The inclusion of a methylene group at the thioamidic N atom of the acetone thiosemicarbazone derivative endows the molecule with greater flexibility and different pathways of association compared to those usually observed in the crystalline structures of these compounds.
Keywords: crystal structure, thiosemicarbazone, thiourea, hydrogen bonding
Abstract
The structure of the title compound, C11H15N3OS, shows the flexibility due to the methylene group at the thioamide N atom in the side chain, resulting in the molecule being non-planar. The dihedral angle between the plane of the benzene ring and that defined by the atoms of the thiosemicarbazide arm is 79.847 (4)°. In the crystal, the donor–acceptor hydrogen-bond character of the –OH group dominates the intermolecular associations, acting as a donor in an O—H⋯S hydrogen bond, as well as being a double acceptor in a centrosymmetric cyclic bridging N—H⋯O,O′ interaction [graph set R 2 2(4)]. The result is a one-dimensional duplex chain structure, extending along [111]. The usual N—H⋯S hydrogen-bonding association common in thiosemicarbazone crystal structures is not observed.
Chemical context
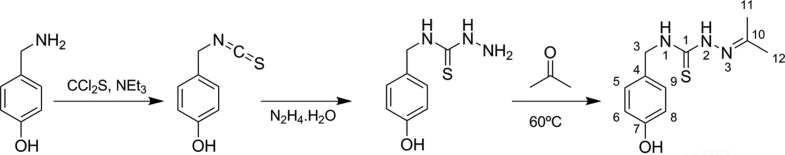
Thiosemicarbazones (TSCs) are an interesting group of compounds because they show diverse biological properties (Serda et al., 2012 ▸) and pharmacological activities (Lukmantara et al., 2013 ▸). They can be easily functionalized to yield different supramolecular arrays through intermolecular hydrogen-bonding interactions (Nuñez-Montenegro et al., 2017 ▸), by selection of suitable aldehyde or ketone reagents. In addition, metal coordination may be used to orient some of their substituents to optimize the interaction with biomolecules (e.g. see Nuñez-Montenegro et al., 2014 ▸). In the present paper, we describe the synthesis and crystal structure of a TSC derivative (Figs. 1 ▸), namely N-(4-hydroxybenzyl)acetone thiosemicarbazone (acTSC), having a 4-hydroxybenzyl substituent at the thioamide N atom (N1), in which the –CH2– group provides more flexibility to establish intermolecular associations.
Figure 1.
Reaction scheme for the synthesis of acTSC.
Structural commentary
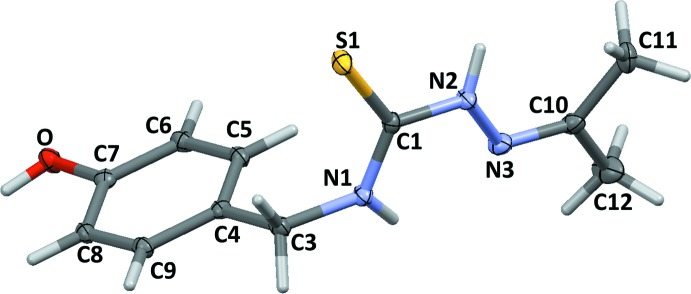
In the acTSC molecule (Fig. 2 ▸), the bond lengths (S1=C1 and C10=N3) and angles in the thiosemicarbazide arm are similar to those observed in other thiosemicarbazones, suggesting that the thione form is predominant. This arm is almost planar, probably due to some π-delocation (r.m.s. deviation of 0.0516 Å for the plane defined by atoms S1/C1/N1/N2/N3). Nevertheless, the ethylene group at N1 allows an almost orthogonal orientation relative to the phenolic substituent group, with a dihedral angle between the two planes of 79.847 (4)°. The interatomic distance N1⋯N3 interaction [2.6074 (18) Å] suggests some kind of intramolecular interaction.
Figure 2.
The molecular structure of acTSC, with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 40% probability level.
