Abstract
Two alternatively spliced products of the human E2A gene, E12 and E47, encode helix-loop-helix DNA-binding proteins. Here we describe the isolation of two Xenopus cDNAs; one, XE12, is structurally similar to human E12 and the other contains a sequence similar to E47. Transcripts of both cDNAs are present at all the stages of Xenopus development tested and in all regions of the embryo. The DNA binding properties of in vitro translated XE12 are indistinguishable from those of human E12. We have shown previously that an embryonic muscle DNA-binding activity, EMF1, that binds to a promoter sequence required for the expression of the cardiac actin gene, contains the Xenopus myogenic factor XMyoD. Here we show that it also contains protein that interacts with an anti-E12 antiserum, suggesting that XE12 and XMyoD proteins, or very similar ones, are present in EMF1. We have addressed the functional role of XE12 in muscle gene transcription in Xenopus embryos by injecting in vitro synthesized RNA into the two cell embryo. Overexpression of XE12 and XMyoD augments by greater than 10-fold the ectopic activation of the endogenous cardiac actin gene that can be produced by XMyoD alone. Our DNA binding results strongly suggest that this effect is mediated through a direct interaction of the XE12-XMyoD complex with specific sites in the cardiac actin promoter. We suggest that XE12 is functionally important in muscle gene activation in embryonic development.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aplan P. D., Begley C. G., Bertness V., Nussmeier M., Ezquerra A., Coligan J., Kirsch I. R. The SCL gene is formed from a transcriptionally complex locus. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6426–6435. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benezra R., Davis R. L., Lockshon D., Turner D. L., Weintraub H. The protein Id: a negative regulator of helix-loop-helix DNA binding proteins. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90214-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Bober E., Winter B., Rosenthal N., Arnold H. H. Myf-6, a new member of the human gene family of myogenic determination factors: evidence for a gene cluster on chromosome 12. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):821–831. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08179.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan T. J., Olson E. N. Myogenin resides in the nucleus and acquires high affinity for a conserved enhancer element on heterodimerization. Genes Dev. 1990 Apr;4(4):582–595. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.4.582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caudy M., Vässin H., Brand M., Tuma R., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. daughterless, a Drosophila gene essential for both neurogenesis and sex determination, has sequence similarities to myc and the achaete-scute complex. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1061–1067. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90250-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty T., Brennan T. J., Li L., Edmondson D., Olson E. N. Inefficient homooligomerization contributes to the dependence of myogenin on E2A products for efficient DNA binding. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3633–3641. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty T., Olson E. N. Domains outside of the DNA-binding domain impart target gene specificity to myogenin and MRF4. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):6103–6108. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.6103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B., Fairman S., Mohun T. J., Brennan S. Activation of muscle-specific actin genes in Xenopus development by an induction between animal and vegetal cells of a blastula. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):913–922. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. P., Melton D. A. Microinjection of synthetic Xhox-1A homeobox mRNA disrupts somite formation in developing Xenopus embryos. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):687–697. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90087-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III in DNA sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:156–165. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henthorn P., Kiledjian M., Kadesch T. Two distinct transcription factors that bind the immunoglobulin enhancer microE5/kappa 2 motif. Science. 1990 Jan 26;247(4941):467–470. doi: 10.1126/science.2105528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henthorn P., McCarrick-Walmsley R., Kadesch T. Sequence of the cDNA encoding ITF-2, a positive-acting transcription factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 11;18(3):678–678. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.3.678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood N. D., Gurdon J. B. Activation of muscle genes without myogenesis by ectopic expression of MyoD in frog embryo cells. