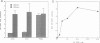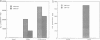Abstract
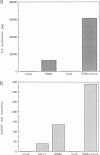
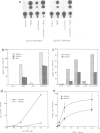
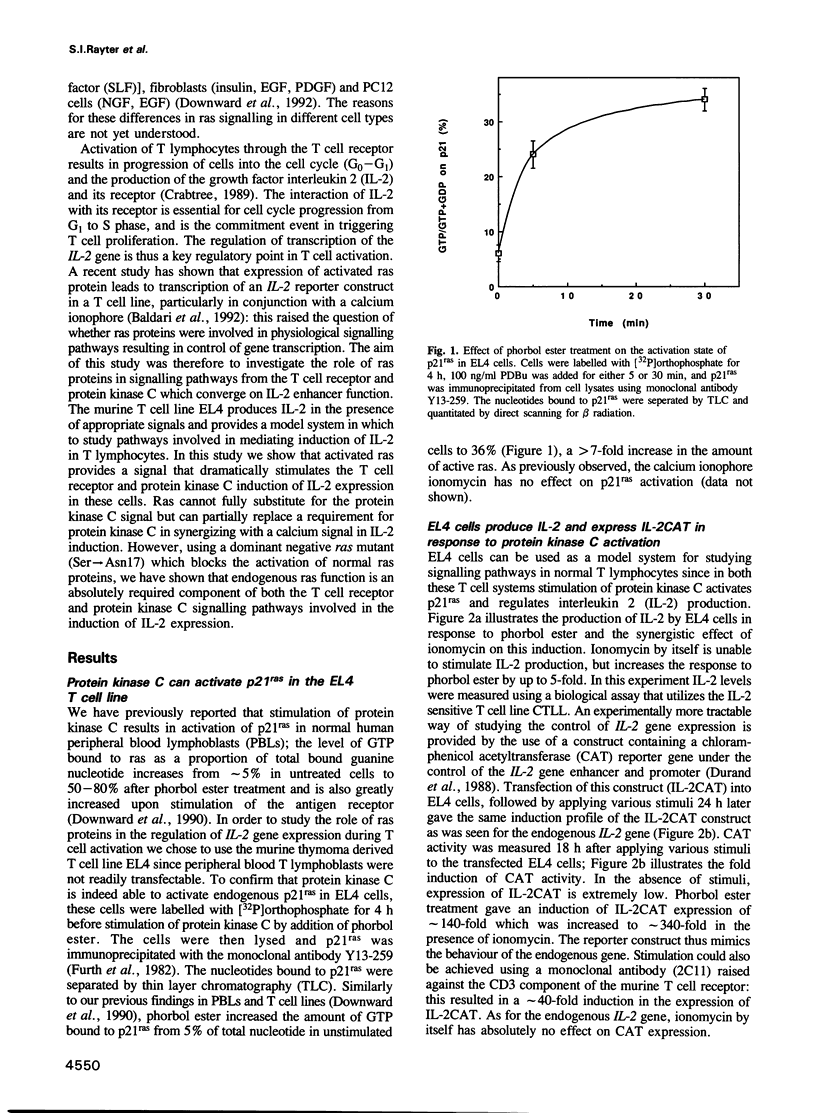
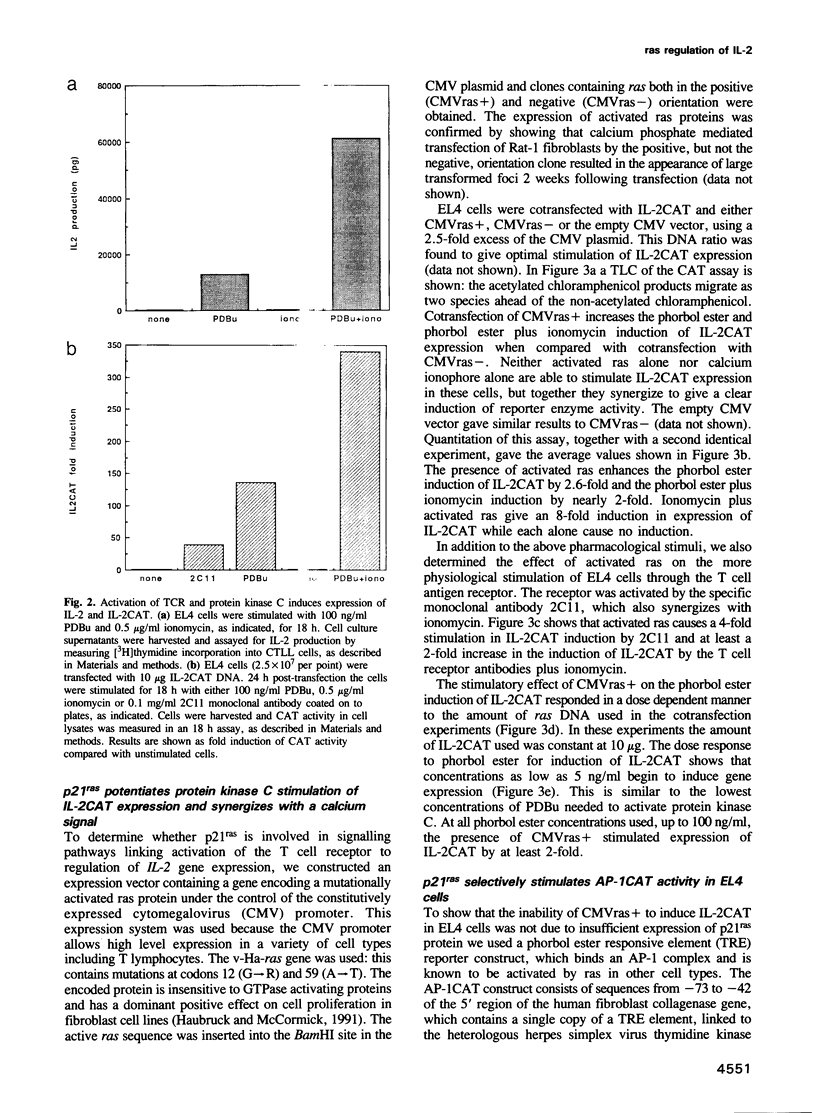
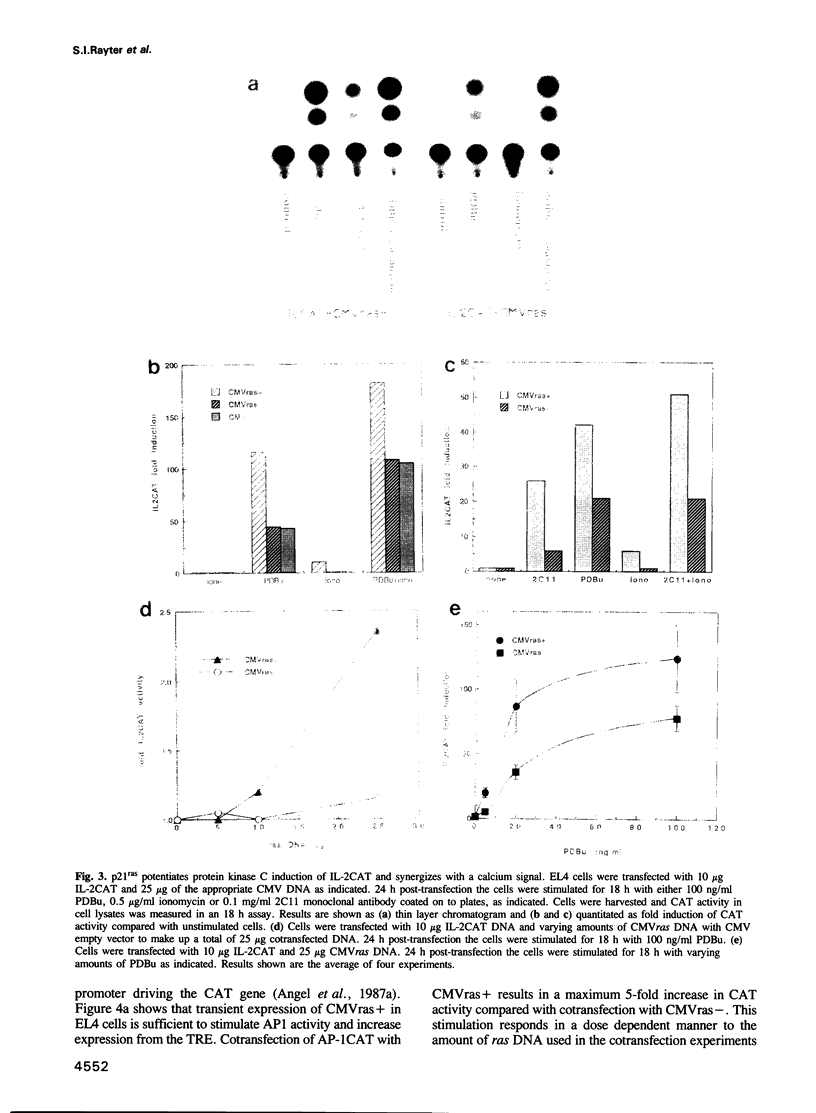
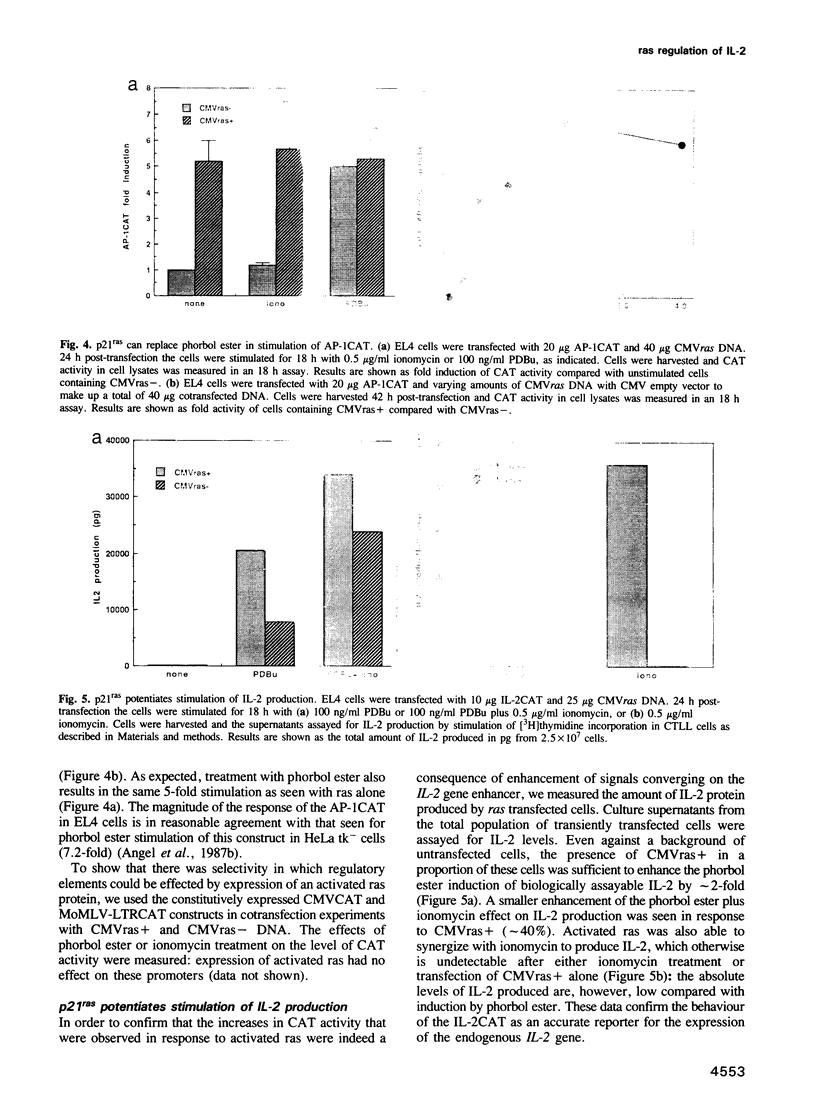
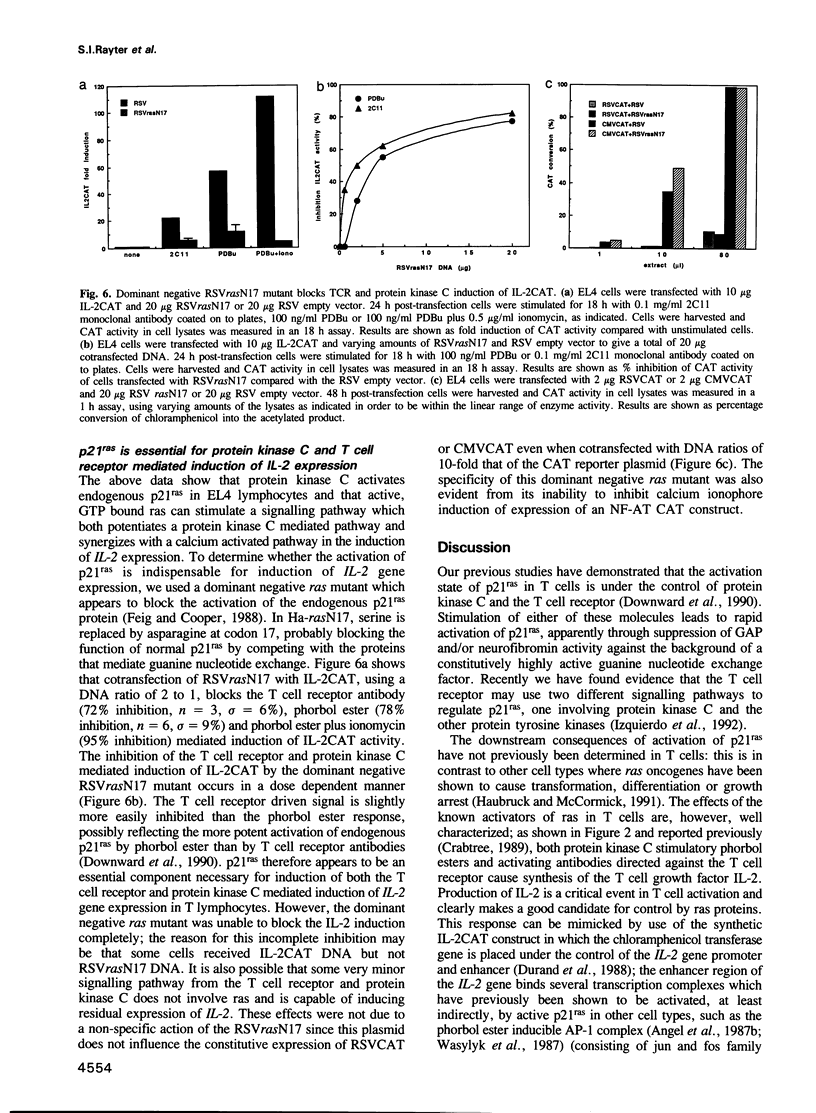
It has been shown previously in T cells that stimulation of protein kinase C or the T cell antigen receptor leads to a rapid and persistent activation of p21ras as measured by a dramatic increase in the amount of bound GTP. These stimuli are also known to induce the expression of the T lymphocyte growth factor, interleukin-2 (IL-2), an essential growth factor for the immune system. Receptor induced activation of p21ras has been demonstrated in several cell types but involvement of protein kinase C as an upstream activator of p21ras appears to be unique to T cells. In this study we show that p21ras acts as a component of the protein kinase C and T cell antigen receptor downstream signalling pathway controlling IL-2 gene expression. In the murine T cell line EL4, constitutively active p21ras greatly potentiates the phorbol ester and T cell receptor agonist induced production of IL-2 as measured both by biological assay for the cytokine and by the use of a reporter construct. Active p21ras also partially replaces the requirement for protein kinase C activation in synergizing with a calcium ionophore to induce production of IL-2. Furthermore, using a dominant negative mutant of ras, Ha-rasN17, we show that endogenous ras function is essential for induction of IL-2 expression in response to protein kinase C or T cell receptor stimulation. Activation of ras proteins is thus a necessary but not sufficient event in the induction of IL-2 synthesis. Ras proteins are therefore pivotal signalling molecules in T cell activation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Baumann I., Stein B., Delius H., Rahmsdorf H. J., Herrlich P. 