Supramolecular features
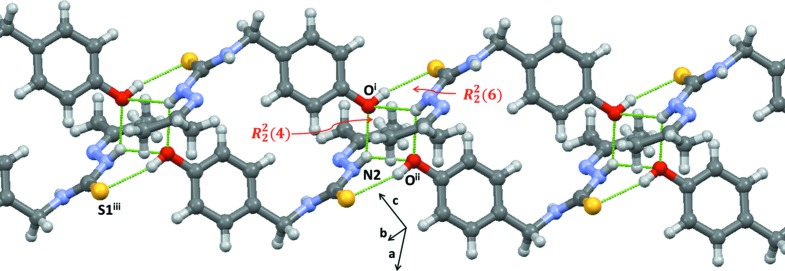
The association of the molecules is strongly affected by the donor–acceptor character of the –OH group, while the usual N—H⋯S hydrogen bonds observed in most TSC structures (Nuñez-Montenegro et al., 2017 ▸; Pino-Cuevas et al., 2014 ▸) are absent. The phenolic –OH group forms an intermolecular hydrogen bond with a S-atom acceptor (O—H0⋯S1iii; Table 1 ▸), while the N2—H group establishes two different hydrogen-bonding interactions with different phenolic O-atom acceptors. The shortest of these is N2—H2⋯Oi (Table 1 ▸), which generates a centrosymmetric cyclic 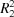 (4) ring-motif association (Etter, 1990 ▸) and also forms a conjoined cyclic
(4) ring-motif association (Etter, 1990 ▸) and also forms a conjoined cyclic 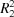 (6) association via an O—H⋯S interaction (see Fig. 3 ▸). The second of the three-centre hydrogen-bonding interactions (N2—H2⋯Oii) extends the structure into one-dimensional duplex chains along [111] (Fig. 3 ▸).
(6) association via an O—H⋯S interaction (see Fig. 3 ▸). The second of the three-centre hydrogen-bonding interactions (N2—H2⋯Oii) extends the structure into one-dimensional duplex chains along [111] (Fig. 3 ▸).
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2—H2⋯Oi | 0.848 (17) | 2.292 (17) | 2.9955 (15) | 140.6 (14) |
| N2—H2⋯Oii | 0.848 (17) | 2.434 (16) | 3.1333 (15) | 140.3 (14) |
| O—H0⋯S1iii | 0.857 (19) | 2.299 (19) | 3.1349 (10) | 165.2 (16) |
Symmetry codes: (i) 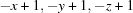 ; (ii)
; (ii) 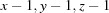 ; (iii)
; (iii) 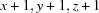 .
.
Figure 3.
Intermolecular hydrogen-bonding associations between molecules in the crystal structure of acTSC, shown as dashed lines.
Database survey
For related structures of thiosemicarbazones derived from acetone, see: Yamin et al. (2014 ▸); Basu & Das (2011 ▸); Venkatraman et al. (2005 ▸); Jian et al. (2005 ▸). For the metal-coordination properties of thiosemicarbazones, see: Paterson & Donnelly (2011 ▸); Casas et al. (2000 ▸). For acetone derivatives, see, for example, Su et al. (2013 ▸); Nuñez-Montenegro et al. (2014 ▸); Swesi et al. (2006 ▸); Paek et al. (1997 ▸).
Synthesis and crystallization
The reaction scheme for the synthesis of the title compound is shown in Fig. 1 ▸. The primary amine 4-hydroxybenzylamine was converted to the corresponding isothiocyanate by reaction with thiophosgene (Sharma, 1978 ▸). This isothiocyanate was treated with hydrazide to form the thiosemicarbazide, as described previously (Reis et al., 2011 ▸). Finally, this compound was reacted with acetone in order to synthesize the desired thiosemicarbazone. In a typical synthesis, 3.4 g (0.017 mol) of thiosemicarbazide was dissolved in acetone (20 ml) and heated to 60°C for 20 min (Fig. 1 ▸). This solution was concentrated and the resultant residue was purified using a silica column (AcOEt–hexane 30%). This solution was vacuum dried giving 1.96 g of acTSC. The solution was also used to obtain single crystals by slow evaporation (yield 48%; m.p. 165°C). C11H15N3OS requires: C 55.7, H 6.4, N 17.7%; found C 55.8, H 7.1,N 16.9%. MS–ESI [m/z (%)]: 238 (100) [M + H]+. IR (ATR, ν/cm−1): 3241 (b) ν(NH, OH); 1536 (w), 1508 (s) ν(C=N); 784 (w) ν(C=S). 1H NMR (DMSO-d 6): 9.95 (s, 1H, N2H), 9.26 (s, 1H, OH), 8.46 (t, 3 J H-NH = 6.2Hz, 1H, N1H), 7.15 (d, 3 J H-H = 8.5Hz, 2H, C5H, C9H), 6.70 (d, 3 J H-H = 8.5Hz, 2H, C6H, C8H), 4.65 (d, 3 J H-H = 6.2Hz, 2H, C3H), 1.92 (d, 3 J H-H = 8.5Hz, 6H, C11H, C12H).
