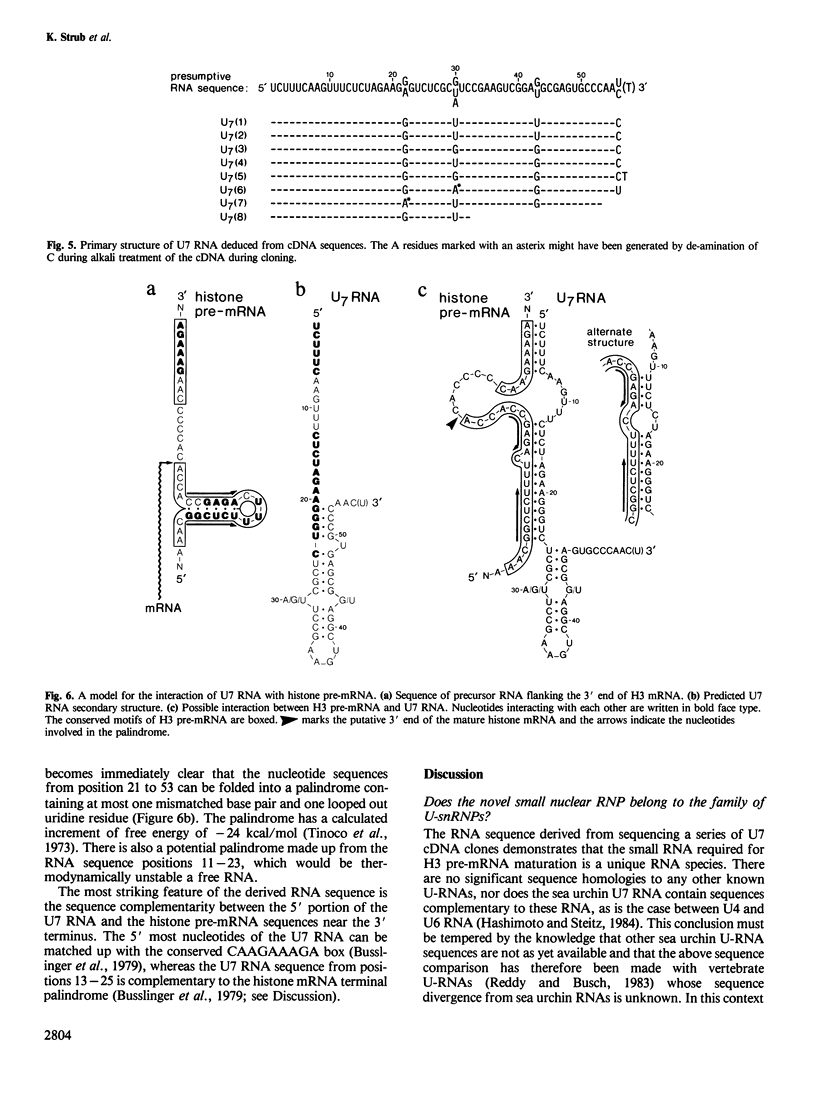
Abstract
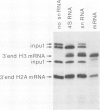
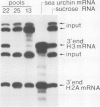
3' Processing of sea urchin H3 histone pre-mRNA depends on a small nuclear RNP which contains an RNA of nominally 60 nucleotide length, referred to below as U7 RNA. The U7 RNA can be enriched by precipitation of sea urchin U-snRNPs with human systematic lupus erythematosus antiserum of the Sm serotype. We have prepared cDNA clones of U7 RNA and determined by hybridization techniques that this RNA is present in sea urchin eggs at 30-fold lower molar concentration than U1 RNA. The RNA sequences derived from an analysis of eight U7 cDNA clones show neither homologies nor complementarities to any other know U-RNAs. The 3' portion of the presumptive RNA sequence can be folded into a stem-loop structure. The 5'-terminal sequences would be largely unstructured as free RNA. Their most striking feature is their base complementarity to the 3' conserved sequences of histone pre-mRNAs. Six out of nine bases of the conserved CAAGAAAGA sequence of the histone mRNA precursor and 13 out of 16 nucleotides from the conserved palindrome can be base paired with presumptive U7 RNA sequence, suggesting a unique hybrid structure for a processing intermediate formed from histone precursor and U7 RNA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akaboshi E., Guerrier-Takada C., Altman S. Veal heart ribonuclease P has an essential RNA component. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Sep 30;96(2):831–837. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91430-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berget S. M. Are U4 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins involved in polyadenylation? Nature. 1984 May 10;309(5964):179–182. doi: 10.1038/309179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billings P. B., Hoch S. O. Isolation of intact Sm/RNP antigens from rabbit thymus. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):347–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birchmeier C., Folk W., Birnstiel M. L. The terminal RNA stem-loop structure and 80 bp of spacer DNA are required for the formation of 3' termini of sea urchin H2A mRNA. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90176-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birchmeier C., Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Generation of authentic 3' termini of an H2A mRNA in vivo is dependent on a short inverted DNA repeat and on spacer sequences. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):739–745. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birchmeier C., Schümperli D., Sconzo G., Birnstiel M. L. 3' editing of mRNAs: sequence requirements and involvement of a 60-nucleotide RNA in maturation of histone mRNA precursors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1057–1061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busslinger M., Portmann R., Birnsteil M. L. A regulatory sequence near the 3' end of sea urchin histone genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jul 11;6(9):2997–3008. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.9.2997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Robertis E. M., Lienhard S., Parisot R. F. Intracellular transport of microinjected 5S and small nuclear RNAs. Nature. 1982 Feb 18;295(5850):572–577. doi: 10.1038/295572a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England T. E., Uhlenbeck O. C. 3'-terminal labelling of RNA with T4 RNA ligase. Nature. 1978 Oct 12;275(5680):560–561. doi: 10.1038/275560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D., Baty D., Chambon P. The repeated GC-rich motifs upstream from the TATA box are important elements of the SV40 early promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2447–2464. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli G., Hofstetter H., Stunnenberg H. G., Birnstiel M. L. Biochemical complementation with RNA in the Xenopus oocyte: a small RNA is required for the generation of 3' histone mRNA termini. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):823–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90539-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Maniatis T., Melton D. A. Human beta-globin pre-mRNA synthesized in vitro is accurately spliced in Xenopus oocyte nuclei. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):681–694. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Spacer DNA sequences upstream of the T-A-T-A-A-A-T-A sequence are essential for promotion of H2A histone gene transcription in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7102–7106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto C., Steitz J. A. U4 and U6 RNAs coexist in a single small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 11;12(7):3283–3293. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.7.3283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C., Probst E., Birnstiel M. L. Transcriptional fidelity of histone genes injected into Xenopus oocyte nuclei. Nature. 1980 Nov 6;288(5786):100–102. doi: 10.1038/288100a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Melton D. A. Formation of the 3' end of histone mRNA by post-transcriptional processing. Nature. 1984 Mar 8;308(5955):203–206. doi: 10.1038/308203a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer A., Keller W., Appel B., Lührmann R. The 5' terminus of the RNA moiety of U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles is required for the splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):299–307. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90551-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Grez M., Hauser H., Lindenmaier W., Schütz G. 5'-Terminal sequences of eucaryotic mRNA can be cloned with high efficiency. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 25;9(10):2251–2266. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.10.2251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Boyle J. A., Mount S. M., Wolin S. L., Steitz J. A. Are snRNPs involved in splicing? Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):220–224. doi: 10.1038/283220a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Antibodies to small nuclear RNAs complexed with proteins are produced by patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5495–5499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B., Pettersson U. The low molecular weight of RNAs of adenovirus 2-infected cells. J Mol Biol. 1978 Feb 25;119(2):293–328. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90439-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M., Pettersson I., Hinterberger M., Karmas A., Steitz J. A. The U1 small nuclear RNA-protein complex selectively binds a 5' splice site in vitro. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):509–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90432-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M., Steitz J. A. Sequence of U1 RNA from Drosophila melanogaster: implications for U1 secondary structure and possible involvement in splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6351–6368. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Hardy S. F., Sharp P. A. Splicing of adenovirus RNA in a cell-free transcription system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5230–5234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock S. L., McIver C. M., Monahan J. J. Transformation of E. coli using homopolymer-linked plasmid chimeras. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Sep 28;655(2):243–250. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(81)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prestayko A. W., Tonato M., Busch H. Low molecular weight RNA associated with 28 s nucleolar RNA. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 14;47(3):505–515. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90318-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy R., Busch H. Small nuclear RNAs and RNA processing. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1983;30:127–162. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60685-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reveillaud I., Lelay-Taha M. N., Sri-Widada J., Brunel C., Jeanteur P. Mg2+ induces a sharp and reversible transition in U1 and U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein configurations. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1890–1899. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi R. P., Miller J. S., Roberts B. E. Purification and mapping of specific mRNAs by hybridization-selection and cell-free translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4927–4931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinke J., Appel B., Blöcker H., Frank R., Lührmann R. The 5'-terminal sequence of U1 RNA complementary to the consensus 5' splice site of hnRNA is single-stranded in intact U1 snRNP particles. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 25;12(10):4111–4126. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.10.4111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Wall R. A mechanism for RNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1877–1879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sippel A. E. Purification and characterization of adenosine triphosphate: ribonucleic acid adenyltransferase from Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Aug 1;37(1):31–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02953.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stunnenberg H. G., Birnstiel M. L. Bioassay for components regulating eukaryotic gene expression: a chromosomal factor involved in the generation of histone mRNA 3' termini. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6201–6204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thimmappaya B., Weinberger C., Schneider R. J., Shenk T. Adenovirus VAI RNA is required for efficient translation of viral mRNAs at late times after infection. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):543–551. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90310-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlenbeck O. C., Carey J., Romaniuk P. J., Lowary P. T., Beckett D. Interaction of R17 coat protein with its RNA binding site for translational repression. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1983 Oct;1(2):539–552. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1983.10507460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Purification of a membrane-associated protein complex required for protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7112–7116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Signal recognition particle contains a 7S RNA essential for protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1982 Oct 21;299(5885):691–698. doi: 10.1038/299691a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang V. W., Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A., Flint S. J. A small nuclear ribonucleoprotein is required for splicing of adenoviral early RNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1371–1375. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeller R., Nyffenegger T., De Robertis E. M. Nucleocytoplasmic distribution of snRNPs and stockpiled snRNA-binding proteins during oogenesis and early development in Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):425–434. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90462-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., DiMaio D., Maniatis T. Identification of two distinct regulatory regions adjacent to the human beta-interferon gene. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):865–879. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90544-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]