Abstract
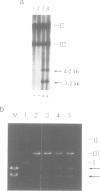
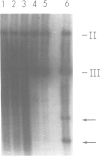
An assay was developed that detected DNA cruciform cutting endonuclease activity in crude extracts of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. A collection of temperature-sensitive strains was screened using this assay, and a mutant lacking the activity was found. The mutation leading to the enzymatic defect was mapped to the left arm of chromosome XI within 3 cM of the centromere. Cloning of the gene for this endonuclease was achieved by chromosome walking from the nearby PUT3 locus. The gene, called CCE1 (cruciform cutting endonuclease), was sequenced and found to have an open reading frame encoding a 41 kDa protein. The amino acid sequence of this eukaryotic endonuclease shows homology neither to its prokaryotic counterparts nor to other proteins in available databases. A cce1 null mutant has no obvious growth defect, and despite the ability of the CCE1 enzyme to cleave Holliday junction analogs, the mutant shows no defect in meiotic or mitotic recombination. A second cruciform cutting activity was detected in extracts from a cce1 null mutant, indicating that yeast has at least two such enzymes. The only phenotype observed for cce1 mutants is a higher than normal frequency of appearance of petite cells, suggesting that the CCE1 protein is important for the maintenance of mitochondrial DNA.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Attardi G., Schatz G. Biogenesis of mitochondria. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:289–333. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly B., Parsons C. A., Benson F. E., Dunderdale H. J., Sharples G. J., Lloyd R. G., West S. C. Resolution of Holliday junctions in vitro requires the Escherichia coli ruvC gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6063–6067. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elborough K. M., West S. C. Resolution of synthetic Holliday junctions in DNA by an endonuclease activity from calf thymus. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2931–2936. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07484.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. H., Kolodner R. Construction of a synthetic Holliday junction analog and characterization of its interaction with a Saccharomyces cerevisiae endonuclease that cleaves Holliday junctions. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9160–9165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. H., Kolodner R. Effect of DNA structure and nucleotide sequence on Holliday junction resolution by a Saccharomyces cerevisiae endonuclease. J Mol Biol. 1988 May 5;201(1):69–80. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90439-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H. Macromolecule synthesis in temperature-sensitive mutants of yeast. J Bacteriol. 1967 May;93(5):1662–1670. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.5.1662-1670.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helms C., Dutchik J. E., Olson M. V. A lambda DNA protocol based on purification of phage on DEAE-cellulose. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:69–82. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53048-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu P. L., Landy A. Resolution of synthetic att-site Holliday structures by the integrase protein of bacteriophage lambda. Nature. 1984 Oct 25;311(5988):721–726. doi: 10.1038/311721a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensch F., Kosak H., Seeman N. C., Kemper B. Cruciform cutting endonucleases from Saccharomyces cerevisiae and phage T4 show conserved reactions with branched DNAs. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4325–4334. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08619.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeyaseelan R., Shanmugam G. Human placental endonuclease cleaves Holliday junctions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 31;156(2):1054–1060. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80951-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemper B., Brown D. T. Function of gene 49 of bacteriophage T4. II. Analysis of intracellular development and the structure of very fast-sedimenting DNA. J Virol. 1976 Jun;18(3):1000–1015. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.3.1000-1015.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klyce H. R., McLaughlin C. S. Characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of yeast by a photomicrographic procedure. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Nov;82(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90243-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosak H. G., Kemper B. W. Large-scale preparation of T4 endonuclease VII from over-expressing bacteria. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Dec 27;194(3):779–784. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19469.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marczak J. E., Brandriss M. C. Isolation of constitutive mutations affecting the proline utilization pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and molecular analysis of the PUT3 transcriptional activator. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4696–4705. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meselson M. S., Radding C. M. A general model for genetic recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):358–361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki J., Ryo Y., Minagawa T. Involvement of gene 49 in recombination of bacteriophage T4. Genetics. 1983 May;104(1):1–9. doi: 10.1093/genetics/104.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson M. V., Dutchik J. E., Graham M. Y., Brodeur G. M., Helms C., Frank M., MacCollin M., Scheinman R., Frank T. Random-clone strategy for genomic restriction mapping in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7826–7830. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W. Fungal recombination. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Mar;49(1):33–58. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.1.33-58.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons C. A., West S. C. Resolution of model Holliday junctions by yeast endonuclease is dependent upon homologous DNA sequences. Cell. 1988 Feb 26;52(4):621–629. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90474-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiestl R. H., Gietz R. D. High efficiency transformation of intact yeast cells using single stranded nucleic acids as a carrier. Curr Genet. 1989 Dec;16(5-6):339–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00340712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Use of bacteriophage T7 lysozyme to improve an inducible T7 expression system. J Mol Biol. 1991 May 5;219(1):37–44. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90855-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symington L. S., Kolodner R. Partial purification of an enzyme from Saccharomyces cerevisiae that cleaves Holliday junctions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7247–7251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S. C., Körner A. Cleavage of cruciform DNA structures by an activity from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6445–6449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcoxen S. E., Peterson C. R., Winkley C. S., Keller M. J., Jaehning J. A. Two forms of RPO41-dependent RNA polymerase. Regulation of the RNA polymerase by glucose repression may control yeast mitochondrial gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12346–12351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zassenhaus H. P., Hofmann T. J., Uthayashanker R., Vincent R. D., Zona M. Construction of a yeast mutant lacking the mitochondrial nuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 25;16(8):3283–3296. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.8.3283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweifel S. G., Fangman W. L. A nuclear mutation reversing a biased transmission of yeast mitochondrial DNA. Genetics. 1991 Jun;128(2):241–249. doi: 10.1093/genetics/128.2.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Massy B., Weisberg R. A., Studier F. W. Gene 3 endonuclease of bacteriophage T7 resolves conformationally branched structures in double-stranded DNA. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jan 20;193(2):359–376. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90224-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]