Abstract
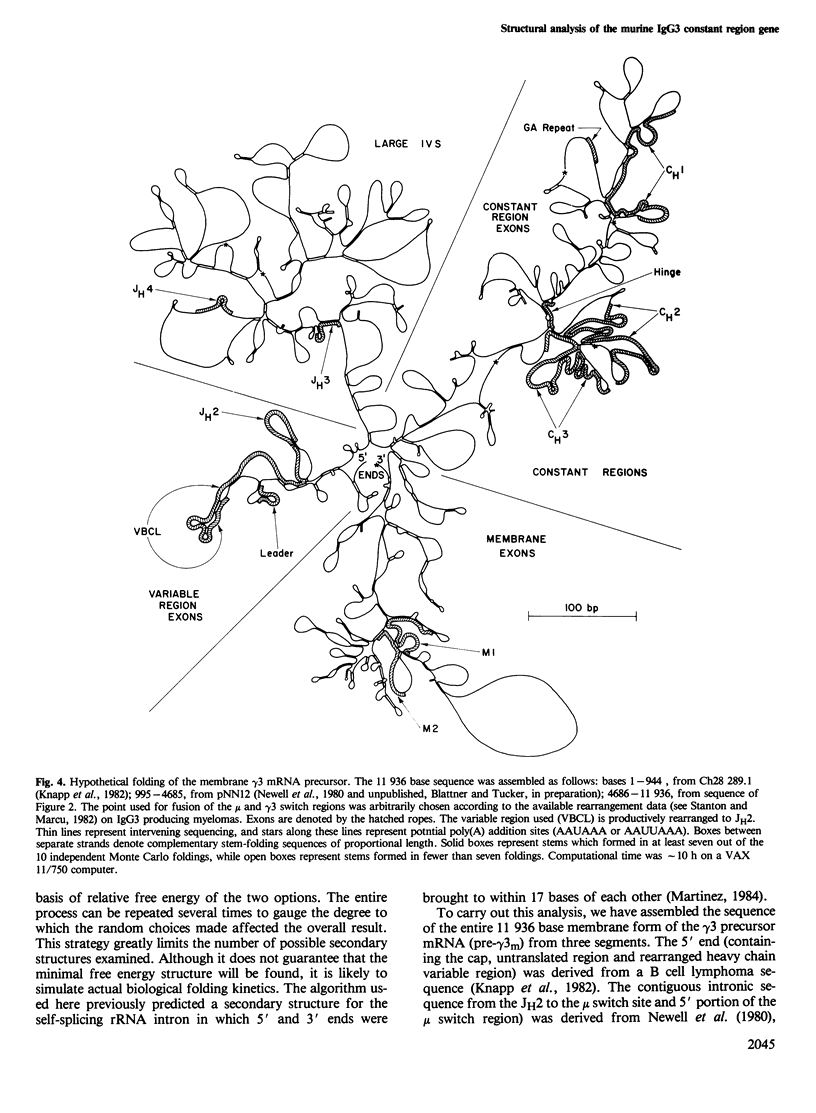
We have determined the complete sequence of the gamma 3 heavy chain constant (C gamma 3) region gene of the BALB/c mouse including the 5'-flanking region up to the switch site and the 3'-flanking region past the end of the membrane exons. The C gamma 3 coding region, typical of other IgGs, is divided into six exons corresponding to the protein domains (C gamma (3)1, hinge, C gamma (3)2, and C gamma (3)3) and to the membrane carboxyl terminus (M1 and M2). The predicted amino acid sequence of the gamma 3 chain has three potential N-linked carbohydrate addition sites (including one in the membrane spacer segment), as compared with a single occurrence in the other mouse IgGs. Between the switch recombination region and the body of the C gamma 3 gene, there is a remarkable homology with a sequence between C mu and C delta which provides a rationale for an alternative, T cell-independent class-switch mechanism. We have used a computer to analyze the secondary structure of the gamma 3 mRNA precursor for the membrane form. We predict that this RNA precursor (approximately 12 000 bp) folds into four leaf-like domains which correspond to the variable region, the large IVS, the body of the constant region, and the membrane exons. This organization may have a role to play in the function of the mRNA precursor.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. M., Webb E., Gerondakis S., Cory S. Cloned embryonic DNA sequences flanking the mouse immunoglobulin C gamma 3 and C gamma 1 genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):6019–6032. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.6019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Schroeder J. L. A computer package for DNA sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):615–617. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Tucker P. W. The molecular biology of immunoglobulin D. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):417–422. doi: 10.1038/307417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng H. L., Blattner F. R., Fitzmaurice L., Mushinski J. F., Tucker P. W. Structure of genes for membrane and secreted murine IgD heavy chains. Nature. 1982 Apr 1;296(5856):410–415. doi: 10.1038/296410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Eustachio P., Bothwell A. L., Takaro T. K., Baltimore D., Ruddle F. H. Chromosomal location of structural genes encoding murine immunoglobulin lambda light chains. Genetics of murine lambda light chains. J Exp Med. 1981 Apr 1;153(4):793–800. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.4.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumas J. P., Ninio J. Efficient algorithms for folding and comparing nucleic acid sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):197–206. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulton R. J., Nahm M. H., Davie J. M. Monoclonal antibodies to streptococcal group A carbohydrate. II. The VK1GAC light chain is preferentially associated with serum IgG3. J Immunol. 1983 Sep;131(3):1326–1331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T., Obata M., Yamawaki-Katoaka Y., Kataoka T., Kawakami T., Takahashi N., Mano Y. Cloning and complete nucleotide sequence of mouse immunoglobulin gamma 1 chain gene. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):559–568. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90072-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida N., Ueda S., Hayashida H., Miyata T., Honjo T. The nucleotide sequence of the mouse immunoglobulin epsilon gene: comparison with the human epsilon gene sequence. EMBO J. 1982;1(9):1117–1123. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01306.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp M. R., Liu C. P., Newell N., Ward R. B., Tucker P. W., Strober S., Blattner F. Simultaneous expression of immunoglobulin mu and delta heavy chains by a cloned B-cell lymphoma: a single copy of the VH gene is shared by two adjacent CH genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2996–3000. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komaromy M., Clayton L., Rogers J., Robertson S., Kettman J., Wall R. The structure of the mouse immunoglobulin in gamma 3 membrane gene segment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 11;11(19):6775–6785. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.19.6775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C. P., Tucker P. W., Mushinski J. F., Blattner F. R. Mapping of heavy chain genes for mouse immunoglobulins M and D. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1348–1353. doi: 10.1126/science.6774414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcu K. B. Immunoglobulin heavy-chain constant-region genes. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):719–721. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90431-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R. D. Glycoproteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1972;41:673–702. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.41.070172.003325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez H. M. An RNA folding rule. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):323–334. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKearn J. P., Paslay J. W., Slack J., Baum C., Davie J. M. B cell subsets and differential responses to mitogens. Immunol Rev. 1982;64:5–23. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00416.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyata T., Yasunaga T., Yamawaki-Kataoka Y., Obata M., Honjo T. Nucleotide sequence divergence of mouse immunoglobulin gamma 1 and gamma 2b chain genes and the hypothesis of intervening sequence-mediated domain transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2143–2147. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mongini P. K., Paul W. E., Metcalf E. S. T cell regulation of immunoglobulin class expression in the antibody response to trinitrophenyl-ficoll. Evidence for T cell enhancement of the immunoglobulin class switch. J Exp Med. 1982 Mar 1;155(3):884–902. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.3.884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newell N., Richards J. E., Tucker P. W., Blattner F. R. J genes for heavy chain immunoglobulins of mouse. Science. 1980 Sep 5;209(4461):1128–1132. doi: 10.1126/science.6250219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido T., Nakai S., Honjo T. Switch region of immunoglobulin Cmu gene is composed of simple tandem repetitive sequences. Nature. 1981 Aug 27;292(5826):845–848. doi: 10.1038/292845a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido T., Yamawaki-Kataoka Y., Honjo T. Nucleotide sequences of switch regions of immunoglobulin C epsilon and C gamma genes and their comparison. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7322–7329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmutter R. M., Hansburg D., Briles D. E., Nicolotti R. A., Davie J. M. Subclass restriction of murine anti-carbohydrate antibodies. J Immunol. 1978 Aug;121(2):566–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter M. Immunoglobulin-producing tumors and myeloma proteins of mice. Physiol Rev. 1972 Jul;52(3):631–719. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1972.52.3.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Choi E., Souza L., Carter C., Word C., Kuehl M., Eisenberg D., Wall R. Gene segments encoding transmembrane carboxyl termini of immunoglobulin gamma chains. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(1 Pt 1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90029-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakano H., Maki R., Kurosawa Y., Roeder W., Tonegawa S. Two types of somatic recombination are necessary for the generation of complete immunoglobulin heavy-chain genes. Nature. 1980 Aug 14;286(5774):676–683. doi: 10.1038/286676a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu A., Takahashi N., Yaoita Y., Honjo T. Organization of the constant-region gene family of the mouse immunoglobulin heavy chain. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):499–506. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90204-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack J., Der-Balian G. P., Nahm M., Davie J. M. Subclass restriction of murine antibodies. II. The IgG plaque-forming cell response to thymus-independent type 1 and type 2 antigens in normal mice and mice expressing an X-linked immunodeficiency. J Exp Med. 1980 Apr 1;151(4):853–862. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.4.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton L. W., Marcu K. B. Nucleotide sequence and properties of the murine gamma 3 immunoglobulin heavy chain gene switch region: implications for successive C gamma gene switching. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 11;10(19):5993–6006. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.19.5993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker P. W., Marcu K. B., Newell N., Richards J., Blattner F. R. Sequence of the cloned gene for the constant region of murine gamma 2b immunoglobulin heavy chain. Science. 1979 Dec 14;206(4424):1303–1306. doi: 10.1126/science.117549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Word C. J., Mushinski J. F., Tucker P. W. The murine immunoglobulin alpha gene expresses multiple transcripts from a unique membrane exon. EMBO J. 1983;2(6):887–898. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01518.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamawaki-Kataoka Y., Miyata T., Honjo T. The complete nucleotide sequence of mouse immunoglobin gamma 2a gene and evolution of heavy chain genes: further evidence for intervening sequence-mediated domain transfer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 25;9(6):1365–1381. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.6.1365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M., Stiegler P. Optimal computer folding of large RNA sequences using thermodynamics and auxiliary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):133–148. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



