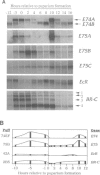
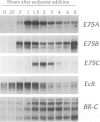
Abstract
In Drosophila, pulses of the steroid hormone ecdysone function as temporal signals that trigger the major postembryonic developmental transitions. The best characterized of these pulses activates a series of puffs in the polytene chromosomes as it triggers metamorphosis. A small set of early puffs is induced as a primary response to the hormone. These puffs encode regulatory proteins that both repress their own expression and activate a large set of late secondary response genes. We have used Northern blot analysis of RNA isolated from staged animals and cultured organs to study the transcription of three primary response regulatory genes, E75, BR-C and EcR. Remarkably, their patterns of transcription in late larvae can be defined in terms of two responses to different ecdysone concentrations. The class I transcripts (E74B and EcR) are induced in mid-third instar larvae in response to the low, but increasing, titer of ecdysone. As the hormone concentration peaks in late third instar larvae, these transcripts are repressed and the class II RNAs (E74A, E75A and E75B) are induced. The BR-C RNAs appear to have both class I and class II characteristics. These data demonstrate that the relatively simple profile of a hormone pulse contains critical temporal information that is transduced into waves of primary response regulatory gene activity.
Full text
PDF

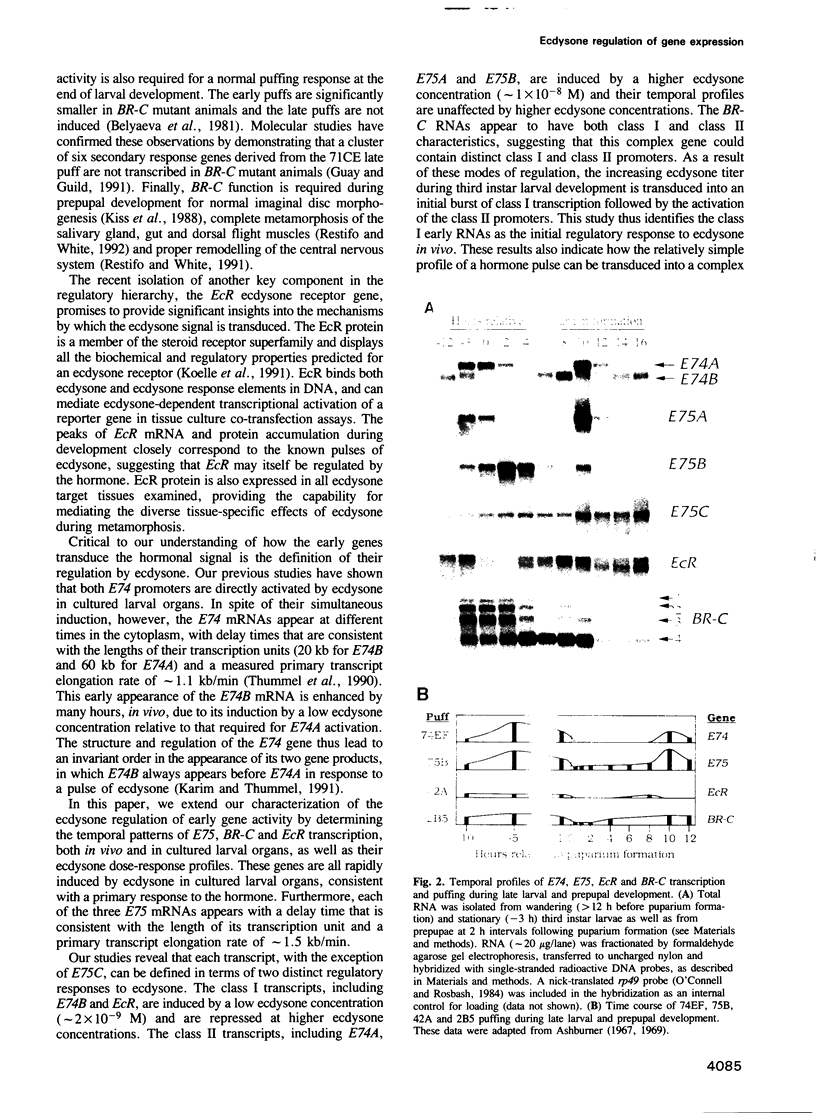


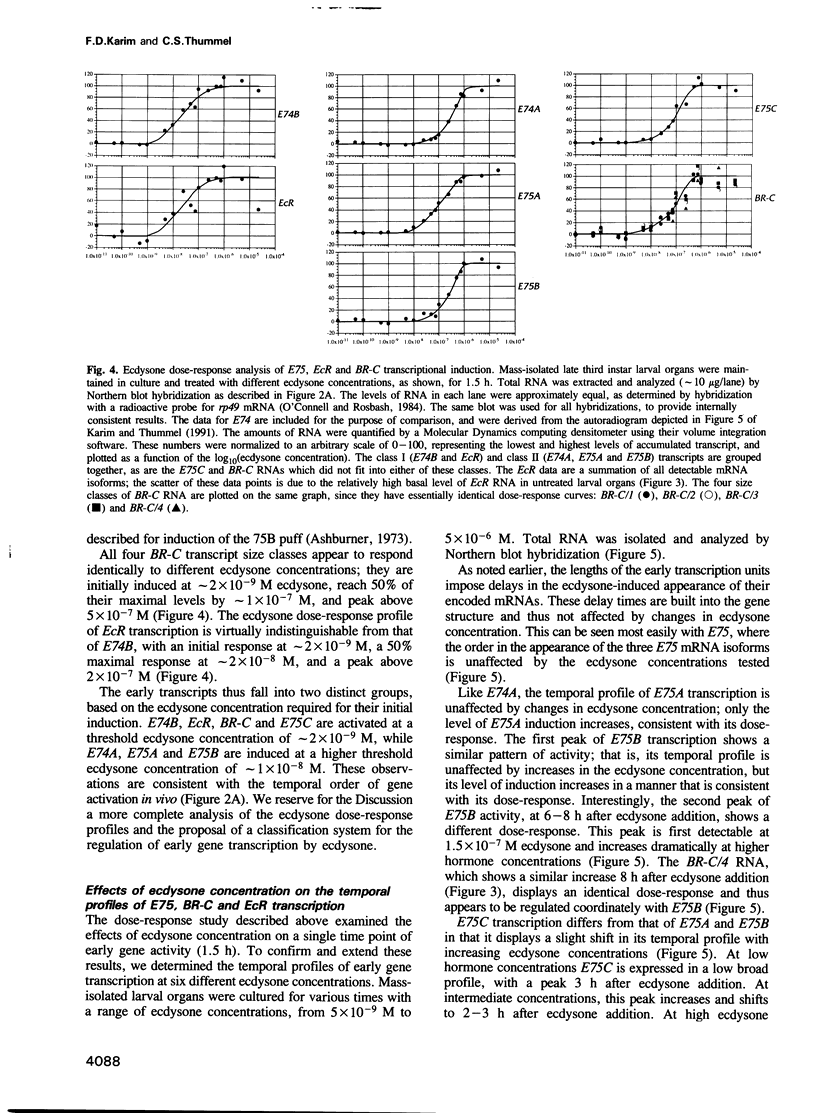




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andres A. J., Thummel C. S. Hormones, puffs and flies: the molecular control of metamorphosis by ecdysone. Trends Genet. 1992 Apr;8(4):132–138. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90371-A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M., Chihara C., Meltzer P., Richards G. Temporal control of puffing activity in polytene chromosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:655–662. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M. Patterns of puffing activity in the salivary gland chromosomes of Drosophila. I. Autosomal puffing patterns in a laboratory stock of Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma. 1967;21(4):398–428. doi: 10.1007/BF00336950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M. Patterns of puffing activity in the salivary gland chromosomes of Drosophila. II. The X-chromosome puffing patterns of D. melanogaster and D. simulans. Chromosoma. 1969;27(1):47–63. doi: 10.1007/BF00326110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M. Patterns of puffing activity in the salivary gland chromosomes of Drosophila. VI. Induction by ecdysone in salivary glands of D. melanogaster cultured in vitro. Chromosoma. 1972;38(3):255–281. doi: 10.1007/BF00290925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M. Puffs, genes, and hormones revisited. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90205-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M. Sequential gene activation by ecdysone in polytene chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. I. Dependence upon ecdysone concentration. Dev Biol. 1973 Nov;35(1):47–61. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(73)90006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M. Sequential gene activation by ecdysone in polytene chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. II. The effects of inhibitors of protein synthesis. Dev Biol. 1974 Jul;39(1):141–157. doi: 10.1016/s0012-1606(74)80016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BECKER H. J. [The puffs of salivary gland chromosomes of Drosophilia melanogaster. Part 1. Observations on the behavior of a typical puff in the normal strain and in two mutants, giant and lethal giant larvae]. Chromosoma. 