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. Interactive H atoms on O and N atoms were located in difference Fourier analyses and were allowed to freely refine, with U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(O,N) and riding. Other H atoms were included at calculated sites and allowed to ride, with U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(aromatic and methylene C) or 1.5U eq(methyl C).
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C11H15N3OS |
| M r | 237.32 |
| Crystal system, space group | Triclinic, P
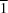
|
| Temperature (K) | 100 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 8.2799 (8), 8.9169 (9), 9.7451 (10) |
| α, β, γ (°) | 104.597 (3), 112.569 (3), 105.220 (3) |
| V (Å3) | 588.7 (1) |
| Z | 2 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.26 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.18 × 0.11 × 0.11 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Bruker D8 Venture Photon 100 CMOS |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2014 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.638, 0.746 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 17083, 2911, 2562 |
| R int | 0.043 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.667 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.032, 0.082, 1.00 |
| No. of reflections | 2911 |
| No. of parameters | 156 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.29, −0.28 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017012129/zs2385sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017012129/zs2385Isup2.hkl
CCDC reference: 1570200
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C11H15N3OS | F(000) = 252 |
| Mr = 237.32 | Dx = 1.339 Mg m−3 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Melting point: 438 K |
| a = 8.2799 (8) Å | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| b = 8.9169 (9) Å | Cell parameters from 9917 reflections |
| c = 9.7451 (10) Å | θ = 2.5–28.3° |
| α = 104.597 (3)° | µ = 0.26 mm−1 |
| β = 112.569 (3)° | T = 100 K |
| γ = 105.220 (3)° | Prism, colourless |
| V = 588.7 (1) Å3 | 0.18 × 0.11 × 0.11 mm |
| Z = 2 |
Data collection
| Bruker D8 Venture Photon 100 CMOS diffractometer | 2562 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| φ and ω scans | Rint = 0.043 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2014) | θmax = 28.3°, θmin = 2.5° |
| Tmin = 0.638, Tmax = 0.746 | h = −11→11 |
| 17083 measured reflections | k = −11→11 |
| 2911 independent reflections | l = −12→13 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.032 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.082 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0325P)2 + 0.3538P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.00 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 2911 reflections | Δρmax = 0.29 e Å−3 |
| 156 parameters | Δρmin = −0.28 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C12 | 0.5032 (2) | −0.1953 (2) | 0.3563 (2) | 0.0345 (4) | |
