Abstract
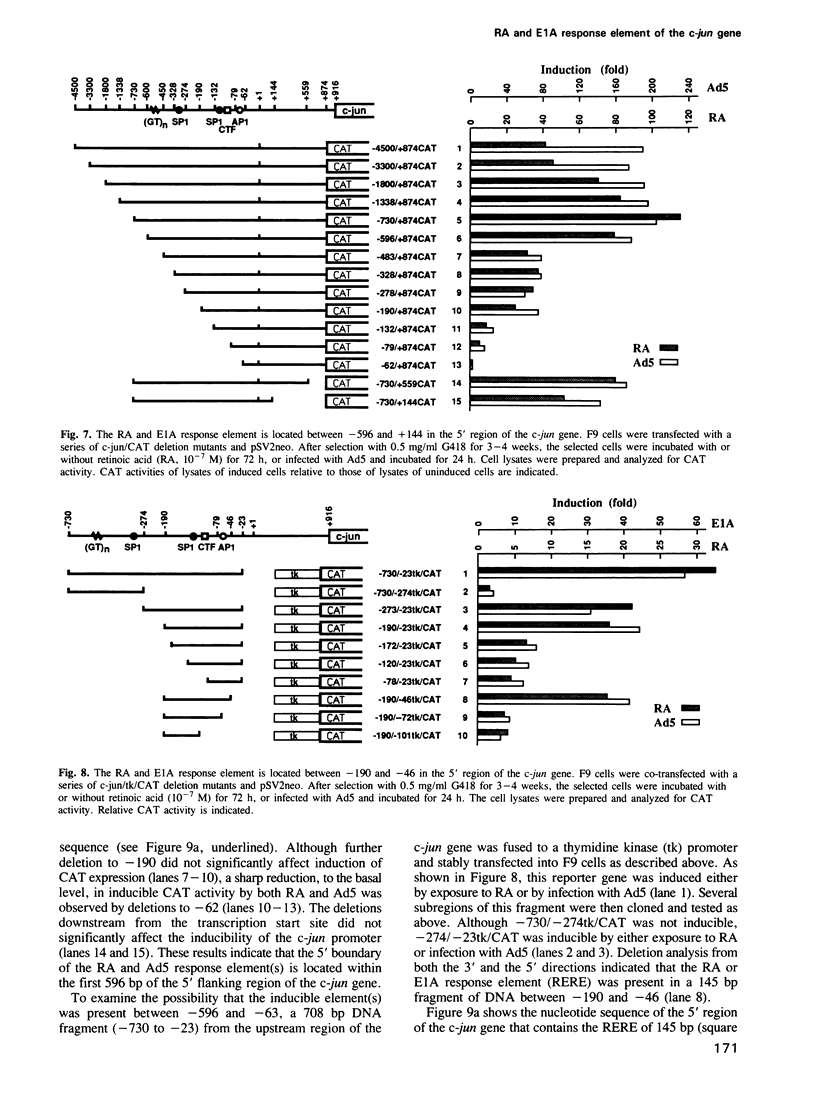
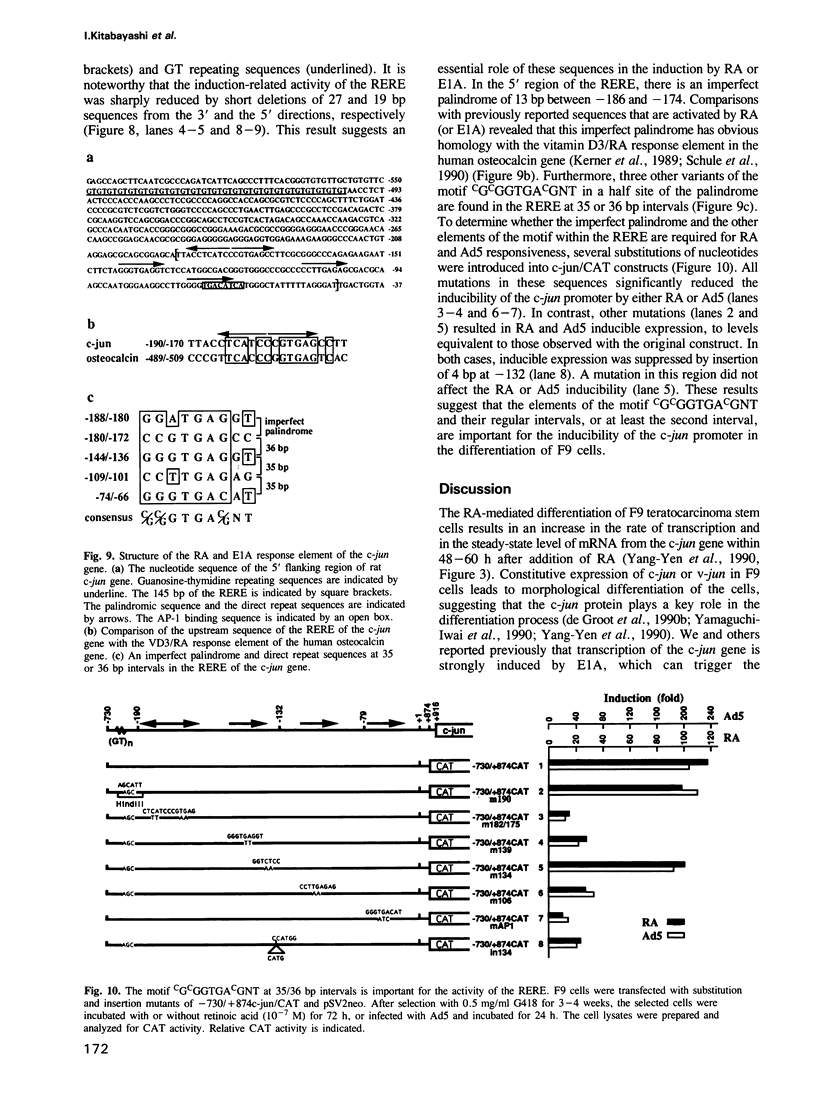
Differentiation of mouse F9 embryonal carcinoma (EC) cells can be induced by exposure to retinoic acid (RA) or by expression of adenovirus E1A. The transcription of the c-jun gene is stimulated by either RA or E1A. We report here that both RA and E1A strongly induce the expression of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) from c-jun promoter/CAT reporter construct (c-jun/CAT), which is stably integrated into F9 cells, in a manner that is independent of both copy number and integration locus. The induction of c-jun/CAT expression is observed in undifferentiated F9 cells, but not in differentiated F9 cells, adenovirus-infected F9 cells or HeLa cells. Deletion analysis of the promoter region of the c-jun gene indicates that the sequence elements required for the RA- and E1A-mediated induction are identical and they have been defined as a region of 145 bp between -190 and -46 of the 5' flanking region of c-jun. This RA and E1A response element (RERE) contains five variants of the motif CGCGGTGACGNT. The upstream two motifs are adjacent and extend in opposite directions, creating an imperfect palindrome. The downstream four motifs are located at 35 or 36 bp intervals in the same orientation. Substitution and insertion analysis indicates that these motifs and their regular intervals are important for the activity of the RERE.
