Abstract
Lysosomal acid phosphatase (LAP) is rapidly internalized from the cell surface due to a tyrosine-containing internalization signal in its 19 amino acid cytoplasmic tail. Measuring the internalization of a series of LAP cytoplasmic tail truncation and substitution mutants revealed that the N-terminal 12 amino acids of the cytoplasmic tail are sufficient for rapid endocytosis and that the hexapeptide 411-PGYRHV-416 is the tyrosine-containing internalization signal. Truncation and substitution mutants of amino acid residues following Val416 can prevent internalization even though these residues do not belong to the internalization signal. It was shown recently that part of the LAP cytoplasmic tail peptide corresponding to 410-PPGY-413 forms a well-ordered beta turn structure in solution. Two-dimensional NMR spectroscopy of two modified LAP tail peptides, in which the single tyrosine was substituted either by phenylalanine or by alanine, revealed that the tendency to form a beta turn is reduced by 25% in the phenylalanine-containing peptide and by approximately 50% in the alanine-containing mutant peptide. Our results suggest, that in the short cytoplasmic tail of LAP tyrosine is required for stabilization of the right turn and that the aromatic ring system of the tyrosine residue is a contact point to the putative cytoplasmic receptor.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Artelt P., Morelle C., Ausmeier M., Fitzek M., Hauser H. Vectors for efficient expression in mammalian fibroblastoid, myeloid and lymphoid cells via transfection or infection. Gene. 1988 Sep 7;68(2):213–219. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bansal A., Gierasch L. M. The NPXY internalization signal of the LDL receptor adopts a reverse-turn conformation. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1195–1201. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90295-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun M., Waheed A., von Figura K. Lysosomal acid phosphatase is transported to lysosomes via the cell surface. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3633–3640. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08537.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canfield W. M., Johnson K. F., Ye R. D., Gregory W., Kornfeld S. Localization of the signal for rapid internalization of the bovine cation-independent mannose 6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor-II receptor to amino acids 24-29 of the cytoplasmic tail. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5682–5688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Causin C., Waheed A., Braulke T., Junghans U., Maly P., Humbel R. E., von Figura K. Mannose 6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor II-binding proteins in human serum and urine. Their relation to the mannose 6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor II receptor. Biochem J. 1988 Jun 15;252(3):795–799. doi: 10.1042/bj2520795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. J., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. NPXY, a sequence often found in cytoplasmic tails, is required for coated pit-mediated internalization of the low density lipoprotein receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3116–3123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collawn J. F., Kuhn L. A., Liu L. F., Tainer J. A., Trowbridge I. S. Transplanted LDL and mannose-6-phosphate receptor internalization signals promote high-efficiency endocytosis of the transferrin receptor. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3247–3253. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04888.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collawn J. F., Stangel M., Kuhn L. A., Esekogwu V., Jing S. Q., Trowbridge I. S., Tainer J. A. Transferrin receptor internalization sequence YXRF implicates a tight turn as the structural recognition motif for endocytosis. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):1061–1072. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90509-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. G., van Driel I. R., Russell D. W., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. The low density lipoprotein receptor. Identification of amino acids in cytoplasmic domain required for rapid endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4075–4082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson H. J., Rance M., Houghten R. A., Wright P. E., Lerner R. A. Folding of immunogenic peptide fragments of proteins in water solution. II. The nascent helix. J Mol Biol. 1988 May 5;201(1):201–217. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90447-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberle W., Sander C., Klaus W., Schmidt B., von Figura K., Peters C. The essential tyrosine of the internalization signal in lysosomal acid phosphatase is part of a beta turn. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1203–1209. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90296-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrer C., Geffen I., Spiess M. Endocytosis of the ASGP receptor H1 is reduced by mutation of tyrosine-5 but still occurs via coated pits. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(3):423–431. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.3.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glickman J. N., Conibear E., Pearse B. M. Specificity of binding of clathrin adaptors to signals on the mannose-6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor II receptor. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1041–1047. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03471.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Anderson R. G., Russell D. W., Schneider W. J. Receptor-mediated endocytosis: concepts emerging from the LDL receptor system. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:1–39. