Abstract
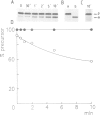
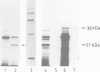
Signal peptidases (SPases) remove signal peptides from secretory proteins. The sipS (signal peptidase of subtilis) gene, which encodes an SPase of Bacillus subtilis, was cloned in Escherichia coli and was also found to be active in E.coli. Its overproduction in B.subtilis resulted in increased rates of processing of a hybrid beta-lactamase precursor. The SipS protein consisted of 184 amino acids (mol. wt 21 kDa). The protein showed sequence similarity with the leader peptidases of E.coli and Salmonella typhimurium, and the mitochondrial inner membrane protease I of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Patterns of conserved amino acids present in these four proteins were also detected in the Sec11 subunit of the SPase complex of S.cerevisiae and the 18 and 21 kDa subunits of the canine SPase complex. Knowledge of the sequence of SipS was essential for the detection of these similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic SPases. The data suggest that these proteins, which have analogous functions, belong to one class of enzymes, the type I SPases.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behnke D., Gerlach D. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, and Streptococcus sanguis of a gene for staphylokinase--a bacterial plasminogen activator. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Dec;210(3):528–534. doi: 10.1007/BF00327208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behrens M., Michaelis G., Pratje E. Mitochondrial inner membrane protease 1 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae shows sequence similarity to the Escherichia coli leader peptidase. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Aug;228(1-2):167–176. doi: 10.1007/BF00282462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilgin N., Lee J. I., Zhu H. Y., Dalbey R., von Heijne G. Mapping of catalytically important domains in Escherichia coli leader peptidase. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2717–2722. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07458.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhni P. C., Deshaies R. J., Schekman R. W. SEC11 is required for signal peptide processing and yeast cell growth. J Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;106(4):1035–1042. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.4.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chevallier M. R., Aigle M. Qualitative detection of penicillinase produced by yeast strains carrying chimeric yeast-coli plasmids. FEBS Lett. 1979 Dec 1;108(1):179–180. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81204-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalbey R. E., Kuhn A., Wickner W. The internal signal sequence of Escherichia coli leader peptidase is necessary, but not sufficient, for its rapid membrane assembly. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 25;262(27):13241–13245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalbey R. E., Wickner W. Leader peptidase catalyzes the release of exported proteins from the outer surface of the Escherichia coli plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15925–15931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Date T., Wickner W. Isolation of the Escherichia coli leader peptidase gene and effects of leader peptidase overproduction in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6106–6110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dev I. K., Ray P. H., Novak P. Minimum substrate sequence for signal peptidase I of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20069–20072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dick T., Matzura H. Chloramphenicol-induced translational activation of cat messenger RNA in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1990 Apr 20;212(4):661–668. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90228-E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dierstein R., Wickner W. Requirements for substrate recognition by bacterial leader peptidase. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):427–431. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04228.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edens L., Heslinga L., Klok R., Ledeboer A. M., Maat J., Toonen M. Y., Visser C., Verrips C. T. Cloning of cDNA encoding the sweet-tasting plant protein thaumatin and its expression in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1982 Apr;18(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90050-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenburg G., Shelness G. S., Blobel G. A subunit of mammalian signal peptidase is homologous to yeast SEC11 protein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):15762–15765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartl F. U., Neupert W. Protein sorting to mitochondria: evolutionary conservations of folding and assembly. Science. 1990 Feb 23;247(4945):930–938. doi: 10.1126/science.2406905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawlitschek G., Schneider H., Schmidt B., Tropschug M., Hartl F. U., Neupert W. Mitochondrial protein import: identification of processing peptidase and of PEP, a processing enhancing protein. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):795–806. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90096-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innis M. A., Tokunaga M., Williams M. E., Loranger J. M., Chang S. Y., Chang S., Wu H. C. Nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli prolipoprotein signal peptidase (lsp) gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3708–3712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaki L., Beers R., Wu H. C. Nucleotide sequence of the Pseudomonas fluorescens signal peptidase II gene (lsp) and flanking genes. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6512–6517. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6512-6517.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaki L., Kawakami M., Beers R., Hom R., Wu H. C. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the Enterobacter aerogenes signal peptidase II (lsp) gene. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;172(1):469–472. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.1.469-472.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R. E., Yaffe M. P. Import of proteins into yeast mitochondria: the nuclear MAS2 gene encodes a component of the processing protease that is homologous to the MAS1-encoded subunit. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3863–3871. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03272.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura F., Doi R. H. Construction of a Bacillus subtilis double mutant deficient in extracellular alkaline and neutral proteases. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):442–444. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.442-444.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiel J. A., Vossen J. P., Venema G. A general method for the construction of Escherichia coli mutants by homologous recombination and plasmid segregation. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 May;207(2-3):294–301. doi: 10.1007/BF00331592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kok J., van der Vossen J. M., Venema G. Construction of plasmid cloning vectors for lactic streptococci which also replicate in Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Oct;48(4):726–731. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.4.726-731.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore K. E., Miura S. A small hydrophobic domain anchors leader peptidase to the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8806–8813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura K., Nakamura A., Takamatsu H., Yoshikawa H., Yamane K. Cloning and characterization of a Bacillus subtilis gene homologous to E. coli secY. J Biochem. 1990 Apr;107(4):603–607. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunn D. N., Lory S. Product of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa gene pilD is a prepilin leader peptidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3281–3285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock R. A., Hartl F. U., Cheng M. Y., Ostermann J., Horwich A., Neupert W. The processing peptidase of yeast mitochondria: the two co-operating components MPP and PEP are structurally related. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3493–3500. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03225.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Korn L. J. A comprehensive sequence analysis program for the IBM personal computer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):581–599. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray P., Dev I., MacGregor C., Bassford P., Jr Signal peptidases. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;125:75–102. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71251-7_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadaie Y., Takamatsu H., Nakamura K., Yamane K. Sequencing reveals similarity of the wild-type div+ gene of Bacillus subtilis to the Escherichia coli secA gene. Gene. 1991 Feb 1;98(1):101–105. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90110-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarvas M. Protein secretion in bacilli. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;125:103–125. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71251-7_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider A., Behrens M., Scherer P., Pratje E., Michaelis G., Schatz G. Inner membrane protease I, an enzyme mediating intramitochondrial protein sorting in yeast. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):247–254. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07944.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelness G. S., Blobel G. Two subunits of the canine signal peptidase complex are homologous to yeast SEC11 protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9512–9519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M. K., Griswold M. D. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with 2,5-diphenyloxazole in acetic acid and its comparison with existing procedures. Biochem J. 1983 Jan 1;209(1):281–284. doi: 10.1042/bj2090281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H., Bron S., Van Ee J., Venema G. Construction and use of signal sequence selection vectors in Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3321–3328. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3321-3328.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H., de Jong A., Bron S., Venema G. Characterization of signal-sequence-coding regions selected from the Bacillus subtilis chromosome. Gene. 1988 Oct 30;70(2):351–361. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90207-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh J. W., Boylan S. A., Thomas S. M., Dolan K. M., Oliver D. B., Price C. W. Isolation of a secY homologue from Bacillus subtilis: evidence for a common protein export pathway in eubacteria. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Feb;4(2):305–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00597.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokunaga M., Loranger J. M., Wolfe P. B., Wu H. C. Prolipoprotein signal peptidase in Escherichia coli is distinct from the M13 procoat protein signal peptidase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):9922–9925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson M. E. Compilation of published signal sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5145–5164. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertman K. F., Wyman A. R., Botstein D. Host/vector interactions which affect the viability of recombinant phage lambda clones. Gene. 1986;49(2):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90286-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner W., Driessen A. J., Hartl F. U. The enzymology of protein translocation across the Escherichia coli plasma membrane. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:101–124. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.000533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte C., Jensen R. E., Yaffe M. P., Schatz G. MAS1, a gene essential for yeast mitochondrial assembly, encodes a subunit of the mitochondrial processing protease. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1439–1447. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02961.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe P. B., Silver P., Wickner W. The isolation of homogeneous leader peptidase from a strain of Escherichia coli which overproduces the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7898–7902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe P. B., Wickner W., Goodman J. M. Sequence of the leader peptidase gene of Escherichia coli and the orientation of leader peptidase in the bacterial envelope. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):12073–12080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe P. B., Zwizinski C., Wickner W. Purification and characterization of leader peptidase from Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 1983;97:40–46. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)97116-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YaDeau J. T., Klein C., Blobel G. Yeast signal peptidase contains a glycoprotein and the Sec11 gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):517–521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada H., Yamagata H., Mizushima S. The major outer membrane lipoprotein and new lipoproteins share a common signal peptidase that exists in the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1984 Jan 23;166(1):179–182. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagata H., Ippolito C., Inukai M., Inouye M. Temperature-sensitive processing of outer membrane lipoprotein in an Escherichia coli mutant. J Bacteriol. 1982 Dec;152(3):1163–1168. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.3.1163-1168.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu F., Yamada H., Daishima K., Mizushima S. Nucleotide sequence of the lspA gene, the structural gene for lipoprotein signal peptidase of Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1984 Jul 23;173(1):264–268. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81060-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu H. Y., Dalbey R. E. Both a short hydrophobic domain and a carboxyl-terminal hydrophilic region are important for signal function in the Escherichia coli leader peptidase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11833–11838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann R., Watts C., Wickner W. The biosynthesis of membrane-bound M13 coat protein. Energetics and assembly intermediates. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6529–6536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dijl J. M., Smith H., Bron S., Venema G. Synthesis and processing of Escherichia coli TEM-beta-lactamase and Bacillus licheniformis alpha-amylase in E. coli: the role of signal peptidase I. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Sep;214(1):55–61. doi: 10.1007/BF00340179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dijl J. M., de Jong A., Smith H., Bron S., Venema G. Non-functional expression of Escherichia coli signal peptidase I in Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Sep;137(9):2073–2083. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-9-2073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dijl J. M., de Jong A., Smith H., Bron S., Venema G. Signal peptidase I overproduction results in increased efficiencies of export and maturation of hybrid secretory proteins in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 May;227(1):40–48. doi: 10.1007/BF00260704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dijl J. M., van den Bergh R., Reversma T., Smith H., Bron S., Venema G. Molecular cloning of the Salmonella typhimurium lep gene in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Sep;223(2):233–240. doi: 10.1007/BF00265059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G., Abrahmsén L. Species-specific variation in signal peptide design. Implications for protein secretion in foreign hosts. FEBS Lett. 1989 Feb 27;244(2):439–446. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80579-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. The signal peptide. J Membr Biol. 1990 May;115(3):195–201. doi: 10.1007/BF01868635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G., Wickner W., Dalbey R. E. The cytoplasmic domain of Escherichia coli leader peptidase is a "translocation poison" sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3363–3366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]