Full text
PDF


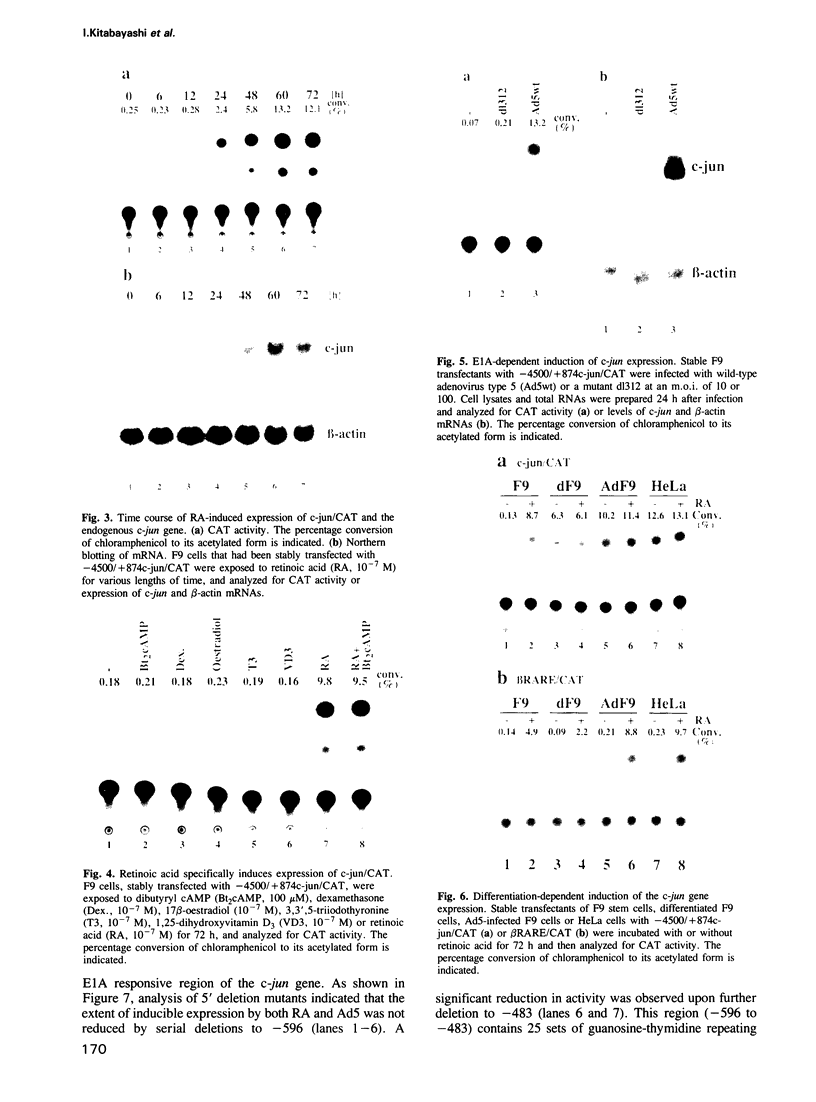



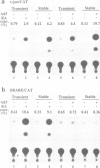
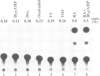
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Allegretto E. A., Okino S. T., Hattori K., Boyle W. J., Hunter T., Karin M. Oncogene jun encodes a sequence-specific trans-activator similar to AP-1. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):166–171. doi: 10.1038/332166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Lee F., Harrison T., Williams J., Sharp P. A. Pre-early adenovirus 5 gene product regulates synthesis of early viral messenger RNAs. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):935–944. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90333-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohmann D., Bos T. J., Admon A., Nishimura T., Vogt P. K., Tjian R. Human proto-oncogene c-jun encodes a DNA binding protein with structural and functional properties of transcription factor AP-1. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1386–1392. doi: 10.1126/science.2825349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buetti E., Kühnel B. Distinct sequence elements involved in the glucocorticoid regulation of the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter identified by linker scanning mutagenesis. J Mol Biol. 1986 Aug 5;190(3):379–389. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casasnovas J. M., Ellison M. J., Rodriguez-Campos A., Martinez-Balbas A., Azorin F. In vivo assessment of the Z-DNA-forming potential of d(CA.GT)n and d(CG.GC)n sequences cloned into SV40 minichromosomes. J Mol Biol. 1989 Aug 20;208(4):537–549. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90146-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu R., Boyle W. J., Meek J., Smeal T., Hunter T., Karin M. The c-Fos protein interacts with c-Jun/AP-1 to stimulate transcription of AP-1 responsive genes. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):541–552. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90076-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint J., Shenk T. Adenovirus E1A protein paradigm viral transactivator. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:141–161. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.001041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Felsenfeld G. Effect of Z-DNA on nucleosome placement. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 5;196(3):581–590. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90034-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguere V., Ong E. S., Segui P., Evans R. M. Identification of a receptor for the morphogen retinoic acid. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):624–629. doi: 10.1038/330624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C. K., Holloway J. M., Devary O. V., Rosenfeld M. G. The thyroid hormone receptor binds with opposite transcriptional effects to a common sequence motif in thyroid hormone and estrogen response elements. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):313–323. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90194-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J., Heijneker H. L. Size and location of the transforming region in human adenovirus type 5 DNA. Nature. 1974 Oct 25;251(5477):687–691. doi: 10.1038/251687a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halazonetis T. D., Georgopoulos K., Greenberg M. E., Leder P. c-Jun dimerizes with itself and with c-Fos, forming complexes of different DNA binding affinities. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):917–924. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90147-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada H., Seidman M., Howard B. H., Gorman C. M. Enhanced gene expression by the poly(dT-dG).poly(dC-dA) sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2622–2630. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haniford D. B., Pulleyblank D. E. Facile transition of poly[d(TG) x d(CA)] into a left-handed helix in physiological conditions. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):632–634. doi: 10.1038/302632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Franza B. R., Jr, Schley C. Monoclonal antibodies specific for adenovirus early region 1A proteins: extensive heterogeneity in early region 1A products. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):533–546. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.533-546.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann B., Lehmann J. M., Zhang X. K., Hermann T., Husmann M., Graupner G., Pfahl M. A retinoic acid receptor-specific element controls the retinoic acid receptor-beta promoter. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Nov;4(11):1727–1736. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-11-1727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N., Shenk T. An adenovirus type 5 early gene function regulates expression of other early viral genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3665–3669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerner S. A., Scott R. A., Pike J. W. Sequence elements in the human osteocalcin gene confer basal activation and inducible response to hormonal vitamin D3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4455–4459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitabayashi I., Chiu R., Gachelin G., Yokoyama K. E1A dependent up-regulation of c-jun/AP-1 activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 11;19(3):649–655. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.3.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitabayashi I., Saka F., Gachelin G., Yokoyama K. Nucleotide sequence of rat c-jun protooncogene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 11;18(11):3400–3400. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.11.3400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouzarides T., Ziff E. The role of the leucine zipper in the fos-jun interaction. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):646–651. doi: 10.1038/336646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kryszke M. H., Piette J., Yaniv M. Induction of a factor that binds to the polyoma virus A enhancer on differentiation of embryonal carcinoma cells. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):254–256. doi: 10.1038/328254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamph W. W., Wamsley P., Sassone-Corsi P., Verma I. M. Induction of proto-oncogene JUN/AP-1 by serum and TPA. Nature. 1988 Aug 18;334(6183):629–631. doi: 10.1038/334629a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichter P., Tang C. J., Call K., Hermanson G., Evans G. A., Housman D., Ward D. C. High-resolution mapping of human chromosome 11 by in situ hybridization with cosmid clones. Science. 1990 Jan 5;247(4938):64–69. doi: 10.1126/science.2294592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Green M., Green M. R. An adenovirus E1a protein region required for transformation and transcriptional repression. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1043–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90704-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maki Y., Bos T. J., Davis C., Starbuck M., Vogt P. K. Avian sarcoma virus 17 carries the jun oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2848–2852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Ong E. S., Dyck J. A., Evans R. M. Nuclear receptor that identifies a novel retinoic acid response pathway. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):224–229. doi: 10.1038/345224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. R. Teratocarcinomas and mammalian embryogenesis. Science. 1980 Aug 15;209(4458):768–776. doi: 10.1126/science.6250214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miksicek R., Borgmeyer U., Nowock J. Interaction of the TGGCA-binding protein with upstream sequences is required for efficient transcription of mouse mammary tumor virus. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1355–1360. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02375.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montano X., Lane D. P. The adenovirus Ela gene induces differentiation of F9 teratocarcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1782–1790. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabeppu Y., Ryder K., Nathans D. DNA binding activities of three murine Jun proteins: stimulation by Fos. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):907–915. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90146-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordheim A., Rich A. The sequence (dC-dA)n X (dG-dT)n forms left-handed Z-DNA in negatively supercoiled plasmids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1821–1825. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petkovich M., Brand N. J., Krust A., Chambon P. A human retinoic acid receptor which belongs to the family of nuclear receptors. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):444–450. doi: 10.1038/330444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Cohen D. R., Curran T., Bos T. J., Vogt P. K., Bohmann D., Tjian R., Franza B. R., Jr Fos-associated protein p39 is the product of the jun proto-oncogene. Science. 1988 May 20;240(4855):1010–1016. doi: 10.1126/science.3130660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Voulalas P. J., Franza B. R., Jr, Curran T. Fos and Jun bind cooperatively to the AP-1 site: reconstitution in vitro. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1687–1699. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder K., Nathans D. Induction of protooncogene c-jun by serum growth factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8464–8467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryseck R. P., Hirai S. I., Yaniv M., Bravo R. Transcriptional activation of c-jun during the G0/G1 transition in mouse fibroblasts. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):535–537. doi: 10.1038/334535a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Lamph W. W., Kamps M., Verma I. M. fos-associated cellular p39 is related to nuclear transcription factor AP-1. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):553–560. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90077-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Sisson J. C., Verma I. M. Transcriptional autoregulation of the proto-oncogene fos. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):314–319. doi: 10.1038/334314a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Umesono K., Mangelsdorf D. J., Bolado J., Pike J. W., Evans R. M. Jun-Fos and receptors for vitamins A and D recognize a common response element in the human osteocalcin gene. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):497–504. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90531-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spindler K. R., Rosser D. S., Berk A. J. Analysis of adenovirus transforming proteins from early regions 1A and 1B with antisera to inducible fusion antigens produced in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):132–141. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.132-141.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland S., Mahdavi V. The induction of differentiation in teratocarcinoma stem cells by retinoic acid. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):393–403. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland S., Smith K. K., Marotti K. R. Hormonal induction of differentiation in teratocarcinoma stem cells: generation of parietal endoderm by retinoic acid and dibutyryl cAMP. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):347–355. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90471-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sucov H. M., Murakami K. K., Evans R. M. Characterization of an autoregulated response element in the mouse retinoic acid receptor type beta gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5392–5396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Giguere V., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Retinoic acid and thyroid hormone induce gene expression through a common responsive element. Nature. 1988 Nov 17;336(6196):262–265. doi: 10.1038/336262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Murakami K. K., Thompson C. C., Evans R. M. Direct repeats as selective response elements for the thyroid hormone, retinoic acid, and vitamin D3 receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1255–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90020-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velcich A., Ziff E. B. The adenovirus-5 12S E1a protein, but not the 13S induces expression of the endoA differentiation marker in F9 cells. Oncogene. 1989 Jun;4(6):707–713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigel R. J., Devoto S. H., Nevins J. R. Adenovirus 12S E1A gene represses differentiation of F9 teratocarcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9878–9882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi-Iwai Y., Satake M., Murakami Y., Sakai M., Muramatsu M., Ito Y. Differentiation of F9 embryonal carcinoma cells induced by the c-jun and activated c-Ha-ras oncogenes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8670–8674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Yen H. F., Chiu R., Karin M. Elevation of AP1 activity during F9 cell differentiation is due to increased c-jun transcription. New Biol. 1990 Apr;2(4):351–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot R. P., Kruyt F. A., van der Saag P. T., Kruijer W. Ectopic expression of c-jun leads to differentiation of P19 embryonal carcinoma cells. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1831–1837. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08308.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot R. P., Pals C., Kruijer W. Transcriptional control of c-jun by retinoic acid. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 11;19(7):1585–1591. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.7.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot R. P., Schoorlemmer J., van Genesen S. T., Kruijer W. Differential expression of jun and fos genes during differentiation of mouse P19 embryonal carcinoma cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 11;18(11):3195–3202. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.11.3195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot R., Foulkes N., Mulder M., Kruijer W., Sassone-Corsi P. Positive regulation of jun/AP-1 by E1A. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):192–201. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Thé H., Vivanco-Ruiz M. M., Tiollais P., Stunnenberg H., Dejean A. Identification of a retinoic acid responsive element in the retinoic acid receptor beta gene. Nature. 1990 Jan 11;343(6254):177–180. doi: 10.1038/343177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dam H., Offringa R., Meijer I., Stein B., Smits A. M., Herrlich P., Bos J. L., van der Eb A. J. Differential effects of the adenovirus E1A oncogene on members of the AP-1 transcription factor family. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5857–5864. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]