Abstract
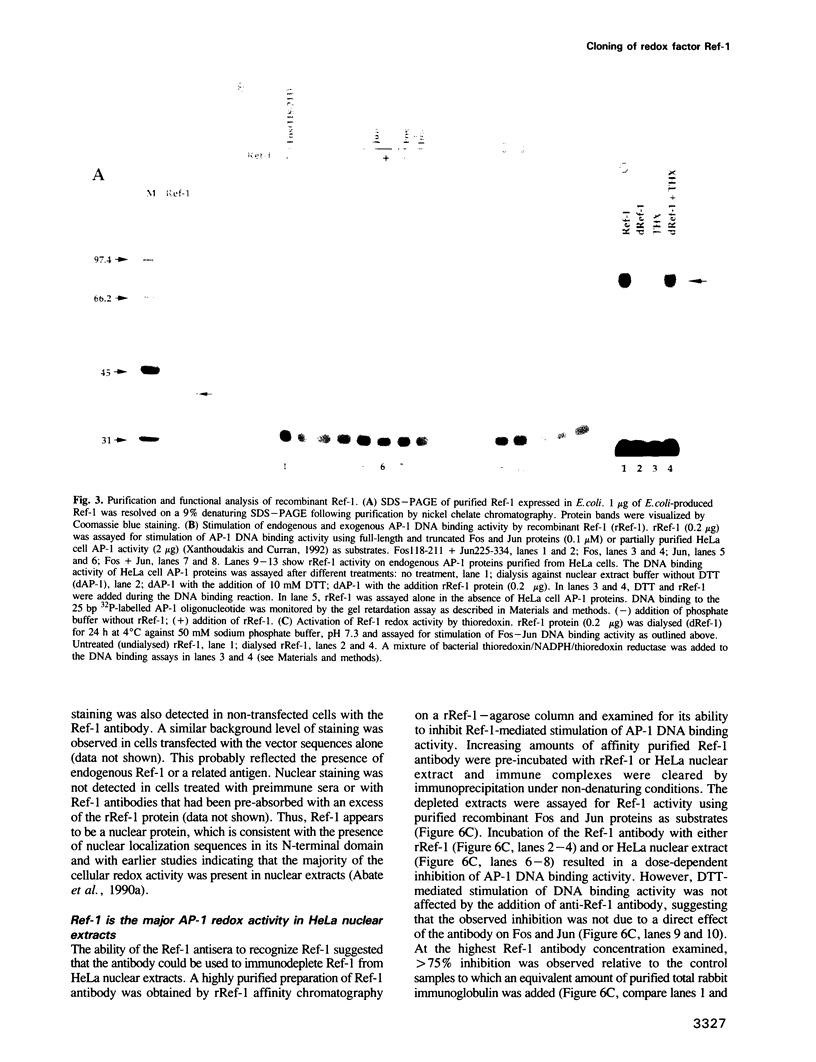
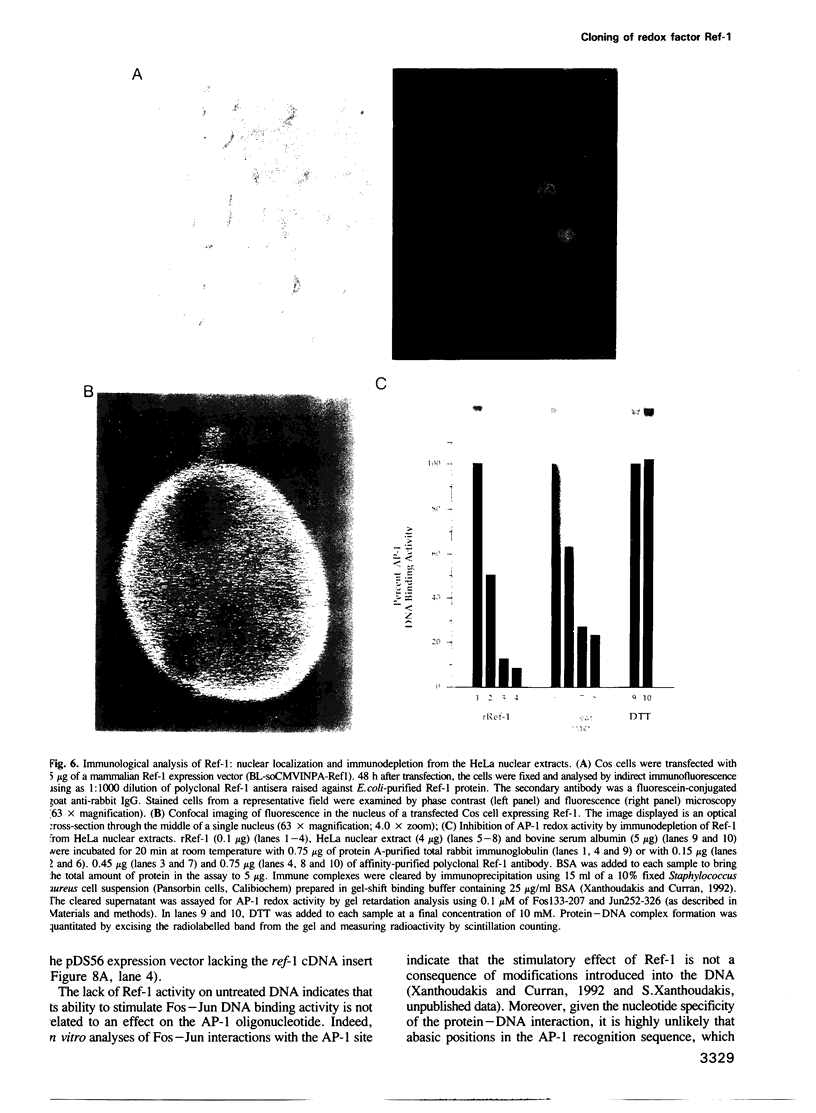
The DNA binding activity of Fos and Jun is regulated in vitro by a post-translational mechanism involving reduction-oxidation. Redox regulation occurs through a conserved cysteine residue located in the DNA binding domain of Fos and Jun. Reduction of this residue by chemical reducing agents or by a ubiquitous nuclear redox factor (Ref-1) recently purified from Hela cells, stimulates AP-1 DNA binding activity in vitro, whereas oxidation or chemical modification of the cysteine has an inhibitory effect on DNA binding activity. Here we demonstrate that the protein product of the ref-1 gene stimulates the DNA binding activity of Fos-Jun heterodimers, Jun-Jun homodimers and Hela cell AP-1 proteins as well as that of several other transcription factors including NF-kappa B, Myb and members of the ATF/CREB family. Furthermore, immunodepletion analysis indicates that Ref-1 is the major AP-1 redox activity in Hela nuclear extracts. Interestingly, Ref-1 is a bifunctional protein; it also possesses an apurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) endonuclease DNA repair activity. However, the redox and DNA repair activities of Ref-1 can, in part, be distinguished biochemically. This study suggests a novel link between transcription factor regulation, oxidative signalling and DNA repair processes in higher eukaryotes.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abate C., Curran T. Encounters with Fos and Jun on the road to AP-1. Semin Cancer Biol. 1990 Feb;1(1):19–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abate C., Luk D., Curran T. A ubiquitous nuclear protein stimulates the DNA-binding activity of fos and jun indirectly. Cell Growth Differ. 1990 Oct;1(10):455–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abate C., Luk D., Gentz R., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Curran T. Expression and purification of the leucine zipper and DNA-binding domains of Fos and Jun: both Fos and Jun contact DNA directly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1032–1036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abate C., Patel L., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Curran T. Redox regulation of fos and jun DNA-binding activity in vitro. Science. 1990 Sep 7;249(4973):1157–1161. doi: 10.1126/science.2118682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Hattori K., Smeal T., Karin M. The jun proto-oncogene is positively autoregulated by its product, Jun/AP-1. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):875–885. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90143-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber J. R., Verma I. M. Modification of fos proteins: phosphorylation of c-fos, but not v-fos, is stimulated by 12-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate and serum. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2201–2211. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benbrook D. M., Jones N. C. Heterodimer formation between CREB and JUN proteins. Oncogene. 1990 Mar;5(3):295–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos T. J., Monteclaro F. S., Mitsunobu F., Ball A. R., Jr, Chang C. H., Nishimura T., Vogt P. K. Efficient transformation of chicken embryo fibroblasts by c-Jun requires structural modification in coding and noncoding sequences. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1677–1687. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., Smeal T., Defize L. H., Angel P., Woodgett J. R., Karin M., Hunter T. Activation of protein kinase C decreases phosphorylation of c-Jun at sites that negatively regulate its DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):573–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90241-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr M. D., Mott R. F. The transcriptional control proteins c-Myb and v-Myb contain a basic region DNA binding motif. FEBS Lett. 1991 May 6;282(2):293–294. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80498-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerutti P. A. Prooxidant states and tumor promotion. Science. 1985 Jan 25;227(4685):375–381. doi: 10.1126/science.2981433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen T. A., Allfrey V. G. Rapid and reversible changes in nucleosome structure accompany the activation, repression, and superinduction of murine fibroblast protooncogenes c-fos and c-myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5252–5256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu R., Angel P., Karin M. Jun-B differs in its biological properties from, and is a negative regulator of, c-Jun. