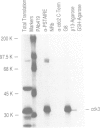
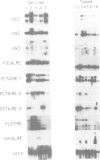
Abstract
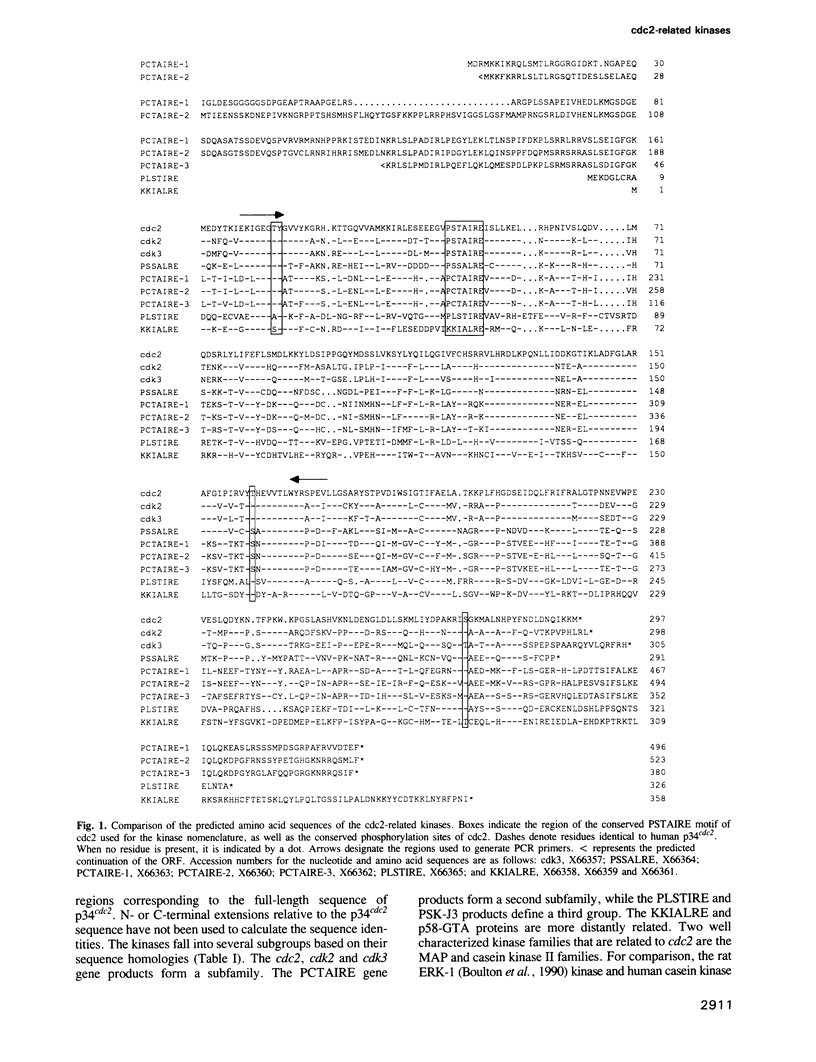
The p34cdc2 protein kinase is known to regulate important transitions in the eukaryotic cell cycle. We have identified 10 human protein kinases based on their structural relation to p34cdc2. Seven of these kinases are novel and the products of five share greater than 50% amino acid sequence identity with p34cdc2. The seven novel genes are broadly expressed in human cell lines and tissues with each displaying some cell type or tissue specificity. The cdk3 gene, like cdc2 and cdk2, can complement cdc28 mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, suggesting that all three of these protein kinases can play roles in the regulation of the mammalian cell cycle. The identification of a large family of cdc2-related kinases opens the possibility of combinatorial regulation of the cell cycle together with the emerging large family of cyclins.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amon A., Surana U., Muroff I., Nasmyth K. Regulation of p34CDC28 tyrosine phosphorylation is not required for entry into mitosis in S. cerevisiae. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):368–371. doi: 10.1038/355368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arion D., Meijer L., Brizuela L., Beach D. cdc2 is a component of the M phase-specific histone H1 kinase: evidence for identity with MPF. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):371–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90060-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton T. G., Yancopoulos G. D., Gregory J. S., Slaughter C., Moomaw C., Hsu J., Cobb M. H. An insulin-stimulated protein kinase similar to yeast kinases involved in cell cycle control. Science. 1990 Jul 6;249(4964):64–67. doi: 10.1126/science.2164259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunnell B. A., Heath L. S., Adams D. E., Lahti J. M., Kidd V. J. Increased expression of a 58-kDa protein kinase leads to changes in the CHO cell cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7467–7471. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cisek L. J., Corden J. L. Phosphorylation of RNA polymerase by the murine homologue of the cell-cycle control protein cdc2. Nature. 1989 Jun 29;339(6227):679–684. doi: 10.1038/339679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colasanti J., Tyers M., Sundaresan V. Isolation and characterization of cDNA clones encoding a functional p34cdc2 homologue from Zea mays. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3377–3381. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R. DAF1, a mutant gene affecting size control, pheromone arrest, and cell cycle kinetics of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4675–4684. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Beach D. Activation of cdc2 protein kinase during mitosis in human cells: cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation and subunit rearrangement. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90175-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Brizuela L., Potashkin J., Beach D. Identification of p34 and p13, human homologs of the cell cycle regulators of fission yeast encoded by cdc2+ and suc1+. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):319–325. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90227-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G. Cell cycle control in eukaryotes: molecular mechanisms of cdc2 activation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Oct;15(10):378–383. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90235-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ducommun B., Brambilla P., Félix M. A., Franza B. R., Jr, Karsenti E., Draetta G. cdc2 phosphorylation is required for its interaction with cyclin. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3311–3319. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04895.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Brizuela L., Beach D., Newport J. The Xenopus cdc2 protein is a component of MPF, a cytoplasmic regulator of mitosis. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):423–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90205-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Spottswood M. R. A new human p34 protein kinase, CDK2, identified by complementation of a cdc28 mutation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, is a homolog of Xenopus Eg1. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2653–2659. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07808.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Rosenthal E. T., Youngblom J., Distel D., Hunt T. Cyclin: a protein specified by maternal mRNA in sea urchin eggs that is destroyed at each cleavage division. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):389–396. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90420-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang F., Newport J. W. Evidence that the G1-S and G2-M transitions are controlled by different cdc2 proteins in higher eukaryotes. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):731–742. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90117-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feiler H. S., Jacobs T. W. Cloning of the pea cdc2 homologue by efficient immunological screening of PCR products. Plant Mol Biol. 1991 Sep;17(3):321–333. doi: 10.1007/BF00040628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galaktionov K., Beach D. Specific activation of cdc25 tyrosine phosphatases by B-type cyclins: evidence for multiple roles of mitotic cyclins. