Abstract
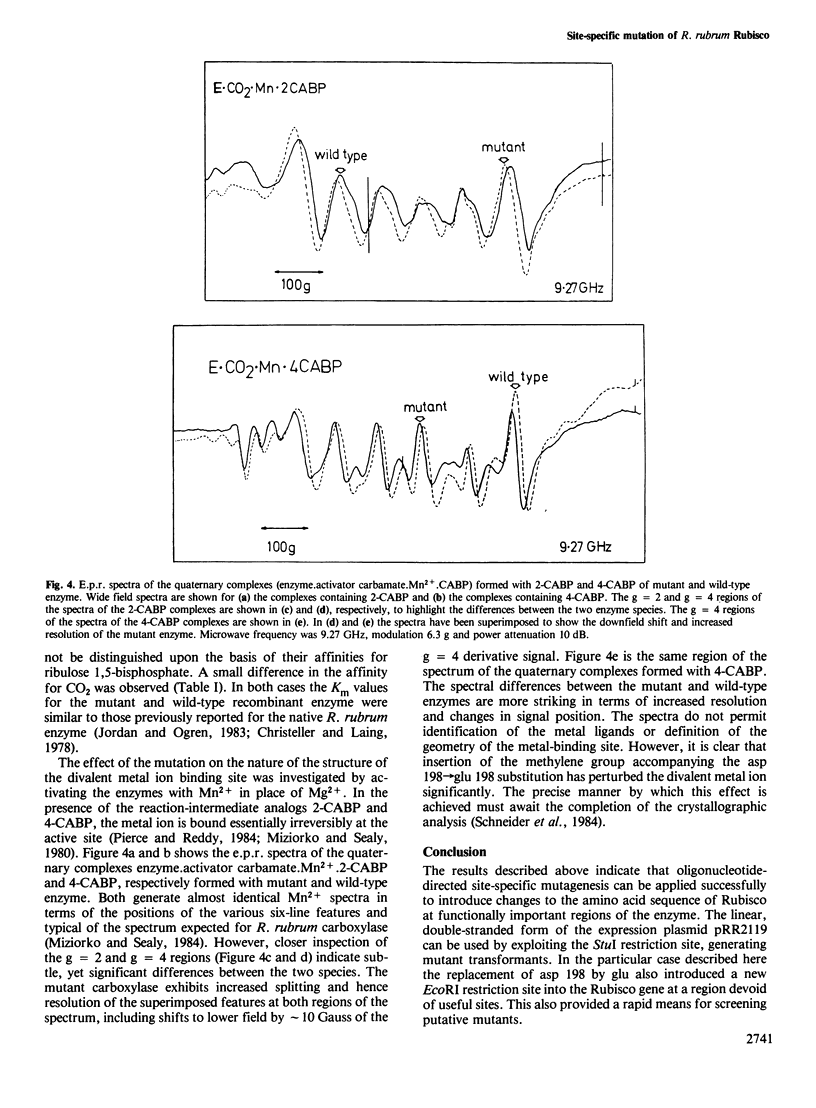
In vitro mutagenic techniques have generated an asp→glu substitution at residue 198 adjacent to the carbamate-divalent metal ion binding site of Rhodospirillum rubrum ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. A single C→A nucleotide change in the coding strand created the mutant and introduced a new EcoRI restriction site on the expression plasmid pRR2119. Although the carboxylase:oxygenase ratio remained the same, the mutant enzyme had slightly altered kinetic properties. The e.p.r. spectra of the quaternary complexes enzyme.activator carbamate.Mn2+.2-carboxyarabinitol 1,5-bisphosphate and enzyme.activator carbamate.Mn2+.4-carboxyarabinitol 1,5-bisphosphate for mutant and wild-type enzymes were different, indicating that the metal ion was in a slightly altered environment. These findings are consistent with the hypothesis that, besides the carbamate at lys 201, the carboxyl group of asp 198 contributes to the formation of the divalent metal ion binding site.