1959;10:654–678. doi: 10.1007/BF00396591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belyaeva E. S., Vlassova I. E., Biyasheva Z. M., Kakpakov V. T., Richards G., Zhimulev I. F. Cytogenetic analysis of the 2B3-4-2B11 region of the X chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. II. Changes in 20-OH ecdysone puffing caused by genetic defects of puff 2B5. Chromosoma. 1981;84(2):207–219. doi: 10.1007/BF00399132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burtis K. C., Thummel C. S., Jones C. W., Karim F. D., Hogness D. S. The Drosophila 74EF early puff contains E74, a complex ecdysone-inducible gene that encodes two ets-related proteins. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):85–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90217-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLEVER U., KARLSON P. [Induction of puff changes in the salivary gland chromosomes of Chironomus tentans by ecdysone]. Exp Cell Res. 1960 Sep;20:623–626. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(60)90141-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao A. T., Guild G. M. Molecular analysis of the ecdysterone-inducible 2B5 "early' puff in Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1986 Jan;5(1):143–150. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04188.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowley T. E., Mathers P. H., Meyerowitz E. M. A trans-acting regulatory product necessary for expression of the Drosophila melanogaster 68C glue gene cluster. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):149–156. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90200-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiBello P. R., Withers D. A., Bayer C. A., Fristrom J. W., Guild G. M. The Drosophila Broad-Complex encodes a family of related proteins containing zinc fingers. Genetics. 1991 Oct;129(2):385–397. doi: 10.1093/genetics/129.2.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feigl G., Gram M., Pongs O. A member of the steroid hormone receptor gene family is expressed in the 20-OH-ecdysone inducible puff 75B in Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7167–7178. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgel P., Ramain P., Giangrande A., Dretzen G., Richards G., Bellard M. Sgs-3 chromatin structure and trans-activators: developmental and ecdysone induction of a glue enhancer-binding factor, GEBF-I, in Drosophila larvae. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):523–532. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guay P. S., Guild G. M. The ecdysone-induced puffing cascade in Drosophila salivary glands: a Broad-Complex early gene regulates intermolt and late gene transcription. Genetics. 1991 Sep;129(1):169–175. doi: 10.1093/genetics/129.1.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handler A. M. Ecdysteroid titers during pupal and adult development in Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1982 Sep;93(1):73–82. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90240-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson L., Lambertsson A. Steroid regulation of glue protein genes in Drosophila melanogaster. Hereditas. 1989;110(1):61–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1989.tb00418.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgetts R. B., Sage B., O'Connor J. D. Ecdysone titers during postembryonic development of Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1977 Oct 1;60(1):310–317. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90128-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine K. D., Helfand S. L., Hogness D. S. The large upstream control region of the Drosophila homeotic gene Ultrabithorax. Development. 1991 Feb;111(2):407–424. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.2.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janknecht R., Taube W., Lüdecke H. J., Pongs O. Characterization of a putative transcription factor gene expressed in the 20-OH-ecdysone inducible puff 74EF in Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4455–4464. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. W., Dalton M. W., Townley L. H. Interspecific comparisons of the structure and regulation of the Drosophila ecdysone-inducible gene E74. Genetics. 1991 Mar;127(3):535–543. doi: 10.1093/genetics/127.3.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim F. D., Thummel C. S. Ecdysone coordinates the timing and amounts of E74A and E74B transcription in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):1067–1079. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.1067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss I., Beaton A. H., Tardiff J., Fristrom D., Fristrom J. W. Interactions and developmental effects of mutations in the Broad-Complex of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1988 Feb;118(2):247–259. doi: 10.1093/genetics/118.2.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koelle M. R., Talbot W. S., Segraves W. A., Bender M. T., Cherbas P., Hogness D. S. The Drosophila EcR gene encodes an ecdysone receptor, a new member of the steroid receptor superfamily. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):59–77. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90572-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miklos G. L., Cotsell J. N. Chromosome structure at interfaces between major chromatin types: alpha- and beta-heterochromatin. Bioessays. 1990 Jan;12(1):1–6. doi: 10.1002/bies.950120102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell P. O., Rosbash M. Sequence, structure, and codon preference of the Drosophila ribosomal protein 49 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5495–5513. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Restifo L. L., White K. Mutations in a steroid hormone-regulated gene disrupt the metamorphosis of the central nervous system in Drosophila. Dev Biol. 1991 Nov;148(1):174–194. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(91)90328-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards G. The radioimmune assay of ecdysteroid titres in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1981 Mar;21(3):181–197. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(81)90013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segraves W. A., Hogness D. S. The E75 ecdysone-inducible gene responsible for the 75B early puff in Drosophila encodes two new members of the steroid receptor superfamily. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):204–219. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segraves W. A. Something old, some things new: the steroid receptor superfamily in Drosophila. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):225–228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90172-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shermoen A. W., O'Farrell P. H. Progression of the cell cycle through mitosis leads to abortion of nascent transcripts. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):303–310. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90182-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sliter T. J., Gilbert L. I. Developmental arrest and ecdysteroid deficiency resulting from mutations at the dre4 locus of Drosophila. Genetics. 1992 Mar;130(3):555–568. doi: 10.1093/genetics/130.3.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thummel C. S., Burtis K. C., Hogness D. S. Spatial and temporal patterns of E74 transcription during Drosophila development. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):101–111. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90218-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urness L. D., Thummel C. S. Molecular interactions within the ecdysone regulatory hierarchy: DNA binding properties of the Drosophila ecdysone-inducible E74A protein. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):47–61. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90287-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]