Abstract
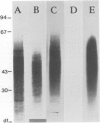
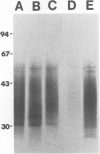
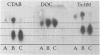
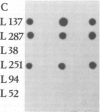
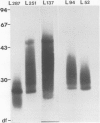
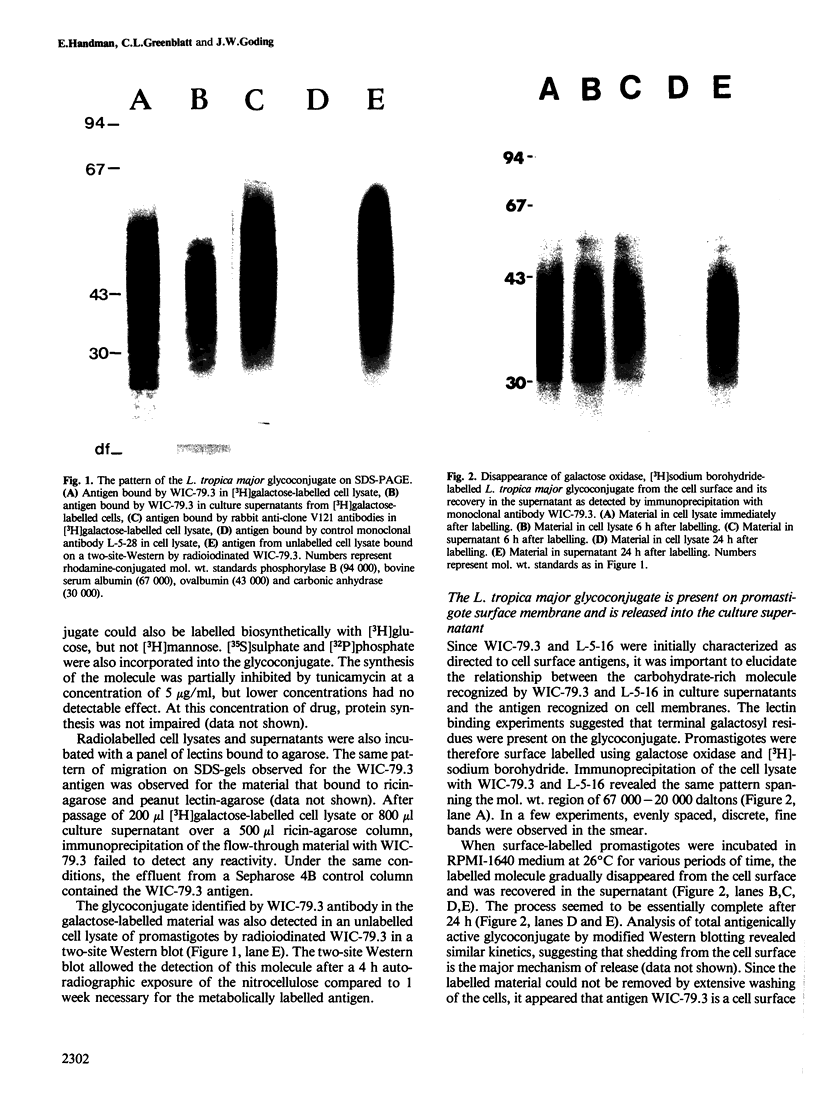
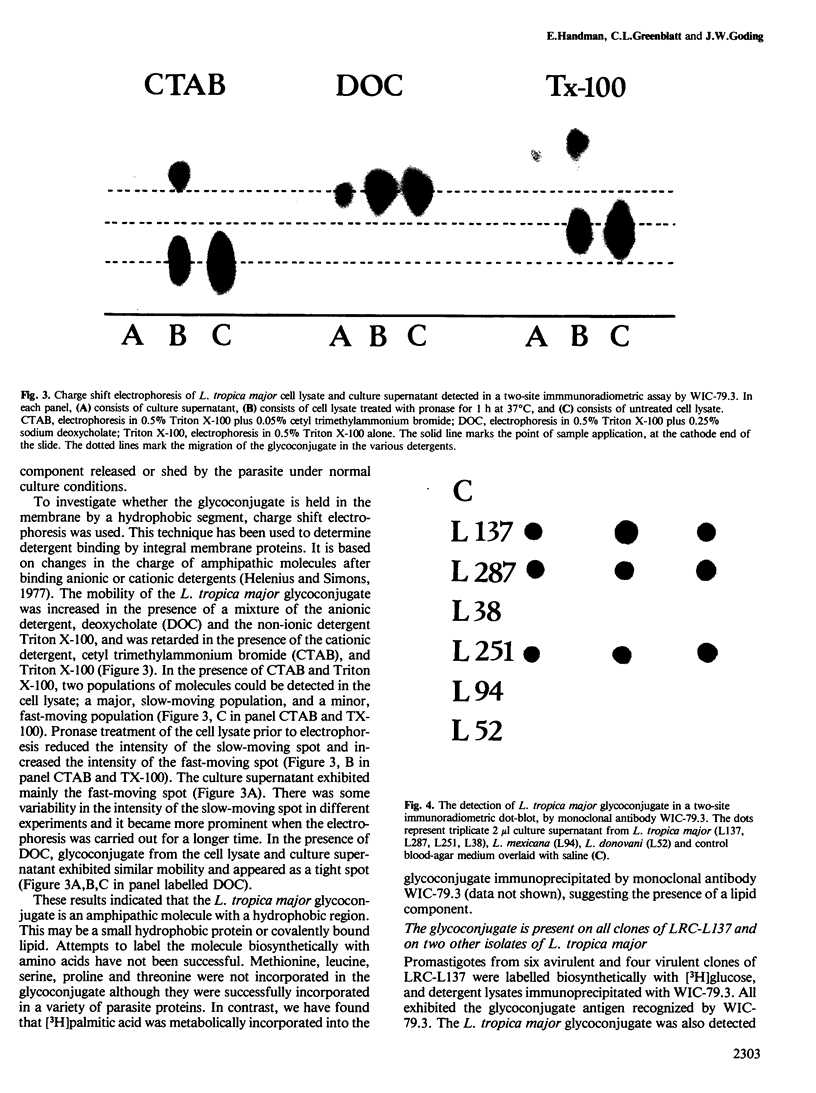
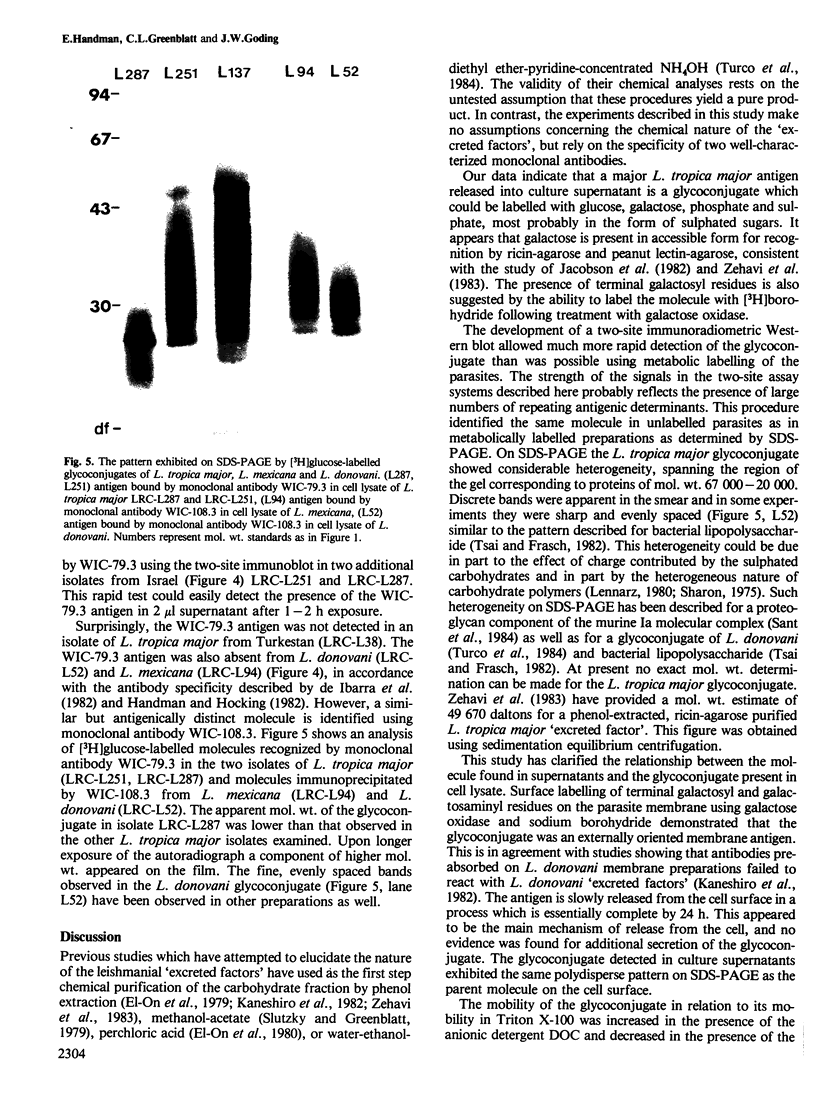
A major glycoconjugate of Leishmania tropica major identified by two monoclonal antibodies was shown to be an externally oriented, amphipathic membrane antigen shed into the culture medium in which the parasites grow. This molecule could be labelled metabolically with [3H]glucose, [3H]galactose, [32P]phosphate and [35S]sulphate. It migrated as a polydisperse band upon electrophoresis in SDS-polyacrylamide gels, spanning the region of the gel corresponding to an apparent mol. wt. of 20 000-67 000 daltons. An apparently identical family of molecules could be labelled on the surface of living promastigotes using galactose oxidase and [3H]-sodium borohydride. This molecule was shown to be released into the supernatant over a period of several hours. Detection of the 3H- or 35S-labelled molecule required several days exposure of autoradiographs, but a novel blotting technique using nitrocellulose coated with monoclonal antibody allowed rapid detection of the molecule in charge shift electrophoresis, Western blotting and dot blotting. The electrophoretic mobility of the glycoconjugate in agarose relative to its mobility in Triton X-100 was increased in the presence of deoxycholate, and decreased in the presence of cetyl trimethyl-ammonium bromide, indicating amphipathic properties consistent with insertion into the lipid bilayer of the membrane. Using the dot-blotting technique the glycoconjugate was detected in all virulent and avirulent clones of LRC-L137 and in two additional isolates of L. tropica major (LRC-L287 and LRC-L251), but not in L. donovani or L. mexicana, consistent with the previously described specificity of the antibodies. However, the general approaches used in this paper showed that L. donovani (LRC-L52) and L. mexicana (LRC-L94) synthesize a similar, but antigenically distinct glycoconjugate.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- El-On J., Bradley D. J., Freeman J. C. Leishmania donovani: action of excreted factor on hydrolytic enzyme activity of macrophages from mice with genetically different resistance to infection. Exp Parasitol. 