Abstract
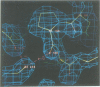
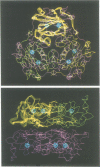
The X-ray structure of a point mutant of nucleoside diphosphate kinase (NDP kinase) from Dictyostelium discoideum has been determined to 2.2 A resolution. The enzyme is a hexamer made of identical subunits with a novel mononucleotide binding fold. Each subunit contains an alpha/beta domain with a four stranded, antiparallel beta-sheet. The topology is different from adenylate kinase, but identical to the allosteric domain of Escherichia coli ATCase regulatory subunits, which bind mononucleotides at an equivalent position. Dimer contacts between NDP kinase subunits within the hexamer are similar to those in ATCase. Trimer contacts involve a large loop of polypeptide chain that bears the site of the Pro----Ser substitution in Killer of prune (K-pn) mutants of the highly homologous Drosophila enzyme. Properties of Drosophila NDP kinase, the product of the awd developmental gene, and of the human enzyme, the product of the nm23 genes in tumorigenesis, are discussed in view of the three-dimensional structure and of possible interactions of NDP kinase with other nucleotide binding proteins.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biggs J., Hersperger E., Steeg P. S., Liotta L. A., Shearn A. A Drosophila gene that is homologous to a mammalian gene associated with tumor metastasis codes for a nucleoside diphosphate kinase. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):933–940. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90496-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brünger A. T., Kuriyan J., Karplus M. Crystallographic R factor refinement by molecular dynamics. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):458–460. doi: 10.1126/science.235.4787.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chothia C., Lesk A. M. The relation between the divergence of sequence and structure in proteins. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):823–826. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04288.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen B. I., Presnell S. R., Cohen F. E. Pattern-based approaches to protein structure prediction. Methods Enzymol. 1991;202:252–268. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)02015-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coll M., Guasch A., Avilés F. X., Huber R. Three-dimensional structure of porcine procarboxypeptidase B: a structural basis of its inactivity. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):1–9. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07914.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dearolf C. R., Tripoulas N., Biggs J., Shearn A. Molecular consequences of awdb3, a cell-autonomous lethal mutation of Drosophila induced by hybrid dysgenesis. Dev Biol. 1988 Sep;129(1):169–178. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90171-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumas C., Lebras G., Wallet V., Lacombe M. L., Véron M., Janin J. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction studies of nucleoside diphosphate kinase from Dictyostelium discoideum. J Mol Biol. 1991 Jan 20;217(2):239–240. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90537-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis B., Overmeyer J., John W., Marshall E., Haley B. Prevalence of nucleoside diphosphate kinase autophosphorylation in human colon carcinoma versus normal colon homogenates. Mol Carcinog. 1989;2(3):168–178. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940020310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friguet B., Chaffotte A. F., Djavadi-Ohaniance L., Goldberg M. E. Measurements of the true affinity constant in solution of antigen-antibody complexes by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Mar 18;77(2):305–319. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90044-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilles A. M., Presecan E., Vonica A., Lascu I. Nucleoside diphosphate kinase from human erythrocytes. Structural characterization of the two polypeptide chains responsible for heterogeneity of the hexameric enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):8784–8789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouaux J. E., Stevens R. C., Lipscomb W. N. Crystal structures of aspartate carbamoyltransferase ligated with phosphonoacetamide, malonate, and CTP or ATP at 2.8-A resolution and neutral pH. Biochemistry. 1990 Aug 21;29(33):7702–7715. doi: 10.1021/bi00485a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hailat N., Keim D. R., Melhem R. F., Zhu X. X., Eckerskorn C., Brodeur G. M., Reynolds C. P., Seeger R. C., Lottspeich F., Strahler J. R. High levels of p19/nm23 protein in neuroblastoma are associated with advanced stage disease and with N-myc gene amplification. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jul;88(1):341–345. doi: 10.1172/JCI115299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson W. A. Stereochemically restrained refinement of macromolecular structures. Methods Enzymol. 1985;115:252–270. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)15021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy C., Henry J. A., May F. E., Westley B. R., Angus B., Lennard T. W. Expression of the antimetastatic gene nm23 in human breast cancer: an association with good prognosis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1991 Feb 20;83(4):281–285. doi: 10.1093/jnci/83.4.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiratsuka T., Uchida K. Preparation and properties of 2'(or 3')-O-(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl) adenosine 5'-triphosphate, an analog of adenosine triphosphate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Oct 5;320(3):635–647. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90143-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. A., Thirup S. Using known substructures in protein model building and crystallography. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):819–822. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04287.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantrowitz E. R., Lipscomb W. N. Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamylase: the relation between structure and function. Science. 1988 Aug 5;241(4866):669–674. doi: 10.1126/science.3041592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keim D., Hailat N., Melhem R., Zhu X. X., Lascu I., Veron M., Strahler J., Hanash S. M. Proliferation-related expression of p19/nm23 nucleoside diphosphate kinase. J Clin Invest. 1992 Mar;89(3):919–924. doi: 10.1172/JCI115672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura N., Shimada N. Evidence for complex formation between GTP binding protein(Gs) and membrane-associated nucleoside diphosphate kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Apr 16;168(1):99–106. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91680-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacombe M. L., Jakobs K. H. Nucleoside diphosphate kinases as potential new targets for control of development and cancer. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Feb;13(2):46–48. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacombe M. L., Sastre-Garau X., Lascu I., Vonica A., Wallet V., Thiery J. P., Véron M. Overexpression of nucleoside diphosphate kinase (Nm23) in solid tumours. Eur J Cancer. 1991;27(10):1302–1307. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(91)90101-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacombe M. L., Wallet V., Troll H., Véron M. Functional cloning of a nucleoside diphosphate kinase from Dictyostelium discoideum. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):10012–10018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leone A., Flatow U., King C. R., Sandeen M. A., Margulies I. M., Liotta L. A., Steeg P. S. Reduced tumor incidence, metastatic potential, and cytokine responsiveness of nm23-transfected melanoma cells. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90404-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai K., Oubridge C., Jessen T. H., Li J., Evans P. R. Crystal structure of the RNA-binding domain of the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein A. Nature. 1990 Dec 6;348(6301):515–520. doi: 10.1038/348515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orevi N., Falk R. Temperature-sensitive prune (pn) mutations of Drosophila melanogaster. Mutat Res. 1975 Dec;33(2-3):193–200. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(75)90195-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastore A., Saudek V., Ramponi G., Williams R. J. Three-dimensional structure of acylphosphatase. Refinement and structure analysis. J Mol Biol. 1992 Mar 20;224(2):427–440. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)91005-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. B., Jr, Brems D. N., Stellwagen E. A monoisozymic nucleoside diphosphate kinase capable of complete phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):10769–10773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosengard A. M., Krutzsch H. C., Shearn A., Biggs J. R., Barker E., Margulies I. M., King C. R., Liotta L. A., Steeg P. S. Reduced Nm23/Awd protein in tumour metastasis and aberrant Drosophila development. Nature. 1989 Nov 9;342(6246):177–180. doi: 10.1038/342177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sastre-Garau X., Lacombe M. L., Jouve M., Véron M., Magdelénat H. Nucleoside diphosphate kinase/NM23 expression in breast cancer: lack of correlation with lymph-node metastasis. Int J Cancer. 1992 Feb 20;50(4):533–538. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910500406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz G. E., Schiltz E., Tomasselli A. G., Frank R., Brune M., Wittinghofer A., Schirmer R. H. Structural relationships in the adenylate kinase family. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Nov 17;161(1):127–132. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10132.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl J. A., Leone A., Rosengard A. M., Porter L., King C. R., Steeg P. S. Identification of a second human nm23 gene, nm23-H2. Cancer Res. 1991 Jan 1;51(1):445–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steeg P. S., Bevilacqua G., Kopper L., Thorgeirsson U. P., Talmadge J. E., Liotta L. A., Sobel M. E. Evidence for a novel gene associated with low tumor metastatic potential. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1988 Apr 6;80(3):200–204. doi: 10.1093/jnci/80.3.200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturtevant A H. A Highly Specific Complementary Lethal System in Drosophila Melanogaster. Genetics. 1956 Jan;41(1):118–123. doi: 10.1093/genetics/41.1.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teng D. H., Engele C. M., Venkatesh T. R. A product of the prune locus of Drosophila is similar to mammalian GTPase-activating protein. Nature. 1991 Oct 3;353(6343):437–440. doi: 10.1038/353437a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallet V., Mutzel R., Troll H., Barzu O., Wurster B., Veron M., Lacombe M. L. Dictyostelium nucleoside diphosphate kinase highly homologous to Nm23 and Awd proteins involved in mammalian tumor metastasis and Drosophila development. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990 Jul 18;82(14):1199–1202. doi: 10.1093/jnci/82.14.1199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang B. C. Resolution of phase ambiguity in macromolecular crystallography. Methods Enzymol. 1985;115:90–112. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)15009-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieland T., Bremerich J., Gierschik P., Jakobs K. H. Contribution of nucleoside diphosphokinase to guanine nucleotide regulation of agonist binding to formyl peptide receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Sep 12;208(1):17–23. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(91)90046-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]