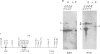Abstract
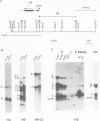
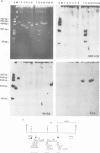
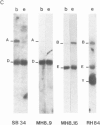
We have investigated the organization and transcription of several genes in Drosophila melanogaster which are clustered on an 18-kb cloned DNA fragment (c25) that maps at 99D on the cytogenetic map. Multiple mRNAs, transcribed from genes which lie adjacent to a ribosomal protein ( rp49 ) gene, are present during oogenesis, embryogenesis, or both. At least five mRNAs are transcribed from one of these genes ( EH8 ); three are zygotic transcripts, of which two are blastoderm stage-specific, whereas two others accumulate during oogenesis and are therefore matenal mRNAs. The complex transcription pattern of this gene indicates that alternate usage of protein-coding exons results in the production of different mRNAs with different coding capabilities during oogenesis and embryogenesis. The EH8 transcription unit is framed by genes actively expressed in the adult male fly; thus, the blastoderm stage-specific promoter may be silent although within a region of transcriptionally active chromatin.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson K. V., Lengyel J. A. Rates of synthesis of major classes of RNA in Drosophila embryos. Dev Biol. 1979 May;70(1):217–231. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90018-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arthur C. G., Weide C. M., Vincent W. S., 3rd, Goldstein E. S. mRNA sequence diversity during early embryogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Jun;121(1):87–94. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90447-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benyajati C., Spoerel N., Haymerle H., Ashburner M. The messenger RNA for alcohol dehydrogenase in Drosophila melanogaster differs in its 5' end in different developmental stages. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90341-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Spliced early mRNAs of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1274–1278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colot H. V., Rosbash M. Behavior of individual maternal pA+ RNAs during embryogenesis of Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1982 Nov;94(1):79–86. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90070-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dente L., Cesareni G., Cortese R. pEMBL: a new family of single stranded plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1645–1655. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald M., Shenk T. The sequence 5'-AAUAAA-3'forms parts of the recognition site for polyadenylation of late SV40 mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90521-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden L., Schafer U., Rosbash M. Accumulation of individual pA+ RNAs during oogenesis of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):835–844. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90560-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. R., Colot H. V., Guarente L., Rosbash M. Open reading frame cloning: identification, cloning, and expression of open reading frame DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6598–6602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbüchle O., Tosi M., Schibler U., Bovey R., Wellauer P. K., Young R. A. Mouse liver and salivary gland alpha-amylase mRNAs differ only in 5' non-translated sequences. Nature. 1981 Feb 19;289(5799):643–646. doi: 10.1038/289643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall L. M., Mason P. J., Spierer P. Transcripts, genes and bands in 315,000 base-pairs of Drosophila DNA. J Mol Biol. 1983 Sep 5;169(1):83–96. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80176-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hough-Evans B. R., Jacobs-Lorena M., Cummings M. R., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Complexity of RNA in eggs of Drosophila melanogaster and Musca domestica. Genetics. 1980 May;95(1):81–94. doi: 10.1093/genetics/95.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu N., Messing J. The making of strand-specific M13 probes. Gene. 1982 Mar;17(3):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90143-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefevre G., Jr The relationship between genes and polytene chromosome bands. Annu Rev Genet. 1974;8:51–62. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.08.120174.000411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsley D. L., Sandler L., Baker B. S., Carpenter A. T., Denell R. E., Hall J. C., Jacobs P. A., Miklos G. L., Davis B. K., Gethmann R. C. Segmental aneuploidy and the genetic gross structure of the Drosophila genome. Genetics. 1972 May;71(1):157–184. doi: 10.1093/genetics/71.1.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcu K. B., Valbuena O., Perry R. P. Isolation, purification, and properties of mouse heavy-chain immunoglobulin mRNAs. Biochemistry. 1978 May 2;17(9):1723–1733. doi: 10.1021/bi00602a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Miller O. L., Jr Ultrastructural patterns of RNA synthesis during early embryogenesis of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1976 Jun;8(2):305–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nüsslein-Volhard C., Wieschaus E. Mutations affecting segment number and polarity in Drosophila. Nature. 1980 Oct 30;287(5785):795–801. doi: 10.1038/287795a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozek C. E., Davidson N. Drosophila has one myosin heavy-chain gene with three developmentally regulated transcripts. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):23–34. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90493-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer G., Telford J., Baldari C., Pirrotta V. Isolation of cloned genes differentially expressed at early and late stages of Drosophila embryonic development. Dev Biol. 1981 Sep;86(2):438–447. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90202-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schibler U., Hagenbüchle O., Wellauer P. K., Pittet A. C. Two promoters of different strengths control the transcription of the mouse alpha-amylase gene Amy-1a in the parotid gland and the liver. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):501–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90431-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seif I., Khoury G., Dhar R. A rapid enzymatic DNA sequencing technique: determination of sequence alterations in early simian virus 40 temperature sensitive and deletion mutants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 24;8(10):2225–2240. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.10.2225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sina B. J., Pellegrini M. Genomic clones coding for some of the initial genes expressed during Drosophila development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7351–7355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spierer P., Spierer A., Bender W., Hogness D. S. Molecular mapping of genetic and chromomeric units in Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 25;168(1):35–50. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80321-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trumbly R. J., Jarry B. Stage-specific protein synthesis during early embryogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1983;2(8):1281–1290. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01582.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaslet C. A., O'Connell P., Izquierdo M., Rosbash M. Isolation and mapping of a cloned ribosomal protein gene of Drosophila melanogaster. Nature. 1980 Jun 26;285(5767):674–676. doi: 10.1038/285674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieschaus E., Gehring W. Clonal analysis of primordial disc cells in the early embryo of Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1976 Jun;50(2):249–263. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90150-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong Y. C., O'Connell P., Rosbash M., Elgin S. C. DNase I hypersensitive sites of the chromatin for Drosophila melanogaster ribosomal protein 49 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6749–6762. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalokar M. Autoradiographic study of protein and RNA formation during early development of Drosophila eggs. Dev Biol. 1976 Apr;49(2):425–437. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90185-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]