1980 Apr;49(2):167–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(80)90114-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-On J., Schnur L. F., Greenblatt C. L. Leishmania donovani: physicochemical, immunological, and biological characterization of excreted factor from promastigotes. Exp Parasitol. 1979 Apr;47(2):254–269. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(79)90078-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahmberg C. G., Hakomori S. I. External labeling of cell surface galactose and galactosamine in glycolipid and glycoprotein of human erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 25;248(12):4311–4317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt C. L., Slutzky G. M., de Ibarra A. A., Snary D. Monoclonal antibodies for serotyping Leishmania strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jul;18(1):191–193. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.1.191-193.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handman E., Greenblatt C. L. Promotion of leishmanial infections in non-permissive host macrophages by conditioned medium. Z Parasitenkd. 1977 Sep 21;53(2):143–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00380458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handman E., Hocking R. E., Mitchell G. F., Spithill T. W. Isolation and characterization of infective and non-infective clones of Leishmania tropica. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1983 Feb;7(2):111–126. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(83)90039-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handman E., Hocking R. E. Stage-specific, strain-specific, and cross-reactive antigens of Leishmania species identified by monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):28–33. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.28-33.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handman E., Mitchell G. F., Goding J. W. Identification and characterization of protein antigens of Leishmania tropica isolates. J Immunol. 1981 Feb;126(2):508–512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Simons K. Charge shift electrophoresis: simple method for distinguishing between amphiphilic and hydrophilic proteins in detergent solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):529–532. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez A. G., Rodriguez N., Dagger F., Greenblatt C. L. Production and secretion of Leishmania braziliensis proteins. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1980 Jun;1(3):143–149. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(80)90013-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernández A. G. Leishmanial excreted factors and their possible biological role. Ciba Found Symp. 1983;99:138–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson R. L., Slutzky G. M., Greenblatt C. L., Schnur L. F. Surface reaction of Leishmania. I. Lectin-mediated agglutination. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1982 Feb;76(1):45–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneshiro E. S., Gottlieb M., Dwyer D. M. Cell surface origin of antigens shed by Leishmania donovani during growth in axenic culture. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):558–567. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.558-567.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Use of protein A-bearing staphylococci for the immunoprecipitation and isolation of antigens from cells. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):442–459. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Enhanced autoradiographic detection of 32P and 125I using intensifying screens and hypersensitized film. FEBS Lett. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):314–316. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80609-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell G. F., Handman E. Leishmania tropica major in mice: vaccination against cutaneous leishmaniasis in mice of high genetic susceptibility. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1983 Feb;61(Pt 1):11–25. doi: 10.1038/icb.1983.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sant A. J., Schwartz B. D., Cullen S. E. Identification of a new component in the murine Ia molecular complex. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):1979–1992. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnur L. F., Zuckerman A., Greenblatt C. L. Leishmanial serotypes as distinguished by the gel diffusion of factors excreted in vitro and in vivo. Isr J Med Sci. 1972 Jul;8(7):932–942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semprevivo L. H., MacLeod M. E. Characterization of the exometabolite of Leishmania donovani as a novel glycopeptidophosphosphingolipid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Dec 31;103(4):1179–1185. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90247-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortman K., Williams N., Adams P. The separation of different cell classes from lymphoid organs. V. Simple procedures for the removal of cell debris. Damaged cells and erythroid cells from lymphoid cell suspensions. J Immunol Methods. 