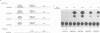Abstract
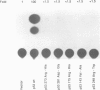
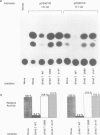
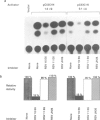
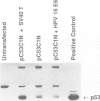
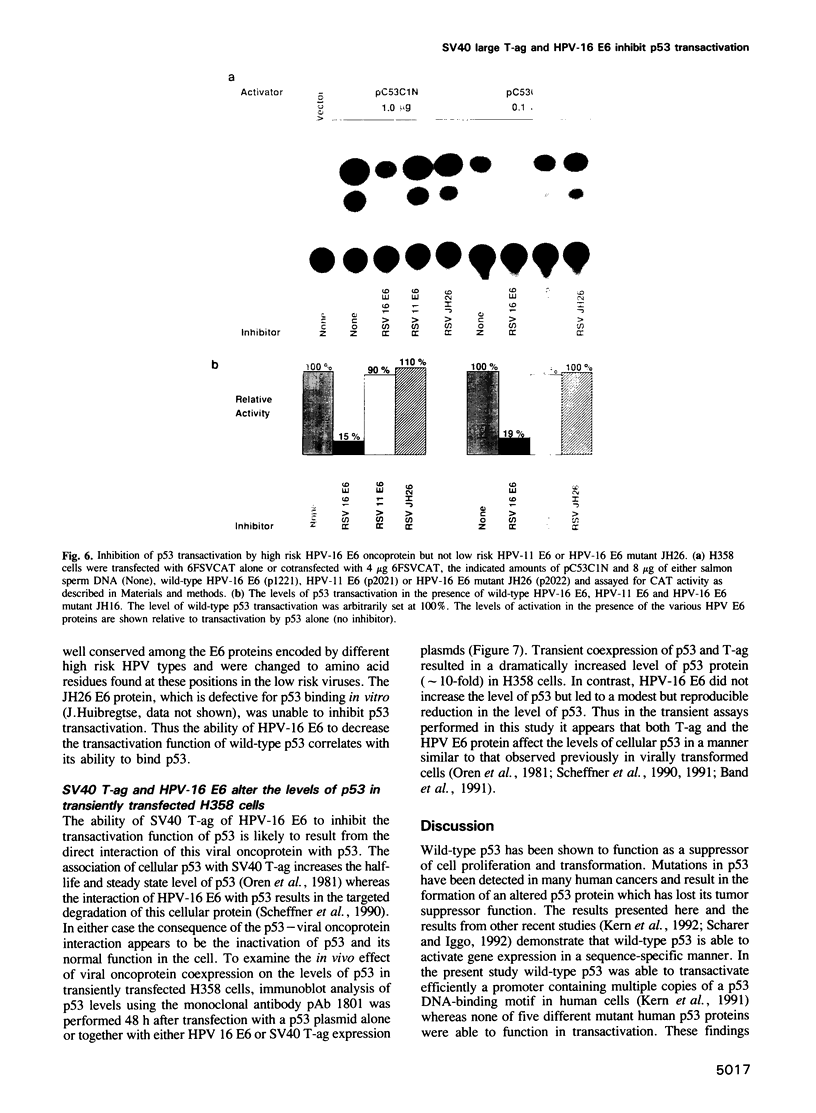
The observed interaction between p53 and the oncoproteins encoded by several DNA tumor viruses suggests that these viruses mediate their transforming activities at least in part by altering the normal growth regulatory function of p53. In this study we examined the effect of viral oncoprotein expression on the transcriptional transactivation function of wild-type p53 in human cells. Plasmids expressing human p53 were cotransfected with either SV40 large T-antigen or human papillomavirus (HPV) type 16 E6 expression plasmids and assayed for transactivation function using a reporter gene driven by a p53-responsive promoter containing multiple copies of the consensus p53 DNA binding motif, TGCCT. Both large T-antigen and E6 were able to inhibit transactivation by wild-type p53. Furthermore, SV40 T-antigen mutants that are defective for p53 binding were not able to inhibit transactivation and HPV E6 proteins that were either mutant or derived from non-oncogenic HPV types and unable to bind p53, had no effect on p53 transactivation. These results demonstrate the physiological relevance of the interaction of SV40 T-antigen and HPV E6 oncoproteins with p53 in vivo and suggest that the transforming functions of these viral oncoproteins may be linked to their ability to inhibit p53-mediated transcriptional activation.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker S. J., Fearon E. R., Nigro J. M., Hamilton S. R., Preisinger A. C., Jessup J. M., vanTuinen P., Ledbetter D. H., Barker D. F., Nakamura Y. Chromosome 17 deletions and p53 gene mutations in colorectal carcinomas. Science. 1989 Apr 14;244(4901):217–221. doi: 10.1126/science.2649981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Band V., De Caprio J. A., Delmolino L., Kulesa V., Sager R. Loss of p53 protein in human papillomavirus type 16 E6-immortalized human mammary epithelial cells. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6671–6676. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6671-6676.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargonetti J., Friedman P. N., Kern S. E., Vogelstein B., Prives C. Wild-type but not mutant p53 immunopurified proteins bind to sequences adjacent to the SV40 origin of replication. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1083–1091. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90560-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartek J., Iggo R., Gannon J., Lane D. P. Genetic and immunochemical analysis of mutant p53 in human breast cancer cell lines. Oncogene. 1990 Jun;5(6):893–899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crook T., Tidy J. A., Vousden K. H. Degradation of p53 can be targeted by HPV E6 sequences distinct from those required for p53 binding and trans-activation. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):547–556. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90529-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Figge J., Shew J. Y., Huang C. M., Lee W. H., Marsilio E., Paucha E., Livingston D. M. SV40 large tumor antigen forms a specific complex with the product of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):275–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90559-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson N., Howley P. M., Münger K., Harlow E. The human papilloma virus-16 E7 oncoprotein is able to bind to the retinoblastoma gene product. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):934–937. doi: 10.1126/science.2537532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliyahu D., Goldfinger N., Pinhasi-Kimhi O., Shaulsky G., Skurnik Y., Arai N., Rotter V., Oren M. Meth A fibrosarcoma cells express two transforming mutant p53 species. Oncogene. 1988 Sep;3(3):313–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliyahu D., Michalovitz D., Eliyahu S., Pinhasi-Kimhi O., Oren M. Wild-type p53 can inhibit oncogene-mediated focus formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8763–8767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer G., Bargonetti J., Zhu H., Friedman P., Prywes R., Prives C. Wild-type p53 activates transcription in vitro. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):83–86. doi: 10.1038/358083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Jang S. K. Presence of a potent transcription activating sequence in the p53 protein. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1046–1049. doi: 10.1126/science.2144363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay C. A., Hinds P. W., Levine A. J. The p53 proto-oncogene can act as a suppressor of transformation. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1083–1093. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90045-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funk W. D., Pak D. T., Karas R. H., Wright W. E., Shay J. W. A transcriptionally active DNA-binding site for human p53 protein complexes. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2866–2871. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley-Nelson P., Vousden K. H., Hubbert N. L., Lowy D. R., Schiller J. T. HPV16 E6 and E7 proteins cooperate to immortalize human foreskin keratinocytes. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3905–3910. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08570.