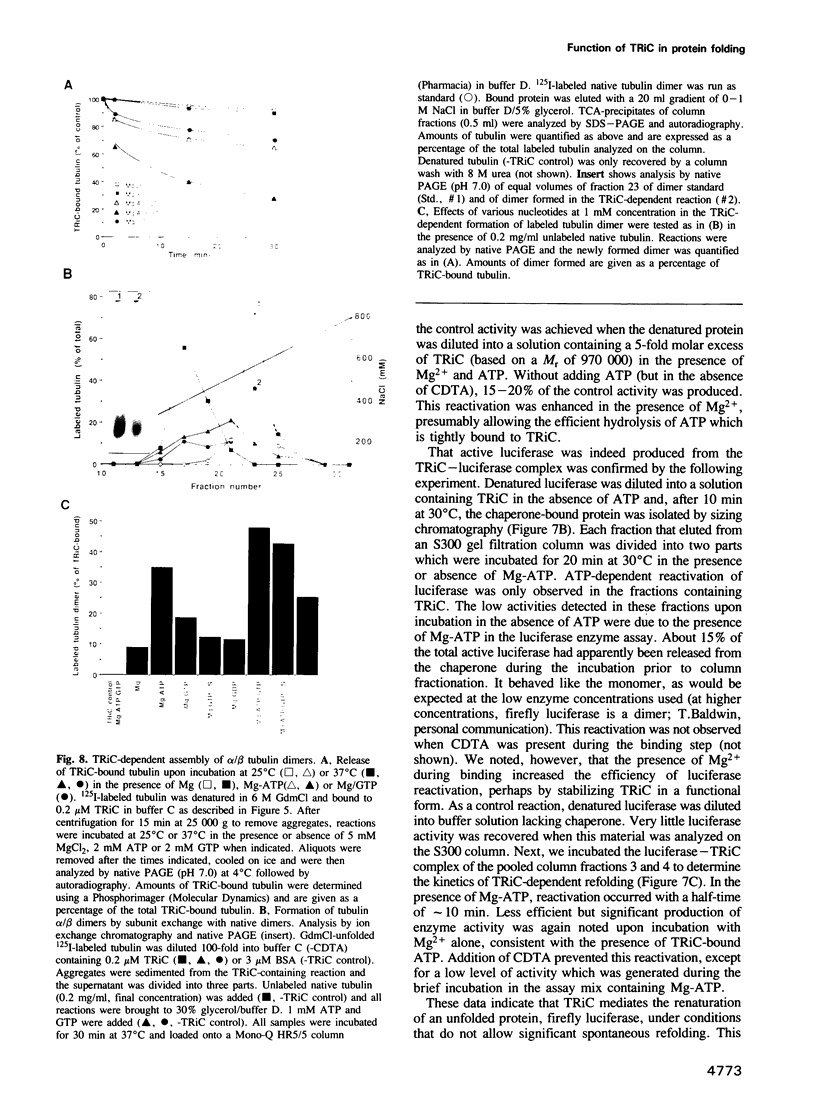
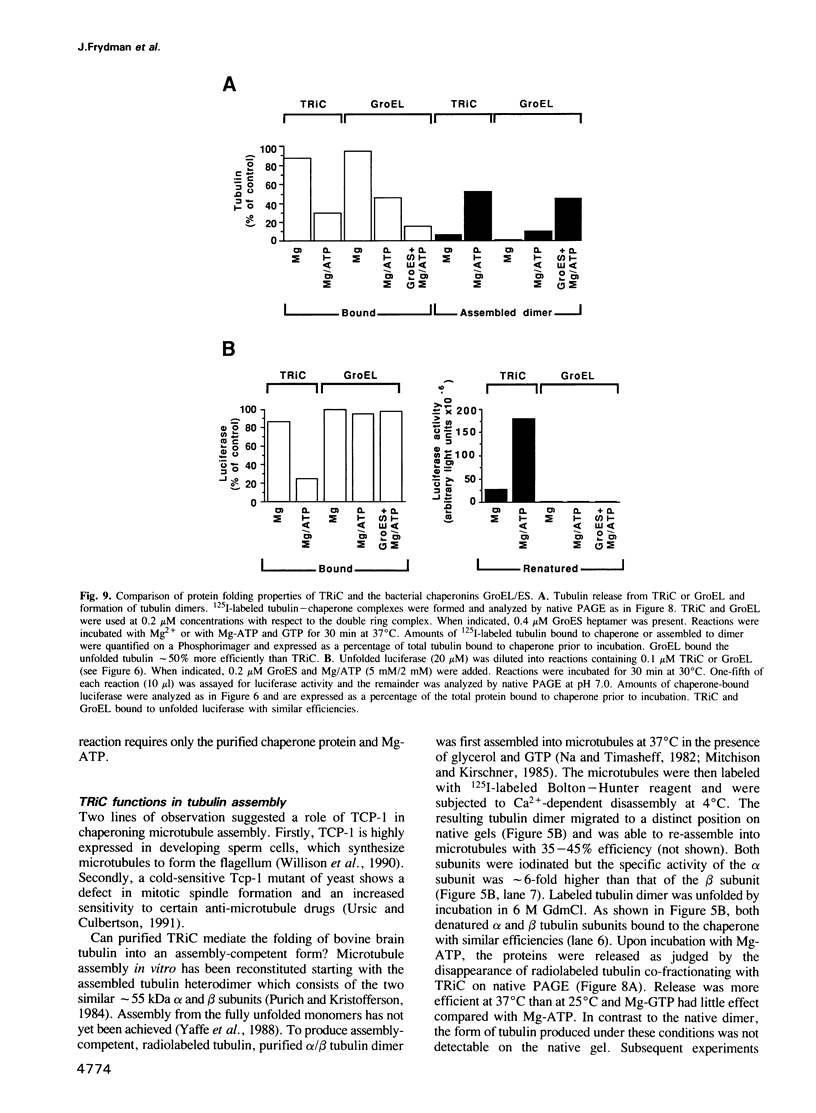
Abstract
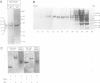
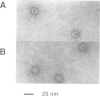
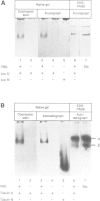
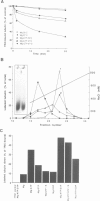
T-complex polypeptide 1 (TCP-1) was analyzed as a potential chaperonin (GroEL/Hsp60) equivalent of the eukaryotic cytosol. We found TCP-1 to be part of a hetero-oligomeric 970 kDa complex containing several structurally related subunits of 52-65 kDa. These members of a new protein family are assembled into a TCP-1 ring complex (TRiC) which resembles the GroEL double ring. The main function of TRiC appears to be in chaperoning monomeric protein folding: TRiC binds unfolded polypeptides, thereby preventing their aggregation, and mediates the ATP-dependent renaturation of unfolded firefly luciferase and tubulin. At least in vitro, TRiC appears to function independently of a small co-chaperonin protein such as GroES. Folding of luciferase is mediated by TRiC but not by GroEL/ES. This suggests that the range of substrate proteins interacting productively with TRiC may differ from that of GroEL. We propose that TRiC mediates the folding of cytosolic proteins by a mechanism distinct from that of the chaperonins in specific aspects.
