Abstract
The C-terminal domain (Iga beta) of the Neisseria IgA protease precursor is involved in the transport of covalently attached proteins across the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. We investigated outer membrane transport in Escherichia coli using fusion proteins consisting of an N-terminal signal sequence for inner membrane transport, the Vibrio cholerae toxin B subunit (CtxB) as a passenger and Iga beta. The process probably involves two distinct steps: (i) integration of Iga beta into the outer membrane and (ii) translocation of the passenger across the membrane. The outer membrane integrated part of Iga beta is the C-terminal 30 kDa core, which serves as a translocator for both the passenger and the linking region situated between the passenger and Iga beta core. The completeness of the translocation is demonstrated by the extracellular release of the passenger protein owing to the action of the E. coli outer membrane OmpT protease. Translocation of the CtxB moiety occurs efficiently under conditions preventing intramolecular disulphide bond formation. In contrast, if disulphide bond formation in the periplasm proceeds, then translocation halts after the export of the linking region. In this situation transmembrane intermediates are generated which give rise to characteristic fragments resulting from rapid proteolytic degradation of the periplasmically trapped portion. Based on the identification of translocation intermediates we propose that the polypeptide chain of the passenger passes in a linear fashion across the bacterial outer membrane.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernstein H. D., Poritz M. A., Strub K., Hoben P. J., Brenner S., Walter P. Model for signal sequence recognition from amino-acid sequence of 54K subunit of signal recognition particle. Nature. 1989 Aug 10;340(6233):482–486. doi: 10.1038/340482a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieker K. L., Silhavy T. J. PrlA (SecY) and PrlG (SecE) interact directly and function sequentially during protein translocation in E. coli. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):833–842. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90193-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass J. M., Higgins C. F., Foley M., Rugman P. A., Birmingham J., Garland P. B. Lateral diffusion of proteins in the periplasm of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):787–795. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.787-795.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly T., Gilmore R. The signal recognition particle receptor mediates the GTP-dependent displacement of SRP from the signal sequence of the nascent polypeptide. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):599–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90129-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilers M., Schatz G. Binding of a specific ligand inhibits import of a purified precursor protein into mitochondria. Nature. 1986 Jul 17;322(6076):228–232. doi: 10.1038/322228a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilers M., Schatz G. Protein unfolding and the energetics of protein translocation across biological membranes. Cell. 1988 Feb 26;52(4):481–483. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90458-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodberg J., Dunn J. J. ompT encodes the Escherichia coli outer membrane protease that cleaves T7 RNA polymerase during purification. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1245–1253. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1245-1253.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halter R., Pohlner J., Meyer T. F. IgA protease of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: isolation and characterization of the gene and its extracellular product. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1595–1601. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02016.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halter R., Pohlner J., Meyer T. F. Mosaic-like organization of IgA protease genes in Neisseria gonorrhoeae generated by horizontal genetic exchange in vivo. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2737–2744. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08415.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartl F. U., Lecker S., Schiebel E., Hendrick J. P., Wickner W. The binding cascade of SecB to SecA to SecY/E mediates preprotein targeting to the E. coli plasma membrane. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):269–279. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90160-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst T. R., Holmgren J. Transient entry of enterotoxin subunits into the periplasm occurs during their secretion from Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1037–1045. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1037-1045.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard S. P., Buckley J. T. Intracellular accumulation of extracellular proteins by pleiotropic export mutants of Aeromonas hydrophila. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):413–418. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.413-418.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellenberger E. The 'Bayer bridges' confronted with results from improved electron microscopy methods. Mol Microbiol. 1990 May;4(5):697–705. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00640.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
