Abstract
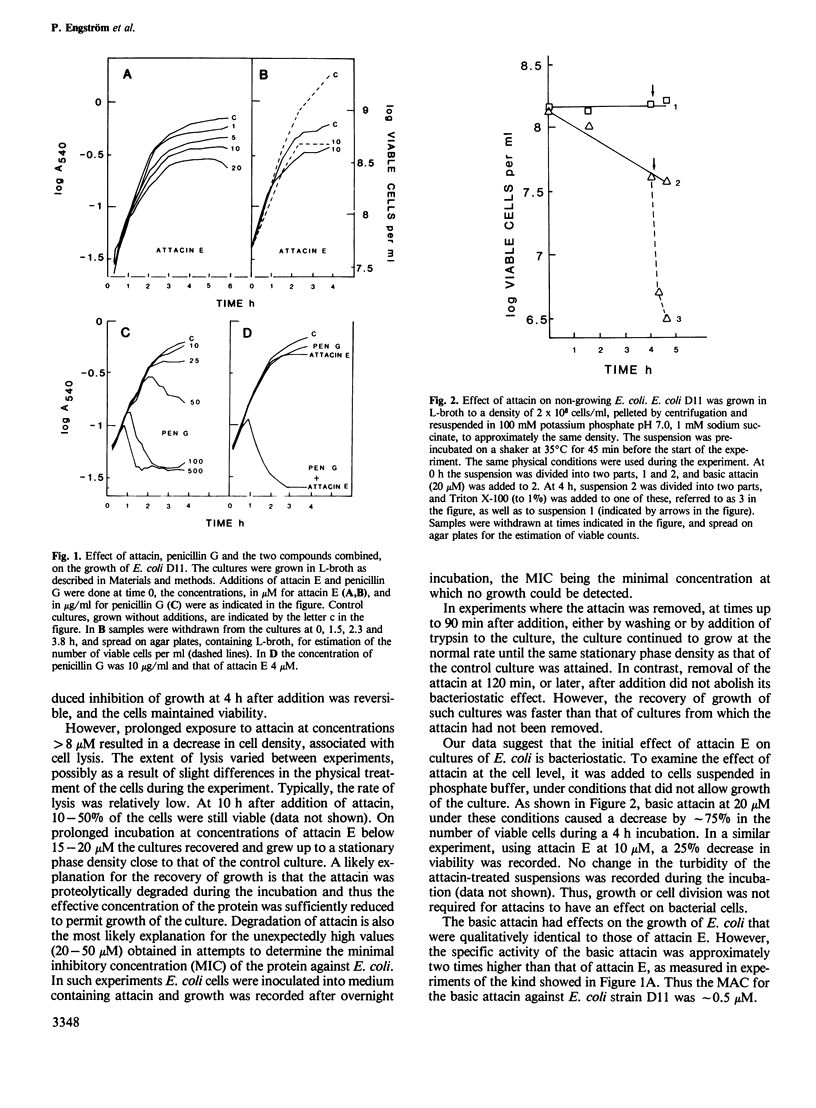
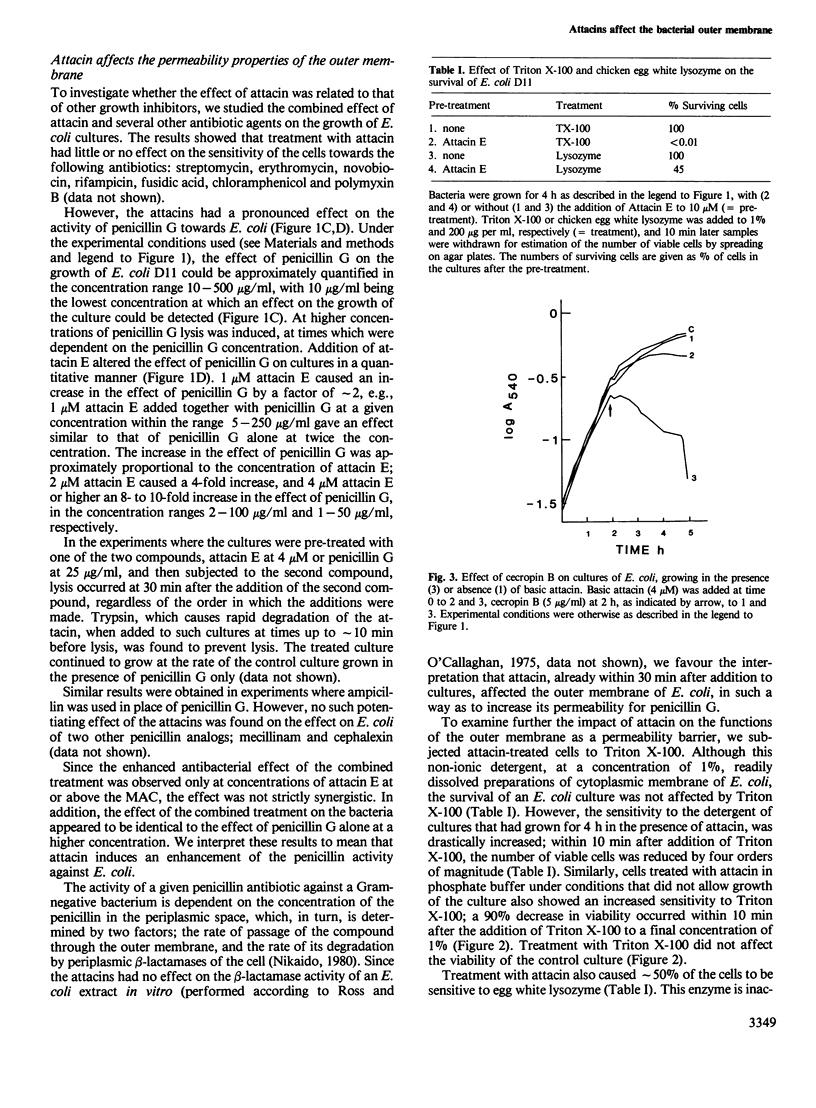
The attacins are antibacterial proteins which accumulate in the hemolymph of the giant silk moth, Hyalophora cecropia, in response to a bacterial infection. Here we show that the permeability barrier function of the outer membrane is affected shortly after addition of attacin to growing cultures of Escherichia coli. Specifically, the penetration through the outer membrane of beta-lactam antibiotics, chicken egg white lysozyme and the detergent Triton X-100 was found to be facilitated. The sensitivity of E. coli to cecropin B, another antibacterial protein present in the hemolymph of H. cecropia, was also found to be increased after treatment with attacin. The results suggest that the target of the attacins in E. coli is the outer membrane. Other effects of the attacins which have been observed are likely to be indirect consequences of the alteration in the properties of the outer membrane. These effects include changes in the cell shape, irregular patterns of cell division and lysis. The minimal concentration at which the attacins affected the growth of E. coli was 1 and 0.5 microM for the neutral (pI 7) and basic (pI 9) attacins, respectively, which corresponds to less than 2% of the concentration of the attacins in the hemolymph of infected pupae.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boman H. G., Steiner H. Humoral immunity in Cecropia pupae. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1981;94-95:75–91. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68120-2_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engström A., Engström P., Tao Z. J., Carlsson A., Bennich H. Insect immunity. The primary structure of the antibacterial protein attacin F and its relation to two native attacins from Hyalophora cecropia. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2065–2070. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02092.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultmark D., Engström A., Andersson K., Steiner H., Bennich H., Boman H. G. Insect immunity. Attacins, a family of antibacterial proteins from Hyalophora cecropia. EMBO J. 1983;2(4):571–576. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01465.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultmark D., Engström A., Bennich H., Kapur R., Boman H. G. Insect immunity: isolation and structure of cecropin D and four minor antibacterial components from Cecropia pupae. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Sep;127(1):207–217. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06857.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultmark D., Steiner H., Rasmuson T., Boman H. G. Insect immunity. Purification and properties of three inducible bactericidal proteins from hemolymph of immunized pupae of Hyalophora cecropia. Eur J Biochem. 1980 May;106(1):7–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb05991.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kockum K., Faye I., Hofsten P. V., Lee J. Y., Xanthopoulos K. G., Boman H. G. Insect immunity. Isolation and sequence of two cDNA clones corresponding to acidic and basic attacins from Hyalophora cecropia. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2071–2075. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02093.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monner D. A., Jonsson S., Boman H. G. Ampicillin-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli K-12 with lipopolysaccharide alterations affecting mating ability and susceptibility to sex-specific bacteriophages. J Bacteriol. 1971 Aug;107(2):420–432. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.2.420-432.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powning R. F., Davidson W. J. Studies on insect bacteriolytic enzymes--II. Some physical and enzymatic properties of lysozyme from haemolymph of Galleria mellonella. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1976;55(2):221–228. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(76)90234-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pye A. E., Boman H. G. Insect immunity. III. Purification and partial characterization of immune protein P5 from hemolymph of Hyalophora cecropia pupae. Infect Immun. 1977 Aug;17(2):408–414. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.2.408-414.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. W., O'Callaghan C. H. Beta-lactamase assays. Methods Enzymol. 1975;43:69–85. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)43081-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner H., Hultmark D., Engström A., Bennich H., Boman H. G. Sequence and specificity of two antibacterial proteins involved in insect immunity. Nature. 1981 Jul 16;292(5820):246–248. doi: 10.1038/292246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