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):979–986. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90754-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu R., Imagawa M., Imbra R. J., Bockoven J. R., Karin M. Multiple cis- and trans-acting elements mediate the transcriptional response to phorbol esters. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):648–651. doi: 10.1038/329648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D. R., Curran T. fra-1: a serum-inducible, cellular immediate-early gene that encodes a fos-related antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2063–2069. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D. R., Ferreira P. C., Gentz R., Franza B. R., Jr, Curran T. The product of a fos-related gene, fra-1, binds cooperatively to the AP-1 site with Jun: transcription factor AP-1 is comprised of multiple protein complexes. Genes Dev. 1989 Feb;3(2):173–184. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.2.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cromlish J. A., Roeder R. G. Human transcription factor IIIC (TFIIIC). Purification, polypeptide structure, and the involvement of thiol groups in specific DNA binding. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):18100–18109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossin K. L. Nitric oxide (NO): a versatile second messenger in brain. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Mar;16(3):81–82. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90036-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham R. P., Saporito S. M., Spitzer S. G., Weiss B. Endonuclease IV (nfo) mutant of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1120–1127. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1120-1127.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Franza B. R., Jr Fos and Jun: the AP-1 connection. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):395–397. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Miller A. D., Zokas L., Verma I. M. Viral and cellular fos proteins: a comparative analysis. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90219-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Miller A. D., Zokas L., Verma I. M. Viral and cellular fos proteins: a comparative analysis. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90219-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Morgan J. I. Superinduction of c-fos by nerve growth factor in the presence of peripherally active benzodiazepines. Science. 1985 Sep 20;229(4719):1265–1268. doi: 10.1126/science.4035354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Van Beveren C., Verma I. M. Viral and cellular fos proteins are complexed with a 39,000-dalton cellular protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):167–172. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deiss L. P., Kimchi A. A genetic tool used to identify thioredoxin as a mediator of a growth inhibitory signal. Science. 1991 Apr 5;252(5002):117–120. doi: 10.1126/science.1901424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demple B., Amábile-Cuevas C. F. Redox redux: the control of oxidative stress responses. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):837–839. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90355-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demple B., Herman T., Chen D. S. Cloning and expression of APE, the cDNA encoding the major human apurinic endonuclease: definition of a family of DNA repair enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11450–11454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devary Y., Gottlieb R. A., Lau L. F., Karin M. Rapid and preferential activation of the c-jun gene during the mammalian UV response. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2804–2811. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillon P. J., Nelbock P., Perkins A., Rosen C. A. Structural and functional analysis of the human immunodeficiency virus type 2 Rev protein. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):445–449. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.445-449.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einck L., Bustin M. The intracellular distribution and function of the high mobility group chromosomal proteins. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Feb;156(2):295–310. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90539-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrest D., Curran T. Crossed signals: oncogenic transcription factors. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1992 Feb;2(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80316-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franza B. R., Jr, Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Josephs S. F., Curran T. The Fos complex and Fos-related antigens recognize sequence elements that contain AP-1 binding sites. Science. 1988 Mar 4;239(4844):1150–1153. doi: 10.1126/science.2964084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartenberg M. R., Ampe C., Steitz T. A., Crothers D. M. Molecular characterization of the GCN4-DNA complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6034–6038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentz R., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Abate C., Curran T. Parallel association of Fos and Jun leucine zippers juxtaposes DNA binding domains. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1695–1699. doi: 10.1126/science.2494702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gius D., Cao X. M., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Cohen D. R., Curran T., Sukhatme V. P. Transcriptional activation and repression by Fos are independent functions: the C terminus represses immediate-early gene expression via CArG elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4243–4255. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg J. T., Monach P., Chou J. H., Josephy P. D., Demple B. Positive control of a global antioxidant defense regulon activated by superoxide-generating agents in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6181–6185. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grippo J. F., Holmgren A., Pratt W. B. Proof that the endogenous, heat-stable glucocorticoid receptor-activating factor is thioredoxin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):93–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Chua A. O., Schoenhaut D. S., Dwyer C. M., McComas W., Motyka R., Nabavi N., Wolitzky A. G., Quinn P. M., Familletti P. C. Coexpression of two distinct genes is required to generate secreted bioactive cytotoxic lymphocyte maturation factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4143–4147. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T., Curran T. Cross-family dimerization of transcription factors Fos/Jun and ATF/CREB alters DNA binding specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3720–3724. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halazonetis T. D., Georgopoulos K., Greenberg M. E., Leder P. c-Jun dimerizes with itself and with c-Fos, forming complexes of different DNA binding affinities. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):917–924. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90147-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell B., Gutteridge J. M. Role of free radicals and catalytic metal ions in human disease: an overview. Methods Enzymol. 1990;186:1–85. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)86093-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentze M. W., Rouault T. A., Harford J. B., Klausner R. D. Oxidation-reduction and the molecular mechanism of a regulatory RNA-protein interaction. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):357–359. doi: 10.1126/science.2711187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewick R. M., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Dreyer W. J. A gas-liquid solid phase peptide and protein sequenator. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7990–7997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai S. I., Ryseck R. P., Mechta F., Bravo R., Yaniv M. Characterization of junD: a new member of the jun proto-oncogene family. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1433–1439. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03525.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook N. J., Fornace A. J., Jr Response to adversity: molecular control of gene activation following genotoxic stress. New Biol. 1991 Sep;3(9):825–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren A. Enzymatic reduction-oxidation of protein disulfides by thioredoxin. Methods Enzymol. 1984;107:295–300. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(84)07019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren A. Thioredoxin and glutaredoxin systems. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):13963–13966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren A. Thioredoxin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:237–271. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.001321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. Cooperation between oncogenes. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):249–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90637-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda S., Seki S., Watanabe S., Hatsushika M., Tsutsui K. Detection of possible DNA repair enzymes on sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels by protein blotting to damaged DNA-fixed membranes. Anal Biochem. 1991 Jan;192(1):96–103. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90191-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane C. M., Linn S. Purification and characterization of an apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease from HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3405–3414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Harford J. B. cis-trans models for post-transcriptional gene regulation. Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):870–872. doi: 10.1126/science.2683086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouzarides T., Ziff E. The role of the leucine zipper in the fos-jun interaction. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):646–651. doi: 10.1038/336646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. M., Lin C., Curran T. Activation of the transforming potential of the human fos proto-oncogene requires message stabilization and results in increased amounts of partially modified fos protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5521–5527. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin J. D., Demple B. Analysis of class II (hydrolytic) and class I (beta-lyase) apurinic/apyrimidinic endonucleases with a synthetic DNA substrate. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5069–5075. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. E., Kessler D. S., Pine R., Darnell J. E., Jr Cytoplasmic activation of ISGF3, the positive regulator of interferon-alpha-stimulated transcription, reconstituted in vitro. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1362–1371. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macgregor P. F., Abate C., Curran T. Direct cloning of leucine zipper proteins: Jun binds cooperatively to the CRE with CRE-BP1. Oncogene. 1990 Apr;5(4):451–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maki Y., Bos T. J., Davis C., Starbuck M., Vogt P. K. Avian sarcoma virus 17 carries the jun oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2848–2852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui M., Tokuhara M., Konuma Y., Nomura N., Ishizaki R. Isolation of human fos-related genes and their expression during monocyte-macrophage differentiation. Oncogene. 1990 Mar;5(3):249–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister A., Anderson M. E. Glutathione. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:711–760. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.003431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer-Siegler K., Mauro D. J., Seal G., Wurzer J., deRiel J. K., Sirover M. A. A human nuclear uracil DNA glycosylase is the 37-kDa subunit of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8460–8464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. I., Curran T. Stimulus-transcription coupling in the nervous system: involvement of the inducible proto-oncogenes fos and jun. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1991;14:421–451. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.14.030191.002225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mroczkowski B., Mosig G., Cohen S. ATP-stimulated interaction between epidermal growth factor receptor and supercoiled DNA. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):270–273. doi: 10.1038/309270a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami Y., Satake M., Yamaguchi-Iwai Y., Sakai M., Muramatsu M., Ito Y. The nuclear protooncogenes c-jun and c-fos as regulators of DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3947–3951. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Bravo R., Müller D., Kurz C., Renz M. Different types of modification in c-fos and its associated protein p39: modulation of DNA binding by phosphorylation. Oncogene Res. 1987;2(1):19–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabeppu Y., Nathans D. A naturally occurring truncated form of FosB that inhibits Fos/Jun transcriptional activity. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):751–759. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90504-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabeppu Y., Ryder K., Nathans D. DNA binding activities of three murine Jun proteins: stimulation by Fos. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):907–915. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90146-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishina H., Sato H., Suzuki T., Sato M., Iba H. Isolation and characterization of fra-2, an additional member of the fos gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3619–3623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizawa M., Goto N., Kawai S. An avian transforming retrovirus isolated from a nephroblastoma that carries the fos gene as the oncogene. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3733–3740. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3733-3740.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea E. K., Rutkowski R., Kim P. S. Evidence that the leucine zipper is a coiled coil. Science. 1989 Jan 27;243(4890):538–542. doi: 10.1126/science.2911757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofir R., Dwarki V. J., Rashid D., Verma I. M. Phosphorylation of the C terminus of Fos protein is required for transcriptional transrepression of the c-fos promoter. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):80–82. doi: 10.1038/348080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuno H., Suzuki T., Yoshida T., Hashimoto Y., Curran T., Iba H. Inhibition of jun transformation by a mutated fos gene: design of an anti-oncogene. Oncogene. 1991 Sep;6(9):1491–1497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel L., Abate C., Curran T. Altered protein conformation on DNA binding by Fos and Jun. Nature. 1990 Oct 11;347(6293):572–575. doi: 10.1038/347572a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peleg S., Schrader W. T., O'Malley B. W. Differential sensitivity of chicken progesterone receptor forms to sulfhydryl reactive reagents. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 5;28(18):7373–7379. doi: 10.1021/bi00444a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins K. K., Admon A., Patel N., Tjian R. The Drosophila Fos-related AP-1 protein is a developmentally regulated transcription factor. Genes Dev. 1990 May;4(5):822–834. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.5.822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulverer B. J., Kyriakis J. M., Avruch J., Nikolakaki E., Woodgett J. R. Phosphorylation of c-jun mediated by MAP kinases. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):670–674. doi: 10.1038/353670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puyet A., Greenberg B., Lacks S. A. The exoA gene of Streptococcus pneumoniae and its product, a DNA exonuclease with apurinic endonuclease activity. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2278–2286. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2278-2286.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Voulalas P. J., Franza B. R., Jr, Curran T. Fos and Jun bind cooperatively to the AP-1 site: reconstitution in vitro. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1687–1699. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts B. Nuclear location signal-mediated protein transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Aug 14;1008(3):263–280. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(89)90016-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson C. N., Hickson I. D. Isolation of cDNA clones encoding a human apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease that corrects DNA repair and mutagenesis defects in E. coli xth (exonuclease III) mutants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5519–5523. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson C. N., Milne A. M., Pappin D. J., Hickson I. D. Isolation of cDNA clones encoding an enzyme from bovine cells that repairs oxidative DNA damage in vitro: homology with bacterial repair enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 11;19(5):1087–1092. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.5.1087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben S. M., Dillon P. J., Schreck R., Henkel T., Chen C. H., Maher M., Baeuerle P. A., Rosen C. A. Isolation of a rel-related human cDNA that potentially encodes the 65-kD subunit of NF-kappa B. Science. 1991 Mar 22;251(5000):1490–1493. doi: 10.1126/science.2006423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruppersberg J. P., Stocker M., Pongs O., Heinemann S. H., Frank R., Koenen M. Regulation of fast inactivation of cloned mammalian IK(A) channels by cysteine oxidation. Nature. 1991 Aug 22;352(6337):711–714. doi: 10.1038/352711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder K., Lanahan A., Perez-Albuerne E., Nathans D. jun-D: a third member of the jun gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1500–1503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryseck R. P., Bravo R. c-JUN, JUN B, and JUN D differ in their binding affinities to AP-1 and CRE consensus sequences: effect of FOS proteins. Oncogene. 1991 Apr;6(4):533–542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüther U., Garber C., Komitowski D., Müller R., Wagner E. F. Deregulated c-fos expression interferes with normal bone development in transgenic mice. 1987 Jan 29-Feb 4Nature. 325(6103):412–416. doi: 10.1038/325412a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüther U., Komitowski D., Schubert F. R., Wagner E. F. c-fos expression induces bone tumors in transgenic mice. Oncogene. 1989 Jul;4(7):861–865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saikumar P., Murali R., Reddy E. P. Role of tryptophan repeats and flanking amino acids in Myb-DNA interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8452–8456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sander M., Lowenhaupt K., Lane W. S., Rich A. Cloning and characterization of Rrp1, the gene encoding Drosophila strand transferase: carboxy-terminal homology to DNA repair endo/exonucleases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 25;19(16):4523–4529. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.16.4523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saporito S. M., Smith-White B. J., Cunningham R. P. Nucleotide sequence of the xth gene of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4542–4547. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4542-4547.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreck R., Rieber P., Baeuerle P. A. Reactive oxygen intermediates as apparently widely used messengers in the activation of the NF-kappa B transcription factor and HIV-1. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2247–2258. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07761.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuermann M., Neuberg M., Hunter J. B., Jenuwein T., Ryseck R. P., Bravo R., Müller R. The leucine repeat motif in Fos protein mediates complex formation with Jun/AP-1 and is required for transformation. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):507–516. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90253-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schütte J., Viallet J., Nau M., Segal S., Fedorko J., Minna J. jun-B inhibits and c-fos stimulates the transforming and trans-activating activities of c-jun. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):987–997. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90755-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva C. M., Cidlowski J. A. Direct evidence for intra- and intermolecular disulfide bond formation in the human glucocorticoid receptor. Inhibition of DNA binding and identification of a new receptor-associated protein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):6638–6647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver P. A. How proteins enter the nucleus. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):489–497. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90233-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeyne R. J., Schilling K., Robertson L., Luk D., Oberdick J., Curran T., Morgan J. I. fos-lacZ transgenic mice: mapping sites of gene induction in the central nervous system. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):13–23. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90105-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein B., Rahmsdorf H. J., Steffen A., Litfin M., Herrlich P. UV-induced DNA damage is an intermediate step in UV-induced expression of human immunodeficiency virus type 1, collagenase, c-fos, and metallothionein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5169–5181. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storz G., Tartaglia L. A., Ames B. N. Transcriptional regulator of oxidative stress-inducible genes: direct activation by oxidation. Science. 1990 Apr 13;248(4952):189–194. doi: 10.1126/science.2183352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki T., Hashimoto Y., Okuno H., Sato H., Nishina H., Iba H. High-level expression of human c-jun gene causes cellular transformation of chicken embryo fibroblasts. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1991 Jan;82(1):58–64. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1991.tb01746.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toledano M. B., Leonard W. J. Modulation of transcription factor NF-kappa B binding activity by oxidation-reduction in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4328–4332. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R., Tjian R. Leucine repeats and an adjacent DNA binding domain mediate the formation of functional cFos-cJun heterodimers. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1689–1694. doi: 10.1126/science.2494701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Beveren C., Enami S., Curran T., Verma I. M. FBR murine osteosarcoma virus. II. Nucleotide sequence of the provirus reveals that the genome contains sequences acquired from two cellular genes. Virology. 1984 May;135(1):229–243. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90133-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Beveren C., van Straaten F., Curran T., Müller R., Verma I. M. Analysis of FBJ-MuSV provirus and c-fos (mouse) gene reveals that viral and cellular fos gene products have different carboxy termini. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1241–1255. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90306-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakasugi N., Tagaya Y., Wakasugi H., Mitsui A., Maeda M., Yodoi J., Tursz T. Adult T-cell leukemia-derived factor/thioredoxin, produced by both human T-lymphotropic virus type I- and Epstein-Barr virus-transformed lymphocytes, acts as an autocrine growth factor and synergizes with interleukin 1 and interleukin 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8282–8286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker G. C. Inducible DNA repair systems. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:425–457. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.002233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J., Chen T. A., Sterner R., Berger M., Winston F., Allfrey V. G. Affinity chromatography of mammalian and yeast nucleosomes. Two modes of binding of transcriptionally active mammalian nucleosomes to organomercurial-agarose columns, and contrasting behavior of the active nucleosomes of yeast. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5736–5746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z. Q., Grigoriadis A. E., Möhle-Steinlein U., Wagner E. F. A novel target cell for c-fos-induced oncogenesis: development of chondrogenic tumours in embryonic stem cell chimeras. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2437–2450. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07783.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk C., Schneikert J., Wasylyk B. Oncogene v-jun modulates DNA replication. Oncogene. 1990 Jul;5(7):1055–1058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K. R., Reddigari S., Patel G. L. Identification of a nucleic acid helix-destabilizing protein from rat liver as lactate dehydrogenase-5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5260–5264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xanthoudakis S., Curran T. Identification and characterization of Ref-1, a nuclear protein that facilitates AP-1 DNA-binding activity. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):653–665. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05097.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerial M., Toschi L., Ryseck R. P., Schuermann M., Müller R., Bravo R. The product of a novel growth factor activated gene, fos B, interacts with JUN proteins enhancing their DNA binding activity. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):805–813. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03441.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]