Abstract
Objective
Epidemiological and clinical data indicate that patients suffering from IBD with long-standing colitis display a higher risk to develop colorectal high-grade dysplasia. Whereas carcinoma invasion and metastasis rely on basement membrane (BM) disruption, experimental evidence is lacking regarding the potential contribution of epithelial cell/BM anchorage on inflammation onset and subsequent neoplastic transformation of inflammatory lesions. Herein, we analyse the role of the α6β4 integrin receptor found in hemidesmosomes that attach intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) to the laminin-containing BM.
Design
We developed new mouse models inducing IEC-specific ablation of α6 integrin either during development (α6ΔIEC) or in adults (α6ΔIEC-TAM).
Results
Strikingly, all α6ΔIEC mutant mice spontaneously developed long-standing colitis, which degenerated overtime into infiltrating adenocarcinoma. The sequence of events leading to disease onset entails hemidesmosome disruption, BM detachment, IL-18 overproduction by IECs, hyperplasia and enhanced intestinal permeability. Likewise, IEC-specific ablation of α6 integrin induced in adult mice (α6ΔIEC-TAM) resulted in fully penetrant colitis and tumour progression. Whereas broad-spectrum antibiotic treatment lowered tissue pathology and IL-1β secretion from infiltrating myeloid cells, it failed to reduce Th1 and Th17 response. Interestingly, while the initial intestinal inflammation occurred independently of the adaptive immune system, tumourigenesis required B and T lymphocyte activation.
Conclusions
We provide for the first time evidence that loss of IECs/BM interactions triggered by hemidesmosome disruption initiates the development of inflammatory lesions that progress into high-grade dysplasia and carcinoma. Colorectal neoplasia in our mouse models resemble that seen in patients with IBD, making them highly attractive for discovering more efficient therapies.
Keywords: INTESTINAL BARRIER FUNCTION, COLORECTAL CANCER, IBD, INTEGRINS, CELL MATRIX INTERACTION
Significance of this study.
What is already known on this subject?
Loss of the major laminin receptor in hemidesmosomes, namely the α6β4 integrin, leads to severe skin barrier defects in mice and humans.
Genome-wide association studies hint at a potential implication of basement membrane (BM) laminins in predisposition to IBD and colorectal cancer (CRC). Laminin expression and distribution are altered in patients with IBD and CRC.
Numerous cytokines have been shown to influence disease progression, along with interleukin-18 (IL-18), which contributes to the regulation of goblet cells (GCs) and to the maintenance of gut barrier function.
Tumour immunosurveillance is thought to be impaired in patients with IBD with long-standing extensive colitis.
What are the new findings?
Mice carrying intestinal epithelial cell (IEC)-specific loss of α6 integrin develop fully penetrant colitis which spontaneously degenerates into carcinoma of the rectal mucosa that is the most intensely subject to environmental stress.
The onset of colitis is preceded by defective anchorage of the mutant IECs to the BM due to loss of hemidesmosomes, which results in a strong activation of caspase-1 leading to the secretion of IL-18, known to regulate GC functions.
Colitis is independent of T and B cell activation, but relies on increased epithelial secretion of IL-18 and important accumulation of intestinal CD11b+ myeloid cells that oversecrete IL-1β as a consequence of bacterial translocation through the defective mucus barrier. Broad spectrum antibiotic treatment partially improves colitis.
Risk of developing dysplasia leading to CRC relies on the activation of the adaptive immune response.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
Our findings reveal that the epithelial barrier/BM connection plays a critical role in the maintenance of intestinal integrity and homeostasis, by contributing to the formation of an efficient epithelial and mucus barrier. Improving weakened epithelial/BM interactions and restoring a functional mucus barrier by targeting epithelial IL-18/IL-18R signalling and by using diet that reduces the mechanical stress may represent novel therapeutic avenues in IBD.
Our results highlight also the crucial role of the IL-1 family of cytokines during progression of the inflammatory lesions into colorectal adenocarcinomas. This work suggests that tumour progression in IBD could be improved or slowed down by reducing the inflammatory context mediated by IL-1/IL-1R with specific drugs or neutralising antibodies.
Introduction
Intestinal homeostasis depends on a fine symbiosis among the epithelium, the immune system and the commensal bacteria present in the lumen. The polarised intestinal epithelium, with its mucus layer on its apical side and the basement membrane (BM) on its basal side, plays a central role in establishing the barrier function essential for symbiotic relationship with the gut microbiota.1–3 Compromising with intestinal homeostasis can lead to pathologies, such as IBD. IBD are relapsing-remitting illnesses, which can evolve into colorectal cancer (CRC) among patients with long-standing extensive colitis.4–6 Immune system dysregulation, mucus layer alterations, aberrant endoplasmic reticulum stress response and abnormal cell–cell junctions have been linked to IBD development.1 7 8 However, how interactions mediated by integrin receptors between the epithelium and its underlying BM contribute to maintain intestinal homeostasis has been largely overlooked.9
Major players of these interactions are the hemidesmosomes, which consist in specific junctions present at the base of all intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) where the α6β4 integrin interconnects the BM laminin-332 to keratin filaments through the cytoplasmic-linker protein plectin.10 11 Interestingly, several genetic studies have indirectly linked BM laminins and their integrin receptors to several intestinal pathologies. First, genome-wide-association studies have identified the LAMB1 (encoding the laminin β1 chain; association probability between 10−6 and 3×10−8) and LAMC1 (encoding the laminin γ1 chain; association probability 10−7) loci as susceptibility loci predisposing to IBD12 13 and CRC,14 respectively. Foremost, intestinal erosions reminiscent to IBD are found in patients suffering from skin disorders that are caused by hemidesmosome defects.15 Conversely, patients with IBD may develop skin lesions such as psoriasis,16 a skin inflammatory defect observed in mice lacking α6 integrin in basal keratinocytes.17
To investigate the potential role of α6β4 integrin in intestinal homeostasis, we generated two mouse models carrying either a targeted deletion of the integrin α6 gene (Itga6) in IECs, named the α6ΔIEC line or a tamoxifen (TAM)-inducible deletion, named the α6ΔIEC-TAM line. Strikingly, all α6ΔIEC and α6ΔIEC-TAM mutant animals developed long-standing extensive colitis. Foremost, inflammatory lesions spontaneously and progressively degenerated into infiltrating colorectal adenocarcinomas in α6ΔIEC mice, as well as in the α6ΔIEC-TAM model. Characterisation of both models demonstrates the central protective role of the epithelial cell/BM connection in preserving intestinal homeostasis and in preventing the risk of colitis-associated cancer.
Results
Epithelial-specific genetic ablation of Itga6 affects intestinal hemidesmosomes
To assay the role of α6 integrin in intestinal homeostasis, we first induced a complete deletion of Itga6 in IECs using the Cre-lox approach18 (α6ΔIEC; figure 1A and online supplementary figure S1). The resulting animals displayed abnormally loose and viscous stools, and frequently developed a rectal prolapse (figure 1B). To determine whether this phenotype was linked to hemidesmosome alterations, we examined the β4 integrin chain, the α6 hemidesmosome heterodimerising partner and found that both chains were removed from IECs at all stages examined (see figure 1C–E and online supplementary figure S2A, B). By contrast, epithelial expression of integrin β1, which can also heterodimerise with other α chains, did not vary (see online supplementary figure S2C), confirming that defects observed in these mice originated from a loss of the α6β4 integrin in the epithelium.
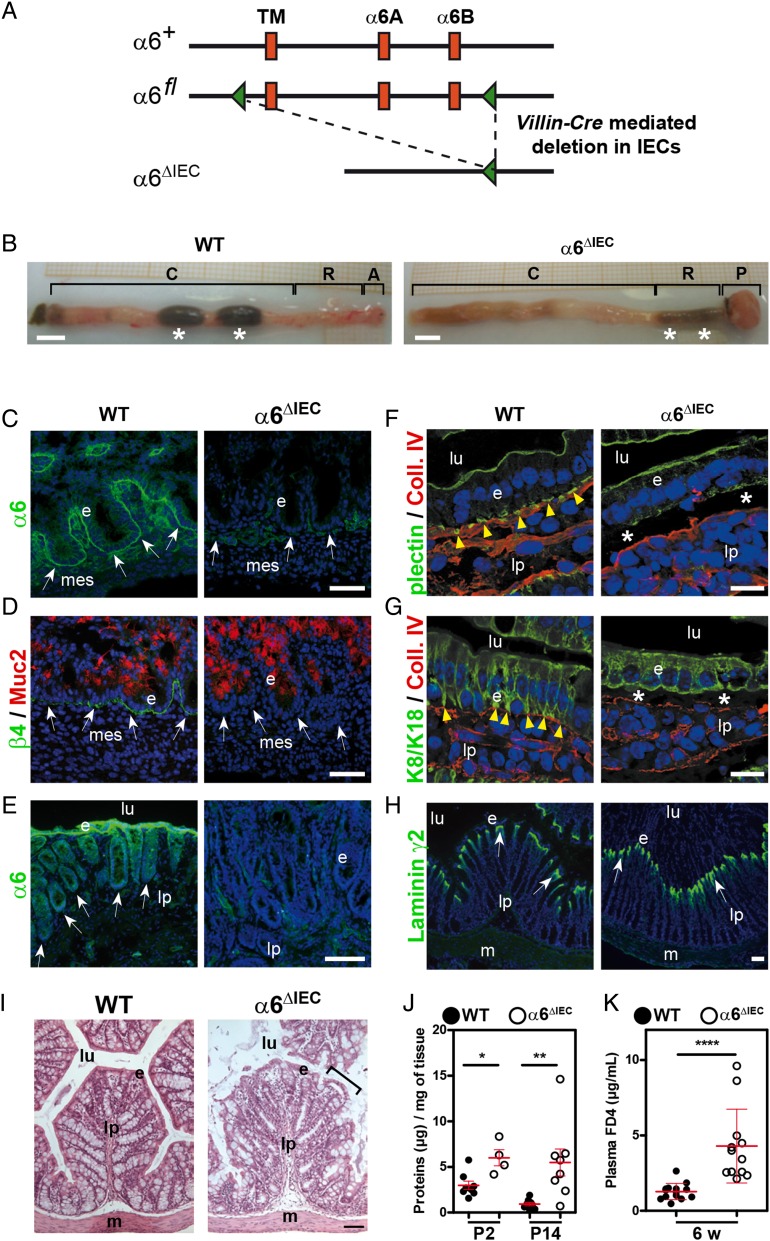
Figure 1.