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1181–1194. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90294-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glotzer M., Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin is degraded by the ubiquitin pathway. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):132–138. doi: 10.1038/349132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Moreno S., Owen D. J., Sazer S., Nurse P. Phosphorylation at Thr167 is required for Schizosaccharomyces pombe p34cdc2 function. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3297–3309. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04894.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Nurse P. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the fission yeast cdc2+ protein kinase regulates entry into mitosis. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):39–45. doi: 10.1038/342039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadwiger J. A., Wittenberg C., Richardson H. E., de Barros Lopes M., Reed S. I. A family of cyclin homologs that control the G1 phase in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6255–6259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K. Homology probing: identification of cDNA clones encoding members of the protein-serine kinase family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):388–392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Crawford L. V., Pim D. C., Williamson N. M. Monoclonal antibodies specific for simian virus 40 tumor antigens. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):861–869. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.861-869.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Franza B. R., Jr, Schley C. Monoclonal antibodies specific for adenovirus early region 1A proteins: extensive heterogeneity in early region 1A products. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):533–546. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.533-546.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H. Three additional genes required for deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):966–974. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.966-974.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirayama T., Imajuku Y., Anai T., Matsui M., Oka A. Identification of two cell-cycle-controlling cdc2 gene homologs in Arabidopsis thaliana. Gene. 1991 Sep 15;105(2):159–165. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90146-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt H., Páy A., Györgyey J., Bakó L., Németh K., Bögre L., Schweyen R. J., Heberle-Bors E., Dudits D. Complementation of a yeast cell cycle mutant by an alfalfa cDNA encoding a protein kinase homologous to p34cdc2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1636–1640. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T. Maturation promoting factor, cyclin and the control of M-phase. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;1(2):268–274. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(89)90099-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irie K., Nomoto S., Miyajima I., Matsumoto K. SGV1 encodes a CDC28/cdc2-related kinase required for a G alpha subunit-mediated adaptive response to pheromone in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):785–795. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90386-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez J., Alphey L., Nurse P., Glover D. M. Complementation of fission yeast cdc2ts and cdc25ts mutants identifies two cell cycle genes from Drosophila: a cdc2 homologue and string. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3565–3571. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07567.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koff A., Cross F., Fisher A., Schumacher J., Leguellec K., Philippe M., Roberts J. M. Human cyclin E, a new cyclin that interacts with two members of the CDC2 gene family. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1217–1228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90044-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krek W., Nigg E. A. Differential phosphorylation of vertebrate p34cdc2 kinase at the G1/S and G2/M transitions of the cell cycle: identification of major phosphorylation sites. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):305–316. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07951.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krek W., Nigg E. A. Mutations of p34cdc2 phosphorylation sites induce premature mitotic events in HeLa cells: evidence for a double block to p34cdc2 kinase activation in vertebrates. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3331–3341. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04897.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krek W., Nigg E. A. Structure and developmental expression of the chicken CDC2 kinase. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):3071–3078. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08458.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapidot-Lifson Y., Patinkin D., Prody C. A., Ehrlich G., Seidman S., Ben-Aziz R., Benseler F., Eckstein F., Zakut H., Soreq H. Cloning and antisense oligodeoxynucleotide inhibition of a human homolog of cdc2 required in hematopoiesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):579–583. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. M., Greenleaf A. L. CTD kinase large subunit is encoded by CTK1, a gene required for normal growth of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene Expr. 1991 May;1(2):149–167. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. G., Nurse P. Complementation used to clone a human homologue of the fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2. Nature. 1987 May 7;327(6117):31–35. doi: 10.1038/327031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner C. F., O'Farrell P. H. Drosophila cdc2 homologs: a functional homolog is coexpressed with a cognate variant. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3573–3581. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07568.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew D. J., Dulić V., Reed S. I. Isolation of three novel human cyclins by rescue of G1 cyclin (Cln) function in yeast. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1197–1206. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90042-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushime H., Jinno A., Takagi N., Shibuya M. A novel mammalian protein kinase gene (mak) is highly expressed in testicular germ cells at and after meiosis. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2261–2268. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushime H., Roussel M. F., Ashmun R. A., Sherr C. J. Colony-stimulating factor 1 regulates novel cyclins during the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):701–713. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90101-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisner H., Heller-Harrison R., Buxton J., Czech M. P. Molecular cloning of the human casein kinase II alpha subunit. Biochemistry. 1989 May 2;28(9):4072–4076. doi: 10.1021/bi00435a066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motokura T., Bloom T., Kim H. G., Jüppner H., Ruderman J. V., Kronenberg H. M., Arnold A. A novel cyclin encoded by a bcl1-linked candidate oncogene. Nature. 1991 Apr 11;350(6318):512–515. doi: 10.1038/350512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullis K., Faloona F., Scharf S., Saiki R., Horn G., Erlich H. Specific enzymatic amplification of DNA in vitro: the polymerase chain reaction. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):263–273. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Dominoes and clocks: the union of two views of the cell cycle. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):614–621. doi: 10.1126/science.2683077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Solomon M. J., Kirschner M. W. The role of cyclin synthesis and degradation in the control of maturation promoting factor activity. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):280–286. doi: 10.1038/339280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash R., Tokiwa G., Anand S., Erickson K., Futcher A. B. The WHI1+ gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae tethers cell division to cell size and is a cyclin homolog. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4335–4346. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03332.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninomiya-Tsuji J., Nomoto S., Yasuda H., Reed S. I., Matsumoto K. Cloning of a human cDNA encoding a CDC2-related kinase by complementation of a budding yeast cdc28 mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9006–9010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norbury C., Blow J., Nurse P. Regulatory phosphorylation of the p34cdc2 protein kinase in vertebrates. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3321–3329. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04896.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P., Bissett Y. Gene required in G1 for commitment to cell cycle and in G2 for control of mitosis in fission yeast. Nature. 1981 Aug 6;292(5823):558–560. doi: 10.1038/292558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P. Universal control mechanism regulating onset of M-phase. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):503–508. doi: 10.1038/344503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osmani A. H., McGuire S. L., Osmani S. A. Parallel activation of the NIMA and p34cdc2 cell cycle-regulated protein kinases is required to initiate mitosis in A. nidulans. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):283–291. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90180-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano M., Draetta G., Jansen-Dürr P. Association of cdk2 kinase with the transcription factor E2F during S phase. Science. 1992 Feb 28;255(5048):1144–1147. doi: 10.1126/science.1312258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano M., Pepperkok R., Verde F., Ansorge W., Draetta G. Cyclin A is required at two points in the human cell cycle. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):961–971. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05135.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paris J., Le Guellec R., Couturier A., Le Guellec K., Omilli F., Camonis J., MacNeill S., Philippe M. Cloning by differential screening of a Xenopus cDNA coding for a protein highly homologous to cdc2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):1039–1043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piggott J. R., Rai R., Carter B. L. A bifunctional gene product involved in two phases of the yeast cell cycle. Nature. 