Abstract
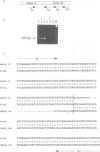
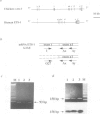
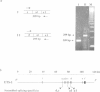
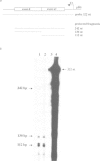
Following our studies which showed that the alpha and beta exons of the chicken c-ets-1 gene are not conserved in the human homologue, we succeeded in identifying a novel human c-ets-1 transcript in which the normal order of exons is scrambled. By PCR and RNase protection assays, we demonstrated that while the order of exons is different from that in genomic DNA, splicing of these exons in aberrant order occurs in pairs and at the same conserved consensus splice sites used in the normally spliced transcript. The scrambled transcript is non-polyadenylated and is expressed at much lower levels than the normal transcript. It is not the consequence of genomic rearrangement at the ets-1 locus nor is it due to the transcription of any ets-1 pseudogene. These results confirm previous observations of scrambled splicing.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agabian N. Trans splicing of nuclear pre-mRNAs. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1157–1160. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90674-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailleul B., Surani M. A., White S., Barton S. C., Brown K., Blessing M., Jorcano J., Balmain A. Skin hyperkeratosis and papilloma formation in transgenic mice expressing a ras oncogene from a suprabasal keratin promoter. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):697–708. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90115-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitbart R. E., Andreadis A., Nadal-Ginard B. Alternative splicing: a ubiquitous mechanism for the generation of multiple protein isoforms from single genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:467–495. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody E., Abelson J. The "spliceosome": yeast pre-messenger RNA associates with a 40S complex in a splicing-dependent reaction. Science. 1985 May 24;228(4702):963–967. doi: 10.1126/science.3890181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duterque-Coquillaud M., Leprince D., Flourens A., Henry C., Ghysdael J., Debuire B., Stehelin D. Cloning and expression of chicken p54c-ets cDNAs: the first p54c-ets coding exon is located into the 40.0 kbp genomic domain unrelated to v-ets. Oncogene Res. 1988 May;2(4):335–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon E. R., Cho K. R., Nigro J. M., Kern S. E., Simons J. W., Ruppert J. M., Hamilton S. R., Preisinger A. C., Thomas G., Kinzler K. W. Identification of a chromosome 18q gene that is altered in colorectal cancers. Science. 1990 Jan 5;247(4938):49–56. doi: 10.1126/science.2294591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gegonne A., Leprince D., Duterque-Coquillaud M., Vandenbunder B., Flourens A., Ghysdael J., Debuire B., Stehelin D. Multiple domains for the chicken cellular sequences homologous to the v-ets oncogene of the E26 retrovirus. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):806–812. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorcyk C. L., Watson D. K., Mavrothalassitis G. J., Papas T. S. The human ETS1 gene: genomic structure, promoter characterization and alternative splicing. Oncogene. 1991 Apr;6(4):523–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerckaert J. P., Duterque-Coquillaud M., Collyn-d'Hooghe M., Morel P., Majérus M. A., Laï J. L., Fenaux P., Bauters F., Debuire B., Loucheux-Lefebvre M. H. Polymorphism of the proto-oncogene ETS-1 in hematological malignancies. Leukemia. 1990 Jan;4(1):16–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koizumi S., Fisher R. J., Fujiwara S., Jorcyk C., Bhat N. K., Seth A., Papas T. S. Isoforms of the human ets-1 protein: generation by alternative splicing and differential phosphorylation. Oncogene. 1990 May;5(5):675–681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leprince D., Duterque-Coquillaud M., Li R. P., Henry C., Flourens A., Debuire B., Stehelin D. Alternative splicing within the chicken c-ets-1 locus: implications for transduction within the E26 retrovirus of the c-ets proto-oncogene. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3233–3241. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3233-3241.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leprince D., Gegonne A., Coll J., de Taisne C., Schneeberger A., Lagrou C., Stehelin D. A putative second cell-derived oncogene of the avian leukaemia retrovirus E26. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):395–397. doi: 10.1038/306395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin B. Alternatives for splicing: recognizing the ends of introns. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):324–326. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90340-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigro J. M., Cho K. R., Fearon E. R., Kern S. E., Ruppert J. M., Oliner J. D., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Scrambled exons. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):607–613. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90244-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunn M. F., Seeburg P. H., Moscovici C., Duesberg P. H. Tripartite structure of the avian erythroblastosis virus E26 transforming gene. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):391–395. doi: 10.1038/306391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy E. S., Rao V. N. Structure, expression and alternative splicing of the human c-ets-1 proto-oncogene. Oncogene Res. 1988;3(3):239–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes A. A., Small S. J., Akeson R. At least 27 alternatively spliced forms of the neural cell adhesion molecule mRNA are expressed during rat heart development. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1654–1661. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robberson B. L., Cote G. J., Berget S. M. Exon definition may facilitate splice site selection in RNAs with multiple exons. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):84–94. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Science. 1987 Feb 13;235(4790):766–771. doi: 10.1126/science.3544217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Flores P., Begue A., Leprince D., Stehelin D. The c-ets proto-oncogenes encode transcription factors that cooperate with c-Fos and c-Jun for transcriptional activation. Nature. 1990 Jul 12;346(6280):191–193. doi: 10.1038/346191a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. K., McWilliams-Smith M. J., Nunn M. F., Duesberg P. H., O'Brien S. J., Papas T. S. The ets sequence from the transforming gene of avian erythroblastosis virus, E26, has unique domains on human chromosomes 11 and 21: both loci are transcriptionally active. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7294–7298. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. K., McWilliams M. J., Lapis P., Lautenberger J. A., Schweinfest C. W., Papas T. S. Mammalian ets-1 and ets-2 genes encode highly conserved proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7862–7866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]