Efficient deletion of Itga6 in α6ΔIEC mice results in compromised hemidesmosomes and epithelial fragility. (A) Strategy to generate an intestinal epithelium-specific Itga6 knockout (for details, see online supplementary figure S1A). The Itga6 floxed allele (α6fl) was obtained after insertion of two loxP cassettes (green triangles) at the Itga6 3′ end including the TM and the cytoplasmic A and B (α6A; α6B) exons. Crossing of the α6fl/fl mice with the transgenic Villin-Cre line results in a truncated Itga6 copy, denoted α6ΔIEC. (B) Morphology of the colorectal region in 15-week-old WT and α6ΔIEC mice. White stars indicate stools. Scale bars, 5 mm. (C–H) Immunodetection of hemidesmosome markers in the colon of E16.5 embryos (C and D) and in intestinal segments of mice aged 9–16 weeks (E–H); (E) rectum; (F and G) jejunum; (H) colon; 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) marks nuclei (blue). (C and E) α6-integrin chain and (D) β4-integrin chain (green) with the mucin Muc2 (red). The remaining signal in (C and E) corresponds to α6 integrin in blood vessels, confirming the specificity of the deletion in the epithelium. (F) Plectin and (G) K8/K18 intermediate filaments (green), with collagen IV (red). (H) Laminin-γ2 chain (green). White arrows, epithelium/lamina propria interface; yellow arrowheads, hemidesmosome patches; stars, areas of epithelial detachment in mutants. Scale bars, 50 µm. (I) Histological analysis of the colon from 3-week-old mice; bracket, detached cells from the surface epithelium. Scale bar, 100 µm. (J) Scattered dot plots showing the protein concentration of epithelial cell lysates obtained from small intestinal tissue of pups aged 2 (P2) and 14 (P14) days submitted to a detachment assay; error bars, SD; *p<0.05, **p<0.01. (K) Scattered dot plots showing the plasma concentration of FITC-dextran (FD4) as a measurement of intestinal permeability in 6-week-old animals fed with FD4; error bars, SD; ****p<10−4. A, anus; C, colon; e, epithelium; lp, lamina propria; lu, lumen; m, muscle layer; mes, mesenchyme; P, prolapse; R, rectum; TM, transmembrane; w, weeks; WT, wildtype.
gutjnl-2015-310847supp001.pdf (5MB, pdf)
We next tested if Itga6 depletion in IECs impaired the assembly of the hemidesmosome component plectin and subsequently of keratins 8/18 (K8/18). Plectin, which interacts with the β4 integrin cytoplasmic domain, was detected in hemidesmosomal basal patches and at the apical membrane of control IECs (figure 1F). In α6ΔIEC mice, plectin staining was strongly reduced basally but not apically; loss of basal plectin was already observed in late α6ΔIEC embryos (see figure 1F and online supplementary figure S2D). Moreover, the K8/18 intermediate filament dimers, which normally are concentrated in the plectin patches basally, were diffusely distributed throughout the cytoplasm (figure 1G). As a result, the shape of epithelial cells appeared less columnar and more cuboidal than in controls (figure 1G). Despite these strong defects, the epithelium retained a characteristic polarised distribution of the apical marker villin, a structural component of microvilli and the tight junction marker cingulin/MAP115 (see online supplementary figure S3). Hence, like in the skin where it nucleates type I hemidesmosomes (containing BP180 and BP230),17 19–21 α6β4 integrin is essential for the assembly of type II hemidesmosomes (that are lacking BP180 and BP230) present in the intestine, but does not contribute to epithelial polarity.
Loss of intestinal hemidesmosomes impacts on gut barrier function
Loss of α6β4 integrin in the skin affects epithelial integrity.17 19–21 In the mutant intestine, collagen IV and plectin costaining revealed that the epithelial layer tends to detach from its BM and the subjacent lamina propria (figure 1F, G), without affecting the distribution of the hemidesmosomal laminin γ2 chain (figure 1H). From 3 weeks after birth, areas of epithelial detachment were observed throughout the mutant intestine (see figure 1I and online supplementary figure S4), suggesting that the disruption of hemidesmosomes results in epithelium weakening and loss of firm anchorage to the BM. To confirm these observations, we used a modified method of IEC dissociation22 in which control and mutant epithelium were subjected to ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) treatment and gentle agitation to assess their ability to resist a slight mechanical stress. Epithelial fragility was significantly increased in the mutant intestines compared with controls as early as 2 days postnatal (P2), and became more prominent at P14 (figure 1J). Alterations affecting the intestinal permeability are frequently observed in patients with IBD and reflect epithelial barrier dysfunction.23 To examine if such dysfunction occurred in mutant mice, we quantified intestinal permeability in vivo by feeding mice with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-dextran and measuring FITC levels in the blood plasma. Intestinal permeability was significantly increased in α6ΔIEC mice (figure 1K). Thus, α6 integrin loss in IECs impairs hemidesmosome formation, epithelial morphology and gut barrier function.
α6ΔIEC Mice develop spontaneous long-standing extensive colitis
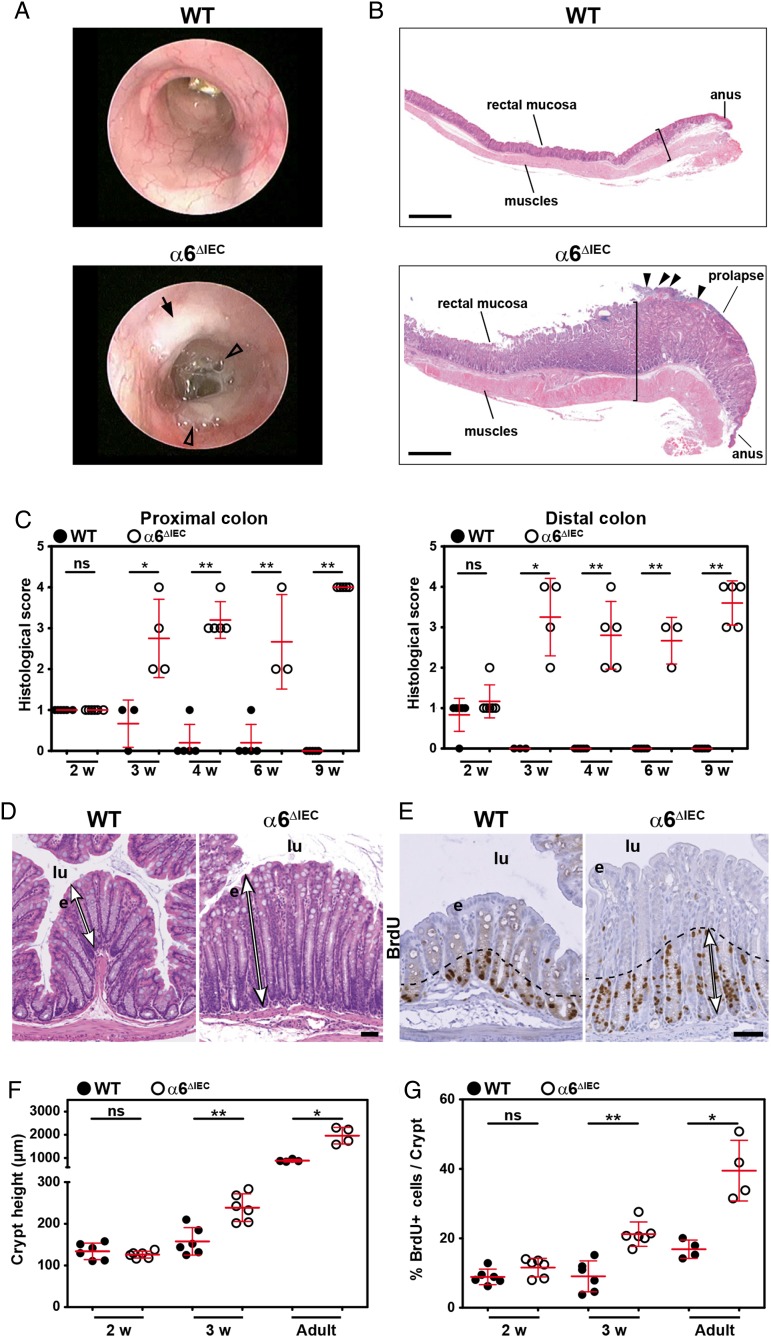
As intestinal barrier defects often lead to inflammation,1 we examined its potential occurrence in α6ΔIEC mice. We observed obvious inflammation in all mutants from 6 to 8 weeks of age as clinically illustrated by loose and/or bloody stools, rectal prolapse and mucus discharge when compared with their control littermates (see figures 1B and 2A). The intestinal wall appeared thickened throughout the colorectal region (figure 2B), with a histological score worsening from 3 weeks after birth (figure 2C). Mutant crypts in the distal colon were on average twice more elongated (figure 2D, F). As early as 3 weeks of age, the proliferation rate was also significantly increased in both colon and rectum of mutants but not in the jejunum as determined by staining for bromodeoxyuridin (BrdU) incorporation (see figure 2E, G and online supplementary figure S5A). These features (figure 2) suggested that α6ΔIEC mice develop spontaneous long-standing extensive colitis from weaning onwards.