Full text
PDF
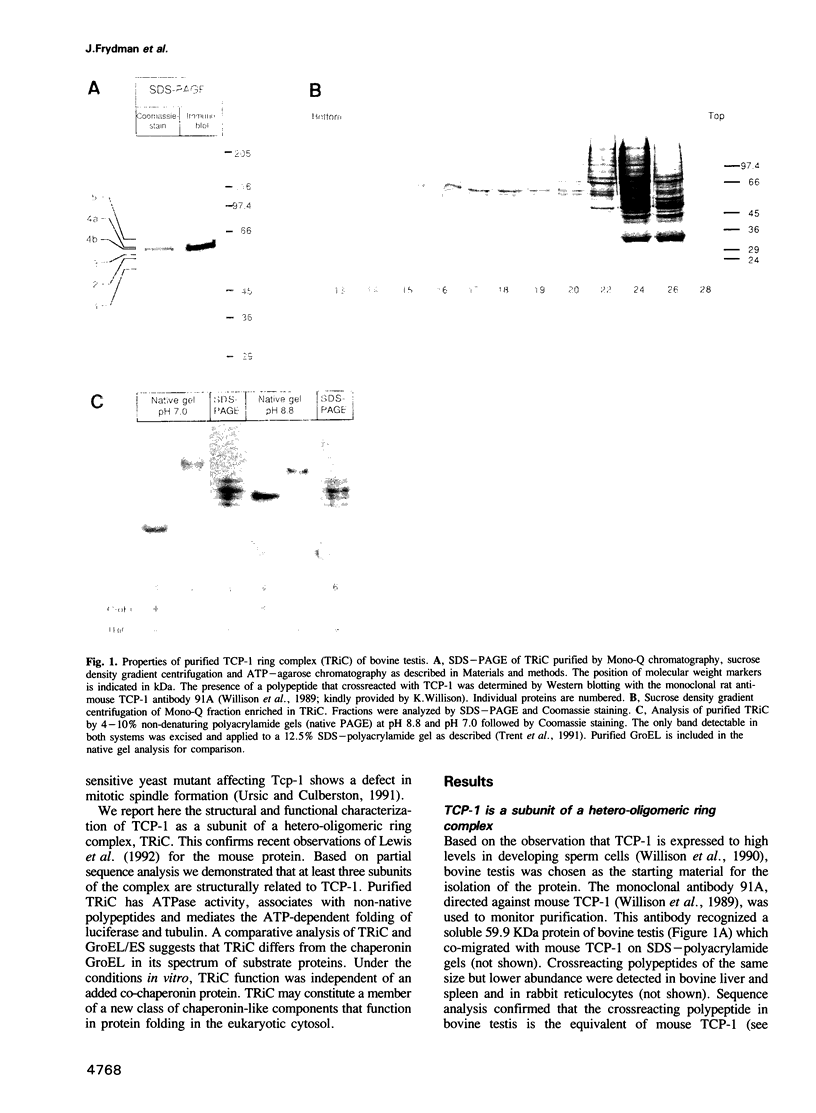
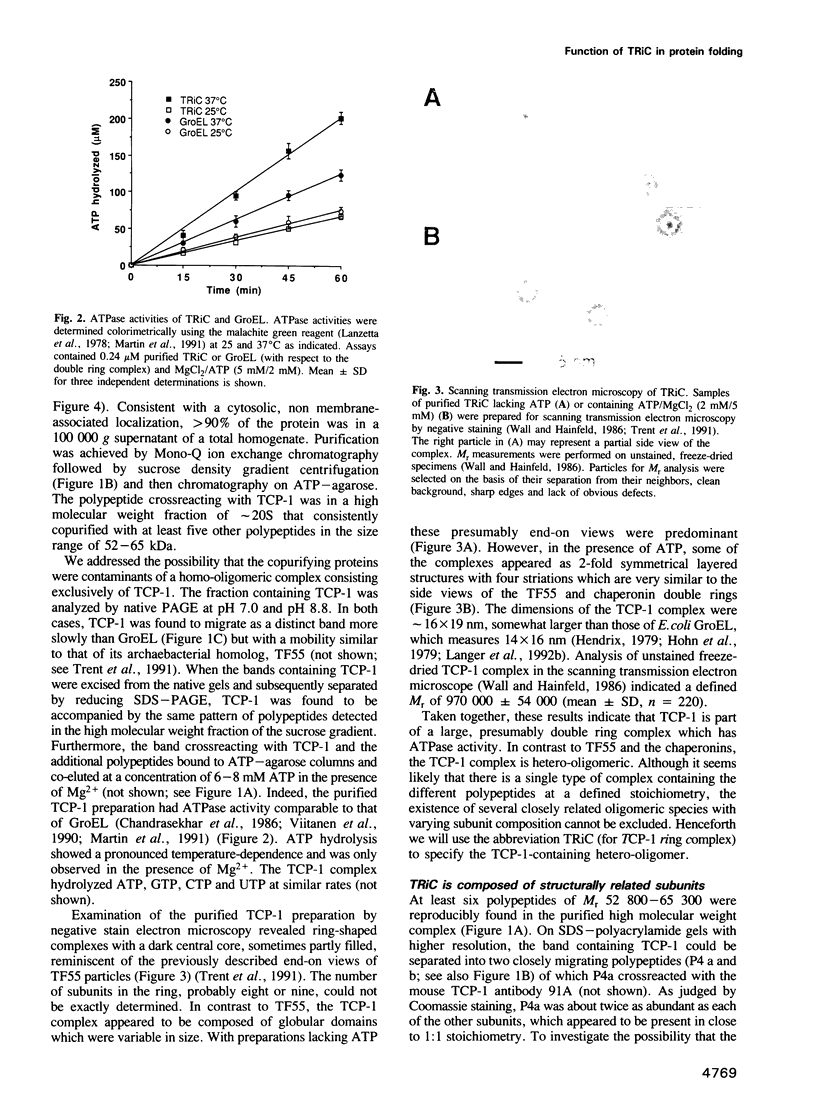

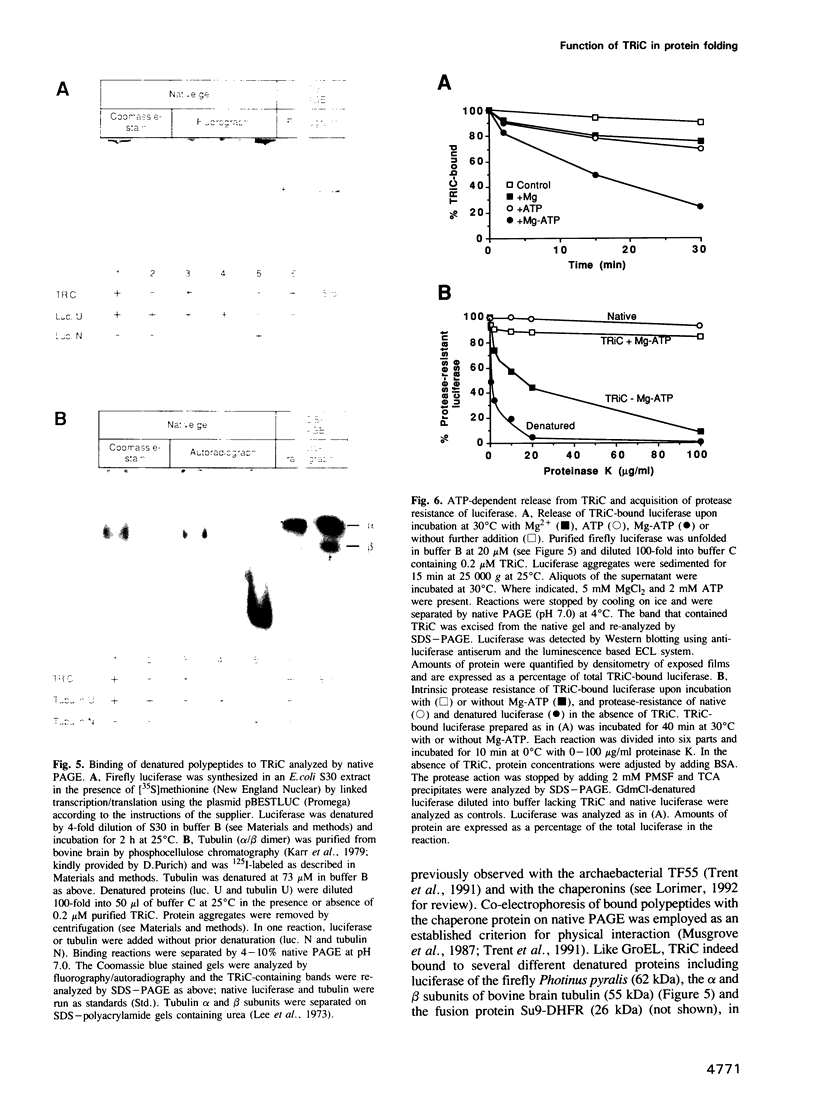
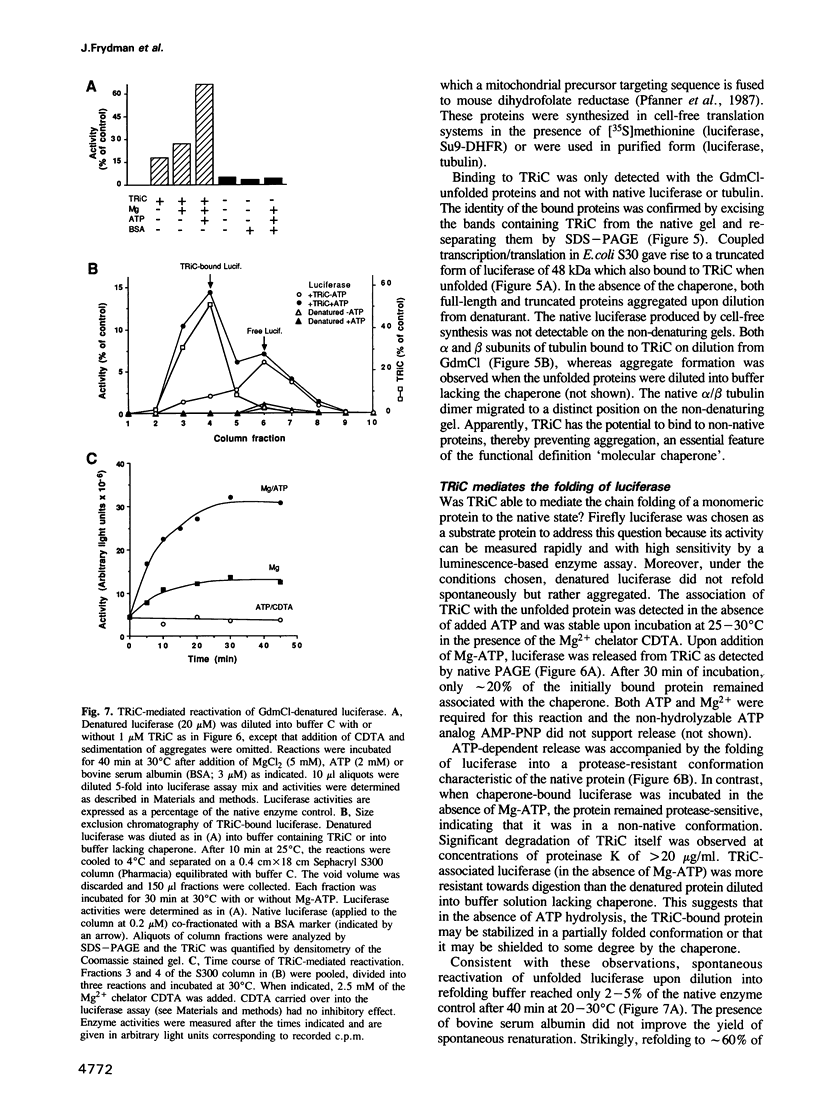




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmad S., Gupta R. S. Cloning of a Chinese hamster protein homologous to the mouse t-complex protein TCP-1: structural similarity to the ubiquitous 'chaperonin' family of heat-shock proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Oct 23;1087(2):253–255. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90214-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atencio D. P., Yaffe M. P. MAS5, a yeast homolog of DnaJ involved in mitochondrial protein import. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):283–291. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bairoch A., Claverie J. M. Sequence patterns in protein kinases. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):22–22. doi: 10.1038/331022a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckmann R. P., Mizzen L. E., Welch W. J. Interaction of Hsp 70 with newly synthesized proteins: implications for protein folding and assembly. Science. 1990 May 18;248(4957):850–854. doi: 10.1126/science.2188360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchner J., Schmidt M., Fuchs M., Jaenicke R., Rudolph R., Schmid F. X., Kiefhaber T. GroE facilitates refolding of citrate synthase by suppressing aggregation. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 12;30(6):1586–1591. doi: 10.1021/bi00220a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplan A. J., Douglas M. G. Characterization of YDJ1: a yeast homologue of the bacterial dnaJ protein. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(4):609–621. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.4.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekhar G. N., Tilly K., Woolford C., Hendrix R., Georgopoulos C. Purification and properties of the groES morphogenetic protein of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12414–12419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detrich H. W., 3rd, Williams R. C. Reversible dissociation of the alpha beta dimer of tubulin from bovine brain. Biochemistry. 1978 Sep 19;17(19):3900–3907. doi: 10.1021/bi00612a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis J. Proteins as molecular chaperones. 1987 Jul 30-Aug 5Nature. 328(6129):378–379. doi: 10.1038/328378a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. J. Molecular chaperones: the plant connection. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):954–959. doi: 10.1126/science.250.4983.954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn G. C., Pohl J., Flocco M. T., Rothman J. E. Peptide-binding specificity of the molecular chaperone BiP. Nature. 1991 Oct 24;353(6346):726–730. doi: 10.1038/353726a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao Y., Thomas J. O., Chow R. L., Lee G. H., Cowan N. J. A cytoplasmic chaperonin that catalyzes beta-actin folding. Cell. 1992 Jun 12;69(6):1043–1050. