Abstract
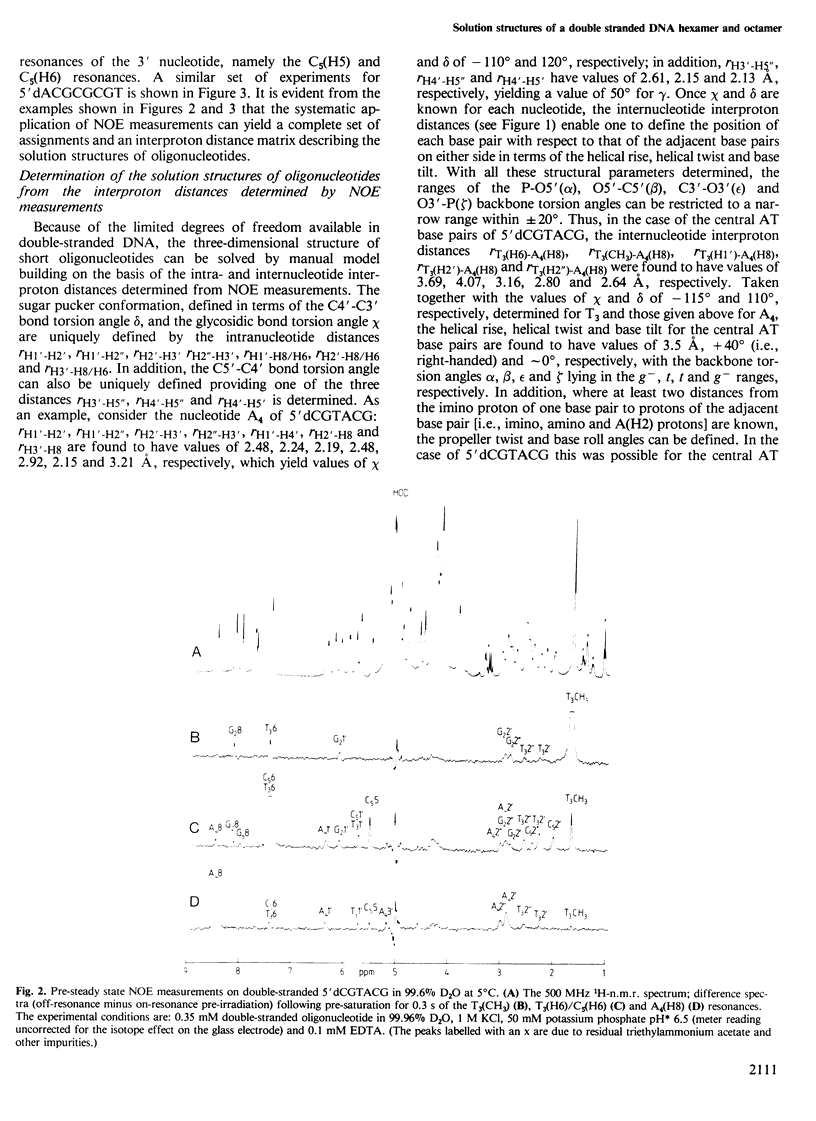
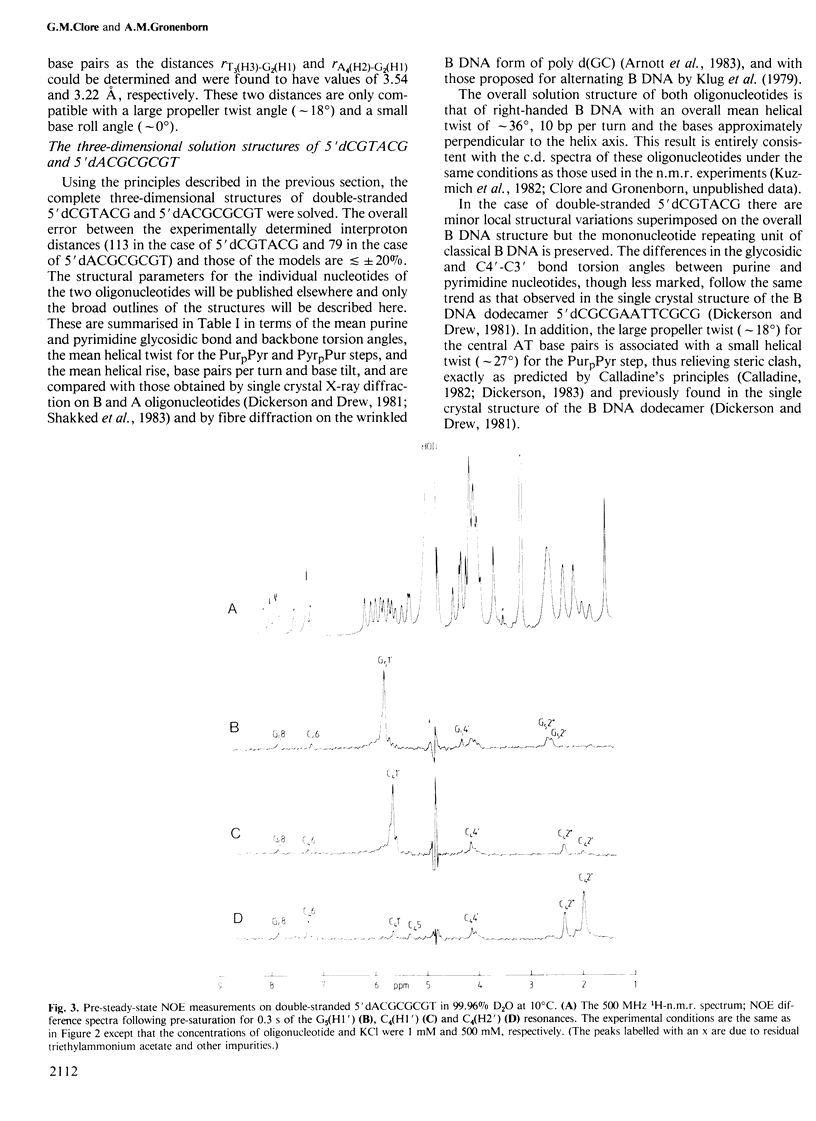
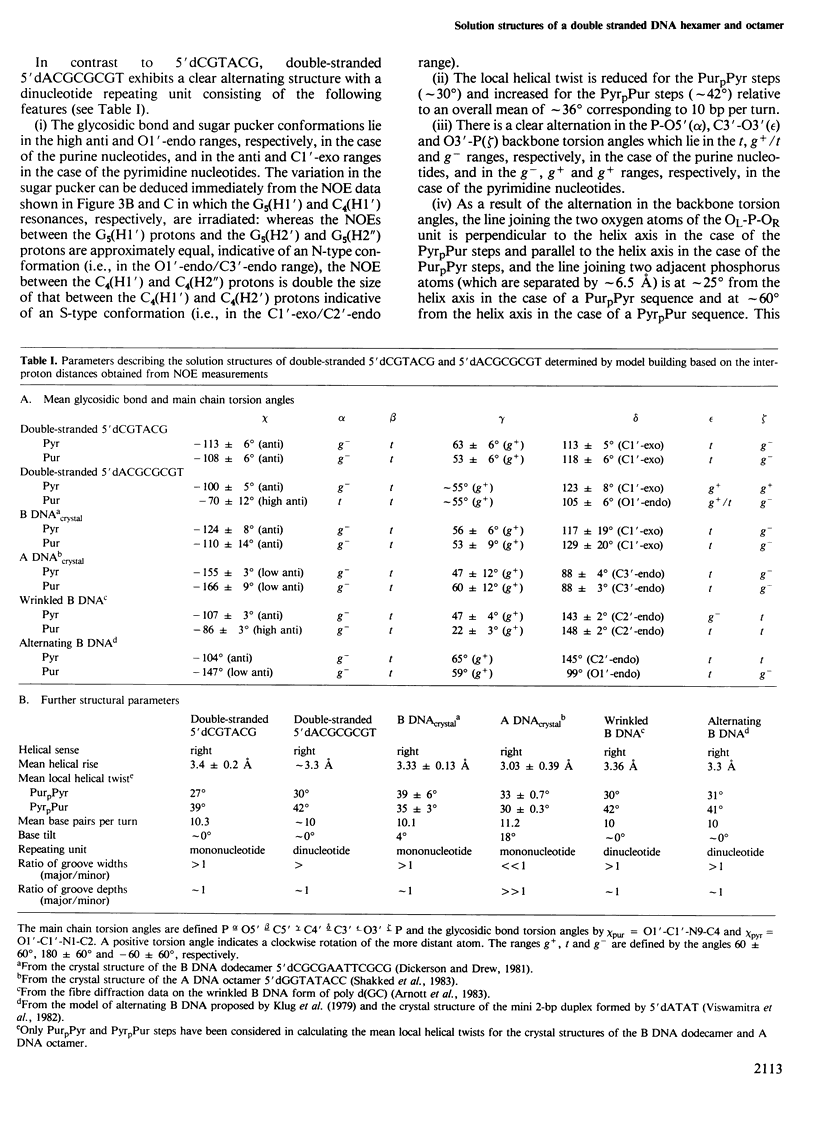
A 500 MHz 1H-n.m.r. study on two right-handed self-complementary double-stranded alternating pyrimidine-purine oligodeoxyribonucleotides, 5'dCGTACG and 5'dACGCGCGT, is presented. Using the proton-proton nuclear Overhauser effect, proton resonances are assigned by a sequential method and a large number of interproton distances, both intra- and internucleotide, are determined (113 for 5'dCGTACG and 79 for 5'dACGCGCGT). The general procedure required to solve the three-dimensional solution structures of oligonucleotides from such distance data is outlined and applied to these two oligonucleotides. In the case of both oligonucleotides the overall solution structure is that of B DNA, namely a right-handed helix with a helical rise of approximately 3.3 A, 10 bp per turn and the base pairs approximately perpendicular to the helix axis. In the case of 5'dCGTACG, subtle local structural variations associated with the pyrimidine and purine nucleotides are superimposed on the overall structure but the mononucleotide repeating unit is preserved. In contrast, 5'dACGCGCGT has a clear alternating structure with a dinucleotide repeat, alternation occurring in the local helical twist and the glycosidic bond, sugar pucker and phosphodiester backbone conformations.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnott S., Chandrasekaran R., Puigjaner L. C., Walker J. K., Hall I. H., Birdsall D. L., Ratliff R. L. Wrinkled DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1457–1474. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnott S., Hukins D. W. Optimised parameters for A-DNA and B-DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jun 28;47(6):1504–1509. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90243-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun W., Bösch C., Brown L. R., Go N., Wüthrich K. Combined use of proton-proton Overhauser enhancements and a distance geometry algorithm for determination of polypeptide conformations. Application to micelle-bound glucagon. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Feb 27;667(2):377–396. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(81)90205-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calladine C. R. Mechanics of sequence-dependent stacking of bases in B-DNA. J Mol Biol. 1982 Oct 25;161(2):343–352. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90157-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. W., Cohen J. S. Salt- and sequence-dependence of the secondary structure of DNA in solution by 31P-NMR spectroscopy. Biopolymers. 1983 Mar;22(3):879–893. doi: 10.1002/bip.360220310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clore G. M., Gronenborn A. M., Mitchinson C., Green N. M. 1H-NMR studies on nucleotide binding to the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase. Determination of the conformations of bound nucleotides by the measurement of proton-proton transferred nuclear Overhauser enhancements. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Nov;128(1):113–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen F. E., Sternberg M. J. On the prediction of protein structure: The significance of the root-mean-square deviation. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr;138(2):321–333. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90289-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. S., Wooten J. B., Chatterjee C. L. Characterization of alternating deoxyribonucleic acid conformations in solution by phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1981 May 26;20(11):3049–3055. doi: 10.1021/bi00514a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E. Base sequence and helix structure variation in B and A DNA. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 25;166(3):419–441. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E., Drew H. R. Structure of a B-DNA dodecamer. II. Influence of base sequence on helix structure. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 15;149(4):761–786. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90357-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronenborn A. M., Clore G. M. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance studies on cyclic nucleotide binding to the Escherichia coli adenosine cyclic 3',5'-phosphate receptor protein. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 17;21(17):4040–4048. doi: 10.1021/bi00260a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hare D. R., Reid B. R. Nuclear Overhauser assignment of the imino protons of the acceptor helix and the ribothymidine helix in the nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum of Escherichia coli isoleucine transfer ribonucleic acid: evidence for costacked helices in solution. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 12;21(21):5129–5135. doi: 10.1021/bi00264a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heerschap A., Haasnoot C. A., Hilbers C. W. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies on yeast tRNAPhe. III. Assignments of the iminoproton resonances of the tertiary structure by means of nuclear Overhauser effect experiments at 500 MHz. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jul 11;11(13):4501–4520. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.13.4501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston P. D., Redfield A. G. Pulsed FT-NMR double resonance studies of yeast tRNAPhe: specific nuclear Overhauser effects and reinterpretation of low temperature relaxation data. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Oct;5(10):3913–3927. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.10.3913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kan L. S., Cheng D. M., Jayaraman K., Leutzinger E. E., Miller P. S., Ts'o P. O. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance study of a self-complementary decadeoxyribonucleotide, C-C-A-A-G-C-T-T-G-G. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 21;21(26):6723–6732. doi: 10.1021/bi00269a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klug A., Jack A., Viswamitra M. A., Kennard O., Shakked Z., Steitz T. A. A hypothesis on a specific sequence-dependent conformation of DNA and its relation to the binding of the lac-repressor protein. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jul 15;131(4):669–680. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90196-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuzmich S., Marky L. A., Jones R. A. Synthesis and physical characterization of the self-complementary, alternating pyrimidine/purine hexanucleotide d[CGTACG]. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6265–6271. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomonossoff G. P., Butler P. J., Klug A. Sequence-dependent variation in the conformation of DNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 15;149(4):745–760. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90356-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidle S., Berman H. M. X-ray crystallographic studies of nucleic acids and nucleic acid-drug complexes. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1983;41(2):43–66. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(83)90025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Kozlowski S. A., Bhatt R. Sequence dependence of base-pair stacking in right-handed DNA in solution: proton nuclear Overhauser effect NMR measurements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3908–3912. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulsen F. M., Hoch J. C., Dobson C. M. A structural study of the hydrophobic box region of lysozyme in solution using nuclear Overhauser effects. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 10;19(12):2597–2607. doi: 10.1021/bi00553a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redfield A. G., Gupta R. K. Pulsed NMR study of the structure of cytochrome c. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1972;36:405–411. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1972.036.01.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid D. G., Salisbury S. A., Bellard S., Shakked Z., Williams D. H. Proton nuclear Overhauser effect study of the structure of a deoxyoligonucleotide duplex in aqueous solution. Biochemistry. 1983 Apr 12;22(8):2019–2025. doi: 10.1021/bi00277a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy S., Redfield A. G. Assignment of imino proton spectra of yeast phenylalanine transfer ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 15;22(6):1386–1390. doi: 10.1021/bi00275a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffler I. E., Elson E. L., Baldwin R. L. Helix formation by dAT oligomers. I. Hairpin and straight-chain helices. J Mol Biol. 1968 Sep 28;36(3):291–304. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90156-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shakked Z., Rabinovich D., Kennard O., Cruse W. B., Salisbury S. A., Viswamitra M. A. Sequence-dependent conformation of an A-DNA double helix. The crystal structure of the octamer d(G-G-T-A-T-A-C-C). J Mol Biol. 1983 May 15;166(2):183–201. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shindo H. 13C NMR study of conformation and mobility of 145-base-pair poly(dA-dT) . poly(dA-dT) in solution. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Nov;120(2):309–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05705.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shindo H., Simpson R. T., Cohen J. S. An alternating conformation characterizes the phosphodiester backbone of poly(dA-dT) in solution. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8125–8128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strop P., Wider G., Wüthrich K. Assignment of the 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum of the proteinase inhibitor IIA from bull seminal plasma by two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance at 500 MHz. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):641–665. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80289-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viswamitra M. A., Shakked Z., Jones P. G., Sheldrick G. M., Salisbury S. A., Kennard O. Structure of the deoxytetranucleotide d-pApTpApT and a sequence-dependent model for poly(dA-dT). Biopolymers. 1982 Mar;21(3):513–533. doi: 10.1002/bip.360210304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner G., Kumar A., Wüthrich K. Systematic application of two-dimensional 1H nuclear-magnetic-resonance techniques for studies of proteins. 2. Combined use of correlated spectroscopy and nuclear Overhauser spectroscopy for sequential assignments of backbone resonances and elucidation of polypeptide secondary structures. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Feb;114(2):375–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05157.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner G., Wüthrich K. Sequential resonance assignments in protein 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectra. Basic pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. J Mol Biol. 1982 Mar 5;155(3):347–366. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wider G., Lee K. H., Wüthrich K. Sequential resonance assignments in protein 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectra. Glucagon bound to perdeuterated dodecylphosphocholine micelles. J Mol Biol. 1982 Mar 5;155(3):367–388. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wüthrich K., Wider G., Wagner G., Braun W. Sequential resonance assignments as a basis for determination of spatial protein structures by high resolution proton nuclear magnetic resonance. J Mol Biol. 1982 Mar 5;155(3):311–319. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]