Abstract
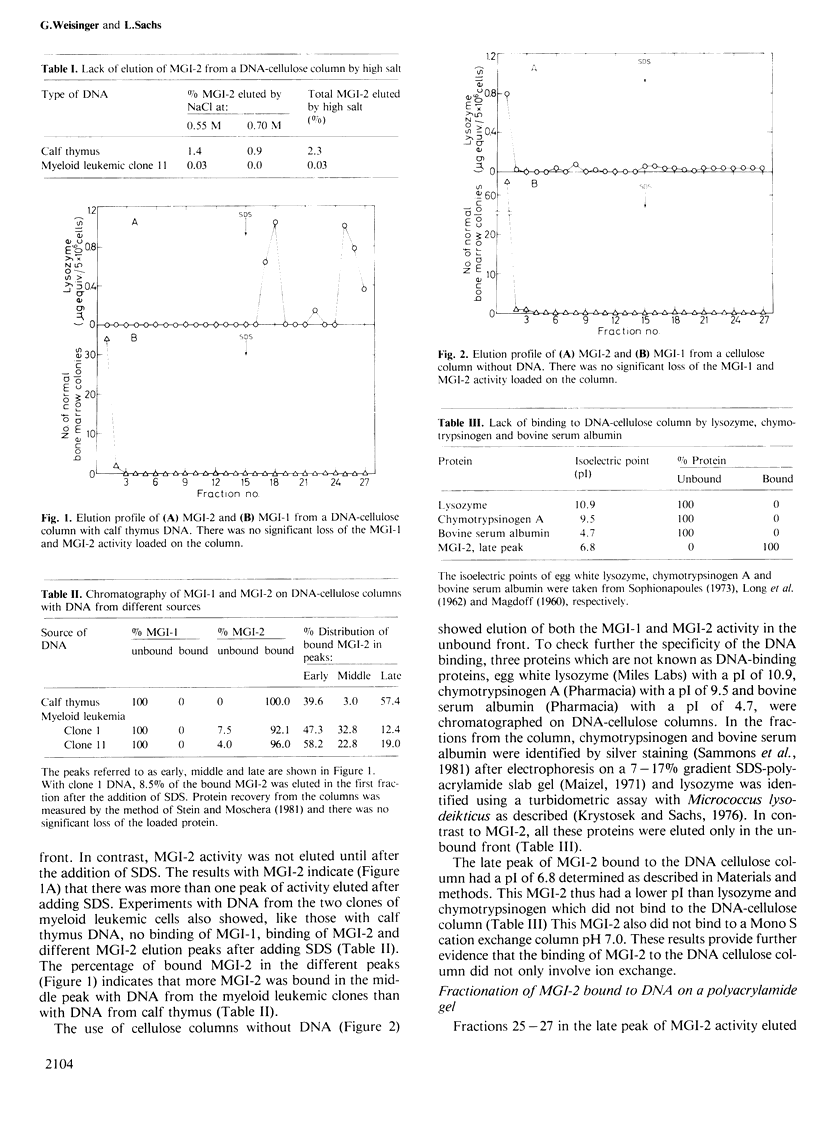
Macrophage and granulocyte-inducing (MGI) proteins regulate the growth and differentiation of myeloid hematopoietic cells. One class of these proteins (MGI-1) induces cell growth and another class (MGI-2) induces cell differentiation. Results obtained with DNA-cellulose column chromatography have shown that the differentiation-inducing protein MGI-2 can bind to double-stranded cellular DNA, but that there was no such binding under the same conditions by the growth-inducing protein MGI-1. DNA binding may thus be used to separate MGI-2 from MGI-1. The MGI-2 from mouse bound to DNA from mouse and calf. There were different elution peaks of the MGI-2 bound to DNA suggesting a heterogeneity of MGI-2 molecules, and the last peak eluted from the DNA cellulose column was enriched for one of the molecular forms of MGI-2. After one further step of purification by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, this molecular form of MGI-2 was active at a concentration of 6.5 X 10(-11) M. In normal development MGI-1 induces MGI-2. This induction of a DNA-binding differentiation-inducing protein by a growth-inducing protein is an efficient mechanism for the normal coupling of growth and differentiation. It is suggested that this may also be a mechanism for the normal coupling of growth and differentiation in other types of cells.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts B. M., Amodio F. J., Jenkins M., Gutmann E. D., Ferris F. L. Studies with DNA-cellulose chromatography. I. DNA-binding proteins from Escherichia coli. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:289–305. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess A. W., Camakaris J., Metcalf D. Purification and properties of colony-stimulating factor from mouse lung-conditioned medium. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):1998–2003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:193–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fibach E., Hayashi M., Sachs L. Control of normal differentiation of myeloid leukemic cells to macrophages and granulocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):343–346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W., Müller-Hill B. Isolation of the lac repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Dec;56(6):1891–1898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.6.1891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N., Keller J., Henderson L., Klein F., Palaszynski E. Procedures for the purification of interleukin 3 to homogeneity. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2431–2436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krystosek A., Sachs L. Control of lysozyme induction in the differentiation of myeloid leukemic cells. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 2):675–684. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90131-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landau T., Sachs L. Characterization of the inducer required for the development of macrophage and granulocyte colonies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2540–2544. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebermann D., Hoffman-Liebermann B., Sachs L. Regulation and role of different macrophage-and granulocyte-inducing proteins in normal and leukemic myeloid cells. Int J Cancer. 1982 Feb 15;29(2):159–161. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910290208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton J. H., Sachs L. Characterization of macrophage- and granulocyte-inducing proteins for normal and leukemic myeloid cells produced by the Krebs ascites tumor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Apr 3;673(4):552–569. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90486-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litman R. M. A deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase from Micrococcus luteus (Micrococcus lysodeikticus) isolated on deoxyribonucleic acid-cellulose. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 10;243(23):6222–6233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotem J., Sachs L. Coupling of growth and differentiation in normal myeloid precursors and the breakdown of this coupling in leukemia. Int J Cancer. 1983 Jul 15;32(1):127–134. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910320120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotem J., Sachs L. Different blocks in the differentiation of myeloid leukemic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3507–3511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotem J., Sachs L. In vivo inhibition of the development of myeloid leukemia by injection of macrophage- and granulocyte-inducing protein. Int J Cancer. 