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90622-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., Sambrook J. Protein folding in the cell. Nature. 1992 Jan 2;355(6355):33–45. doi: 10.1038/355033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Gifford A. M., Riviere L. R., Tempst P., Nolan G. P., Baltimore D. Cloning of the p50 DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B: homology to rel and dorsal. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1019–1029. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90276-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goloubinoff P., Christeller J. T., Gatenby A. A., Lorimer G. H. Reconstitution of active dimeric ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase from an unfoleded state depends on two chaperonin proteins and Mg-ATP. Nature. 1989 Dec 21;342(6252):884–889. doi: 10.1038/342884a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R. S. Sequence and structural homology between a mouse T-complex protein TCP-1 and the 'chaperonin' family of bacterial (GroEL, 60-65 kDa heat shock antigen) and eukaryotic proteins. Biochem Int. 1990;20(4):833–841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartl F. U., Martin J., Neupert W. Protein folding in the cell: the role of molecular chaperones Hsp70 and Hsp60. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1992;21:293–322. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.21.060192.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmingsen S. M., Ellis R. J. Purification and properties of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase large subunit binding protein. Plant Physiol. 1986 Jan;80(1):269–276. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.1.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmingsen S. M., Woolford C., van der Vies S. M., Tilly K., Dennis D. T., Georgopoulos C. P., Hendrix R. W., Ellis R. J. Homologous plant and bacterial proteins chaperone oligomeric protein assembly. Nature. 1988 May 26;333(6171):330–334. doi: 10.1038/333330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrix R. W. Purification and properties of groE, a host protein involved in bacteriophage assembly. J Mol Biol. 1979 Apr 15;129(3):375–392. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90502-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn T., Hohn B., Engel A., Wurtz M., Smith P. R. Isolation and characterization of the host protein groE involved in bacteriophage lambda assembly. J Mol Biol. 1979 Apr 15;129(3):359–373. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90501-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii N., Taguchi H., Sumi M., Yoshida M. Structure of holo-chaperonin studied with electron microscopy. Oligomeric cpn10 on top of two layers of cpn60 rings with two stripes each. FEBS Lett. 1992 Mar 9;299(2):169–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80240-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jindal S., Dudani A. K., Singh B., Harley C. B., Gupta R. S. Primary structure of a human mitochondrial protein homologous to the bacterial and plant chaperonins and to the 65-kilodalton mycobacterial antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2279–2283. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang P. J., Ostermann J., Shilling J., Neupert W., Craig E. A., Pfanner N. Requirement for hsp70 in the mitochondrial matrix for translocation and folding of precursor proteins. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):137–143. doi: 10.1038/348137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karr T. L., White H. D., Purich D. L. Characterization of brain microtubule proteins prepared by selective removal of mitochondrial and synaptosomal components. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):6107–6111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchhoff C., Willison K. Nucleotide and amino-acid sequence of human testis-derived TCP1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 25;18(14):4247–4247. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.14.4247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubota H., Morita T., Nagata T., Takemoto Y., Nozaki M., Gachelin G., Matsushiro A. Nucleotide sequence of mouse Tcp-1a cDNA. Gene. 1991 Sep 15;105(2):269–273. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90162-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landry S. J., Jordan R., McMacken R., Gierasch L. M. Different conformations for the same polypeptide bound to chaperones DnaK and GroEL. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):455–457. doi: 10.1038/355455a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer T., Lu C., Echols H., Flanagan J., Hayer M. K., Hartl F. U. Successive action of DnaK, DnaJ and GroEL along the pathway of chaperone-mediated protein folding. Nature. 1992 Apr 23;356(6371):683–689. doi: 10.1038/356683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer T., Pfeifer G., Martin J., Baumeister W., Hartl F. U. Chaperonin-mediated protein folding: GroES binds to one end of the GroEL cylinder, which accommodates the protein substrate within its central cavity. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4757–4765. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05581.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzetta P. A., Alvarez L. J., Reinach P. S., Candia O. A. An improved assay for nanomole amounts of inorganic phosphate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Nov 15;100(1):95–97. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. C., Frigon R. P., Timasheff S. N. The chemical characterization of calf brain microtubule protein subunits. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 25;248(20):7253–7262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis V. A., Hynes G. M., Zheng D., Saibil H., Willison K. T-complex polypeptide-1 is a subunit of a heteromeric particle in the eukaryotic cytosol. Nature. 1992 Jul 16;358(6383):249–252. doi: 10.1038/358249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luke M. M., Sutton A., Arndt K. T. Characterization of SIS1, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae homologue of bacterial dnaJ proteins. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(4):623–638. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.4.623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon M. F. Search for differences among t haplotypes in distorter and responder genes. Genet Res. 1990 Feb;55(1):13–19. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300025143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning-Krieg U. C., Scherer P. E., Schatz G. Sequential action of mitochondrial chaperones in protein import into the matrix. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3273–3280. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04891.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martel R., Cloney L. P., Pelcher L. E., Hemmingsen S. M. Unique composition of plastid chaperonin-60: alpha and beta polypeptide-encoding genes are highly divergent. Gene. 1990 Oct 15;94(2):181–187. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90385-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J., Langer T., Boteva R., Schramel A., Horwich A. L., Hartl F. U. Chaperonin-mediated protein folding at the surface of groEL through a 'molten globule'-like intermediate. Nature. 1991 Jul 4;352(6330):36–42. doi: 10.1038/352036a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza J. A., Rogers E., Lorimer G. H., Horowitz P. M. Chaperonins facilitate the in vitro folding of monomeric mitochondrial rhodanese. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):13044–13049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison T. J., Kirschner M. W. Properties of the kinetochore in vitro. I. Microtubule nucleation and tubulin binding. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):755–765. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musgrove J. E., Johnson R. A., Ellis R. J. Dissociation of the ribulosebisphosphate-carboxylase large-subunit binding protein into dissimilar subunits. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Mar 16;163(3):529–534. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10900.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Na G. C., Timasheff S. N. Physical properties of purified calf brain tubulin. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):393–408. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85040-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palleros D. R., Welch W. J., Fink A. L. Interaction of hsp70 with unfolded proteins: effects of temperature and nucleotides on the kinetics of binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5719–5723. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive sequence comparison with FASTP and FASTA. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:63–98. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83007-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfanner N., Tropschug M., Neupert W. Mitochondrial protein import: nucleoside triphosphates are involved in conferring import-competence to precursors. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):815–823. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90619-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phipps B. M., Hoffmann A., Stetter K. O., Baumeister W. A novel ATPase complex selectively accumulated upon heat shock is a major cellular component of thermophilic archaebacteria. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1711–1722. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07695.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purich D. L., Kristofferson D. Microtubule assembly: a review of progress, principles, and perspectives. Adv Protein Chem. 1984;36:133–212. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60297-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E. Polypeptide chain binding proteins: catalysts of protein folding and related processes in cells. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):591–601. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saibil H., Dong Z., Wood S., auf der Mauer A. Binding of chaperonins. Nature. 1991 Sep 5;353(6339):25–26. doi: 10.1038/353025b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders S. L., Whitfield K. M., Vogel J. P., Rose M. D., Schekman R. W. Sec61p and BiP directly facilitate polypeptide translocation into the ER. Cell. 1992 Apr 17;69(2):353–365. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90415-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer P. E., Krieg U. C., Hwang S. T., Vestweber D., Schatz G. A precursor protein partly translocated into yeast mitochondria is bound to a 70 kd mitochondrial stress protein. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4315–4322. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07880.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver L. M., Artzt K., Bennett D. A major testicular cell protein specified by a mouse T/t complex gene. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):275–284. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90153-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver L. M., Remis D. Five of the nine genetically defined regions of mouse t haplotypes are involved in transmission ratio distortion. Genet Res. 1987 Feb;49(1):51–56. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300026720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempst P., Link A. J., Riviere L. R., Fleming M., Elicone C. Internal sequence analysis of proteins separated on polyacrylamide gels at the submicrogram level: improved methods, applications and gene cloning strategies. Electrophoresis. 1990 Jul;11(7):537–553. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150110704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempst P., Riviere L. Examination of automated polypeptide sequencing using standard phenyl isothiocyanate reagent and subpicomole high-performance liquid chromatographic analysis. Anal Biochem. 1989 Dec;183(2):290–300. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90482-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trent J. D., Nimmesgern E., Wall J. S., Hartl F. U., Horwich A. L. A molecular chaperone from a thermophilic archaebacterium is related to the eukaryotic protein t-complex polypeptide-1. Nature. 1991 Dec 12;354(6353):490–493. doi: 10.1038/354490a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ursic D., Culbertson M. R. The yeast homolog to mouse Tcp-1 affects microtubule-mediated processes. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2629–2640. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ursic D., Ganetzky B. A Drosophila melanogaster gene encodes a protein homologous to the mouse t complex polypeptide 1. Gene. 1988 Sep 7;68(2):267–274. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90029-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vachereau A. Luminescent immunodetection of western-blotted proteins from coomassie-stained polyacrylamide gel. Anal Biochem. 1989 May 15;179(1):206–208. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90227-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viitanen P. V., Lubben T. H., Reed J., Goloubinoff P., O'Keefe D. P., Lorimer G. H. Chaperonin-facilitated refolding of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase and ATP hydrolysis by chaperonin 60 (groEL) are K+ dependent. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 19;29(24):5665–5671. doi: 10.1021/bi00476a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall J. S., Hainfeld J. F. Mass mapping with the scanning transmission electron microscope. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1986;15:355–376. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.15.060186.002035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willison K. R., Dudley K., Potter J. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of a haploid expressed gene encoding t complex polypeptide 1. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):727–738. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90839-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willison K. R., Hynes G., Davies P., Goldsborough A., Lewis V. A. Expression of three t-complex genes, Tcp-1, D17Leh117c3, and D17Leh66, in purified murine spermatogenic cell populations. Genet Res. 1990 Oct-Dec;56(2-3):193–201. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300035291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willison K., Lewis V., Zuckerman K. S., Cordell J., Dean C., Miller K., Lyon M. F., Marsh M. The t complex polypeptide 1 (TCP-1) is associated with the cytoplasmic aspect of Golgi membranes. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):621–632. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90131-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe M. B., Farr G. W., Miklos D., Horwich A. L., Sternlicht M. L., Sternlicht H. TCP1 complex is a molecular chaperone in tubulin biogenesis. Nature. 1992 Jul 16;358(6383):245–248. doi: 10.1038/358245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe M. B., Levison B. S., Szasz J., Sternlicht H. Expression of a human alpha-tubulin: properties of the isolated subunit. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 22;27(6):1869–1880. doi: 10.1021/bi00406a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., Helinski D. R., DeLuca M. Cloning firefly luciferase. Methods Enzymol. 1986;133:3–14. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)33050-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]