Abstract
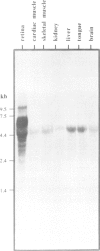
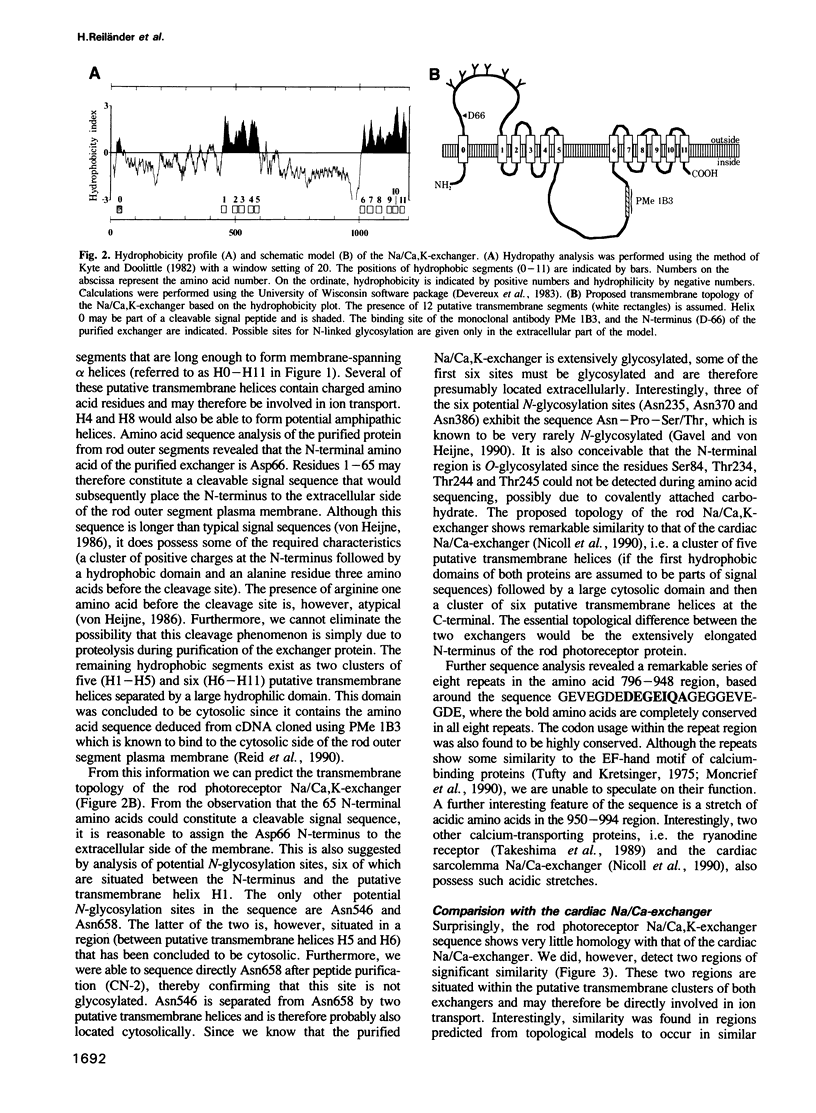
Complementary DNA encoding the Na/Ca,K-exchanger was isolated from bovine retina cDNA libraries. The complete full-length cDNA is approximately 4 kb long and contains an open reading frame of 3597 bp. The deduced amino acid sequence corresponds to a protein of 1199 amino acids with a calculated molecular weight of approximately 130 kDa. Hydrophobicity analysis revealed the presence of two alternating sets of hydrophobic and hydrophilic domains. There also exists a hydrophobic region at the N-terminus which may be part of a cleavable signal peptide. The protein shares limited sequence homology with the Na/Ca-exchanger from cardiac sarcolemma. Northern blot analysis indicates that the approximately 6 kb transcript is highly specific for retinal tissue. Insect cells infected with recombinant baculovirus bearing the full-length cDNA express a functional Na/Ca,K-exchanger with an apparent relative molecular weight of approximately 210 kDa, as determined by Western blotting.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baylor D. A., Lamb T. D., Yau K. W. The membrane current of single rod outer segments. J Physiol. 1979 Mar;288:589–611. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capovilla M., Caretta A., Cervetto L., Torre V. Ionic movements through light-sensitive channels of toad rods. J Physiol. 1983 Oct;343:295–310. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cervetto L., Lagnado L., Perry R. J., Robinson D. W., McNaughton P. A. Extrusion of calcium from rod outer segments is driven by both sodium and potassium gradients. Nature. 1989 Feb 23;337(6209):740–743. doi: 10.1038/337740a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook N. J., Kaupp U. B. Solubilization, purification, and reconstitution of the sodium-calcium exchanger from bovine retinal rod outer segments. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11382–11388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook N. J., Zeilinger C., Koch K. W., Kaupp U. B. Solubilization and functional reconstitution of the cGMP-dependent cation channel from bovine rod outer segments. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 25;261(36):17033–17039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahan D., Spanier R., Rahamimoff H. The modulation of rat brain Na(+)-Ca2+ exchange by K+. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2067–2075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Sal G., Manfioletti G., Schneider C. A one-tube plasmid DNA mini-preparation suitable for sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9878–9878. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckerskorn C., Mewes W., Goretzki H., Lottspeich F. A new siliconized-glass fiber as support for protein-chemical analysis of electroblotted proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Oct 1;176(3):509–519. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14308.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fesenko E. E., Kolesnikov S. S., Lyubarsky A. L. Induction by cyclic GMP of cationic conductance in plasma membrane of retinal rod outer segment. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):310–313. doi: 10.1038/313310a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedel U., Wolbring G., Wohlfart P., Cook N. J. The sodium-calcium exchanger of bovine rod photoreceptors: K(+)-dependence of the purified and reconstituted protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jan 30;1061(2):247–252. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90290-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung M. C., Chiu K. Y., Weber T., Chang T. W., Chang N. T. Detection and purification of a recombinant human B lymphotropic virus (HHV-6) in the baculovirus expression system by limiting dilution and DNA dot-blot hybridization. J Virol Methods. 1988 Jan;19(1):33–42. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(88)90005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavel Y., von Heijne G. Sequence differences between glycosylated and non-glycosylated Asn-X-Thr/Ser acceptor sites: implications for protein engineering. Protein Eng. 1990 Apr;3(5):433–442. doi: 10.1093/protein/3.5.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gribskov M., McLachlan A. D., Eisenberg D. Profile analysis: detection of distantly related proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4355–4358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gros P., Croop J., Housman D. Mammalian multidrug resistance gene: complete cDNA sequence indicates strong homology to bacterial transport proteins. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):371–380. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90594-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haase W., Friese W., Gordon R. D., Müller H., Cook N. J. Immunological characterization and localization of the Na+/Ca2(+)-exchanger in bovine retina. J Neurosci. 1990 May;10(5):1486–1494. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-05-01486.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin A. L., McNaughton P. A., Nunn B. J. The ionic selectivity and calcium dependence of the light-sensitive pathway in toad rods. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:447–468. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupinski J., Coussen F., Bakalyar H. A., Tang W. J., Feinstein P. G., Orth K., Slaughter C., Reed R. R., Gilman A. G. Adenylyl cyclase amino acid sequence: possible channel- or transporter-like structure. Science. 1989 Jun 30;244(4912):1558–1564. doi: 10.1126/science.2472670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagnado L., Cervetto L., McNaughton P. A. Ion transport by the Na-Ca exchange in isolated rod outer segments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4548–4552. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncrief N. D., Kretsinger R. H., Goodman M. Evolution of EF-hand calcium-modulated proteins. I. Relationships based on amino acid sequences. J Mol Evol. 1990 Jun;30(6):522–562. doi: 10.1007/BF02101108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll D. A., Longoni S., Philipson K. D. Molecular cloning and functional expression of the cardiac sarcolemmal Na(+)-Ca2+ exchanger. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):562–565. doi: 10.1126/science.1700476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid D. M., Friedel U., Molday R. S., Cook N. J. Identification of the sodium-calcium exchanger as the major ricin-binding glycoprotein of bovine rod outer segments and its localization to the plasma membrane. Biochemistry. 1990 Feb 13;29(6):1601–1607. doi: 10.1021/bi00458a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riordan J. R., Rommens J. M., Kerem B., Alon N., Rozmahel R., Grzelczak Z., Zielenski J., Lok S., Plavsic N., Chou J. L. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: cloning and characterization of complementary DNA. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1066–1073. doi: 10.1126/science.2475911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnetkamp P. P., Basu D. K., Szerencsei R. T. Na+-Ca2+ exchange in bovine rod outer segments requires and transports K+. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jul;257(1 Pt 1):C153–C157. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.257.1.C153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnetkamp P. P. Sodium-calcium exchange in the outer segments of bovine rod photoreceptors. J Physiol. 1986 Apr;373:25–45. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M., Elledge S., Sweetser D., Young R. A., Davis R. W. Lambda gt 11: gene isolation with antibody probes and other applications. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:107–128. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54073-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L. Cyclic GMP cascade of vision. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1986;9:87–119. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.09.030186.000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshima H., Nishimura S., Matsumoto T., Ishida H., Kangawa K., Minamino N., Matsuo H., Ueda M., Hanaoka M., Hirose T. Primary structure and expression from complementary DNA of skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):439–445. doi: 10.1038/339439a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tufty R. M., Kretsinger R. H. Troponin and parvalbumin calcium binding regions predicted in myosin light chain and T4 lysozyme. Science. 1975 Jan 17;187(4172):167–169. doi: 10.1126/science.1111094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasudevan S., Reiländer H., Maul G., Michel H. Expression and cell membrane localization of rat M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor produced in Sf9 insect cells using the baculovirus system. FEBS Lett. 1991 May 20;283(1):52–56. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80551-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yau K. W., Baylor D. A. Cyclic GMP-activated conductance of retinal photoreceptor cells. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1989;12:289–327. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.12.030189.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yau K. W., Nakatani K. Cation selectivity of light-sensitive conductance in retinal rods. Nature. 1984 May 24;309(5966):352–354. doi: 10.1038/309352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yau K. W., Nakatani K. Electrogenic Na-Ca exchange in retinal rod outer segment. Nature. 1984 Oct 18;311(5987):661–663. doi: 10.1038/311661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]