Abstract
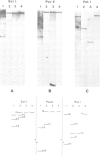
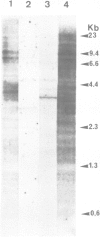
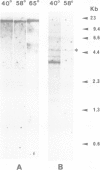
We have used Southern blot hybridization to analyze the genomic structure encoding the alpha-subunit of the acetylcholine receptor (AChR) in Torpedo marmorata, with cDNA probes isolated from the electric organ. Four different radiolabelled probes, corresponding to various parts of the alpha-subunit mRNA, hybridized to several genomic fragments of T. marmorata DNA generated by digestion with the restriction enzymes SstI, PvuII and PstI. The same hybridization pattern was observed after washing the blots under low- or high-stringency conditions. As a check for detection sensitivity of heterologous sequences, the same probes were hybridized to PvuII-digested chicken DNA, revealing bands at low stringency which disappeared at higher stringencies. Unambiguously, two of our probes (one of them entirely within the coding region) hybridized to a single genomic fragment from T. marmorata DNA. This feature, as well as the results of an extensive study of the whole hybridization pattern, points towards the uniqueness of alpha-subunit-specific sequences in the genome of T. marmorata. Since overall more bands were found than expected from the cDNA sequence, this alpha-subunit gene must be split by several introns (at least four, possibly more). The length of this gene is at least 20 kb. The existence of a single alpha-subunit gene is consistent with the absence of chemical heterogeneity in the NH2-terminal sequence of the purified alpha-chain, and supports the view that the two alpha-chains belonging to one AChR oligomer have an identical primary structure. It also suggests that localization and stabilization of the AChR in well-defined post-synaptic areas of T. marmorata electric organ basically relies, during development, on 'epigenetic' mechanisms.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballivet M., Patrick J., Lee J., Heinemann S. Molecular cloning of cDNA coding for the gamma subunit of Torpedo acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4466–4470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blin N., Stafford D. W. A general method for isolation of high molecular weight DNA from eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2303–2308. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner T. I., Brenner D. J., Neufeld B. R., Britten R. J. Reduction in the rate of DNA reassociation by sequence divergence. J Mol Biol. 1973 Dec 5;81(2):123–135. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90184-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner H. R., Sakmann B. Neurotrophic control of channel properties at neuromuscular synapses of rat muscle. J Physiol. 1983 Apr;337:159–171. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burden S. J., Sargent P. B., McMahan U. J. Acetylcholine receptors in regenerating muscle accumulate at original synaptic sites in the absence of the nerve. J Cell Biol. 1979 Aug;82(2):412–425. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.2.412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartaud J., Sobel A., Rousselet A., Devaux P. F., Changeux J. P. Consequences of alkaline treatment for the ultrastructure of the acetylcholine-receptor-rich membranes from Torpedo marmorata electric organ. J Cell Biol. 1981 Aug;90(2):418–426. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.2.418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P., Danchin A. Selective stabilisation of developing synapses as a mechanism for the specification of neuronal networks. Nature. 1976 Dec 23;264(5588):705–712. doi: 10.1038/264705a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P., Kasai M., Huchet M., Meunier J. C. Extraction à partir du tissu électrique de gymnote d'une protéine présentant plusieurs propriétés caractéristiques du récepteur physiologique de l'acétylcholine. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1970 Jun 8;270(23):2864–2867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P. The acetylcholine receptor: an "allosteric" membrane protein. Harvey Lect. 1979 1980;75:85–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claudio T., Ballivet M., Patrick J., Heinemann S. Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor gamma subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):1111–1115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti-Tronconi B. M., Gotti C. M., Hunkapiller M. W., Raftery M. A. Mammalian muscle acetylcholine receptor: a supramolecular structure formed by four related proteins. Science. 1982 Dec 17;218(4578):1227–1229. doi: 10.1126/science.7146904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti-Tronconi B. M., Hunkapiller M. W., Lindstrom J. M., Raftery M. A. Amino acid sequence homology between "alpha" subunits from Torpedo and Electrophorus acetylcholine receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 May 31;106(2):312–318. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91111-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti-Tronconi B. M., Raftery M. A. The nicotinic cholinergic receptor: correlation of molecular structure with functional properties. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:491–530. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.002423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. G., Gordon A. S., Diamond I. Specificity and localization of the acetylcholine receptor kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3666–3670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devillers-Thiery A., Changeux J. P., Paroutaud P., Strosberg A. D. The amino-terminal sequence of the 40,000 molecular weight subunit of the acetylcholine receptor protein from Torpedo marmorata. FEBS Lett. 1979 Aug 1;104(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81092-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devillers-Thiery A., Giraudat J., Bentaboulet M., Changeux J. P. Complete mRNA coding sequence of the acetylcholine binding alpha-subunit of Torpedo marmorata acetylcholine receptor: a model for the transmembrane organization of the polypeptide chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):2067–2071. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.2067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fambrough D. M. Control of acetylcholine receptors in skeletal muscle. Physiol Rev. 1979 Jan;59(1):165–227. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.1.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firtel R. A. Multigene families encoding actin and tubulin. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):6–7. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90494-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W. Why genes in pieces? Nature. 1978 Feb 9;271(5645):501–501. doi: 10.1038/271501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giraudat J., Devillers-Thiery A., Auffray C., Rougeon F., Changeux J. P. Identification of a cDNA clone coding for the acetylcholine binding subunit of Torpedo marmorata acetylcholine receptor. EMBO J. 1982;1(6):713–717. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01235.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godson G. N., Vapnek D. A simple method of preparing large amounts of phiX174 RF 1 supercoiled DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 11;299(4):516–520. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90223-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon A. S., Davis C. G., Diamond I. Phosphorylation of membrane proteins at a cholinergic synapse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):263–267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gysin R., Wirth M., Flanagan S. D. Structural heterogeneity and subcellular distribution of nicotinic synapse-associated proteins. