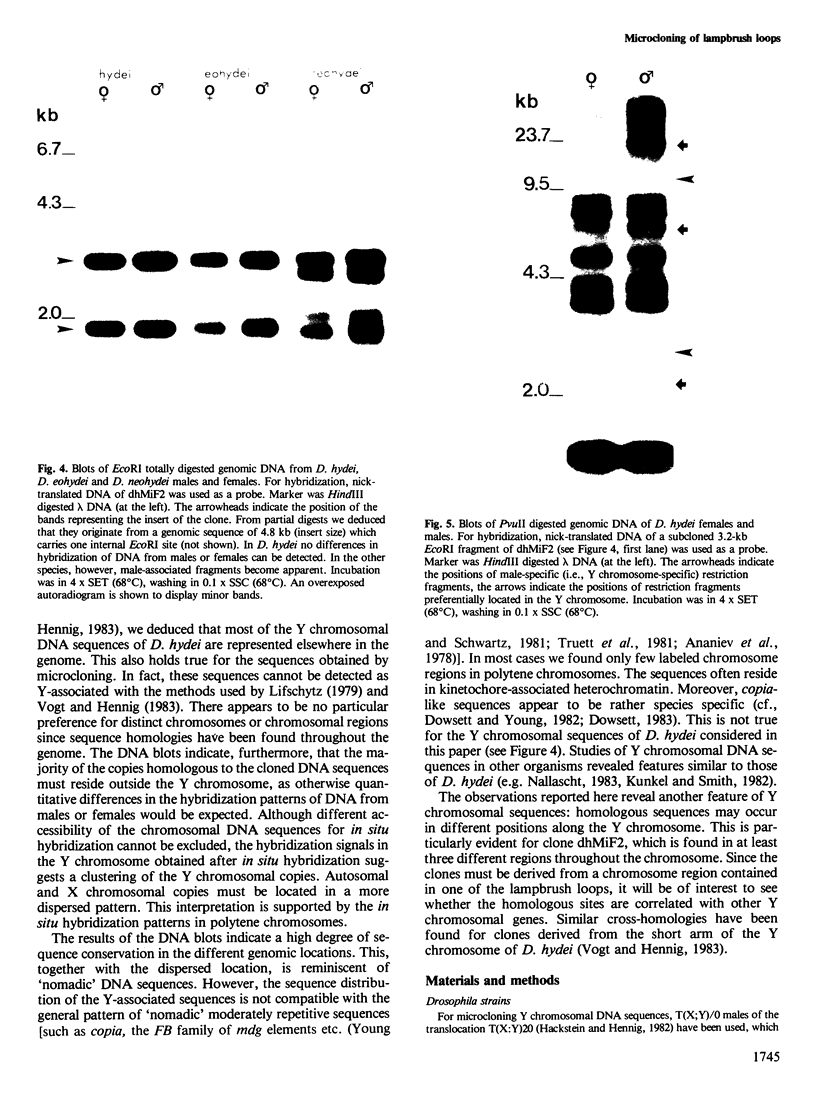

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ananiev E. V., Polukarova L. G., Yurov Y. B. Replication of chromosomal DNA in diploid Drosophila melanogaster cells cultured in vitro. Chromosoma. 1977 Feb 3;59(3):259–272. doi: 10.1007/BF00292782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonaccorsi S., Pimpinelli S., Gatti M. Cytological dissection of sex chromosome heterochromatin of Drosophila hydei. Chromosoma. 1981;84(3):391–403. doi: 10.1007/BF00286028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowsett A. P. Closely related species of Drosophila can contain different libraries of middle repetitive DNA sequences. Chromosoma. 1983;88(2):104–108. doi: 10.1007/BF00327329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowsett A. P., Young M. W. Differing levels of dispersed repetitive DNA among closely related species of Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4570–4574. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackstein J. H., Leoncini O., Beck H., Peelen G., Hennig W. Genetic fine structure of the Y chromosome of Drosophila hydei. Genetics. 1982 Jun;101(2):257–277. doi: 10.1093/genetics/101.2.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennig W., Meyer G. F., Hennig I., Leoncini O. Structure and function of the Y chromosome of Drosophila hydei. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:673–683. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Smith K. D. Evolution of human Y-chromosome DNA. Chromosoma. 1982;86(2):209–228. doi: 10.1007/BF00288677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifschytz E. A procedure for the cloning and identification of Y-specific middle repetitive sequences in Drosophila hydei. J Mol Biol. 1979 Sep 15;133(2):267–277. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90534-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifschytz E., Hareven D., Azriel A., Brodsly H. DNA clones and RNA transcripts of four lampbrush loops from the Y chromosome of Drosophila hydei. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):191–199. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90509-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nallaseth F. S., Lawther R. P., Stallcup M. R., Dewey M. J. Isolation of recombinant bacteriophage containing male-specific mouse DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;190(1):80–84. doi: 10.1007/BF00330327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scalenghe F., Turco E., Edström J. E., Pirrotta V., Melli M. Microdissection and cloning of DNA from a specific region of Drosophila melanogaster polytene chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1981;82(2):205–216. doi: 10.1007/BF00286105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truett M. A., Jones R. S., Potter S. S. Unusual structure of the FB family of transposable elements in Drosophila. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):753–763. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90101-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt P., Hennig W., Siegmund I. Identification of cloned Y chromosomal DNA sequences from a lampbrush loop of Drosophila hydei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5132–5136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt P., Hennig W. Y chromosomal DNA of Drosophila hydei. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 15;167(1):37–56. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki N. Differential staining of Y chromosomal lampbrush loops of Drosophila hydei. Chromosoma. 1981;83(5):679–684. doi: 10.1007/BF00328526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki N. Selective staining of Y chromosomal loops in Drosophila hydei, D. neohydei, and D. eohydei. Chromosoma. 1977 Mar 7;60(1):27–37. doi: 10.1007/BF00330408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young M. W., Schwartz H. E. Nomadic gene families in Drosophila. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 2):629–640. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]