Figure 2.
α6ΔIEC Mice develop colitis soon after weaning. (A) Representative images of WT and α6ΔIEC adult colons observed by mini-endoscopy. Black arrow, lesion affecting the mutant mucosa; arrowheads, presence of abundant mucinous material in the lumen of the mutant colon. (B) Longitudinal H&E stained sections of the recto-anal region from animals aged 15 weeks. The bracket in mutants highlights the hyperplasia in mucosa and thickened muscle layers (arrowheads, ulcerated surface). Scale bars, 500 µm. (C) Histological scores displayed as scattered dot plots (error bars, SD) measured in the proximal and distal colons of WT and α6ΔIEC mice from 2 to 9 weeks (w) of age. (D) Transverse H&E stained sections of the distal colons of WT and α6ΔIEC mice at 4 weeks. Double arrows, crypt height. Scale bar, 50 µm. (E) Immunohistochemical BrdU detection (brown nuclei) on colon sections of 3-week-old animals; dashed lines and double arrows, area of expanded proliferation in the mutant colon. Scale bar, 50 µm. (F and G) Proliferation and crypt height measurement in colons of WT and α6ΔIEC mice aged 2 and 3 weeks, and adult stages displayed as scattered dot plots (error bars, SD). (F) Quantification of crypt height. (G) Quantification of BrdU-positive cells. *p<0.05, **p<0.01. e, epithelium; lu, lumen; ns, not significant; w, weeks; WT, wildtype.
Colitis severity in α6ΔIEC mice is independent of the adaptive immune response
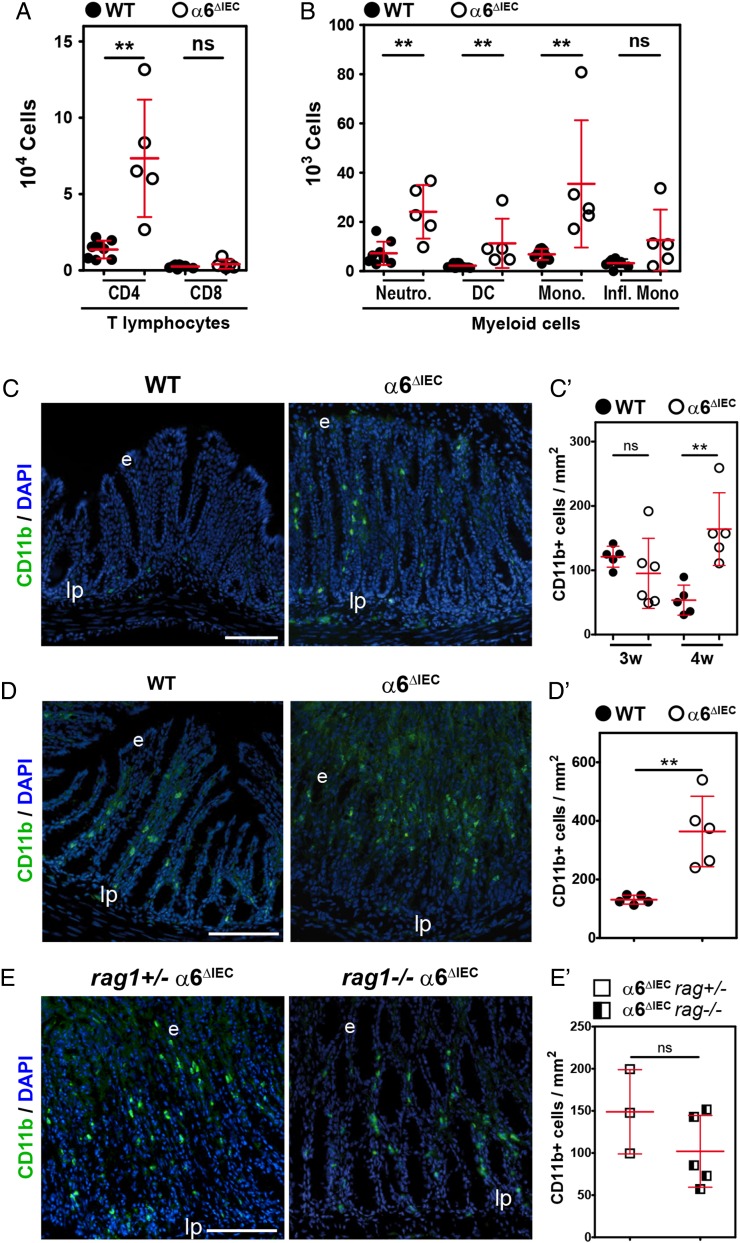
Studies in mice and humans have strongly suggested that intestinal inflammation results from an impaired innate immune response to the gut microbiota, which results in dysregulation of the adaptive immune system.7 8 To examine if inflammation in α6ΔIEC intestine follows this paradigm, we first defined the immunological profile by fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS) of immune cells isolated from the colonic lamina propria (referred to as lamina propria mononuclear cells). Mutant mice displayed ∼five-fold increase in CD4+ T lymphocytes and of several myeloid cells including neutrophils, dendritic cells and monocytes (figure 3A, B). Notably, there was a >40-fold increased recruitment of Ly-6G+/CD11b+ neutrophils within the colonic mucosa of mutant mice when compared with controls (figure 3B). By contrast, the number of CD8+ T lymphocytes and inflammatory monocytes did not vary (figure 3A, B). Histological analysis confirmed the presence of extensive immune cell infiltrates in the mutant colon/rectum/prolapse area (see online supplementary figure S5B, C). Those were mostly identified as CD11b+ cells by immunostaining, and were recruited as soon as 4 weeks (figure 3C, C′). Of note, the recruitment of these cells was even stronger at 9 weeks (figure 3D, D′).
Figure 3.
Inflammation onset in α6ΔIEC mice is mediated by myeloid cells recruitment, independently of the adaptive immune system. (A and B) FACS analysis and quantification of immune cell subpopulations present in colonic lamina propria extracts from animals raised in conventional conditions. LPMCs originate from WT and α6ΔIEC animals aged 9–15 weeks. Results are displayed as scattered dot plots (error bars, SD); each dot represents the number of positive cells present in the extract for each animal. (A) CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes; (B) Cells of myeloid origin defined as: neutrophils, Ly-6G+ CD11b+; DC, Ly-6G− CD11c+ MHC class IIintermediate; monocytes, Ly-6G− Ly-6C+ MHC class II−; pro-inflammatory monocytes, Ly-6G− Ly-6C+ CD11clow MHC class II+ CD64+. (C–E) Immunodetection of CD11b+ cells (green) in the colon of WT and α6ΔIEC mice aged 4 (C) and 9 (D) weeks, and of combined rag1+/− α6ΔIEC and rag1−/− α6ΔIEC animals (E). Scale bars, 100 µm. (C′–E′) Quantification of the number of CD11b+ infiltrating cells per mm2 of colon from images illustrated in (C–E), displayed as scattered dot plots (error bars, SD). (C′) WT and α6ΔIEC mice aged 3 and 4 weeks; (D′) 9-week-old WT and α6ΔIEC mice; (E′) combined rag1+/− α6ΔIEC and rag1−/− α6ΔIEC; rag1 α6ΔIEC mice were raised in SPF conditions. **p<0.01. DC, dendritic cells; e, epithelium; FACS, fluorescence activated cell sorting; Infl. Mono, pro-inflammatory monocytes; lp, lamina propria; LPMCs, lamina propria mononuclear cells; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; Mono., monocytes; Neutro., neutrophils; ns, not significant; SPF, specific pathogen-free; w, weeks.
To formally assess the potential involvement of T lymphocytes and B lymphocytes on disease onset, we crossed α6ΔIEC mice with rag1 −/− mice, which lack mature B lymphocytes and T lymphocytes.24 Remarkably, histopathological analyses revealed that rag1 −/− α6ΔIEC double mutant mice developed inflammation similar to that of single rag1+/− α6ΔIEC mutants, with the presence of large immune infiltrates throughout the colorectal mucosa (see online supplementary figure S5C) and high levels of CD11b+ myeloid cells (figure 3E, E′). Collectively, these results demonstrate that the onset of colitis is independent of T lymphocyte and B lymphocyte activation.
We next examined whether the inflammation observed in α6ΔIEC mice was associated with the MyD88 pathway, a major player of the innate immune response. Colitis occurred similarly in both MyD88 −/− α6ΔIEC and MyD88 +/− α6ΔIEC mutant animals suggesting that MyD88 signalling was not primarily required to initiate inflammation in α6ΔIEC intestine (see online supplementary figure S5D). Hence, inflammation onset did not involve classical toll-like receptor (TLR) pathways going through MyD88.