Keywords: active site, in vitro mutagenesis, site-specific mutation, ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews T. J., Ballment B. The function of the small subunits of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7514–7518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christeller J. T., Laing W. A. A kinetic study of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase from the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodospirillum rubrum. Biochem J. 1978 Aug 1;173(2):467–473. doi: 10.1042/bj1730467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christeller J. T. The effects of bivalent cations on ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase. Biochem J. 1981 Mar 1;193(3):839–844. doi: 10.1042/bj1930839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalbadie-McFarland G., Cohen L. W., Riggs A. D., Morin C., Itakura K., Richards J. H. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis as a general and powerful method for studies of protein function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6409–6413. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraij B., Hartman F. C. Isolation and sequencing of an active-site peptide from Rhodospirillum rubrum ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase after affinity labeling with 2-[(bromoacetyl)amino]pentitol 1,5-bisphosphate. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 15;22(6):1515–1520. doi: 10.1021/bi00275a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz H. J., Belagaje R., Brown E. L., Fritz R. H., Jones R. A., Lees R. G., Khorana H. G. High-pressure liquid chromatography in polynucleotide synthesis. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 4;17(7):1257–1267. doi: 10.1021/bi00600a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman F. C., Stringer C. D., Omnaas J., Donnelly M. I., Fraij B. Purification and sequencing of cyanogen bromide fragments from ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase from Rhodospirillum rubrum. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Dec;219(2):422–437. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herndon C. S., Hartman F. C. 2-(4-Bromoacetamido)anilino-2-deoxypentitol 1,5-bisphosphate, a new affinity label for ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase from Rhodospirillum rubrum. Determination of reaction parameters and characterization of an active site peptide. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3102–3110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herndon C. S., Norton I. L., Hartman F. C. Reexamination of the binding site for pyridoxal 5'-phosphate in ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase from Rhodospirillum rubrum. Biochemistry. 1982 Mar 16;21(6):1380–1385. doi: 10.1021/bi00535a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan D. B., Ogren W. L. Species variation in kinetic properties of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Dec;227(2):425–433. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90472-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorimer G. H., Badger M. R., Andrews T. J. D-Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase. Improved methods for the activation and assay of catalytic activities. Anal Biochem. 1977 Mar;78(1):66–75. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorimer G. H., Miziorko H. M. Carbamate formation on the epsilon-amino group of a lysyl residue as the basis for the activation of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase by CO2 and Mg2+. Biochemistry. 1980 Nov 11;19(23):5321–5328. doi: 10.1021/bi00564a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorimer G. H. Ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase: amino acid sequence of a peptide bearing the activator carbon dioxide. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 3;20(5):1236–1240. doi: 10.1021/bi00508a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden B. A. The oxygenase activity of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from Rhodospirillum rubrum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Sep 9;60(1):312–317. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90206-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miziorko H. M., Behnke C. E., Houkom E. C. Protein liganding to the activator cation of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 21;21(26):6669–6674. doi: 10.1021/bi00269a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miziorko H. M., Lorimer G. H. Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:507–535. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.002451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miziorko H. M., Sealy R. C. Characterization of the ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase-carbon dioxide-divalent cation-carboxypentitol bisphosphate complex. Biochemistry. 1980 Mar 18;19(6):1167–1171. doi: 10.1021/bi00547a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce J., Tolbert N. E., Barker R. Interaction of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase with transition-state analogues. Biochemistry. 1980 Mar 4;19(5):934–942. doi: 10.1021/bi00546a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schloss J. V., Lorimer G. H. The stereochemical course of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase. Reductive trapping of the 6-carbon reaction-intermediate. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):4691–4694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider G., Brändén C. I., Lorimer G. Preliminary X-ray diffraction study of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from Rhodospirillum rubrum. J Mol Biol. 1984 May 5;175(1):99–102. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90450-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigal I. S., Harwood B. G., Arentzen R. Thiol-beta-lactamase: replacement of the active-site serine of RTEM beta-lactamase by a cysteine residue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7157–7160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., McFadden B. A. D-ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase from Rhodospirillum rubrum. II. Quaternary structure, composition, catalytic, and immunological properties. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3459–3464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson A. J., Fersht A. R., Blow D. M., Carter P., Winter G. A large increase in enzyme-substrate affinity by protein engineering. Nature. 1984 Jan 12;307(5947):187–188. doi: 10.1038/307187a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter G., Fersht A. R., Wilkinson A. J., Zoller M., Smith M. Redesigning enzyme structure by site-directed mutagenesis: tyrosyl tRNA synthetase and ATP binding. Nature. 1982 Oct 21;299(5885):756–758. doi: 10.1038/299756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]