| H12A | 0.6301 | −0.1042 | 0.4309 | 0.052* | |
| H12B | 0.5165 | −0.2971 | 0.3036 | 0.052* | |
| H12C | 0.4356 | −0.2199 | 0.4166 | 0.052* | |
| C11 | 0.1912 (2) | −0.26338 (16) | 0.10998 (17) | 0.0243 (3) | |
| H11A | 0.1070 | −0.2506 | 0.1562 | 0.036* | |
| H11B | 0.1842 | −0.3793 | 0.0828 | 0.036* | |
| H11C | 0.1508 | −0.2401 | 0.0118 | 0.036* | |
| S1 | 0.33739 (4) | 0.28903 (4) | 0.00401 (4) | 0.02014 (10) | |
| O | 0.96910 (14) | 0.95385 (12) | 0.83590 (11) | 0.0206 (2) | |
| H0 | 1.063 (3) | 1.046 (2) | 0.864 (2) | 0.031* | |
| N2 | 0.37419 (16) | 0.05734 (13) | 0.12372 (13) | 0.0170 (2) | |
| H2 | 0.254 (2) | 0.024 (2) | 0.0853 (19) | 0.020* | |
| N1 | 0.65479 (15) | 0.27673 (13) | 0.21157 (13) | 0.0163 (2) | |
| H1 | 0.701 (2) | 0.225 (2) | 0.2663 (19) | 0.020* | |
| N3 | 0.47907 (15) | 0.00499 (14) | 0.23774 (13) | 0.0194 (2) | |
| C6 | 0.79084 (18) | 0.67223 (16) | 0.64146 (15) | 0.0173 (2) | |
| H6 | 0.7308 | 0.6484 | 0.7038 | 0.021* | |
| C3 | 0.77639 (18) | 0.44581 (15) | 0.24342 (15) | 0.0171 (2) | |
| H3A | 0.7100 | 0.4789 | 0.1551 | 0.021* | |
| H3B | 0.8951 | 0.4438 | 0.2427 | 0.021* | |
| C1 | 0.46524 (17) | 0.20611 (15) | 0.12097 (14) | 0.0147 (2) | |
| C4 | 0.82883 (17) | 0.57817 (15) | 0.40388 (14) | 0.0148 (2) | |
| C7 | 0.92864 (17) | 0.83296 (15) | 0.69457 (14) | 0.0158 (2) | |
| C9 | 0.96926 (17) | 0.73918 (15) | 0.46107 (15) | 0.0170 (2) | |
| H9 | 1.0319 | 0.7622 | 0.4003 | 0.020* | |
| C8 | 1.01956 (17) | 0.86683 (15) | 0.60508 (15) | 0.0164 (2) | |
| H8 | 1.1150 | 0.9760 | 0.6419 | 0.020* | |
| C5 | 0.74164 (17) | 0.54680 (15) | 0.49646 (15) | 0.0162 (2) | |
| H5 | 0.6466 | 0.4376 | 0.4600 | 0.019* | |
| C10 | 0.39253 (19) | −0.14134 (17) | 0.23078 (16) | 0.0197 (3) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C12 | 0.0274 (8) | 0.0421 (9) | 0.0502 (10) | 0.0188 (7) | 0.0187 (7) | 0.0374 (8) |
| C11 | 0.0297 (7) | 0.0153 (6) | 0.0263 (7) | 0.0065 (5) | 0.0131 (6) | 0.0090 (5) |
| S1 | 0.01646 (16) | 0.01708 (15) | 0.02248 (17) | 0.00497 (12) | 0.00379 (13) | 0.01202 (12) |
| O | 0.0182 (5) | 0.0184 (4) | 0.0173 (4) | 0.0022 (4) | 0.0071 (4) | 0.0030 (4) |
| N2 | 0.0138 (5) | 0.0164 (5) | 0.0197 (5) | 0.0056 (4) | 0.0053 (4) | 0.0104 (4) |
| N1 | 0.0152 (5) | 0.0145 (5) | 0.0182 (5) | 0.0059 (4) | 0.0059 (4) | 0.0083 (4) |
| N3 | 0.0174 (5) | 0.0228 (5) | 0.0238 (6) | 0.0108 (4) | 0.0097 (5) | 0.0157 (5) |
| C6 | 0.0154 (6) | 0.0201 (6) | 0.0178 (6) | 0.0059 (5) | 0.0085 (5) | 0.0101 (5) |
| C3 | 0.0151 (6) | 0.0164 (6) | 0.0187 (6) | 0.0042 (5) | 0.0081 (5) | 0.0076 (5) |
| C1 | 0.0163 (6) | 0.0135 (5) | 0.0139 (5) | 0.0060 (5) | 0.0075 (5) | 0.0046 (4) |
| C4 | 0.0131 (5) | 0.0158 (5) | 0.0161 (6) | 0.0072 (5) | 0.0055 (5) | 0.0082 (5) |
| C7 | 0.0134 (5) | 0.0169 (6) | 0.0144 (6) | 0.0067 (5) | 0.0036 (5) | 0.0065 (4) |
| C9 | 0.0154 (6) | 0.0182 (6) | 0.0202 (6) | 0.0065 (5) | 0.0094 (5) | 0.0110 (5) |
| C8 | 0.0131 (5) | 0.0146 (5) | 0.0194 (6) | 0.0041 (4) | 0.0056 (5) | 0.0086 (5) |