Early onset of colitis is linked to epithelial caspase-1 activation and IL-18 secretion in α6ΔIEC mice
To further define the pathways mediating inflammation, we next examined the levels of well-characterised pro-inflammatory cytokines involved in IBD, released by colon explants cultured for 24 hours (see online supplementary materials and methods). Cytokine screening revealed that IL-1β and IL-18 levels were the most prominently increased in mutants compared with controls (see figure 4A and online supplementary figure S6A). Among eight additional cytokines that we assayed, IFNγ, IL-17 and IL-22 levels were also increased in α6ΔIEC mice, though less prominently (see online supplementary figure S6A, B).
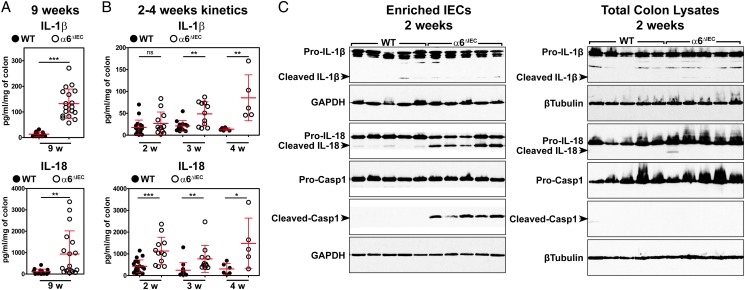
Figure 4.
Colitis initiation in α6ΔIEC mice is triggered by strong epithelial IL-18 secretion and colitis worsening by IL-1β hypersecretion. (A and B) Scattered dot plot quantification of IL-1β and IL-18 levels measured by ELISA starting from colon explants of WT and α6ΔIEC mice at 9 weeks (A) and at 2, 3 or 4 weeks of age (B) (error bars, SD; ns, not significant; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001). (C) Western blot analysis performed on protein extracts obtained from an enriched epithelial fraction (enriched IECs) or from whole colon segments (total colon lysates) of 2-week-old WT and α6ΔIEC mice. Representative blots of three independent experiments performed on at least five animals per group are illustrated. Western blot with GAPDH and β-Tubulin are presented as loading controls. Casp1, caspase-1; enriched IECs, enriched intestinal epithelial cells; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; w, weeks.
To better characterise the sequence of events occurring during disease onset, we specifically focused on the timing of IL-1β and IL-18 increase relative to the earliest abnormalities observed in mutant mice (see figure 2C–G). In particular, we examined animals aged 2–3 weeks when the epithelial barrier, the immune system and the microbiota are progressively established.25 We observed a clear difference between the initial secretion of both cytokines, since IL-18 was already significantly increased in the mutant colons at 2 weeks, whereas IL-1β was not detectable at this time point (figure 4B). From 3 weeks onwards, the secretion of both cytokines was significantly increased in the α6ΔIEC colons (figure 4B).
To identify the most likely cellular source of IL-18 and IL-1β, we used western blot analysis, to screen their expression in whole protein extracts (total colon lysates) and in an enriched epithelial fraction (enriched IECs) obtained by scraping of the colorectal mucosa (see figure 4C and online supplementary figure S7). Since both cytokines are produced as inactive forms (pro-IL-18 and pro-IL-1β) that must be cleaved by caspase-1 to be active and secreted, we also checked the expression of active caspase-1 (resulting from pro-caspase-1 cleavage). Expression levels of pro-IL-18, pro-IL-1β and pro-caspase-1 inactive forms were similar in wildtype (WT) and α6ΔIEC extracts, regardless of the stage (2 or 3 weeks) or the source of the extract (total colon vs enriched IECs) (see figure 4C and online supplementary figure S7). By contrast, a strong increase of cleaved IL-18 and cleaved caspase-1 was observed in α6ΔIEC enriched IECs as early as 2 weeks (figure 4C) and was maintained at 3 weeks (see online supplementary figure S7), but was barely detectable in total mutant colon lysates. Cleaved-IL-1β was not or barely detected.
Altogether, our data establish that IL-18 is specifically activated in α6 deficient IECs prior to any clinical and histological signs of colitis, and that its epithelial release precedes the secretion of IL-1β. Furthermore, since the active form of IL-1β was not detected in the mutant IECs, it suggests that it was probably produced by immune cells infiltrating the mucosa.
α6ΔIEC Colons display defective mucus barrier
One of the factors exacerbating inflammation in patients with IBD comes from defects in the mucus layer that protects from microbial translocation.3 26 Interestingly, very recent data have linked epithelial IL-18 signalling to mucus production by goblet cells (GCs) and to GC maturation.27
To examine the properties of the mucus layer in α6ΔIEC mice, we used periodic acid Schiff/alcian blue (PAS/AB) staining. We found that the PAS+ GC which faced the lumen displayed a larger apical compartment or theca in 4-week-old mutant distal colon (see online supplementary figure S8A–D), as also observed in keratin K8-deficient mice.28 In addition, the number of PAS+ GC detected at the base of the mutant crypts was significantly increased, while the average number of PAS+ GC over crypt height was unchanged (see online supplementary figure S8A–D). From 6 weeks of age, Muc2 and PAS/AB staining revealed abundant mucus discharge presenting altered properties in the mutant colonic lumen (see online supplementary figure S8E, F), although the ratio GC/total epithelial cells was similar (59.0±4.6% for controls and 59.7±2.7% for α6ΔIEC mice, n=3). At later stages, the normally bacteria-free inner mucus layer appeared irregular in α6ΔIEC mice (see online supplementary figure S8G). To elucidate the potential cause of the mucus defects, we analysed the distribution of the anion transporter SLC26A3 and the Na+/H+ exchanger NHE3, described as being involved in the formation and maintenance of the mucus layer,29–31 and known to be affected in the K8−/− mutant mice.28 We found that SLC26A3 and to a lesser extent NHE3 were less abundant at the apical surface of α6ΔIEC colons (see online supplementary figure S8H, H′), arguing for their involvement in the observed mucus defects in association with the altered keratin distribution.
Antibiotic treatment improves disease severity
Alterations of the mucus layer can favour a physical interaction of bacteria with the epithelium.29 30 32 We thus examined the spatial segregation of the microbiota from the epithelium in the distal colon, using fluorescence in situ hybridisation (FISH) to detect bacterial 16S ribosomal RNA, and Muc2-immunostaining to delineate the mucin layer and the epithelial border. At 3 weeks of age, when histological defects and cytokine levels were already abnormal, bacteria were clearly physically separated from IECs (see online supplementary figure S9A). By contrast, bacteria were attached to the mutant colonic epithelial surface in older diseased mice as judged by the presence of bacterial 16S rRNA in direct contact with IECs (see online supplementary figure S9B).
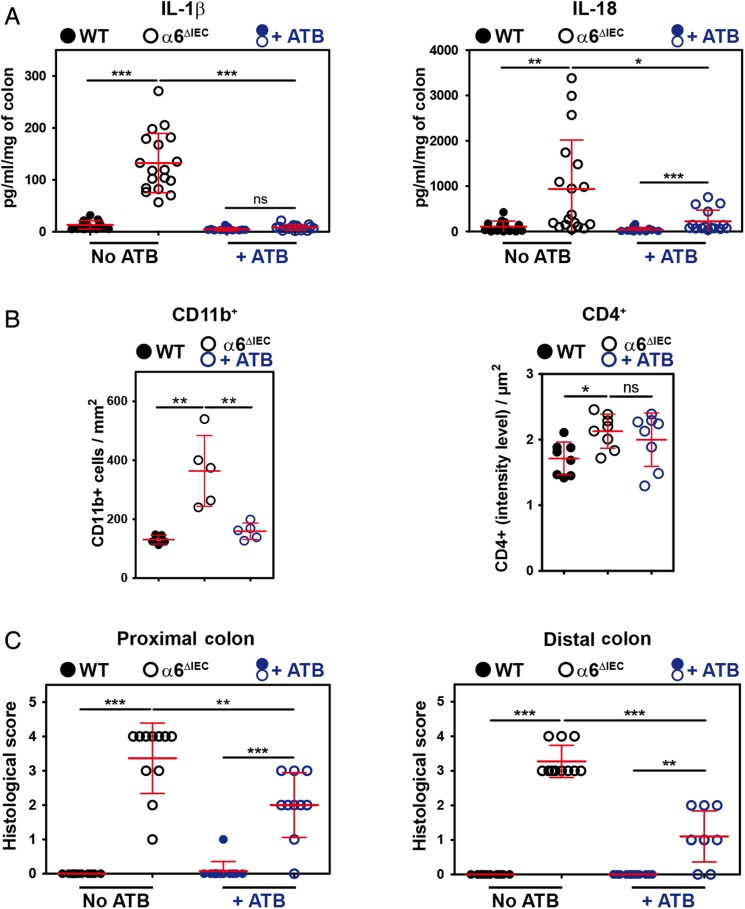
Given the close contacts between bacteria and mutant IECs, we next assessed whether bacteria had a role in eliciting colitis in α6ΔIEC mice. We treated 9-week-old animals with a cocktail of broad-spectrum antibiotics prior to collecting intestinal explants in order to deplete a large range of bacterial species. Overall, antibiotics reduced the levels of IL-1β to those observed in untreated controls and halved those observed for IL-18 (see figure 5A and online supplementary figure S9C), and had no effects on the levels of IFNγ, IL-17 and IL-22 (see online supplementary figure S9C). In addition, antibiotics improved disease severity by reducing the number of CD11b+ cells infiltrated into the mutant colonic mucosa (figure 5B), whereas they had no major effect on CD4+ T cells (figure 5B). Consequently, antibiotics reduced the colitis histological score in the mutant colon (figure 5C).