1981 Sep 15;28(3):375–386. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910280318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotem J., Sachs L. Mechanisms that uncouple growth and differentiation in myeloid leukemia cells: restoration of requirement for normal growth-inducing protein without restoring induction of differentiation-inducing protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4347–4351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mier J. W., Gallo R. C. Purification and some characteristics of human T-cell growth factor from phytohemagglutinin-stimulated lymphocyte-conditioned media. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6134–6138. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfahl M. Specific binding of the glucocorticoid-receptor complex to the mouse mammary tumor proviral promoter region. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):475–482. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90140-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluznik D. H., Sachs L. The cloning of normal "mast" cells in tissue culture. J Cell Physiol. 1965 Dec;66(3):319–324. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030660309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. ISOLATION OF THE lambda PHAGE REPRESSOR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Feb;57(2):306–313. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. P. The binding of RNA polymerase to DNA. J Mol Biol. 1966 Oct 28;21(1):83–114. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs L. Constitutive uncoupling of pathways of gene expression that control growth and differentiation in myeloid leukemia: a model for the origin and progression of malignancy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6152–6156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs L. Control of normal cell differentiation and the phenotypic reversion of malignancy in myeloid leukaemia. Nature. 1978 Aug 10;274(5671):535–539. doi: 10.1038/274535a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sophianopoulos A. J. Differential conductimetry. Methods Enzymol. 1973;27:557–590. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(73)27027-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley E. R., Heard P. M. Factors regulating macrophage production and growth. Purification and some properties of the colony stimulating factor from medium conditioned by mouse L cells. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 25;252(12):4305–4312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein S., Moschera J. High-performance liquid chromatography and picomole-level detection of peptides and proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1981;79(Pt B):7–16. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)79006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symonds G., Sachs L. Autoinduction of differentiation in myeloid leukemic cells: restoration of normal coupling between growth and differentiation in leukemic cells that constitutively produce their own growth-inducing protein. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1343–1346. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01320.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symonds G., Sachs L. Synchrony of gene expression and the differentiation of myeloid leukemic cells: reversion from constitutive to inducible protein synthesis. EMBO J. 1983;2(5):663–667. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01481.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weideli H., Brack C., Gehring W. J. Characterization of Drosophila DNA-binding protein DB-2: demonstration of its sequence-specific interaction with DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3773–3777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weideli H., Schedl P., Artavanis-Tsakonas S., Steward R., Yuan R., Gehring W. J. Purification of a protein from unfertilized eggs of Drosophila with specific affinity for a defined DNA sequence and the cloning of this DNA sequence in bacterial plasmids. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):693–700. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss B., Sachs L. Indirect induction of differentiation in myeloid leukemic cells by lipid A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1374–1378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yankner B. A., Shooter E. M. The biology and mechanism of action of nerve growth factor. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:845–868. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.004213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


