Abstract
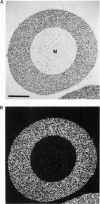
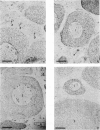
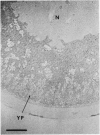
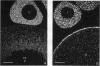
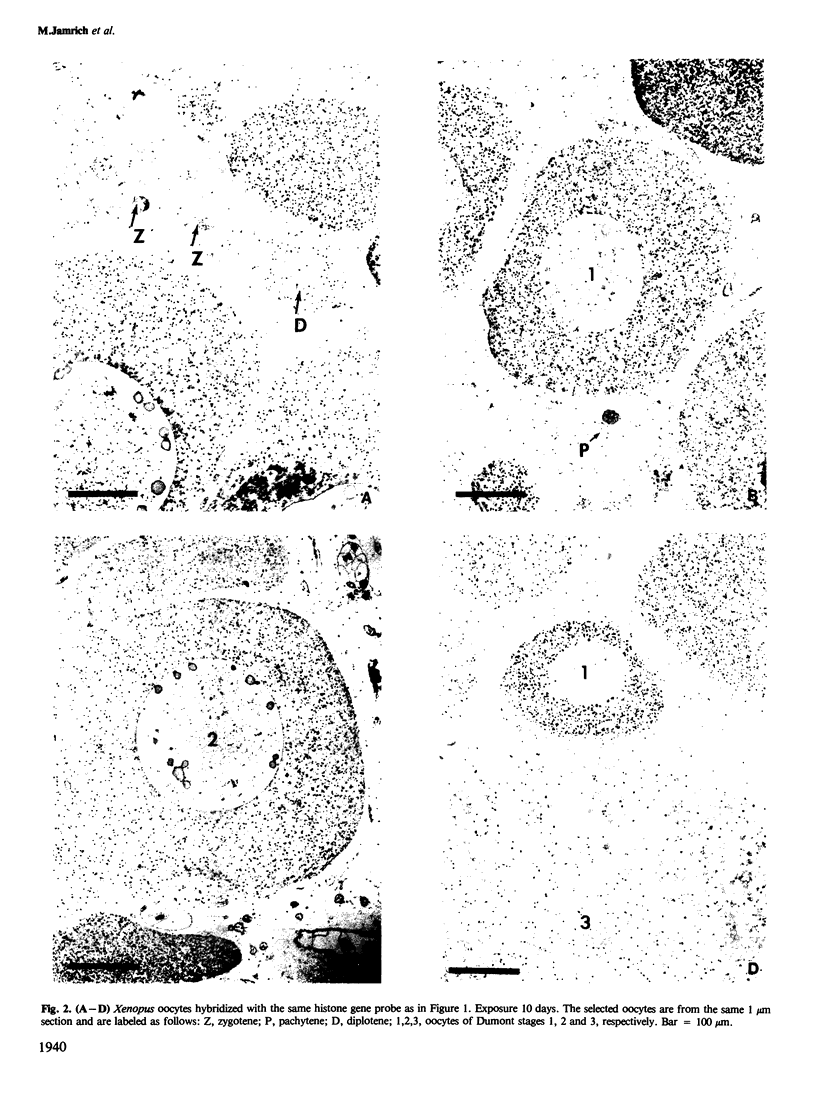
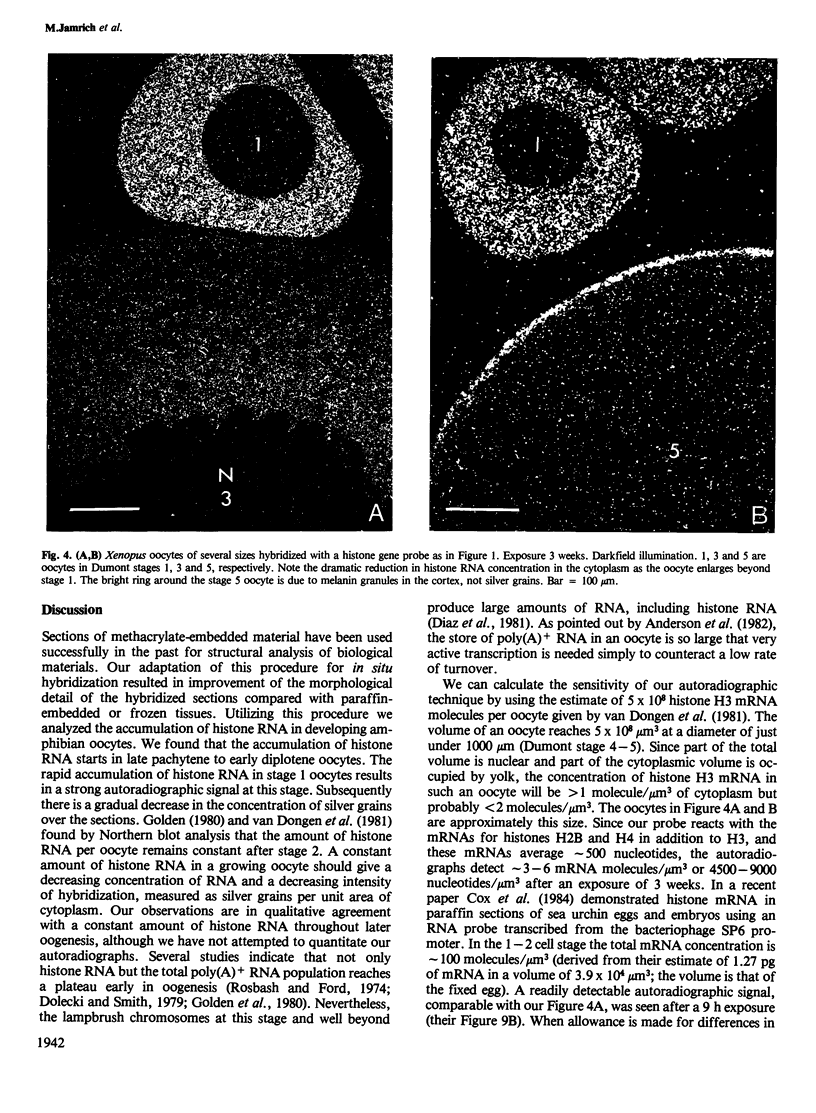
We present an in situ hybridization method for detecting cellular RNAs in tissue sections using methacrylate as the embedding medium. The technique offers the advantage of superior morphological preservation compared with previously published procedures. Since sections can be cut 1 micron or less in thickness, full advantage is taken of the short path length of 3H electrons. Applying this procedure to developing amphibian oocytes, we investigated the accumulation and localization of RNA complementary to the histone genes and their adjacent spacers. Histone RNA begins to accumulate in the cytoplasm of late pachytene-early diplotene oocytes, rapidly reaching a maximum concentration during Dumont stage 1. After this stage the concentration of histone RNA declines. RNA transcribed from histone coding regions is located almost exclusively in the cytoplasm of oocytes. Transcripts of the spacer regions, which are known to be synthesized on oocyte lampbrush chromosomes, do not accumulate in the oocytes. [3H]RNA complementary to U2 small nuclear RNA, used in these experiments as a control, hybridized predominantly to the nucleus of the oocytes.
Full text
PDF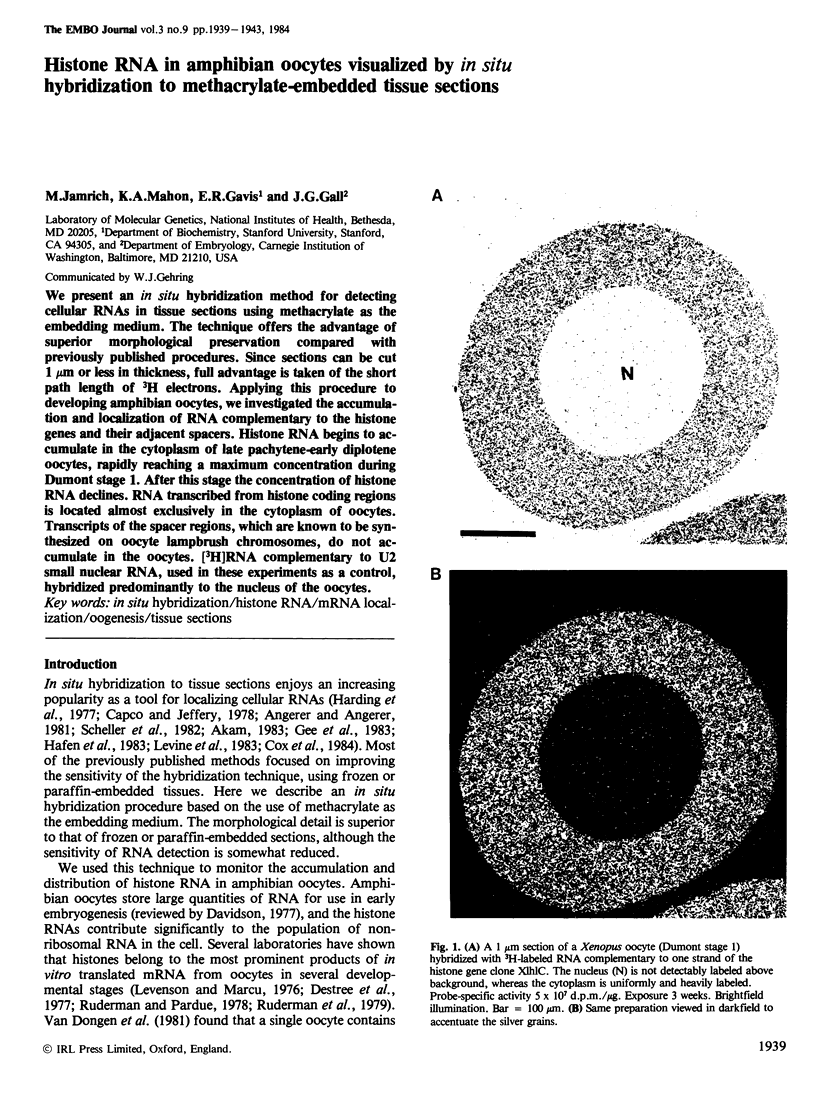


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akam M. E. The location of Ultrabithorax transcripts in Drosophila tissue sections. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):2075–2084. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01703.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. M., Richter J. D., Chamberlin M. E., Price D. H., Britten R. J., Smith L. D., Davidson E. H. Sequence organization of the poly(A) RNA synthesized and accumulated in lampbrush chromosome stage Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Mol Biol. 1982 Mar 5;155(3):281–309. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angerer L. M., Angerer R. C. Detection of poly A+ RNA in sea urchin eggs and embryos by quantitative in situ hybridization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2819–2840. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capco D. G., Jeffery W. R. Differential distribution of poly(A)-containing RNA in the embryonic cells of Oncopeltus fasciatus. Analysis by in situ hybridization with a [3H]poly(U) probe. Dev Biol. 1978 Nov;67(1):137–151. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90305-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox K. H., DeLeon D. V., Angerer L. M., Angerer R. C. Detection of mrnas in sea urchin embryos by in situ hybridization using asymmetric RNA probes. Dev Biol. 1984 Feb;101(2):485–502. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90162-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Destrée O. H., Haenni A. L., Birnstiel M. L. Histone mRNA in Xenopus laevis ovaries: identification of the H4 messenger. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Apr;4(4):801–811. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.4.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz M. O., Barsacchi-Pilone G., Mahon K. A., Gall J. G. Transcripts from both strands of a satellite DNA occur on lampbrush chromosome loops of the newt Notophthalmus. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):649–659. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90091-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolecki G. J., Smith L. D. Poly(A)+ RNA metabolism during oogenesis in Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1979 Mar;69(1):217–236. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90287-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont J. N. Oogenesis in Xenopus laevis (Daudin). I. Stages of oocyte development in laboratory maintained animals. J Morphol. 1972 Feb;136(2):153–179. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051360203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frangioni G., Borgioli G. Polystyrene embedding: a new method for light and electron microscopy. Stain Technol. 1979 Jul;54(4):167–172. doi: 10.3109/10520297909112678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gee C. E., Chen C. L., Roberts J. L., Thompson R., Watson S. J. Identification of proopiomelanocortin neurones in rat hypothalamus by in situ cDNA-mRNA hybridization. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):374–376. doi: 10.1038/306374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden L., Schafer U., Rosbash M. Accumulation of individual pA+ RNAs during oogenesis of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):835–844. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90560-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafen E., Levine M., Garber R. L., Gehring W. J. An improved in situ hybridization method for the detection of cellular RNAs in Drosophila tissue sections and its application for localizing transcripts of the homeotic Antennapedia gene complex. EMBO J. 1983;2(4):617–623. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01472.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding J. D., MacDonald R. J., Przybyla A. E., Chirgwin J. M., Pictet R. L., Rutter W. J. Changes in the frequency of specific transcripts during development of the pancreas. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7391–7397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levenson R. G., Marcu K. B. On the existence of polyadenylated histone mRNA in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Cell. 1976 Oct;9(2):311–322. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90121-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M., Hafen E., Garber R. L., Gehring W. J. Spatial distribution of Antennapedia transcripts during Drosophila development. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):2037–2046. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01697.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., Zeller R. Xenopus laevis U2 snRNA genes: tandemly repeated transcription units sharing 5' and 3' flanking homology with other RNA polymerase II transcribed genes. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):1883–1891. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01675.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardue M. L., Gall J. G. Nucleic acid hybridization to the DNA of cytological preparations. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;10:1–16. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60727-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosbash M. Polyadenylic acid-containing RNA in Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Mol Biol. 1974 May 5;85(1):87–101. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman J. V., Pardue M. L. A portion of all major classes of histone messenger RNA in amphibian oocytes is polyadenylated. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 25;253(6):2018–2025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman J. V., Woodland H. R., Sturgess E. A. Modulations of histone messenger RNA during the early development of Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1979 Jul;71(1):71–82. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90083-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheller R. H., Jackson J. F., McAllister L. B., Schwartz J. H., Kandel E. R., Axel R. A family of genes that codes for ELH, a neuropeptide eliciting a stereotyped pattern of behavior in Aplysia. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):707–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90050-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson E. C., Erba H. P., Gall J. G. Histone gene clusters of the newt notophthalmus are separated by long tracts of satellite DNA. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):639–647. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90090-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeller R., Nyffenegger T., De Robertis E. M. Nucleocytoplasmic distribution of snRNPs and stockpiled snRNA-binding proteins during oogenesis and early development in Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):425–434. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90462-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zernik M., Heintz N., Boime I., Roeder R. G. Xenopus laevis histone genes: variant H1 genes are present in different clusters. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):807–815. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90557-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dongen W., Zaal R., Moorman A., Destrée O. Quantitation of the accumulation of histone messenger RNA during oogenesis in Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1981 Sep;86(2):303–314. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90188-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]