Figure 5.
Colitis in α6ΔIEC mice is partially improved by antibiotic treatment. (A–C) Scattered dot plot representations showing the quantification of cytokine levels measured by ELISA starting from colon explants (A), of the CD11b+ and CD4+ cells infiltrating the colonic mucosa (B), and of histological scores (C), in 9-week-old WT and α6ΔIEC mice treated with antibiotics (+ATB) or not. In each scattered dot plot, error bars represent SD; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. (A) ELISA quantification of IL-1β and IL-18 levels. (B) Quantification of CD11b+ and CD4+ infiltrating cells per surface of colon. (C) Colitis histological scores established in the proximal and distal colons. +ATB, with antibiotics; ns, not significant.
Overall, our results show that bacteria play a role in worsening colitis in α6ΔIEC mice, but disease onset precedes bacterial attachment to the intestinal epithelial layer. In addition, the fact that antibiotic treatment only partially restored a normal healthy mucosa with normal IL-18 levels further supports the notion that IL-18 plays a key role in triggering inflammation.
α6 Integrin loss in adults recapitulates colitis occurrence observed in α6ΔIEC animals
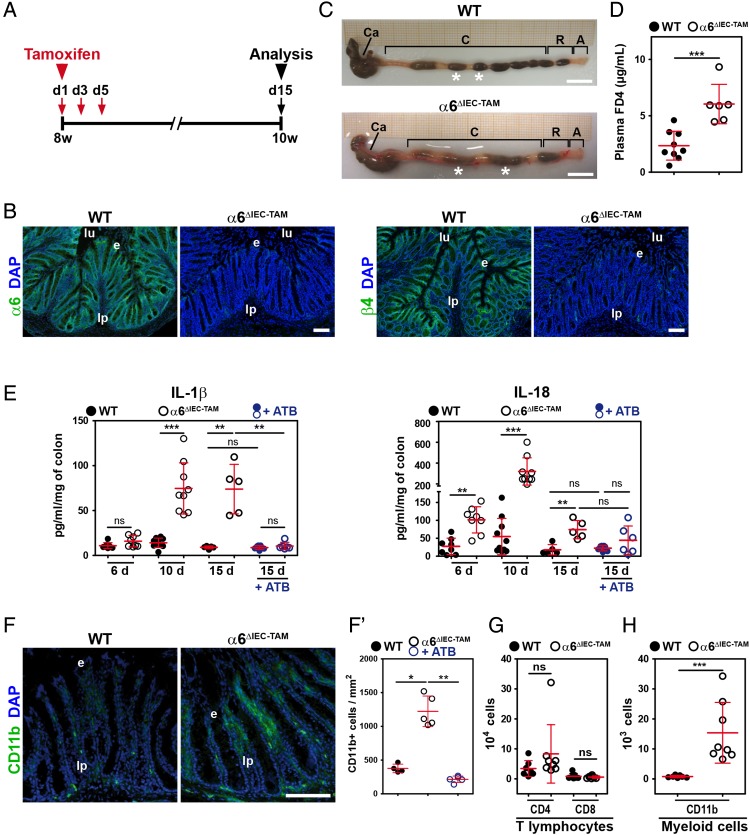
To discriminate between direct and indirect effects of α6 integrin ablation, we controlled the timing of Itga6 ablation in IECs by using the TAM-inducible Cre-ERT2 system (α6ΔIEC-TAM line).18 We treated adult mice with TAM at 8 weeks—stage at which animals have a fully mature intestine and immune system—and analysed them 2 weeks later (figure 6A). Immunodetection of α6β4 integrin in α6ΔIEC-TAM colons revealed an efficient and homogeneous removal of the α6 and β4 signals in the mutant IECs (figure 6B). Interestingly, α6ΔIEC-TAM mutants displayed colorectal swelling and loose stools (figure 6C), and an increased intestinal permeability (figure 6D) similar to those observed in the α6ΔIEC line. To better define how early molecular signs of colitis arise, we examined animals at 6, 10 and 15 days post-TAM administration. At day 6 post-TAM, mutant colons displayed significant epithelial detachment and an increase in IL-18 secretion (see figure 6E and online supplementary figure S10A, B), as what also observed in α6ΔIEC animals (see figures 1I, 4B and online supplementary figure S4B, C). α6ΔIEC-TAM Mutant mice started to develop hyperplasia (assessed by the proliferative marker Ki-67), CD11b+ cell infiltration and increased IL-1β secretion at days 10 and 15 post-TAM (see figure 6E–F′ and online supplementary figure S10A–D), with no difference in T lymphocyte subsets (figure 6G, H). In line with our previous findings in the constitutive α6ΔIEC model, antibiotic treatment applied prior to TAM administration reduced signs of inflammation (see figure 6E–F′ and online supplementary figure S10), without reducing epithelial detachment and restoring IL-18 secretion to control levels (see figure 6E and online supplementary figure S10). Thus, α6ΔIEC-TAM mice phenocopied the α6ΔIEC line.
Figure 6.
Colorectal inflammation occurs quickly after α6 integrin ablation in adult IECs. (A) Experimental procedure of TAM treatment (red arrows indicate the days of TAM administration) and subsequent analysis (black arrow) of WT and α6ΔIEC-TAM mice, illustrated for the time point 15 days post-TAM administration. Animal age is indicated in weeks. (A–D and F–H) Eight-week-old WT and α6ΔIEC-TAM mice were treated with TAM and analysed 15 days after the first TAM gavage. (B) Immunodetection of α6-integrin and β4-integrin chains (green) on colon sections of WT and α6ΔIEC-TAM. DAPI marks nuclei (blue). Scale bars, 50 µm. (C) Morphology of the colorectal region of WT and α6ΔIEC-TAM mice. Scale bars, 5 mm. (D) Scattered dot plots showing the plasma concentration of FITC-dextran (FD4) in WT and α6ΔIEC-TAM mice fed with FD4; error bars, SD. (E) ELISA quantification of the levels of IL-1β and IL-18 secreted by colon explants cultured for 24 hours. Samples were analysed 6, 10 and 15 days after the first TAM gavage in WT and α6ΔIEC-TAM mice treated with antibiotics or not. Results are displayed as scattered dot plots; error bars, SD; ns, not significant. (F and F′) Immunodetection (F) and quantification (F′) of CD11b+ cells (green) in the colon of 10-week-old TAM treated WT and α6ΔIEC-TAM mice, 15 days post TAM gavage. Scale bar, 100 µm. (G and H) Quantification by FACS analysis of the immune cell subpopulations present in LPMCs of 10-week-old TAM treated WT and α6ΔIEC-TAM mice, 15 days post TAM gavage. (G) CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes; (H) Cells of myeloid origin defined as Ly-6G+ CD11b+. Results are displayed as scattered dot plots (error bars, SD); each dot represents the number of positive cells present in the extract for each animal. *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001. A, anus; Asterisks (*), stools; +ATB, with antibiotics; C, colon; Ca, caecum; d, day; e, epithelium; FACS, fluorescence activated cell sorting; IECs, intestinal epithelial cells; LPMCs, lamina propria mononuclear cells; lp, lamina propria; lu, lumen; ns, not significant; R, rectum; TAM, tamoxifen; w, week.
We next aimed at further delineating the molecular signature of inflammation upon loss of the α6β4 integrin. To this end, we performed a transcriptome analysis on mRNAs extracted from the rectal compartment of WT and α6ΔIEC-TAM mice 15 days post-TAM treatment. Microarray data (Affymetrix) were analysed using the ‘Ingenuity Pathway Analysis’ (IPA) which helped us to define molecular interaction networks. The most activated network in α6ΔIEC-TAM mutants included the gene encoding IL-1β (see online supplementary figure S11A), confirming the leading role of the latter regulatory circuit in disease severity. Additional genes with ascribed function related to this ‘IL-1β-inflammatory network’ encoded pro-inflammatory molecules (IL1-RL1, CXCL5/CXCL6 and CXCR2) or extracellular matrix (ECM) remodelling factors (such as MMP10). Their differential expression was validated by RT-qPCR (see online supplementary figure S11B).
Altogether the phenocopy of colitis in adults having an already well-established immune system and microbiota highlights that the origin of colitis in the absence of α6 integrin is primarily associated with IEC detachment from the BM, secretion of epithelial IL-18 and exacerbation due to bacteria.