1982 Jul 22;298(5872):391–393. doi: 10.1038/298391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Human cyclin A is adenovirus E1A-associated protein p60 and behaves differently from cyclin B. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):760–763. doi: 10.1038/346760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Isolation of a human cyclin cDNA: evidence for cyclin mRNA and protein regulation in the cell cycle and for interaction with p34cdc2. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):833–846. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90936-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. p34cdc2: the S and M kinase? New Biol. 1990 May;2(5):389–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I. The selection of S. cerevisiae mutants defective in the start event of cell division. Genetics. 1980 Jul;95(3):561–577. doi: 10.1093/genetics/95.3.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riabowol K., Draetta G., Brizuela L., Vandre D., Beach D. The cdc2 kinase is a nuclear protein that is essential for mitosis in mammalian cells. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):393–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90914-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson H. E., Stueland C. S., Thomas J., Russell P., Reed S. I. Human cDNAs encoding homologs of the small p34Cdc28/Cdc2-associated protein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1332–1344. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblatt J., Gu Y., Morgan D. O. Human cyclin-dependent kinase 2 is activated during the S and G2 phases of the cell cycle and associates with cyclin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2824–2828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Bugawan T. L., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Analysis of enzymatically amplified beta-globin and HLA-DQ alpha DNA with allele-specific oligonucleotide probes. Nature. 1986 Nov 13;324(6093):163–166. doi: 10.1038/324163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuttleworth J., Godfrey R., Colman A. p40MO15, a cdc2-related protein kinase involved in negative regulation of meiotic maturation of Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3233–3240. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07522.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M., Seraphin B., Faye G. KIN28, a yeast split gene coding for a putative protein kinase homologous to CDC28. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2697–2701. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04553.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Glotzer M., Lee T. H., Philippe M., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin activation of p34cdc2. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):1013–1024. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90504-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Lee T., Kirschner M. W. Role of phosphorylation in p34cdc2 activation: identification of an activating kinase. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Jan;3(1):13–27. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Murray A. W. S-phase feedback control in budding yeast independent of tyrosine phosphorylation of p34cdc28. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):365–368. doi: 10.1038/355365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surana U., Robitsch H., Price C., Schuster T., Fitch I., Futcher A. B., Nasmyth K. The role of CDC28 and cyclins during mitosis in the budding yeast S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):145–161. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90416-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Th'ng J. P., Wright P. S., Hamaguchi J., Lee M. G., Norbury C. J., Nurse P., Bradbury E. M. The FT210 cell line is a mouse G2 phase mutant with a temperature-sensitive CDC2 gene product. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):313–324. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90164-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai L. H., Harlow E., Meyerson M. Isolation of the human cdk2 gene that encodes the cyclin A- and adenovirus E1A-associated p33 kinase. Nature. 1991 Sep 12;353(6340):174–177. doi: 10.1038/353174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uesono Y., Tanaka K., Toh-e A. Negative regulators of the PHO system in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: isolation and structural characterization of PHO85. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10299–10309. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Gray A., Wood W. I., Hayflick J., Seeburg P. H. Isolation of a cDNA clone coding for the gamma-subunit of mouse nerve growth factor using a high-stringency selection procedure. DNA. 1984 Oct;3(5):387–392. doi: 10.1089/dna.1984.3.387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J., Chenivesse X., Henglein B., Bréchot C. Hepatitis B virus integration in a cyclin A gene in a hepatocellular carcinoma. Nature. 1990 Feb 8;343(6258):555–557. doi: 10.1038/343555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Connolly T., Futcher B., Beach D. Human D-type cyclin. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):691–699. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90100-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]