1972 May;1(3):273–287. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(72)90005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slutzky G. M., El-On J., Greenblatt C. L. Leishmanial excreted factor: protein-bound and free forms from promastigote cultures of Leishmania tropica and Leishmania donovani. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):916–924. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.916-924.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slutzky G. M., Greenblatt C. L. Analysis by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of an immunologically active factor of Leishmania tropica from growth media, promastigotes, and infected macrophages. Biochem Med. 1979 Feb;21(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(79)90057-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slutzky G. M., Greenblatt C. L. Isolation of a carbohydrate-rich immunologically active factor from cultures of Leishmania tropica. FEBS Lett. 1977 Aug 15;80(2):401–404. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80485-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOBIE E. J., VON BRAND T., MEHLMAN B. Cultural and physiological observations on Trypanosoma rhodesiense and Trypanosoma gambiense. J Parasitol. 1950 Feb;36(1):48–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco S. J., Wilkerson M. A., Clawson D. R. Expression of an unusual acidic glycoconjugate in Leishmania donovani. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3883–3889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yelton D. E., Desaymard C., Scharff M. D. Use of monoclonal anti-mouse immunoglobulin to detect mouse antibodies. Hybridoma. 1981;1(1):5–11. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1.1981.1.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zehavi U., Abrahams J. C., Granoth R., Greenblatt C. L., Slutzky G. M., El-On J. Leishmanial excreted factors (EFs): purification by affinity chromatography. Z Parasitenkd. 1983;69(6):695–701. doi: 10.1007/BF00927419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Ibarra A. A., Howard J. G., Snary D. Monoclonal antibodies to Leishmania tropica major: specificities and antigen location. Parasitology. 1982 Dec;85(Pt 3):523–531. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000056304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]