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate induction of the human collagenase gene is mediated by an inducible enhancer element located in the 5'-flanking region. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2256–2266. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldari C. T., Macchia G., Telford J. L. Interleukin-2 promoter activation in T-cells expressing activated Ha-ras. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4289–4291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basu T. N., Gutmann D. H., Fletcher J. A., Glover T. W., Collins F. S., Downward J. Aberrant regulation of ras proteins in malignant tumour cells from type 1 neurofibromatosis patients. Nature. 1992 Apr 23;356(6371):713–715. doi: 10.1038/356713a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos J. L. ras oncogenes in human cancer: a review. Cancer Res. 1989 Sep 1;49(17):4682–4689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai H., Szeberényi J., Cooper G. M. Effect of a dominant inhibitory Ha-ras mutation on mitogenic signal transduction in NIH 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5314–5323. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabtree G. R. Contingent genetic regulatory events in T lymphocyte activation. Science. 1989 Jan 20;243(4889):355–361. doi: 10.1126/science.2783497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Graves J. D., Warne P. H., Rayter S., Cantrell D. A. Stimulation of p21ras upon T-cell activation. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):719–723. doi: 10.1038/346719a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Graves J., Cantrell D. The regulation and function of p21ras in T cells. Immunol Today. 1992 Mar;13(3):89–92. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90148-Z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J. Ras regulation: putting back the GTP. Curr Biol. 1992 Jun;2(6):329–331. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(92)90897-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J. Regulation of p21ras by GTPase activating proteins and guanine nucleotide exchange proteins. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1992 Feb;2(1):13–18. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80315-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durand D. B., Bush M. R., Morgan J. G., Weiss A., Crabtree G. R. A 275 basepair fragment at the 5' end of the interleukin 2 gene enhances expression from a heterologous promoter in response to signals from the T cell antigen receptor. J Exp Med. 1987 Feb 1;165(2):395–407. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.2.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durand D. B., Shaw J. P., Bush M. R., Replogle R. E., Belagaje R., Crabtree G. R. Characterization of antigen receptor response elements within the interleukin-2 enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1715–1724. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar J. J., Fuller-Farrar J., Simon P. L., Hilfiker M. L., Stadler B. M., Farrar W. L. Thymoma production of T cell growth factor (Interleukin 2). J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2555–2558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feig L. A., Cooper G. M. Inhibition of NIH 3T3 cell proliferation by a mutant ras protein with preferential affinity for GDP. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3235–3243. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth M. E., Davis L. J., Fleurdelys B., Scolnick E. M. Monoclonal antibodies to the p21 products of the transforming gene of Harvey murine sarcoma virus and of the cellular ras gene family. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):294–304. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.294-304.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutman A., Wasylyk B. Nuclear targets for transcription regulation by oncogenes. Trends Genet. 1991 Feb;7(2):49–54. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90231-E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haubruck H., McCormick F. Ras p21: effects and regulation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Dec 10;1072(2-3):215–229. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(91)90015-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hivroz-Burgaud C., Clipstone N. A., Cantrell D. A. Signaling requirements for the expression of the transactivating factor NF-AT in human T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Nov;21(11):2811–2819. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830211124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izquierdo M., Downward J., Graves J. D., Cantrell D. A. Role of protein kinase C in T-cell antigen receptor regulation of p21ras: evidence that two p21ras regulatory pathways coexist in T cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):3305–3312. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.3305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Samelson L. E. T cell antigen receptor activation pathways: the tyrosine kinase connection. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):875–878. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90310-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall C. J. How does p21ras transform cells? Trends Genet. 1991 Mar;7(3):91–95. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90278-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattila P. S., Ullman K. S., Fiering S., Emmel E. A., McCutcheon M., Crabtree G. R., Herzenberg L. A. The actions of cyclosporin A and FK506 suggest a novel step in the activation of T lymphocytes. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4425–4433. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07893.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medema R. H., Wubbolts R., Bos J. L. Two dominant inhibitory mutants of p21ras interfere with insulin-induced gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):5963–5967. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.5963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szeberényi J., Cai H., Cooper G. M. Effect of a dominant inhibitory Ha-ras mutation on neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5324–5332. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas S. M., DeMarco M., D'Arcangelo G., Halegoua S., Brugge J. S. Ras is essential for nerve growth factor- and phorbol ester-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of MAP kinases. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1031–1040. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90075-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk C., Imler J. L., Perez-Mutul J., Wasylyk B. The c-Ha-ras oncogene and a tumor promoter activate the polyoma virus enhancer. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):525–534. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90203-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood K. W., Sarnecki C., Roberts T. M., Blenis J. ras mediates nerve growth factor receptor modulation of three signal-transducing protein kinases: MAP kinase, Raf-1, and RSK. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1041–1050. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90076-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]