The spontaneous and fully penetrant development of adenocarcinomas in α6ΔIEC mice requires activation of B lymphocytes and T lymphocytes
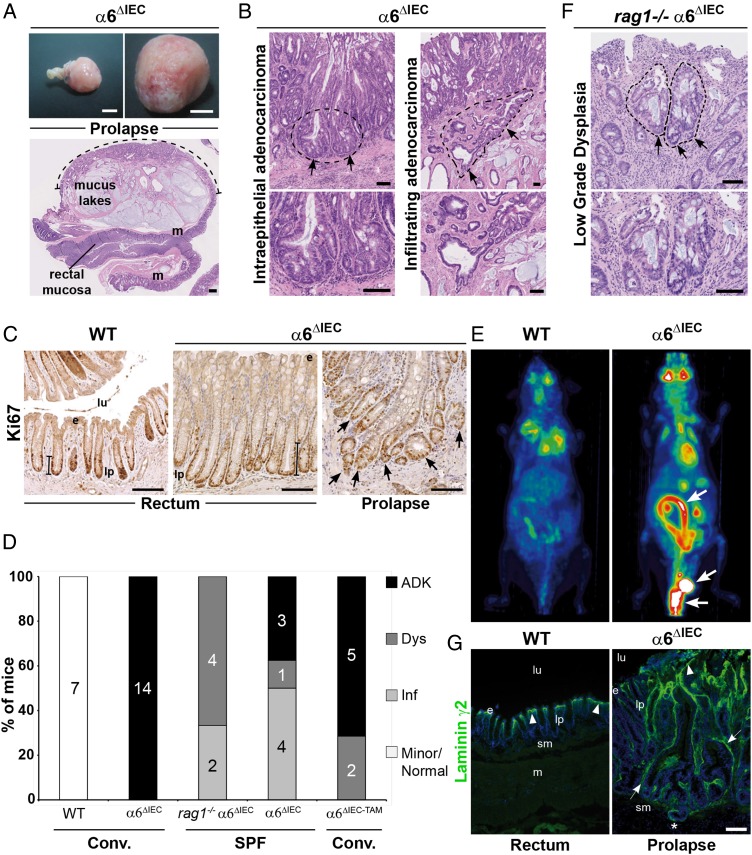
Some animal models of IBD can develop adenocarcinomas, although at a low prevalence unless treated with dextran sodium sulfate and azoxymethane.7 33 By contrast, we observed that all α6ΔIEC mice spontaneously developed colorectal adenocarcinomas by 1 year of age, and without any further chemical treatment. Adenocarcinomas and/or high-grade dysplasia were mostly located in the rectal prolapse (figure 7A), and were found very rarely in the small intestine (two out of the eight cases analysed). Histopathological analyses revealed different degrees of mucosal infiltration (figure 7B) and numerous Ki-67 positive cells were observed in invading glands within the rectal prolapse (figure 7C). Among 14 mutant mice aged 48–80 weeks, all had adenocarcinomas (figure 7D). Interestingly, α6ΔIEC-TAM mice treated with TAM at 8 weeks and analysed 1 year later or more developed also adenocarcinomas / high grade dysplasia (five out of the seven cases analysed) or at least low grade dysplasia (2/7) in the rectal prolapse, indicating that the depletion of α6 integrin even when induced in the mature intestine can trigger colitis-associated carcinogenesis (figure 7D). We next used positron emission tomography (PET scan) to test for the presence of metastasis. We detected a high metabolic level of fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) uptake in the whole large intestine of 1-year-old α6ΔIEC mice, but failed to observe distant metastasis (figure 7E).
Figure 7.
All α6ΔIEC mice spontaneously develop colitis-associated adenocarcinomas. (A–G) Tumour features in ≥1-year-old α6ΔIEC mutant mice. (A) Wide-field view (top) and histological section (bottom) of a large prolapse with an infiltrating mucinous adenocarcinoma invading the submucosa and muscle layers (m). Dotted line, region comprising tumour lesions. Scale bars: 5 mm (top); 500 µm (bottom). (B) Views of prolapse-associated tumours: (left) intraepithelial adenocarcinoma and (right) highly infiltrating adenocarcinoma (dotted lines, arrows). Higher magnifications are shown in the lower panels. Scale bars: 100 µm. (C) Ki67 immunostaining (brown nuclei) on rectal sections from 1-year-old WT and α6ΔIEC mice. Ki67+ cells are located at the base of the crypts (bar), and in the invading glands of the prolapse associated-adenocarcinoma (right panel, arrows). Scale bars: 100 µm. (D) Schematic representation showing the repartition of 1-year-old affected mice according to their genotype and the type of intestinal lesions they displayed; numbers mentioned in histogram columns and percentage (y-axis) of affected mice as well as the lesion types are indicated. The genotype of mice and the housing conditions (conventional (conv.) vs SPF) are indicated under the chart. (E) FDG-PET images of WT and α6ΔIEC mice showing a significant FDG uptake in the mutant large intestine and the rectal prolapse area (arrows). (F) Section through the recto-anal region of a combined rag1−/− α6ΔIEC mutant showing a low grade dysplasia (dotted line, arrows). Lower panel: high magnification of the dysplasia. Scale bars: 100 µm. (G) Immunodetection of laminin γ2 chain (green) in WT rectum and α6ΔIEC prolapse. DAPI (in blue) marks nuclei. Arrowheads, basement membrane underlying the surface epithelium. Arrows, increased deposits of laminin γ2 in the basement membrane and around tumour areas in α6ΔIEC prolapse. Asterisks (*), invasive gland infiltrated into the sm. Scale bar: 100 µm. ADK, adenocarcinoma; Dys, low grade dysplasia; e, epithelium; FDG, fluorodeoxyglucose; Inf, inflammation; lp, lamina propria; lu, lumen; m, muscle layer; sm, submucosa; SPF, specific pathogen-free; PET, positron emission tomography.
As reported above, the adaptive immune system does not play an obvious role in the onset of colitis. To define whether or not activation of the adaptive immune system might also be dispensable for progression to adenocarcinomas, we compared single α6ΔIEC and rag1−/− α6ΔIEC double mutant mice raised in specific pathogen-free (SPF) conditions. Out of eight α6ΔIEC animals aged 45–76 weeks, three had developed an adenocarcinoma, one displayed a severe dysplasia, whereas the four remaining had inflammation (figure 7D). By contrast, none of the 50–64 weeks old rag1−/− α6ΔIEC double mutants (6/6) developed an adenocarcinoma; instead they showed very discrete low grade dysplasia lesions (4/6) and chronic inflammation (6/6) (figure 7D, F), suggesting a critical role for the T and B cell activation on disease progression.
To know if local alterations of the microenvironment, in particular of the laminins, might contribute to tumour development, WT and mutant rectal tissues were immunostained with laminin γ2, the hemidesmosome ligand of α6β4, that is known to be overexpressed and associated with poor prognosis in CRC.34 Large laminin γ2 deposits were detected throughout the whole tumoural area within the rectal prolapse in mutant mice while the signal was restricted to the BM at the upper part of the crypts in controls (figure 7G).
Finally, to better understand the mechanisms underlying tumour aggressiveness, we defined the specific transcriptomic signature associated with carcinogenesis in the α6ΔIEC model by comparing gene expression in three distinct samples: (1) adenocarcinoma-comprising areas from the mutant prolapse, (2) inflamed but non-cancerous adjacent rectal mucosa and (3) rectal mucosa obtained from WT mice. A first IPA analysis allowed to identify significantly overexpressed or underexpressed genes in the tumour areas versus the inflamed mucosa (Student's t-test, p value ≤0.001; fold change ≥+2 or ≤−2) and to define the most activated gene network in the tumours (see online supplementary figure S12A). Many molecules involved in ECM composition and degradation/remodelling, as well as inflammatory components belong to this genes network. Interestingly, several of them have been described as being involved in colorectal carcinogenesis such as MMP9, MMP13 or TIMP1 (for review see ref. 35) or in inflammatory pathways (for review see ref. 36). Moreover, as previously described for the inflammation worsening, network analysis emphasised the prominent role of IL-1 cytokines and IL-1R signalling, suggesting that this inflammatory signature was required for tumour progression.
We further characterised the molecular signature of inflamed or cancerous lesions comparing them to the normal rectal mucosa by using a second IPA analysis which revealed the different categories of gene functions significantly affected. The results are summarised in online supplementary table S1 and figure S12B.
Altogether, the intestinal inflammation observed in α6ΔIEC mice results from epithelial detachment and IL-18 secretion leading to defective mucus barrier, independently of T lymphocyte and B lymphocyte activation and of MyD88 signalling. Furthermore, our results suggest that intestinal tumourigenesis is likely caused by continuous IL-1 signalling together with BM remodelling and B cell and T cell activation.
Discussion
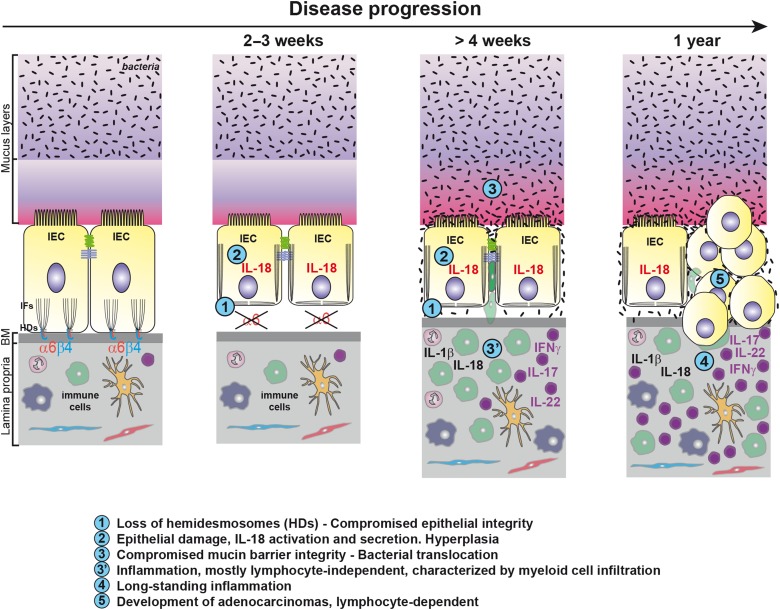
We report for the first time the key physiological protective function of the α6 integrin-mediated signalling in IECs against intestinal inflammation and tumourigenesis in mice. Our data suggest that the sequence of events leading to inflammation after intestinal epithelial-specific Itga6 ablation during development or induced in adults, first entailed hemidesmosome disruption leading to IEC detachment from the BM and to epithelium weakening. In turn, this induced sustained caspase-1 activation and IL-18 secretion in damaged IECs. Subsequently, the mucus barrier became progressively defective, promoting the exposure of IECs to bacterial and/or luminal components. Consequently, chronic inflammation was mediated by IL-1β oversecretion and myeloid cell accumulation. Importantly, the same cascade of events was observed when Itga6 deletion was induced in the adult intestine, ruling out indirect cumulative effects related to developmental defects. Finally, all α6ΔIEC and α6ΔIEC-TAM animals developed spontaneous infiltrating tumours after 1 year without any further chemical treatment. Such tumour development was dependent on the activation of the adaptive immune system (figure 8).