| C5 | 0.0131 (5) | 0.0154 (5) | 0.0186 (6) | 0.0042 (4) | 0.0060 (5) | 0.0087 (5) |
| C10 | 0.0213 (6) | 0.0225 (6) | 0.0263 (7) | 0.0131 (5) | 0.0155 (5) | 0.0152 (5) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—C1 | 1.6959 (14) | C8—C9 | 1.3914 (18) |
| O—C7 | 1.3708 (16) | C10—C11 | 1.498 (2) |
| O—H0 | 0.86 (2) | C10—C12 | 1.495 (2) |
| N1—C3 | 1.4527 (19) | C3—H3A | 0.9900 |
| N1—C1 | 1.3328 (19) | C3—H3B | 0.9900 |
| N2—N3 | 1.3929 (17) | C5—H5 | 0.9500 |
| N2—C1 | 1.3554 (19) | C6—H6 | 0.9500 |
| N3—C10 | 1.284 (2) | C8—H8 | 0.9500 |
| N1—H1 | 0.839 (18) | C9—H9 | 0.9500 |
| N2—H2 | 0.849 (18) | C11—H11A | 0.9800 |
| C3—C4 | 1.5186 (18) | C11—H11B | 0.9800 |
| C4—C5 | 1.391 (2) | C11—H11C | 0.9800 |
| C4—C9 | 1.395 (2) | C12—H12A | 0.9800 |
| C5—C6 | 1.3914 (19) | C12—H12B | 0.9800 |
| C6—C7 | 1.392 (2) | C12—H12C | 0.9800 |
| C7—C8 | 1.391 (2) | ||
| C7—O—H0 | 111.1 (13) | N1—C3—H3B | 109.00 |
| C1—N1—C3 | 124.73 (12) | C4—C3—H3A | 109.00 |
| N2—N3—C10 | 116.82 (12) | C4—C3—H3B | 109.00 |
| S1—C1—N1 | 124.19 (11) | H3A—C3—H3B | 108.00 |
| S1—C1—N2 | 119.75 (11) | C4—C5—H5 | 119.00 |
| C1—N1—H1 | 115.1 (12) | C6—C5—H5 | 119.00 |
| C3—N1—H1 | 119.1 (12) | C5—C6—H6 | 120.00 |
| N1—C1—N2 | 116.05 (12) | C7—C6—H6 | 120.00 |
| N3—N2—H2 | 120.9 (12) | C7—C8—H8 | 120.00 |
| C1—N2—H2 | 116.2 (13) | C9—C8—H8 | 120.00 |
| N1—C3—C4 | 113.39 (12) | C4—C9—H9 | 119.00 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 122.91 (12) | C8—C9—H9 | 119.00 |
| C5—C4—C9 | 118.17 (12) | C10—C11—H11A | 109.00 |
| C3—C4—C9 | 118.92 (12) | C10—C11—H11B | 109.00 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 121.31 (13) | C10—C11—H11C | 109.00 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 119.54 (13) | H11A—C11—H11B | 109.00 |
| O—C7—C6 | 117.57 (13) | H11A—C11—H11C | 109.00 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 120.21 (12) | H11B—C11—H11C | 109.00 |
| O—C7—C8 | 122.21 (12) | C10—C12—H12A | 109.00 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 119.30 (13) | C10—C12—H12B | 109.00 |
| C4—C9—C8 | 121.46 (13) | C10—C12—H12C | 109.00 |
| N3—C10—C12 | 116.82 (14) | H12A—C12—H12B | 109.00 |
| C11—C10—C12 | 116.61 (14) | H12A—C12—H12C | 109.00 |
| N3—C10—C11 | 126.57 (13) | H12B—C12—H12C | 109.00 |
| N1—C3—H3A | 109.00 | ||
| C3—N1—C1—S1 | 10.03 (19) | C3—C4—C9—C8 | 178.25 (13) |
| C3—N1—C1—N2 | −171.02 (12) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | −178.75 (14) |
| C1—N1—C3—C4 | 97.14 (15) | C9—C4—C5—C6 | 0.6 (2) |
| C1—N2—N3—C10 | −175.62 (14) | C5—C4—C9—C8 | −1.1 (2) |
| N3—N2—C1—S1 | −170.98 (10) | C4—C5—C6—C7 | 0.7 (2) |
| N3—N2—C1—N1 | 10.02 (19) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | −1.4 (2) |
| N2—N3—C10—C12 | −178.18 (13) | C5—C6—C7—O | 178.34 (13) |
| N2—N3—C10—C11 | 1.5 (2) | O—C7—C8—C9 | −178.83 (13) |
| N1—C3—C4—C9 | 169.60 (13) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | 0.9 (2) |
| N1—C3—C4—C5 | −11.0 (2) | C7—C8—C9—C4 | 0.4 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H2···Oi | 0.848 (17) | 2.292 (17) | 2.9955 (15) | 140.6 (14) |