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11373–11376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidmann O., Rougeon F. Multiple sequences related to a constant-region kappa light chain gene in the rabbit genome. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):507–513. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90205-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huganir R. L., Greengard P. cAMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylates the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):1130–1134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.1130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Strader C. D., Hood L., Raftery M. A. Amino terminal amino acid sequence of the major polypeptide subunit of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Nov 14;91(1):164–169. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90598-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inana G., Piatigorsky J., Norman B., Slingsby C., Blundell T. Gene and protein structure of a beta-crystallin polypeptide in murine lens: relationship of exons and structural motifs. Nature. 1983 Mar 24;302(5906):310–315. doi: 10.1038/302310a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. R., Piatigorsky J. Alternative RNA splicing of the murine alpha A-crystallin gene: protein-coding information within an intron. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):707–712. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90056-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosower E. M. Partial tertiary structure assignment for the acetylcholine receptor on the basis of the hydrophobicity of amino acid sequences and channel location using single group rotation theory. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Mar 29;111(3):1022–1026. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91402-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebhaber S. A., Goossens M., Kan Y. W. Homology and concerted evolution at the alpha 1 and alpha 2 loci of human alpha-globin. Nature. 1981 Mar 5;290(5801):26–29. doi: 10.1038/290026a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Merlie J., Yogeeswaran G. Biochemical properties of acteylcholine receptor subunits from Torpedo californica. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 16;18(21):4465–4470. doi: 10.1021/bi00588a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Walter B., Einarson B. Immunochemical similarities between subunits of acetylcholine receptors from Torpedo, Electrophorus, and mammalian muscle. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 16;18(21):4470–4480. doi: 10.1021/bi00588a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its thermal denaturation temperature. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jul;5:109–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlie J. P., Sebbane R. Acetylcholine receptor subunits transit a precursor pool before acquiring alpha-bungarotoxin binding activity. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3605–3608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelson A. M., Orkin S. H. The 3' untranslated regions of the duplicated human alpha-globin genes are unexpectedly divergent. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):371–377. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90347-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Molinoff P., Potter L. T. Isolation of the cholinergic receptor protein of Torpedo electric tissue. Nature. 1971 Feb 19;229(5286):554–557. doi: 10.1038/229554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A. J., Alonso S., Caravatti M., Buckingham M. E. A fetal skeletal muscle actin mRNA in the mouse and its identity with cardiac actin mRNA. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):185–192. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momoi M. Y., Lennon V. A. Purification and biochemical characterization of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors of human muscle. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12757–12764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Takahashi H., Tanabe T., Toyosato M., Furutani Y., Hirose T., Asai M., Inayama S., Miyata T., Numa S. Primary structure of alpha-subunit precursor of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor deduced from cDNA sequence. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):793–797. doi: 10.1038/299793a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Takahashi H., Tanabe T., Toyosato M., Kikyotani S., Furutani Y., Hirose T., Takashima H., Inayama S., Miyata T. Structural homology of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor subunits. Nature. 1983 Apr 7;302(5908):528–532. doi: 10.1038/302528a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Takahashi H., Tanabe T., Toyosato M., Kikyotani S., Hirose T., Asai M., Takashima H., Inayama S., Miyata T. Primary structures of beta- and delta-subunit precursors of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor deduced from cDNA sequences. Nature. 1983 Jan 20;301(5897):251–255. doi: 10.1038/301251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Gil A., Maniatis T. The structure of the human zeta-globin gene and a closely linked, nearly identical pseudogene. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):553–563. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90311-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raftery M. A., Hunkapiller M. W., Strader C. D., Hood L. E. Acetylcholine receptor: complex of homologous subunits. Science. 1980 Jun 27;208(4451):1454–1456. doi: 10.1126/science.7384786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. A., Karlin A. Molecular weight in detergent solution of acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. Biochemistry. 1978 May 30;17(11):2035–2038. doi: 10.1021/bi00604a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh T., Changeux J. P. Change in state of phosphorylation of acetylcholine receptor during maturation of the electromotor synapse in Torpedo marmorata electric organ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4430–4434. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh T., Oswald R., Wennogle L. P., Changeux J. P. Conditions for the selective labelling of the 66 000 dalton chain of the acetylcholine receptor by the covalent non-competitive blocker 5-azido-[3H]trimethisoquin. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jul 11;116(1):30–36. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80522-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh T., Wennogle L. P., Changeux J. P. Factors regulating the susceptibility of the acetylcholine receptor protein to heat inactivation. FEBS Lett. 1979 Dec 15;108(2):489–494. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80595-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. Conversion of RNA to DNA in mammals: Alu-like elements and pseudogenes. Nature. 1983 Feb 10;301(5900):471–472. doi: 10.1038/301471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel A., Heidmann T., Hofler J., Changeux J. P. Distinct protein components from Torpedo marmorata membranes carry the acetylcholine receptor site and the binding site for local anesthetics and histrionicotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):510–514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumikawa K., Houghton M., Smith J. C., Bell L., Richards B. M., Barnard E. A. The molecular cloning and characterisation of cDNA coding for the alpha subunit of the acetylcholine receptor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 11;10(19):5809–5822. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.19.5809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teichberg V. I., Sobel A., Changeux J. P. In vitro phosphorylation of the acetylcholine receptor. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):540–542. doi: 10.1038/267540a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]