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds P., Finlay C., Levine A. J. Mutation is required to activate the p53 gene for cooperation with the ras oncogene and transformation. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):739–746. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.739-746.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollstein M., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Harris C. C. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):49–53. doi: 10.1126/science.1905840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Smith A. E. In vitro mutagenesis of a putative DNA binding domain of SV40 large-T. Virology. 1984 Nov;139(1):109–137. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90334-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern S. E., Kinzler K. W., Bruskin A., Jarosz D., Friedman P., Prives C., Vogelstein B. Identification of p53 as a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1708–1711. doi: 10.1126/science.2047879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern S. E., Pietenpol J. A., Thiagalingam S., Seymour A., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Oncogenic forms of p53 inhibit p53-regulated gene expression. Science. 1992 May 8;256(5058):827–830. doi: 10.1126/science.1589764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P., Crawford L. V. T antigen is bound to a host protein in SV40-transformed cells. Nature. 1979 Mar 15;278(5701):261–263. doi: 10.1038/278261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Levine A. J. Characterization of a 54K dalton cellular SV40 tumor antigen present in SV40-transformed cells and uninfected embryonal carcinoma cells. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90293-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkin D., Li F. P., Strong L. C., Fraumeni J. F., Jr, Nelson C. E., Kim D. H., Kassel J., Gryka M. A., Bischoff F. Z., Tainsky M. A. Germ line p53 mutations in a familial syndrome of breast cancer, sarcomas, and other neoplasms. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1233–1238. doi: 10.1126/science.1978757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez J., Georgoff I., Martinez J., Levine A. J. Cellular localization and cell cycle regulation by a temperature-sensitive p53 protein. Genes Dev. 1991 Feb;5(2):151–159. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.2.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner J., Medcalf E. A. Cotranslation of activated mutant p53 with wild type drives the wild-type p53 protein into the mutant conformation. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):765–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90384-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan L. M., Matlashewski G. J., Scrable H. J., Cavenee W. K. Mechanisms of p53 loss in human sarcomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5863–5867. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Münger K., Phelps W. C., Bubb V., Howley P. M., Schlegel R. The E6 and E7 genes of the human papillomavirus type 16 together are necessary and sufficient for transformation of primary human keratinocytes. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4417–4421. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4417-4421.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Münger K., Werness B. A., Dyson N., Phelps W. C., Harlow E., Howley P. M. Complex formation of human papillomavirus E7 proteins with the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor gene product. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4099–4105. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08594.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigro J. M., Baker S. J., Preisinger A. C., Jessup J. M., Hostetter R., Cleary K., Bigner S. H., Davidson N., Baylin S., Devilee P. Mutations in the p53 gene occur in diverse human tumour types. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):705–708. doi: 10.1038/342705a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Rourke R. W., Miller C. W., Kato G. J., Simon K. J., Chen D. L., Dang C. V., Koeffler H. P. A potential transcriptional activation element in the p53 protein. Oncogene. 1990 Dec;5(12):1829–1832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oren M., Maltzman W., Levine A. J. Post-translational regulation of the 54K cellular tumor antigen in normal and transformed cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;1(2):101–110. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.2.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peden K. W., Srinivasan A., Farber J. M., Pipas J. M. Mutants with changes within or near a hydrophobic region of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen are defective for binding cellular protein p53. Virology. 1989 Jan;168(1):13–21. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90398-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps W. C., Yee C. L., Münger K., Howley P. M. The human papillomavirus type 16 E7 gene encodes transactivation and transformation functions similar to those of adenovirus E1A. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):539–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90570-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raycroft L., Schmidt J. R., Yoas K., Hao M. M., Lozano G. Analysis of p53 mutants for transcriptional activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):6067–6074. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.6067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raycroft L., Wu H. Y., Lozano G. Transcriptional activation by wild-type but not transforming mutants of the p53 anti-oncogene. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1049–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.2144364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich N. C., Oren M., Levine A. J. Two distinct mechanisms regulate the levels of a cellular tumor antigen, p53. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2143–2150. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarnow P., Ho Y. S., Williams J., Levine A. J. Adenovirus E1b-58kd tumor antigen and SV40 large tumor antigen are physically associated with the same 54 kd cellular protein in transformed cells. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):387–394. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90356-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Münger K., Byrne J. C., Howley P. M. The state of the p53 and retinoblastoma genes in human cervical carcinoma cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5523–5527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Werness B. A., Huibregtse J. M., Levine A. J., Howley P. M. The E6 oncoprotein encoded by human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 promotes the degradation of p53. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1129–1136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90409-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schärer E., Iggo R. Mammalian p53 can function as a transcription factor in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 11;20(7):1539–1545. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.7.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedman S. A., Barbosa M. S., Vass W. C., Hubbert N. L., Haas J. A., Lowy D. R., Schiller J. T. The full-length E6 protein of human papillomavirus type 16 has transforming and trans-activating activities and cooperates with E7 to immortalize keratinocytes in culture. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4860–4866. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4860-4866.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompayrac L., Danna K. J. A new SV40 mutant that encodes a small fragment of T antigen transforms established rat and mouse cells. Virology. 1988 Apr;163(2):391–396. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90279-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalholz B. A., Lambert P. F., Yee C. L., Howley P. M. Bovine papillomavirus transcriptional regulation: localization of the E2-responsive elements of the long control region. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2128–2137. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2128-2137.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan A., Peden K. W., Pipas J. M. The large tumor antigen of simian virus 40 encodes at least two distinct transforming functions. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5459–5463. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5459-5463.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Nau M. M., Chiba I., Birrer M. J., Rosenberg R. K., Vinocour M., Levitt M., Pass H., Gazdar A. F., Minna J. D. p53: a frequent target for genetic abnormalities in lung cancer. Science. 1989 Oct 27;246(4929):491–494. doi: 10.1126/science.2554494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger T., Nau M. M., Segal S., Minna J. D. p53: a transdominant regulator of transcription whose function is ablated by mutations occurring in human cancer. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1383–1390. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05183.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Hauschka S., Tapscott S. J. The MCK enhancer contains a p53 responsive element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4570–4571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werness B. A., Levine A. J., Howley P. M. Association of human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 E6 proteins with p53. Science. 1990 Apr 6;248(4951):76–79. doi: 10.1126/science.2157286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte P., Buchkovich K. J., Horowitz J. M., Friend S. H., Raybuck M., Weinberg R. A., Harlow E. Association between an oncogene and an anti-oncogene: the adenovirus E1A proteins bind to the retinoblastoma gene product. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):124–129. doi: 10.1038/334124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yew P. R., Berk A. J. Inhibition of p53 transactivation required for transformation by adenovirus early 1B protein. Nature. 1992 May 7;357(6373):82–85. doi: 10.1038/357082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu J. Y., Abate M., Rice P. W., Cole C. N. The ability of simian virus 40 large T antigen to immortalize primary mouse embryo fibroblasts cosegregates with its ability to bind to p53. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6872–6880. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6872-6880.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu J. Y., Cole C. N. Linker insertion mutants of simian virus 40 large T antigen that show trans-dominant interference with wild-type large T antigen map to multiple sites within the T-antigen gene. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4777–4786. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4777-4786.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]