Figure 8.
Model of the sequence of events leading to colorectal inflammation and carcinogenesis. Schematic drawing illustrating two IECs of the large intestine attached through α6β4 integrin to the BM via the HDs. By compelling the data obtained from α6ΔIEC and α6ΔIEC-TAM models, we suggest that the following sequence of events occurs. First, loss of the integrin impairs epithelial integrity causing epithelium fragility and detachment from the BM. The absence of tight anchorage to the BM results in disruption of the IFs network and impaired cell architecture. Second, epithelial damage triggers activation of caspase-1 in IECs followed by a drastic activation and secretion of IL-18. Intestinal permeability increases, and hyperplasia occurs in the epithelium (not illustrated). Third, presumably as a secondary consequence (defective cytoskeleton, changes in mucosal pH, cytokine release), the integrity and composition of the mucin layer become altered, favouring bacterial penetration and translocation. Concomitantly, altered epithelial barrier function triggers an inflammatory response, induced in part by exposure of the immune system to bacteria. Inflammation relies on engagement of the innate immune system, mostly independently of the lymphocyte-mediated immunity. It is characterised by enhanced secretion of epithelial IL-18 and immune-mediated IL-1β, and infiltration of CD11b+ myeloid cells into the colonic mucosa. In parallel, lymphoid cells secrete IL-17, IL-22 and IFNγ and sustain chronic inflammation over a long period. Lastly, perpetuation of long-standing colitis associated with alterations of the microbiota invariably induces the spontaneous development of adenocarcinomas in all α6ΔIEC mutants, tumour progression being dependent on the adaptive immune system. BM, basement membrane; HDs, hemidesmosomes; IECs, intestinal epithelial cells; IFs, intermediate filaments.
We suggest that defective α6 integrin function at the hemidesmosome, and its induced mechanical epithelial fragility, is ultimately responsible for colitis. The concomitant loss of the β4 integrin subunit, which has already been observed in Itga6 knockout,17 20 37 might unbalance some signalling events modulated by this integrin chain,38 and could thereby trigger caspase-1 activation and IL-18 secretion. Expression of the β1 integrin chain was not significantly affected in α6ΔIEC mice, consistent with the fact that β1 depletion in the intestine led to more severe phenotypes.39 We further suggest that the absence of stable hemidesmosomal junctions leads to a reduced capacity of IECs to resist mechanical stress, leading to epithelial detachment in particular at weaning when such stress dramatically increases due to changes in diet and amplification of muscle contractions. The role of mechanical stress in the induction of a severe intestinal dysfunction has been shown in mice deficient for the integrin-associated protein kindlin-1, in which IECs fail to properly adhere to the BM and to form an efficient epithelial barrier, resulting in a severe colitis and perinatal lethality.40 Intestinal dysfunction due to α6β4 integrin absence in the intestine and a complete epithelium detachment, was also reported in a clinical case, and supports our findings.41 Interestingly, it has also been shown that hemidesmosome disturbance in Caenorhabditis elegans epidermis triggers an innate immune response.42
The activation of IL-18 downstream of the epithelial detachment induced by α6 integrin loss occurs independently of MyD88 through yet unknown mechanisms. As the caspase-1 is activated, we speculate that epithelial detachment leads to mechanical stress damage signals triggering the assembly of an inflammasome, which remains to be identified. Alterations that accumulate as a result of these initial inflammatory signals greatly contribute to increase disease severity. In particular, impairment of the mucus barrier and the subsequent exposure of the epithelial mucosa to bacterial compounds can exacerbate colitis, as was observed in mice displaying defective mucus due to the loss of core 1-derived O-glycans.43 Mucosal defects in α6ΔIEC mice are presumably caused by: (i) the abnormal localisation of keratins K8/18,28 44 (ii) the abnormal distribution of the ion transporters SLC26A3 and NHE3, implicated in mucus barrier formation29–31 and (iii) increased levels of IL-18, which controls the maturation and secretion of the mucus.27 Interestingly, it has been suggested that IL-18 controls the maturation of GCs by regulating the expression of the transcription factors Gfi1, Spdef and KLF4.27
Mechanistically, we identified that inflammation worsening required innate but not adaptive immunity mainly through the secretion of IL-1β, presumably by the infiltrating CD11b+ myeloid cells as a consequence of greater bacterial translocation. We also suggest that bacteria strongly contribute to exacerbate disease severity in our models, since antibiotic treatment strongly lowered IL-1β secretion levels, and partially IL-18. Mutant α6ΔIEC mice also displayed enhanced and antibiotic-insensitive IL-17, IL-22 and IFNγ levels, which might contribute to inflammation and later to adenocarcinoma formation, since IL-17 and IL-22 have been involved in tumour progression.45–47
A most notable feature of the α6ΔIEC model is the spontaneous development of colorectal adenocarcinomas, which had not been observed to occur with full penetrance in previously described mouse models of intestinal inflammation.33 Unexpectedly, the IBD-like phenotype observed in mice deficient in keratin-8 (K8), another key component of intestinal hemidesmosomes, relies on T lymphocytes rather than myeloid cells but was not sufficient to lead to carcinoma development.28 48 49 The latter findings suggest that hemidesmosome function was not similarly affected in K8−/− and α6ΔIEC models. In K8 deficient colon, the β4 integrin was overexpressed and led to the activation of survival signals mediated by focal adhesion kinase (FAK) phosphorylation, suggesting that the hemidesmosomes remained at least partially functional.50 By contrast, hemidesmosomes were totally disrupted in the intestine of Itga6-deficient mice, which probably led to an altered signalling cascade and keratin network.
Based on the tumourigenesis observed in α6ΔIEC mice, α6β4 integrin could be classified as a tumour suppressor. This conclusion seems at odds with other results establishing that α6β4 integrin behaves as an oncogene when it cooperates with ErbB2 in the formation of mammary tumours.51 However, the function of α6β4 is fully dependent on the tissue context.52 Likewise, in the skin, α6β4 integrin can either suppress or promote tumour growth depending on whether or not cells express Ras (V12), which is the oncogenic form of the small GTPase.53
In future studies, it will be important to further assess whether it is the microbiota imbalance, changes in the homeostasis of the immune system or some other factors that play a prevalent role in tumour formation. Besides host-microbiota interactions, mechanical stress might also influence the process, since adenocarcinomas appeared mostly in the rectal region which is the most intensely subjected to such stress and to interactions with the gut microbiota. Interestingly, hemidesmosomes have recently been found to act as a mechanotransduction platform;54 in this framework, the lack of response to mechanical stimuli in α6ΔIEC mice might contribute to impair epithelial homeostasis.
A large number of studies, mainly based on the development of genetically engineered mouse models,33 have been conducted for many years to define the origin of colitis-associated CRC. In this study we revealed the key role of the integrin/BM connection and suggest that besides microbial cues, biomechanical cues contribute to intestinal homeostasis. The key interest of the α6ΔIEC line is that it recapitulates most of the events occurring during colitis-associated carcinogenesis, with alterations very similar to those observed in many patients with IBD at high risk of developing CRC. In addition, our molecular characterisation of tumours bring new interesting leads for understanding the mechanisms involved in the progression of colitis-associated cancer. Thereby, the α6ΔIEC model provides valuable tools to develop new preventive/curative treatments for such unpredictable and invalidating diseases.
Materials and methods
The generation of mouse lines, their manipulation and other specific analyses (antibiotic treatment, epithelial cell detachment assay, FITC-dextran assay, endoscopy, histological analysis, immunofluorescence, immunohistochemistry, FISH, FACS analysis, image analysis, cytokine measurements, preparation of colon protein extracts and western blotting, RT-qPCR, transcriptome analysis, FDG-microPET imaging and study approval) as well as statistics used in this study are described in online supplementary materials and methods.
Acknowledgments
We thank D Ferrandon, D Louvard, T Mayadas, J-M Reichhart, B Reina and L Sorokin for critical reading of the manuscript, A Klein and C Arnold for technical assistance, C Ebel for help with FACS analysis, J-P Ghnassia for anatomopathogical analysis, the IGBMC-histology platform for technical support, J Pontabry for CD4-SLC26A3 image analysis, L Cao (Inviscan SAS) for PET scan image reconstruction, M-F Champy for cytokine multiplex measurements, C Thibault-Carpentier and V Alunni for microarray analysis, A Van Es and the IGBMC animal facility staff for help and advice in animal experimentation, D Metzger, P Chambon, M Li, S Chan and T Sasaki for gift of reagents and S Bour for help in figure preparation.