| N2—H2···Oii | 0.848 (17) | 2.434 (16) | 3.1333 (15) | 140.3 (14) |
| O—H0···S1iii | 0.857 (19) | 2.299 (19) | 3.1349 (10) | 165.2 (16) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1; (ii) x−1, y−1, z−1; (iii) x+1, y+1, z+1.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by Ministry of Economy, Industry and Competitiveness (Spain) and European Regional Development Fund (EU) (CTQ2015-71211-REDT and CTQ2015-7091-R) grant .
References
- Basu, A. & Das, G. (2011). Dalton Trans. 40, 2837–2843. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2014). APEX3, SAINT and SADABS, Bruker ASX Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruno, I. J., Cole, J. C., Edgington, P. R., Kessler, M., Macrae, C. F., McCabe, P., Pearson, J. & Taylor, R. (2002). Acta Cryst. B58, 389–397. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Casas, J. S., García-Tasende, M. S. & Sordo, J. (2000). Coord. Chem. Rev. 209, 197–261.
- Etter, M. C. (1990). Acc. Chem. Res. 23, 120–126.
- Jian, F.-F., Bai, Z.-S., Xiao, H.-L. & Li, K. (2005). Acta Cryst. E61, o653–o654.
- Lukmantara, A. Y., Kalinowski, D. S., Kumar, N. & Richardson, D. R. (2013). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 23, 967–974. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Nuñez-Montenegro, A., Argibay-Otero, S., Carballo, R., Graña, A. & Vázquez-López, E. M. (2017). Cryst. Growth Des. 17, 3338–3349.
- Nuñez-Montenegro, A., Carballo, R. & Vázquez-López, E. M. (2014). J. Inorg. Biochem. 140, 53–63. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Paek, C., Kang, S. O., Ko, J. & Carroll, P. J. (1997). Organometallics, 16, 2110–2115.
- Paterson, B. M. & Donnelly, P. S. (2011). Chem. Soc. Rev. 40, 3005–3018. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Pino-Cuevas, A., Carballo, R. & Vázquez-López, E. M. (2014). Acta Cryst. E70, o926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Reis, C. M., Pereira, D. S., Paiva, R. O., Kneipp, L. F. & Echevarria, A. (2011). Molecules, 16, 10668–10684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Serda, M., Mrozek-Wilczkiewicz, A., Jampilek, J., Pesko, M., Kralova, K., Vejsova, M., Musiol, R., Ratuszna, A. & Polanski, J. (2012). Molecules, 17, 13483–13502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S. (1978). Synthesis, pp. 803–820.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Su, W., Quia, Q., Li, P., Lei, X., Xiao, Q., Huan, S., Huang, C. & Cui, J. (2013). Inorg. Chem. 52, 12440–12449. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Swesi, A. T., Farina, Y., Venkatraman, R. & Ng, S. W. (2006). Acta Cryst. E62, m3020–m3021.
- Venkatraman, R., Swesi, A. T. & Yamin, B. M. (2005). Acta Cryst. E61, o3914–o3916.
- Yamin, B. M., Rodis, M. L. & Chee, D. N. B. A. (2014). Acta Cryst. E70, o1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017012129/zs2385sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017012129/zs2385Isup2.hkl
CCDC reference: 1570200
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report