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschalk S., Waheed A., Schmidt B., Laidler P., von Figura K. Sequential processing of lysosomal acid phosphatase by a cytoplasmic thiol proteinase and a lysosomal aspartyl proteinase. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3215–3219. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08480.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard A. L. Endocytosis. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;1(4):675–683. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(89)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iacopetta B. J., Rothenberger S., Kühn L. C. A role for the cytoplasmic domain in transferrin receptor sorting and coated pit formation during endocytosis. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):485–489. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90069-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jadot M., Canfield W. M., Gregory W., Kornfeld S. Characterization of the signal for rapid internalization of the bovine mannose 6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor-II receptor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):11069–11077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller G. A., Siegel M. W., Caras I. W. Endocytosis of glycophospholipid-anchored and transmembrane forms of CD4 by different endocytic pathways. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):863–874. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05124.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarovits J., Roth M. A single amino acid change in the cytoplasmic domain allows the influenza virus hemagglutinin to be endocytosed through coated pits. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):743–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90092-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisanti M. P., Sargiacomo M., Graeve L., Saltiel A. R., Rodriguez-Boulan E. Polarized apical distribution of glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins in a renal epithelial cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9557–9561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobel P., Fujimoto K., Ye R. D., Griffiths G., Kornfeld S. Mutations in the cytoplasmic domain of the 275 kd mannose 6-phosphate receptor differentially alter lysosomal enzyme sorting and endocytosis. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):787–796. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90793-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGraw T. E., Maxfield F. R. Human transferrin receptor internalization is partially dependent upon an aromatic amino acid on the cytoplasmic domain. Cell Regul. 1990 Mar;1(4):369–377. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.4.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mostov K. E., de Bruyn Kops A., Deitcher D. L. Deletion of the cytoplasmic domain of the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor prevents basolateral localization and endocytosis. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):359–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90592-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamaye K. L., Eckstein F. Inhibition of restriction endonuclease Nci I cleavage by phosphorothioate groups and its application to oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 22;14(24):9679–9698. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.24.9679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
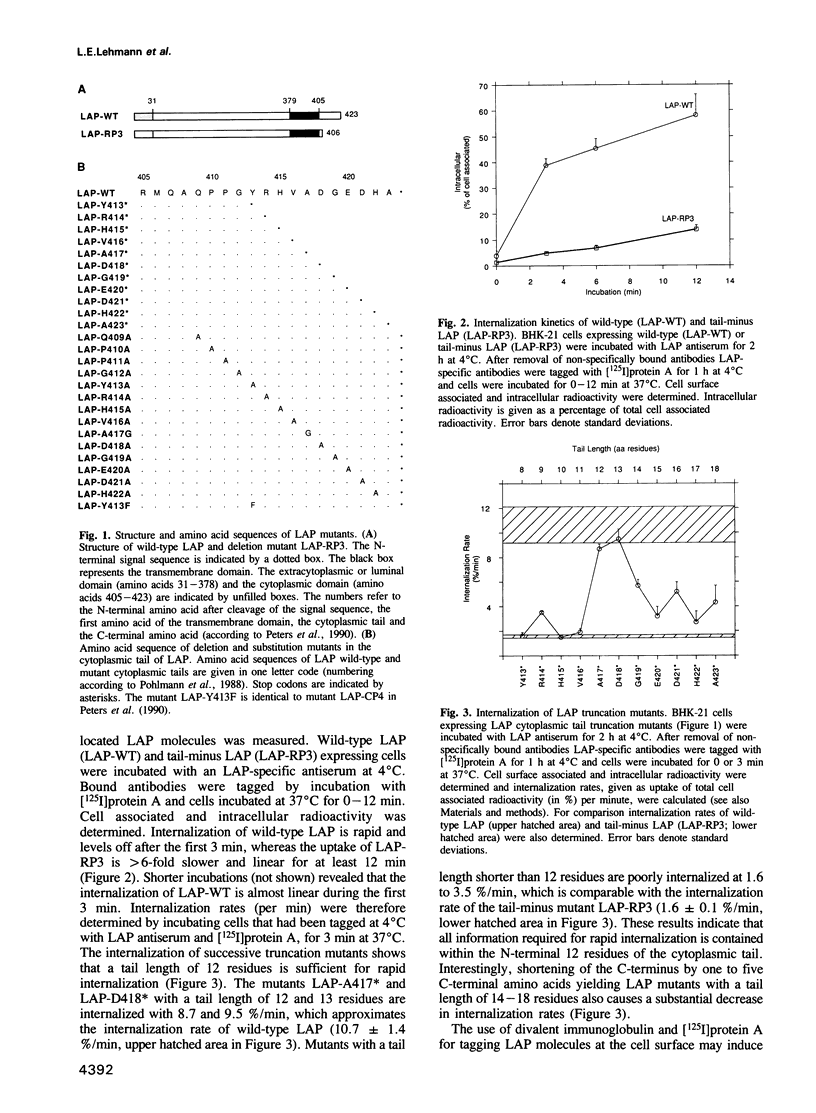
- Peters C., Braun M., Weber B., Wendland M., Schmidt B., Pohlmann R., Waheed A., von Figura K. Targeting of a lysosomal membrane protein: a tyrosine-containing endocytosis signal in the cytoplasmic tail of lysosomal acid phosphatase is necessary and sufficient for targeting to lysosomes. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3497–3506. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07558.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohlmann R., Krentler C., Schmidt B., Schröder W., Lorkowski G., Culley J., Mersmann G., Geier C., Waheed A., Gottschalk S. Human lysosomal acid phosphatase: cloning, expression and chromosomal assignment. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2343–2350. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03078.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rance M., Sørensen O. W., Bodenhausen G., Wagner G., Ernst R. R., Wüthrich K. Improved spectral resolution in cosy 1H NMR spectra of proteins via double quantum filtering. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Dec 16;117(2):479–485. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91225-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothberg K. G., Heuser J. E., Donzell W. C., Ying Y. S., Glenney J. R., Anderson R. G. Caveolin, a protein component of caveolae membrane coats. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):673–682. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90143-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., van Deurs B. Selective modulation of the endocytic uptake of ricin and fluid phase markers without alteration in transferrin endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 15;265(11):6382–6388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waheed A., Van Etten R. L. Biosynthesis and processing of lysosomal acid phosphatase in cultured human cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Nov 15;243(1):274–283. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90796-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. A., Fukuda M. Accumulation of membrane glycoproteins in lysosomes requires a tyrosine residue at a particular position in the cytoplasmic tail. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):955–966. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]