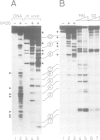
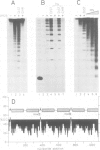
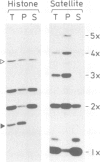
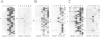Abstract
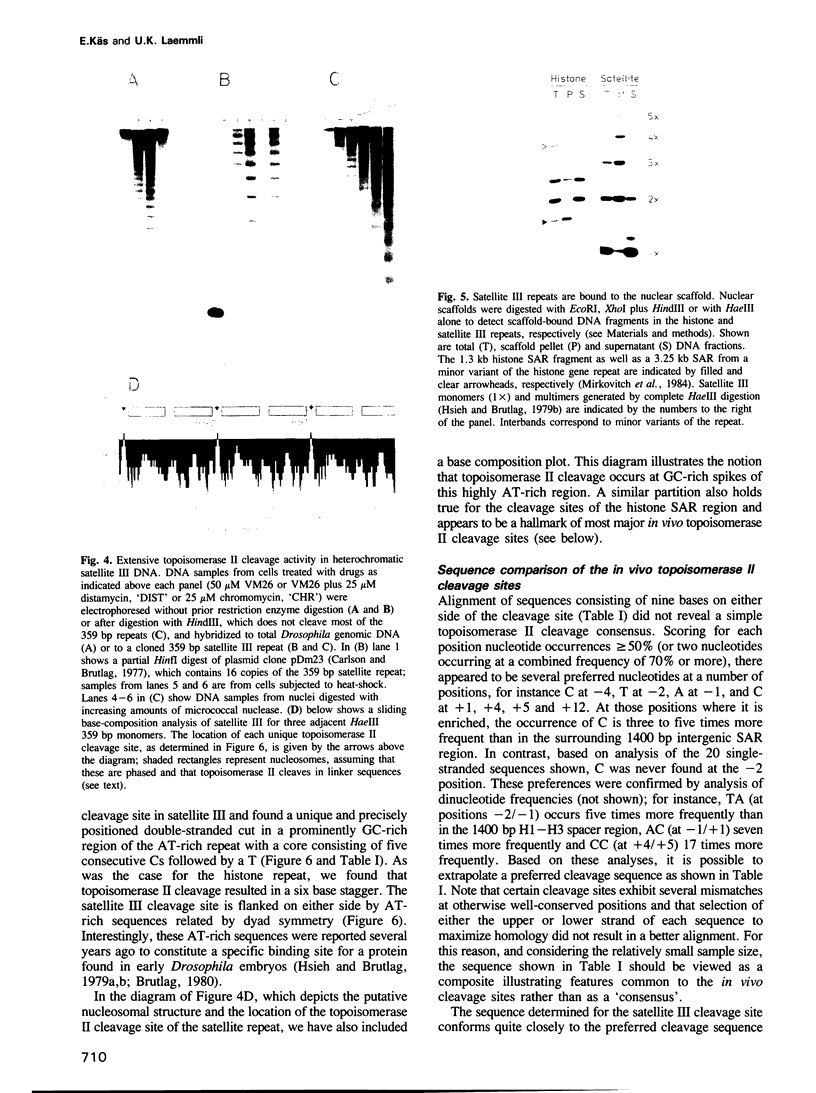
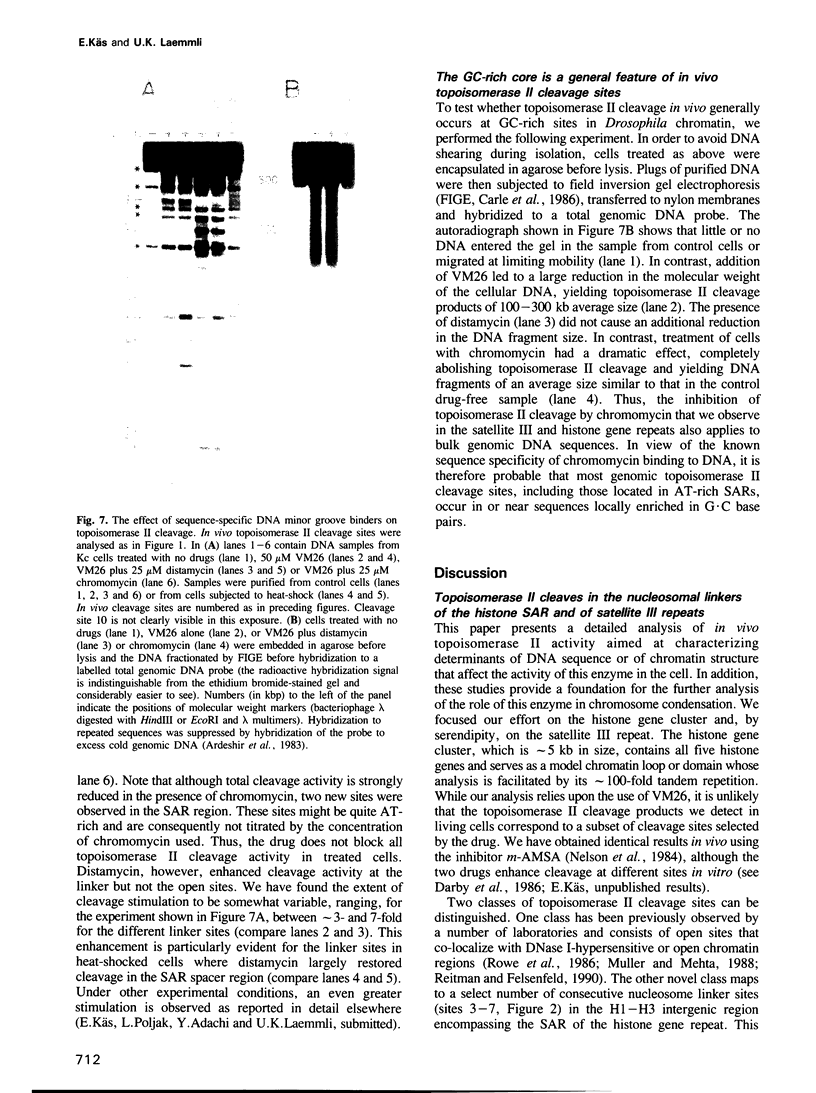
We have identified two classes of in vivo topoisomerase II cleavage sites in the Drosophila histone gene repeat. One class co-localizes with DNase I-hypersensitive regions and another novel class maps to a subset of consecutive nucleosome linker sites in the scaffold-associated region (SAR) of the histone gene loop. Prominent topoisomerase II cleavage is also observed in one of the linker regions of the two nucleosomes spanning satellite III, a centromeric SAR-like DNA sequence with a repeat length of 359 bp. At the sequence level, in vivo topoisomerase II cleavage is highly site specific. Comparison of 10 nucleosome linker sites defines an in vivo cleavage sequence whose major characteristic is a prominent GC-rich core. These GC-rich cleavage sites are flanked by extensive arrays of oligo(dA).oligo(dT) tracts characteristic of SAR sequences. Treatment of cells with distamycin selectively enhances cleavage at nucleosome linker sites of the SAR and satellite regions, suggesting that AT-rich sequences flanking cleavage sites may be involved in determining topoisomerase II activity in the cell. These observations provide evidence for the association of topoisomerase II with SARS in vivo.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi Y., Käs E., Laemmli U. K. Preferential, cooperative binding of DNA topoisomerase II to scaffold-associated regions. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):3997–4006. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08582.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adachi Y., Luke M., Laemmli U. K. Chromosome assembly in vitro: topoisomerase II is required for condensation. Cell. 1991 Jan 11;64(1):137–148. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90215-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amati B. B., Gasser S. M. Chromosomal ARS and CEN elements bind specifically to the yeast nuclear scaffold. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):967–978. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90111-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ardeshir F., Giulotto E., Zieg J., Brison O., Liao W. S., Stark G. R. Structure of amplified DNA in different Syrian hamster cell lines resistant to N-(phosphonacetyl)-L-aspartate. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;3(11):2076–2088. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.11.2076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berrios M., Osheroff N., Fisher P. A. In situ localization of DNA topoisomerase II, a major polypeptide component of the Drosophila nuclear matrix fraction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4142–4146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brill S. J., Sternglanz R. Transcription-dependent DNA supercoiling in yeast DNA topoisomerase mutants. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):403–411. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90203-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brutlag D. L. Molecular arrangement and evolution of heterochromatic DNA. Annu Rev Genet. 1980;14:121–144. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.14.120180.001005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burckhardt J., Birnstiel M. L. Analysis of histone messenger RNA of Drosophila melanogaster by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1978 Jan 5;118(1):61–79. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90244-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capranico G., Jaxel C., Roberge M., Kohn K. W., Pommier Y. Nucleosome positioning as a critical determinant for the DNA cleavage sites of mammalian DNA topoisomerase II in reconstituted simian virus 40 chromatin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 11;18(15):4553–4559. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.15.4553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Frank M., Olson M. V. Electrophoretic separations of large DNA molecules by periodic inversion of the electric field. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):65–68. doi: 10.1126/science.3952500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Brutlag D. Cloning and characterization of a complex satellite DNA from Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1977 Jun;11(2):371–381. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90054-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen G. L., Yang L., Rowe T. C., Halligan B. D., Tewey K. M., Liu L. F. Nonintercalative antitumor drugs interfere with the breakage-reunion reaction of mammalian DNA topoisomerase II. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13560–13566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockerill P. N., Garrard W. T. Chromosomal loop anchorage of the kappa immunoglobulin gene occurs next to the enhancer in a region containing topoisomerase II sites. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):273–282. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90761-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darby M. K., Herrera R. E., Vosberg H. P., Nordheim A. DNA topoisomerase II cleaves at specific sites in the 5' flanking region of c-fos proto-oncogenes in vitro. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2257–2265. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04493.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiNardo S., Voelkel K., Sternglanz R. DNA topoisomerase II mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: topoisomerase II is required for segregation of daughter molecules at the termination of DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2616–2620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Travers A. A. DNA bending and its relation to nucleosome positioning. J Mol Biol. 1985 Dec 20;186(4):773–790. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90396-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnshaw W. C., Halligan B., Cooke C. A., Heck M. M., Liu L. F. Topoisomerase II is a structural component of mitotic chromosome scaffolds. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1706–1715. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eissenberg J. C. Position effect variegation in Drosophila: towards a genetics of chromatin assembly. Bioessays. 1989 Jul;11(1):14–17. doi: 10.1002/bies.950110105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fesen M., Pommier Y. Mammalian topoisomerase II activity is modulated by the DNA minor groove binder distamycin in simian virus 40 DNA. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 5;264(19):11354–11359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filipski J., Leblanc J., Youdale T., Sikorska M., Walker P. R. Periodicity of DNA folding in higher order chromatin structures. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1319–1327. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08241.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox K. R., Howarth N. R. Investigations into the sequence-selective binding of mithramycin and related ligands to DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8695–8714. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox K. R., Waring M. J. DNA structural variations produced by actinomycin and distamycin as revealed by DNAase I footprinting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9271–9285. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser S. M., Laemmli U. K. The organisation of chromatin loops: characterization of a scaffold attachment site. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):511–518. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04240.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser S. M., Laroche T., Falquet J., Boy de la Tour E., Laemmli U. K. Metaphase chromosome structure. Involvement of topoisomerase II. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 20;188(4):613–629. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(86)80010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm C., Goto T., Wang J. C., Botstein D. DNA topoisomerase II is required at the time of mitosis in yeast. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):553–563. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard M. T., Lee M. P., Hsieh T. S., Griffith J. D. Drosophila topoisomerase II-DNA interactions are affected by DNA structure. J Mol Biol. 1991 Jan 5;217(1):53–62. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90610-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh T., Brutlag D. L. A protein that preferentially binds Drosophila satellite DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):726–730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh T., Brutlag D. Sequence and sequence variation within the 1.688 g/cm3 satellite DNA of Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol. 1979 Dec 5;135(2):465–481. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90447-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käs E., Izaurralde E., Laemmli U. K. Specific inhibition of DNA binding to nuclear scaffolds and histone H1 by distamycin. The role of oligo(dA).oligo(dT) tracts. J Mol Biol. 1989 Dec 5;210(3):587–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90134-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. P., Sander M., Hsieh T. S. Single strand DNA cleavage reaction of duplex DNA by Drosophila topoisomerase II. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13510–13518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinger L., Varshavsky A. Protein D1 preferentially binds A + T-rich DNA in vitro and is a component of Drosophila melanogaster nucleosomes containing A + T-rich satellite DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7152–7156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinger L., Varshavsky A. Selective arrangement of ubiquitinated and D1 protein-containing nucleosomes within the Drosophila genome. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):375–385. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90355-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis C. D., Laemmli U. K. Higher order metaphase chromosome structure: evidence for metalloprotein interactions. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):171–181. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90101-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Rowe T. C., Yang L., Tewey K. M., Chen G. L. Cleavage of DNA by mammalian DNA topoisomerase II. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15365–15370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Wang J. C. Supercoiling of the DNA template during transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7024–7027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohka M. J., Maller J. L. Induction of nuclear envelope breakdown, chromosome condensation, and spindle formation in cell-free extracts. