Abstract
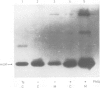
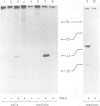
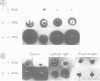
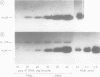
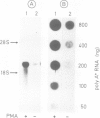
In mouse MSV-3T3 cells the synthesis of the urokinase form of plasminogen activator was increased 10-fold after addition of the tumor promoter phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate (PMA). PMA also stimulated the secretion of the protein into the culture medium, mostly in the form of enzymatically inactive pro-urokinase. When assayed by injecting RNA into Xenopus laevis oocytes, the concentration of functional urokinase mRNA was found to be 6- to 10-fold higher in the PMA-treated cells; a similar increase in urokinase mRNA content was measured by hybridisation with a mouse urokinase cDNA probe. Thus, the induction of plasminogen activator by PMA in MSV-3T3 cells is accounted for by an increased content of urokinase mRNA.
Full text
PDF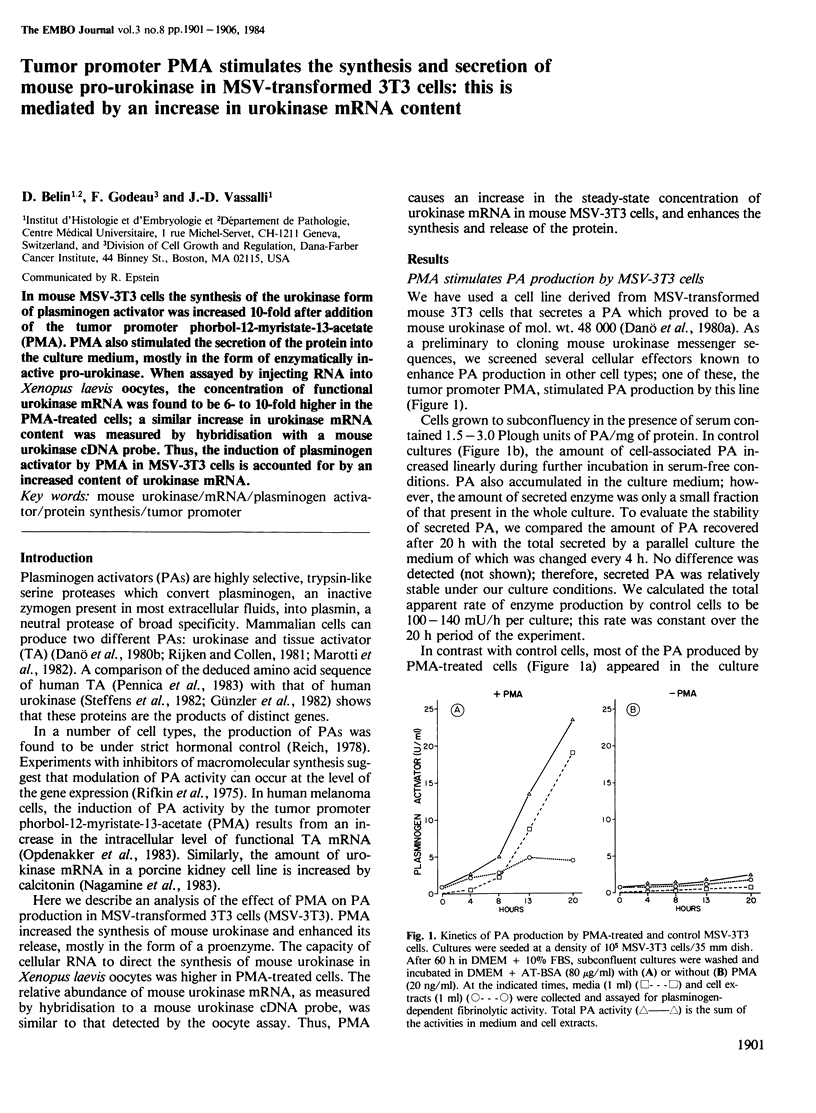





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker J. B., Low D. A., Simmer R. L., Cunningham D. D. Protease-nexin: a cellular component that links thrombin and plasminogen activator and mediates their binding to cells. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):37–45. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90112-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berenblum I., Armuth V. Two independent aspects of tumor promotion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Aug 31;651(1):51–63. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(81)90005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7847–7851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christman J. K., Copp R. P., Pedrinan L., Whalen C. E. Specificity of response in hamster cells induced to produce plasminogen activator by the tumor promoter, 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate. Cancer Res. 1978 Nov;38(11 Pt 1):3854–3860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danø K., Moller V., Ossowski L., Nielsen L. S. Purification and characterization of a plasminogen activator from mouse cells transformed by an oncogenic virus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jun 13;613(2):542–555. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90110-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danø K., Nielsen L. S., Møller V., Engelhart M. Inhibition of a plasminogen activator from oncogenic virus-transformed mouse cells by rabbit antibodies against the enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jun 5;630(1):146–151. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90146-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danø K., Reich E. Plasminogen activator from cells transformed by an oncogenic virus: inhibitors of the activation reaction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jan 12;566(1):138–151. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(79)90256-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch D. G., Mertz E. T. Plasminogen: purification from human plasma by affinity chromatography. Science. 1970 Dec 4;170(3962):1095–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton D. L., Baker J. B. Phorbol ester and mitogens stimulate human fibroblast secretions of plasmin-activatable plasminogen activator and protease nexin, an antiactivator/antiplasmin. J Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;97(2):323–328. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.2.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough N. M., Adams J. M. Immunoprecipitation of specific polysomes using Staphylococcus aureus: purification of the immunoglobulin k chain messenger RNA from the mouse myeloma MPC11. Biochemistry. 1978 Dec 12;17(25):5560–5566. doi: 10.1021/bi00618a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granelli-Piperno A., Reich E. A study of proteases and protease-inhibitor complexes in biological fluids. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):223–234. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granelli-Piperno A., Vassalli J. D., Reich E. Secretion of plasminogen activator by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Modulation by glucocorticoids and other effectors. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1693–1706. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Günzler W. A., Steffens G. J., Otting F., Kim S. M., Frankus E., Flohé L. The primary structure of high molecular mass urokinase from human urine. The complete amino acid sequence of the A chain. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1982 Oct;363(10):1155–1165. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1982.363.2.1155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiwasa T., Fujimura S., Sakiyama S. Tumor promoters increase the synthesis of a 32,000-dalton protein in BALB/c 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1800–1804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman-Liebermann B., Liebermann D., Sachs L. Regulation of gene expression by tumor promoters. III. Complementation of the developmental program in myeloid leukemic cells by regulating mRNA production and mRNA translation. Int J Cancer. 1981 Nov 15;28(5):615–620. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910280514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaken S., Black P. H. Regulation of plasminogen activator in 3T3 cells: effect of phorbol myristate acetate on subcellular distribution and molecular weight. J Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;90(3):727–731. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.3.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucherlapati R., Tepper R., Granelli-Piperno A., Reich E. Modulation and mapping of a human plasminogen activator by cell fusion. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1331–1340. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90058-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskin J. D., Mufson R. A., Piccinini L., Engelhardt D. L., Weinstein I. B. Effects of the tumor promoter 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate on newly synthesized proteins in mouse epidermis. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):441–449. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90062-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loskutoff D. J. Effects of acidified fetal bovine serum on the fibrinolytic activity and growth of cells in culture. J Cell Physiol. 1978 Sep;96(3):361–369. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040960312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markus G., Camiolo S. M., Kohga S., Madeja J. M., Mittelman A. Plasminogen activator secretion of human tumors in short-term organ culture, including a comparison of primary and metastatic colon tumors. Cancer Res. 1983 Nov;43(11):5517–5525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marotti K. R., Belin D., Strickland S. The production of distinct forms of plasminogen activator by mouse embryonic cells. Dev Biol. 1982 Mar;90(1):154–159. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90220-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miskin R., Soreq H. Microinjected Xenopus oocytes synthesize active human plasminogen activator. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 24;9(14):3355–3363. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.14.3355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagamine Y., Sudol M., Reich E. Hormonal regulation of plasminogen activator mRNA production in porcine kidney cells. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1181–1190. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90301-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opdenakker G., Ashino-Fuse H., Van Damme J., Billiau A., De Somer P. Effects of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate on the production of mRNAs for human tissue-type plasminogen activator. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Apr 5;131(3):481–487. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07287.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne R., Tashjian A. H., Jr Tumor-promoting phorbol esters affect production of prolactin and growth hormone by rat pituitary cells. Endocrinology. 1981 Apr;108(4):1164–1170. doi: 10.1210/endo-108-4-1164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossowski L., Reich E. Antibodies to plasminogen activator inhibit human tumor metastasis. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):611–619. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90093-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossowski L., Reich E. Experimental model for quantitative study of metastasis. Cancer Res. 1980 Jul;40(7):2300–2309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennica D., Holmes W. E., Kohr W. J., Harkins R. N., Vehar G. A., Ward C. A., Bennett W. F., Yelverton E., Seeburg P. H., Heyneker H. L. Cloning and expression of human tissue-type plasminogen activator cDNA in E. coli. Nature. 1983 Jan 20;301(5897):214–221. doi: 10.1038/301214a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijken D. C., Collen D. Purification and characterization of the plasminogen activator secreted by human melanoma cells in culture. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):7035–7041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skriver L., Nielsen L. S., Stephens R., Danø K. Plasminogen activator released as inactive proenzyme from murine cells transformed by sarcoma virus. Eur J Biochem. 1982 May 17;124(2):409–414. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06608.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffens G. J., Günzler W. A., Otting F., Frankus E., Flohé L. The complete amino acid sequence of low molecular mass urokinase from human urine. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1982 Sep;363(9):1043–1058. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1982.363.2.1043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Hamilton J., Reich E. Macrophage plasminogen activator: induction by concanavalin A and phorbol myristate acetate. Cell. 1977 Jul;11(3):695–705. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90086-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waller E. K., Schleuning W. D., Reich E. Complex-formation and inhibition of urokinase by blood plasma proteins. Biochem J. 1983 Oct 1;215(1):123–131. doi: 10.1042/bj2150123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Weinstein I. B. Tumour promotor induces plasminogen activator. Nature. 1976 Jan 22;259(5540):232–233. doi: 10.1038/259232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wun T. C., Ossowski L., Reich E. A proenzyme form of human urokinase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):7262–7268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YoungLai E. V., Godeau F., Mulvihill B., Baulieu E. E. Effects of cholera toxin and actinomycin on synthesis of [35s]methionine-labeled proteins during progesterone-induced maturation of Xenopus laevis oocytes. Dev Biol. 1982 May;91(1):36–42. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]