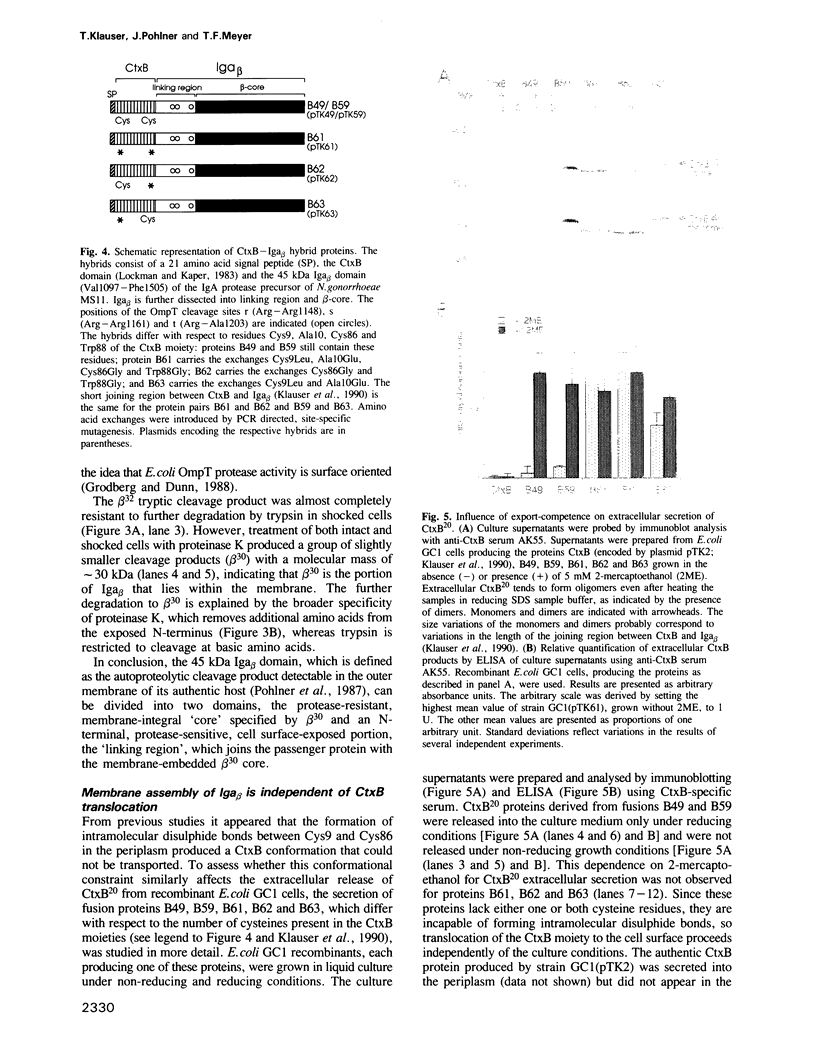
- Klauser T., Pohlner J., Meyer T. F. Extracellular transport of cholera toxin B subunit using Neisseria IgA protease beta-domain: conformation-dependent outer membrane translocation. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1991–1999. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08327.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg U. C., Johnson A. E., Walter P. Protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum membrane: identification by photocross-linking of a 39-kD integral membrane glycoprotein as part of a putative translocation tunnel. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2033–2043. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecker S. H., Driessen A. J., Wickner W. ProOmpA contains secondary and tertiary structure prior to translocation and is shielded from aggregation by association with SecB protein. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2309–2314. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07402.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lill R., Dowhan W., Wickner W. The ATPase activity of SecA is regulated by acidic phospholipids, SecY, and the leader and mature domains of precursor proteins. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):271–280. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90742-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockman H., Kaper J. B. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the A2 and B subunits of Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13722–13726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. F., Mlawer N., So M. Pilus expression in Neisseria gonorrhoeae involves chromosomal rearrangement. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki H., Yanagida N., Horinouchi S., Beppu T. Characterization of the precursor of Serratia marcescens serine protease and COOH-terminal processing of the precursor during its excretion through the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6566–6572. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6566-6572.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORN M. J., ROSEN S. M., ROTHFIELD L., ZELEZNICK L. D., HORECKER B. L. LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE OF THE GRAM-NEGATIVE CELL WALL. Science. 1964 Aug 21;145(3634):783–789. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3634.783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson G. D., Mekalanos J. J. Molecular cloning of Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin genes in Escherichia coli K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2976–2980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
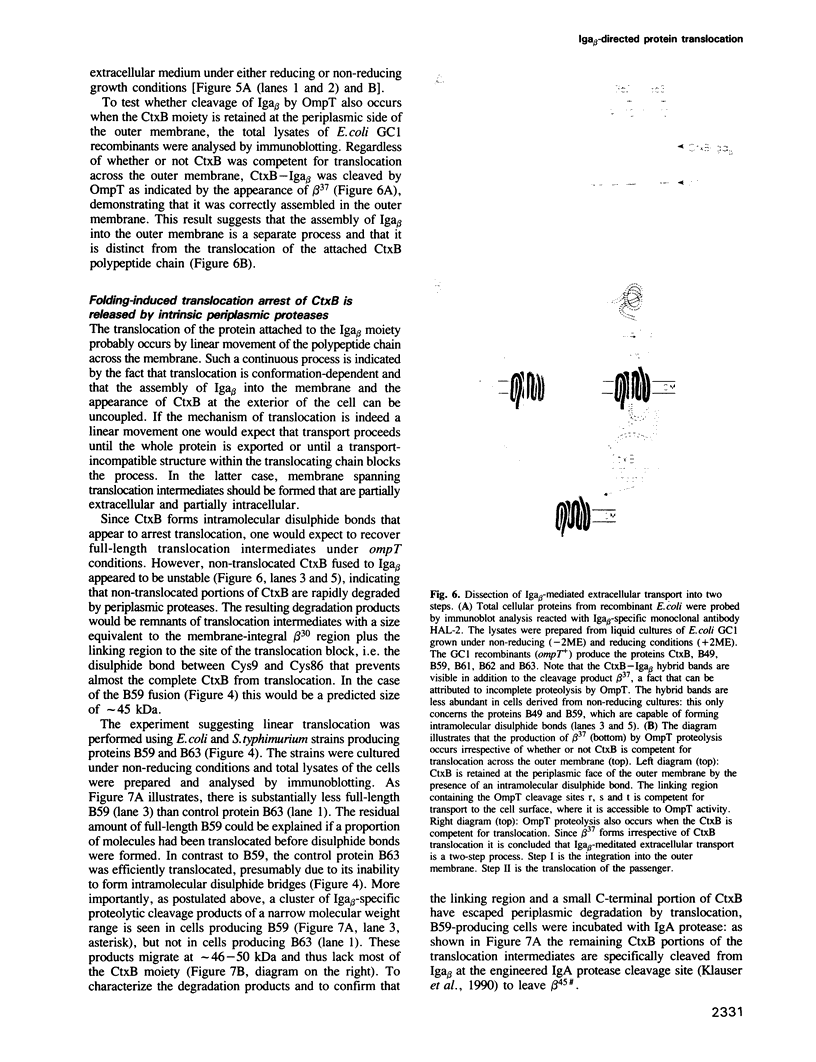
- Pohlner J., Halter R., Beyreuther K., Meyer T. F. Gene structure and extracellular secretion of Neisseria gonorrhoeae IgA protease. 1987 Jan 29-Feb 4Nature. 325(6103):458–462. doi: 10.1038/325458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulsen K., Brandt J., Hjorth J. P., Thøgersen H. C., Kilian M. Cloning and sequencing of the immunoglobulin A1 protease gene (iga) of Haemophilus influenzae serotype b. Infect Immun. 1989 Oct;57(10):3097–3105. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.10.3097-3105.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall L. L., Hardy S. J. Correlation of competence for export with lack of tertiary structure of the mature species: a study in vivo of maltose-binding protein in E. coli. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90074-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rassow J., Guiard B., Wienhues U., Herzog V., Hartl F. U., Neupert W. Translocation arrest by reversible folding of a precursor protein imported into mitochondria. A means to quantitate translocation contact sites. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1421–1428. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanz P., Meyer D. I. Signal recognition particle (SRP) stabilizes the translocation-competent conformation of pre-secretory proteins. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3553–3557. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03232.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz P. J., Beckwith J. Genetic analysis of protein export in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:215–248. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.001243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiebel E., Driessen A. J., Hartl F. U., Wickner W. Delta mu H+ and ATP function at different steps of the catalytic cycle of preprotein translocase. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):927–939. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90317-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleyer M., Neupert W. Transport of proteins into mitochondria: translocational intermediates spanning contact sites between outer and inner membranes. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):339–350. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90039-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen K., Hellman J., Nikaido H. Porin channels in intact cells of Escherichia coli are not affected by Donnan potentials across the outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1182–1187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struyvé M., Moons M., Tommassen J. Carboxy-terminal phenylalanine is essential for the correct assembly of a bacterial outer membrane protein. J Mol Biol. 1991 Mar 5;218(1):141–148. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90880-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart R. A., Nicholson D. W., Neupert W. Early steps in mitochondrial protein import: receptor functions can be substituted by the membrane insertion activity of apocytochrome c. Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90713-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimura K., Nishihara T. Purification, characterization, and primary structure of Escherichia coli protease VII with specificity for paired basic residues: identity of protease VII and OmpT. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5625–5632. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5625-5632.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tani K., Shiozuka K., Tokuda H., Mizushima S. In vitro analysis of the process of translocation of OmpA across the Escherichia coli cytoplasmic membrane. A translocation intermediate accumulates transiently in the absence of the proton motive force. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18582–18588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tani K., Tokuda H., Mizushima S. Translocation of ProOmpA possessing an intramolecular disulfide bridge into membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. Effect of membrane energization. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17341–17347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teo I. A. Proteolytic processing of the Ada protein that repairs DNA O6-methylguanine residues in E. coli. Mutat Res. 1987 Mar;183(2):123–127. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(87)90054-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vestweber D., Brunner J., Baker A., Schatz G. A 42K outer-membrane protein is a component of the yeast mitochondrial protein import site. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):205–209. doi: 10.1038/341205a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vestweber D., Schatz G. Mitochondria can import artificial precursor proteins containing a branched polypeptide chain or a carboxy-terminal stilbene disulfonate. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2045–2049. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel H., Jähnig F. Models for the structure of outer-membrane proteins of Escherichia coli derived from raman spectroscopy and prediction methods. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jul 20;190(2):191–199. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90292-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wandersman C., Delepelaire P. TolC, an Escherichia coli outer membrane protein required for hemolysin secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4776–4780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. R., Buckley J. T. Proton motive force involved in protein transport across the outer membrane of Aeromonas salmonicida. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):654–656. doi: 10.1126/science.2814486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- d'Enfert C., Ryter A., Pugsley A. P. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the Klebsiella pneumoniae genes for production, surface localization and secretion of the lipoprotein pullulanase. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3531–3538. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02679.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Ley P., Amesz H., Tommassen J., Lugtenberg B. Monoclonal antibodies directed against the cell-surface-exposed part of PhoE pore protein of the Escherichia coli K-12 outer membrane. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Mar 1;147(2):401–407. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08764.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]