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):518–523. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkovitch J., Mirault M. E., Laemmli U. K. Organization of the higher-order chromatin loop: specific DNA attachment sites on nuclear scaffold. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90208-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller M. T., Mehta V. B. DNase I hypersensitivity is independent of endogenous topoisomerase II activity during chicken erythrocyte differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3661–3669. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson E. M., Tewey K. M., Liu L. F. Mechanism of antitumor drug action: poisoning of mammalian DNA topoisomerase II on DNA by 4'-(9-acridinylamino)-methanesulfon-m-anisidide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1361–1365. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newport J. Nuclear reconstitution in vitro: stages of assembly around protein-free DNA. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):205–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90424-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newport J., Spann T. Disassembly of the nucleus in mitotic extracts: membrane vesicularization, lamin disassembly, and chromosome condensation are independent processes. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):219–230. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90425-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulson J. R., Laemmli U. K. The structure of histone-depleted metaphase chromosomes. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):817–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90280-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirrotta V. Transvection and long-distance gene regulation. Bioessays. 1990 Sep;12(9):409–414. doi: 10.1002/bies.950120903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitman M., Felsenfeld G. Developmental regulation of topoisomerase II sites and DNase I-hypersensitive sites in the chicken beta-globin locus. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2774–2786. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe T. C., Wang J. C., Liu L. F. In vivo localization of DNA topoisomerase II cleavage sites on Drosophila heat shock chromatin. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):985–992. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saluz H., Jost J. P. A simple high-resolution procedure to study DNA methylation and in vivo DNA-protein interactions on a single-copy gene level in higher eukaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2602–2606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sander M., Hsieh T. S. Drosophila topoisomerase II double-strand DNA cleavage: analysis of DNA sequence homology at the cleavage site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1057–1072. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sander M., Hsieh T. Double strand DNA cleavage by type II DNA topoisomerase from Drosophila melanogaster. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8421–8428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperry A. O., Blasquez V. C., Garrard W. T. Dysfunction of chromosomal loop attachment sites: illegitimate recombination linked to matrix association regions and topoisomerase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5497–5501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitzner J. R., Muller M. T. A consensus sequence for cleavage by vertebrate DNA topoisomerase II. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 24;16(12):5533–5556. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.12.5533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternglanz R. DNA topoisomerases. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;1(3):533–535. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(89)90016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udvardy A., Schedl P., Sander M., Hsieh T. S. Novel partitioning of DNA cleavage sites for Drosophila topoisomerase II. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):933–941. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90353-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udvardy A., Schedl P., Sander M., Hsieh T. S. Topoisomerase II cleavage in chromatin. J Mol Biol. 1986 Sep 20;191(2):231–246. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90260-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura T., Ohkura H., Adachi Y., Morino K., Shiozaki K., Yanagida M. DNA topoisomerase II is required for condensation and separation of mitotic chromosomes in S. pombe. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):917–925. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90518-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura T., Yanagida M. Isolation of type I and II DNA topoisomerase mutants from fission yeast: single and double mutants show different phenotypes in cell growth and chromatin organization. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1737–1744. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02040.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. W., Dervan P. B. Chromomycin, mithramycin, and olivomycin binding sites on heterogeneous deoxyribonucleic acid. Footprinting with (methidiumpropyl-EDTA)iron(II). Biochemistry. 1983 May 10;22(10):2373–2377. doi: 10.1021/bi00279a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. W., Hertzberg R. P., Dervan P. B. Map of distamycin, netropsin, and actinomycin binding sites on heterogeneous DNA: DNA cleavage-inhibition patterns with methidiumpropyl-EDTA.Fe(II). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5470–5474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villeponteau B. Characterization of a topoisomerase-like activity at specific hypersensitive sites in the Drosophila histone gene cluster. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jul 14;162(1):232–237. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91986-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. Recent studies of DNA topoisomerases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jun 6;909(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(87)90040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
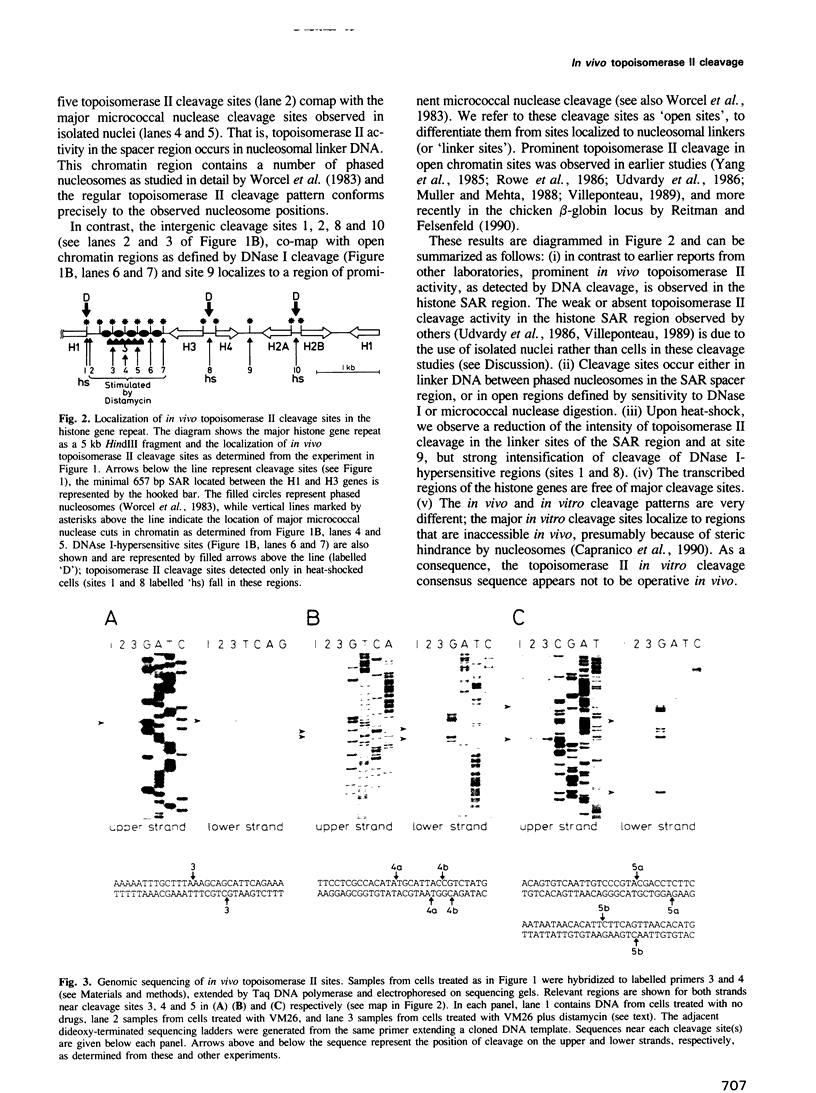
- Worcel A., Gargiulo G., Jessee B., Udvardy A., Louis C., Schedl P. Chromatin fine structure of the histone gene complex of Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 25;11(2):421–439. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.2.421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. The locus of sequence-directed and protein-induced DNA bending. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):509–513. doi: 10.1038/308509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang L., Rowe T. C., Nelson E. M., Liu L. F. In vivo mapping of DNA topoisomerase II-specific cleavage sites on SV40 chromatin. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):127–132. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90067-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zechiedrich E. L., Christiansen K., Andersen A. H., Westergaard O., Osheroff N. Double-stranded DNA cleavage/religation reaction of eukaryotic topoisomerase II: evidence for a nicked DNA intermediate. Biochemistry. 1989 Jul 25;28(15):6229–6236. doi: 10.1021/bi00441a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]