Abstract
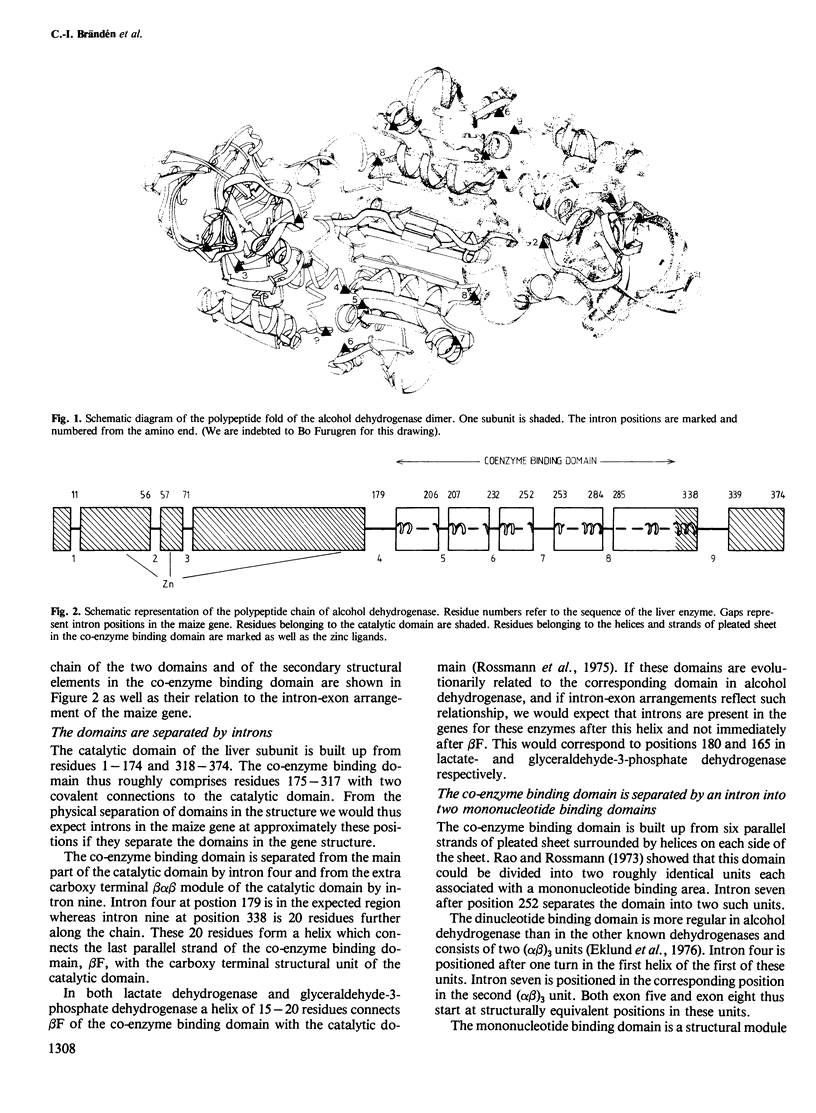
The intron/exon arrangement in the gene sequence of maize alcohol dehydrogenase has been compared to the three dimensional structure of liver alcohol dehydrogenase. The co-enzyme binding domain is separated from the catalytic domain by introns four and nine. Intron seven separates the co-enzyme binding domain into two structurally similar mononucleotide binding units. The first of these units is divided by introns five and six into three structurally similar alpha beta modules. Implications of these results for protein evolution is discussed. All splice junctions map close to or at the surface of the domains, and several of these cannot be identified by distance maps.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams M. J., Ford G. C., Koekoek R., Lentz P. J., McPherson A., Jr, Rossmann M. G., Smiley I. E., Schevitz R. W., Wonacott A. J. Structure of lactate dehydrogenase at 2-8 A resolution. Nature. 1970 Sep 12;227(5263):1098–1103. doi: 10.1038/2271098a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banner D. W., Bloomer A. C., Petsko G. A., Phillips D. C., Pogson C. I., Wilson I. A., Corran P. H., Furth A. J., Milman J. D., Offord R. E. Structure of chicken muscle triose phosphate isomerase determined crystallographically at 2.5 angstrom resolution using amino acid sequence data. Nature. 1975 Jun 19;255(5510):609–614. doi: 10.1038/255609a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennetzen J. L., Hall B. D. The primary structure of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene for alcohol dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3018–3025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake C. Exons--present from the beginning? Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):535–537. doi: 10.1038/306535a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brändeén C. I. Relation between structure and function of alpha/beta-proteins. Q Rev Biophys. 1980 Aug;13(3):317–338. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brändén C. I., Eklund H., Nordström B., Boiwe T., Söderlund G., Zeppezauer E., Ohlsson I., Akeson A. Structure of liver alcohol dehydrogenase at 2.9-angstrom resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2439–2442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buehner M., Ford G. C., Moras D., Olsen K. W., Rossman M. G. D-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase: three-dimensional structure and evolutionary significance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Nov;70(11):3052–3054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.11.3052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craik C. S., Sprang S., Fletterick R., Rutter W. J. Intron-exon splice junctions map at protein surfaces. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):180–182. doi: 10.1038/299180a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eklund H., Nordström B., Zeppezauer E., Söderlund G., Ohlsson I., Boiwe T., Söderberg B. O., Tapia O., Brändén C. I., Akeson A. Three-dimensional structure of horse liver alcohol dehydrogenase at 2-4 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1976 Mar 25;102(1):27–59. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90072-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W. Why genes in pieces? Nature. 1978 Feb 9;271(5645):501–501. doi: 10.1038/271501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jörnvall H. Horse liver alcohol dehydrogenase. The primary structure of an N-terminal part of the protein chain of the ethanol-active isoenzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Jul;14(3):521–534. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00319.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B., Richards F. M. The interpretation of protein structures: estimation of static accessibility. J Mol Biol. 1971 Feb 14;55(3):379–400. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90324-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindqvist Y., Brändén C. I. Structure of glycolate oxidase from spinach at a resolution of 5.5 A. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):201–211. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90198-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson I., Nordström B., Brändén C. I. Structural and functional similarities within the coenzyme binding domains of dehydrogenases. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 25;89(2):339–354. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90523-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao S. T., Rossmann M. G. Comparison of super-secondary structures in proteins. J Mol Biol. 1973 May 15;76(2):241–256. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90388-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann M. G., Moras D., Olsen K. W. Chemical and biological evolution of nucleotide-binding protein. Nature. 1974 Jul 19;250(463):194–199. doi: 10.1038/250194a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. W., Smith M., Williamson V. M., Young E. T. Nucleotide sequence of the yeast alcohol dehydrogenase II gene. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2674–2682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart D. I., Levine M., Muirhead H., Stammers D. K. Crystal structure of cat muscle pyruvate kinase at a resolution of 2.6 A. J Mol Biol. 1979 Oct 15;134(1):109–142. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90416-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