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):197–200. doi: 10.1038/347197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood N. D., Pluck A., Gurdon J. B. A Xenopus mRNA related to Drosophila twist is expressed in response to induction in the mesoderm and the neural crest. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):893–903. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90612-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood N. D., Pluck A., Gurdon J. B., Dilworth S. M. Expression of XMyoD protein in early Xenopus laevis embryos. Development. 1992 Jan;114(1):31–38. doi: 10.1242/dev.114.1.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood N. D., Pluck A., Gurdon J. B. MyoD expression in the forming somites is an early response to mesoderm induction in Xenopus embryos. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3409–3417. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08505.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood N. D., Pluck A., Gurdon J. B. Xenopus Myf-5 marks early muscle cells and can activate muscle genes ectopically in early embryos. Development. 1991 Feb;111(2):551–560. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.2.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. J., Hunt T. Preparation and use of nuclease-treated rabbit reticulocyte lysates for the translation of eukaryotic messenger RNA. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:50–74. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javaux F., Donda A., Vassart G., Christophe D. Cloning and sequence analysis of TFE, a helix-loop-helix transcription factor able to recognize the thyroglobulin gene promoter in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 11;19(5):1121–1127. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.5.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Roberts B. L., Richardson W. D., Smith A. E. A short amino acid sequence able to specify nuclear location. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):499–509. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90457-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Murre C., Sun X. H., Baltimore D. A new homeobox gene contributes the DNA binding domain of the t(1;19) translocation protein in pre-B ALL. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):547–555. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90658-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kintner C. R., Brockes J. P. Monoclonal antibodies identify blastemal cells derived from dedifferentiating limb regeneration. Nature. 1984 Mar 1;308(5954):67–69. doi: 10.1038/308067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kintner C. R., Melton D. A. Expression of Xenopus N-CAM RNA in ectoderm is an early response to neural induction. Development. 1987 Mar;99(3):311–325. doi: 10.1242/dev.99.3.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Melton D. A. Functional messenger RNAs are produced by SP6 in vitro transcription of cloned cDNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7057–7070. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Melton D. A. In vitro RNA synthesis with SP6 RNA polymerase. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:397–415. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55027-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Varnum S. M., Wormington W. M., Melton D. A. The mRNA encoding elongation factor 1-alpha (EF-1 alpha) is a major transcript at the midblastula transition in Xenopus. Dev Biol. 1989 May;133(1):93–100. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90300-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Buskin J. N., Lockshon D., Davis R. L., Apone S., Hauschka S. D., Weintraub H. MyoD is a sequence-specific DNA binding protein requiring a region of myc homology to bind to the muscle creatine kinase enhancer. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):823–831. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90935-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Davis R. L., Wright W. E., Kadesch T., Murre C., Voronova A., Baltimore D., Weintraub H. Functional activity of myogenic HLH proteins requires hetero-oligomerization with E12/E47-like proteins in vivo. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):305–315. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90620-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H., Yutzey K. E., Konieczny S. F. Muscle-specific expression of the troponin I gene requires interactions between helix-loop-helix muscle regulatory factors and ubiquitous transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):267–280. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon A. P., Moon R. T. Ectopic expression of the proto-oncogene int-1 in Xenopus embryos leads to duplication of the embryonic axis. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1075–1084. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90506-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M., Park M. K., Hanover J. A. Nuclear pore complex: structure, function, and regulation. Physiol Rev. 1991 Jul;71(3):909–949. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1991.71.3.909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohun T. J., Brennan S., Dathan N., Fairman S., Gurdon J. B. Cell type-specific activation of actin genes in the early amphibian embryo. Nature. 1984 Oct 25;311(5988):716–721. doi: 10.1038/311716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohun T. J., Garrett N., Gurdon J. B. Upstream sequences required for tissue-specific activation of the cardiac actin gene in Xenopus laevis embryos. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3185–3193. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04628.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohun T. J., Taylor M. V., Garrett N., Gurdon J. B. The CArG promoter sequence is necessary for muscle-specific transcription of the cardiac actin gene in Xenopus embryos. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1153–1161. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03486.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Vaessin H., Caudy M., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N., Cabrera C. V., Buskin J. N., Hauschka S. D., Lassar A. B. Interactions between heterologous helix-loop-helix proteins generate complexes that bind specifically to a common DNA sequence. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90434-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., Voronova A., Baltimore D. B-cell- and myocyte-specific E2-box-binding factors contain E12/E47-like subunits. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):1156–1160. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.1156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson C., Shen L. P., Meister A., Fodor E., Rutter W. J. Pan: a transcriptional regulator that binds chymotrypsin, insulin, and AP-4 enhancer motifs. Genes Dev. 1990 Jun;4(6):1035–1043. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.6.1035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piette J., Bessereau J. L., Huchet M., Changeux J. P. Two adjacent MyoD1-binding sites regulate expression of the acetylcholine receptor alpha-subunit gene. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):353–355. doi: 10.1038/345353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J., Dilworth S. M., Laskey R. A., Dingwall C. Two interdependent basic domains in nucleoplasmin nuclear targeting sequence: identification of a class of bipartite nuclear targeting sequence. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):615–623. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90245-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sartorelli V., Webster K. A., Kedes L. Muscle-specific expression of the cardiac alpha-actin gene requires MyoD1, CArG-box binding factor, and Sp1. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1811–1822. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyu A. B., Belasco J. G., Greenberg M. E. Two distinct destabilizing elements in the c-fos message trigger deadenylation as a first step in rapid mRNA decay. Genes Dev. 1991 Feb;5(2):221–231. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.2.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyu A. B., Greenberg M. E., Belasco J. G. The c-fos transcript is targeted for rapid decay by two distinct mRNA degradation pathways. Genes Dev. 1989 Jan;3(1):60–72. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.1.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. H., Baltimore D. An inhibitory domain of E12 transcription factor prevents DNA binding in E12 homodimers but not in E12 heterodimers. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):459–470. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90653-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapscott S. J., Davis R. L., Thayer M. J., Cheng P. F., Weintraub H., Lassar A. B. MyoD1: a nuclear phosphoprotein requiring a Myc homology region to convert fibroblasts to myoblasts. Science. 1988 Oct 21;242(4877):405–411. doi: 10.1126/science.3175662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
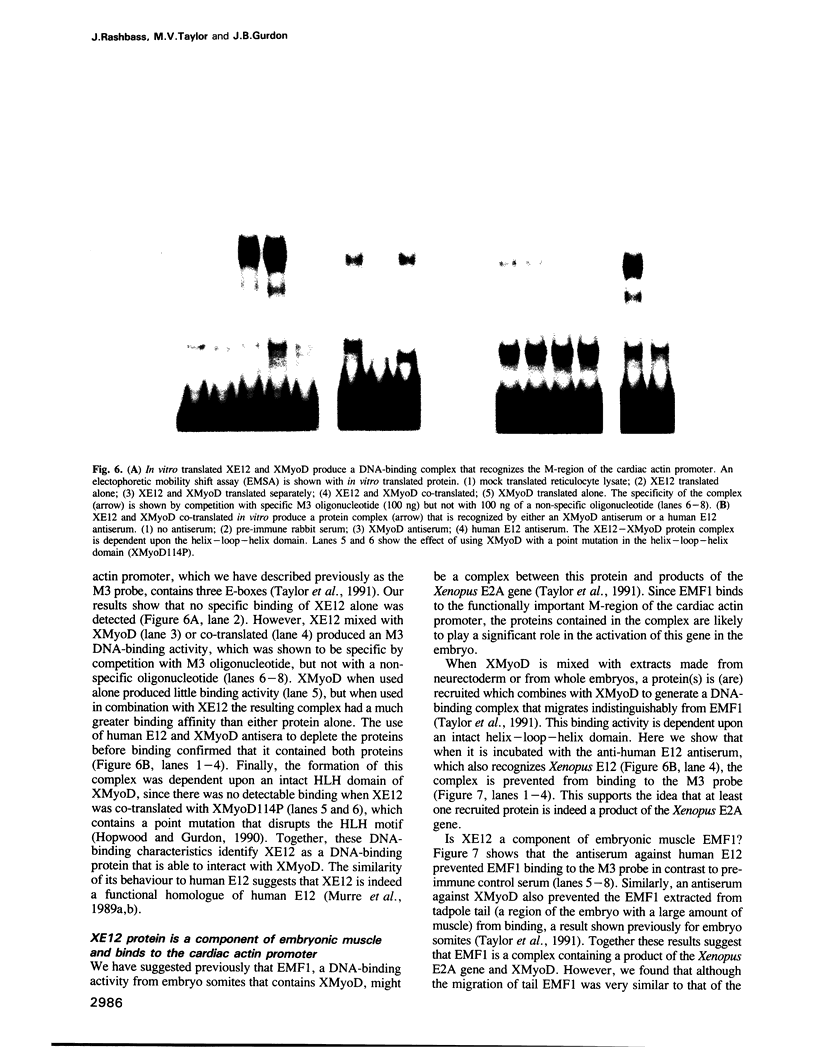
- Taylor M. V., Gurdon J. B., Hopwood N. D., Towers N., Mohun T. J. Xenopus embryos contain a somite-specific, MyoD-like protein that binds to a promoter site required for muscle actin expression. Genes Dev. 1991 Jul;5(7):1149–1160. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.7.1149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Davis R., Tapscott S., Thayer M., Krause M., Benezra R., Blackwell T. K., Turner D., Rupp R., Hollenberg S. The myoD gene family: nodal point during specification of the muscle cell lineage. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):761–766. doi: 10.1126/science.1846704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wentworth B. M., Donoghue M., Engert J. C., Berglund E. B., Rosenthal N. Paired MyoD-binding sites regulate myosin light chain gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1242–1246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]