Footnotes
Contributors: EG-L conceived and supervised the project until mid-2012; ADA and ML supervised the project afterwards. EG-L and ADA generated the α6ΔIEC mice. ADA characterised the phenotypes. HH developed and analysed the α6ΔIEC-TAM line, and contributed to IPA analysis. FA, OL, PS-A and MK made the initial phenotype description. SN and MC analysed the microbial flora and ELISA assays. SS, VP and S Rodius assisted ADA for various technical aspects. EB and IVS examined some mucus defects. AM-N performed anatomo-pathological analyses. AM-N and MC assessed the histological scores. P Laquerriere performed PET scan analysis. DD contributed in Affymetrix and IPA analysis. P Lepage realised the bacterial bioinformatics analysis. ADC performed ELISA experiments. S Robine provided the Villin-Cre transgenic lines. ML and ADA wrote the manuscript, with inputs from EG-L, PSA and MC.
Funding: This work was supported by funds from CNRS, Inserm and Université de Strasbourg, by grants from the Association pour la Recherche sur le Cancer and Ligue Régionale contre le Cancer (EG-L), the Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale (‘Equipe FRM 2009’ to MC), the Institut National du Cancer (Appel à projets ‘Formes précoces du cancer colorectal’ to EG-L and PS-A and to EG-L and MC), Agence Nationale pour la Recherche (EG-L and ML) and LabEx INRT (IGBMC, UdS). SN was a recipient of a Postdoctoral Fellowship from the Ligue contre le Cancer.
Competing interests: None declared.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
References
- 1. McGuckin MA, Eri R, Simms LA, et al. . Intestinal barrier dysfunction in inflammatory bowel diseases. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2009;15:100–13. 10.1002/ibd.20539 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Okamoto R, Watanabe M. Role of epithelial cells in the pathogenesis and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. J Gastroenterol 2016;51:11–21. 10.1007/s00535-015-1098-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Salim SY, Söderholm JD. Importance of disrupted intestinal barrier in inflammatory bowel diseases. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2010;17:362–81. 10.1002/ibd.21403 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Abraham C, Cho JH. Inflammatory bowel disease. N Engl J Med 2009;361:2066–78. 10.1056/NEJMra0804647 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Grivennikov SI. Inflammation and colorectal cancer: colitis-associated neoplasia. Semin Immunopathol 2013;35:229–44. 10.1007/s00281-012-0352-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Ullman TA, Itzkowitz SH. Intestinal inflammation and cancer. Gastroenterology 2011;140:1807–16. 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.01.057 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Kaser A, Zeissig S, Blumberg RS. Inflammatory bowel disease. Annu Rev Immunol 2010;28:573–621. 10.1146/annurev-immunol-030409-101225 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Maloy KJ, Powrie F. Intestinal homeostasis and its breakdown in inflammatory bowel disease. Nature 2011;474:298–306. 10.1038/nature10208 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Spenlé C, Hussenet T, Lacroute J, et al. . Dysregulation of laminins in intestinal inflammation. Pathol Biol 2012;60:41–7. 10.1016/j.patbio.2011.10.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Nievers MG, Schaapveld RQ, Sonnenberg A. Biology and function of hemidesmosomes. Matrix Biol 1999;18:5–17. 10.1016/S0945-053X(98)00003-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Stutzmann J, Bellissent-Waydelich A, Fontao L, et al. . Adhesion complexes implicated in intestinal epithelial cell-matrix interactions. Microsc Res Tech 2000;51:179–90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Barrett JC, Lee JC, Lees CW, et al. . Genome-wide association study of ulcerative colitis identifies three new susceptibility loci, including the HNF4A region. Nat Genet 2009;41:1330–4. 10.1038/ng.483 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Thompson AI, Lees CW. Genetics of ulcerative colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2011;17:831–48. 10.1002/ibd.21375 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Peters U, Jiao S, Schumacher FR, et al. . Identification of Genetic Susceptibility Loci for Colorectal Tumors in a Genome-Wide Meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2013;144:799–807.e24. 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.12.020 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Fine JD, Mellerio JE. Extracutaneous manifestations and complications of inherited epidermolysis bullosa: part I. Epithelial associated tissues. J Am Acad Dermatol 2009;61:367–84; quiz 385–6 10.1016/j.jaad.2009.03.052 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Huang BL, Chandra S, Shih DQ. Skin manifestations of inflammatory bowel disease. Front Physiol 2012;3:13 10.3389/fphys.2012.00013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Niculescu C, Ganguli-Indra G, Pfister V, et al. . Conditional ablation of integrin alpha-6 in mouse epidermis leads to skin fragility and inflammation. Eur J Cell Biol 2011;90:270–7. 10.1016/j.ejcb.2010.09.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. el Marjou F, Janssen KP, Chang BH, et al. . Tissue-specific and inducible Cre-mediated recombination in the gut epithelium. Genesis 2004;39:186–93. 10.1002/gene.20042 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Dowling J, Yu QC, Fuchs E. Beta4 integrin is required for hemidesmosome formation, cell adhesion and cell survival. J Cell Biol 1996;134:559–72. 10.1083/jcb.134.2.559 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Georges-Labouesse E, Messaddeq N, Yehia G, et al. . Absence of integrin alpha 6 leads to epidermolysis bullosa and neonatal death in mice. Nat Genet 1996;13:370–3. 10.1038/ng0796-370 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. van der Neut R, Krimpenfort P, Calafat J, et al. . Epithelial detachment due to absence of hemidesmosomes in integrin beta 4 null mice. Nat Genet 1996;13:366–9. 10.1038/ng0796-366 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Raul F, Simon P, Kedinger M, et al. . Intestinal enzymes activities in isolated villus and crypt cells during postnatal development of the rat. Cell Tissue Res 1977;176:167–78. 10.1007/BF00229460 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Toedter G, Li K, Sague S, et al. . Genes associated with intestinal permeability in ulcerative colitis: changes in expression following infliximab therapy. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2012;18:1399–410. 10.1002/ibd.22853 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Mombaerts P, Iacomini J, Johnson RS, et al. . RAG-1-deficient mice have no mature B and T lymphocytes. Cell 1992;68:869–77. 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90030-G [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Tourneur E, Chassin C. Neonatal immune adaptation of the gut and its role during infections. Clin Dev Immunol 2013;2013:270301 10.1155/2013/270301 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Sheng YH, Hasnain SZ, Florin TH, et al. . Mucins in inflammatory bowel diseases and colorectal cancer. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012;27:28–38. 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2011.06909.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Nowarski R, Jackson R, Gagliani N, et al. . Epithelial IL-18 Equilibrium Controls Barrier Function in Colitis. Cell 2015;163:1444–56. 10.1016/j.cell.2015.10.072 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Toivola DM, Krishnan S, Binder HJ, et al. . Keratins modulate colonocyte electrolyte transport via protein mistargeting. J Cell Biol 2004;164:911–21. 10.1083/jcb.200308103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Johansson ME, Gustafsson JK, Holmén-Larsson J, et al. . Bacteria penetrate the normally impenetrable inner colon mucus layer in both murine colitis models and patients with ulcerative colitis. Gut 2014; 63:281–91. 10.1136/gutjnl-2012-303207 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Larmonier CB, Laubitz D, Hill FM, et al. . Reduced colonic microbial diversity is associated with colitis in NHE3-deficient mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2013;305:G667–77. 10.1152/ajpgi.00189.2013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Xiao F, Yu Q, Li J, et al. . Slc26a3 deficiency is associated with loss of colonic HCO3 (-) secretion, absence of a firm mucus layer and barrier impairment in mice. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 2014;211:161–75. 10.1111/apha.12220 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Vaishnava S, Yamamoto M, Severson KM, et al. . The antibacterial lectin RegIIIgamma promotes the spatial segregation of microbiota and host in the intestine. Science 2011;334:255–8. 10.1126/science.1209791 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Kanneganti M, Mino-Kenudson M, Mizoguchi E. Animal models of colitis-associated carcinogenesis. J Biomed Biotechnol 2011;2011:342637 10.1155/2011/342637 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Miyazaki K. Laminin-5 (laminin-332): Unique biological activity and role in tumor growth and invasion. Cancer Sci 2006;97:91–8. 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2006.00150.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Said AH, Raufman JP, Xie G. The role of matrix metalloproteinases in colorectal cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2014;6:366–75. 10.3390/cancers6010366 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. West NR, McCuaig S, Franchini F, et al. . Emerging cytokine networks in colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Immunol 2015;15:615–29. 10.1038/nri3896 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Rodius S, Indra G, Thibault C, et al. . Loss of alpha6 integrins in keratinocytes leads to an increase in TGFbeta and AP1 signaling and in expression of differentiation genes. J Cell Physiol 2007;212:439–49. 10.1002/jcp.21040 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Giancotti FG. Targeting integrin beta4 for cancer and anti-angiogenic therapy. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2007;28:506–11. 10.1016/j.tips.2007.08.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Jones RG, Li X, Gray PD, et al. . Conditional deletion of beta1 integrins in the intestinal epithelium causes a loss of Hedgehog expression, intestinal hyperplasia, and early postnatal lethality. J Cell Biol 2006;175:505–14. 10.1083/jcb.200602160 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Ussar S, Moser M, Widmaier M, et al. . Loss of Kindlin-1 causes skin atrophy and lethal neonatal intestinal epithelial dysfunction. PLoS Genet 2008;4:e1000289 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000289 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Lachaux A, Bouvier R, Loras-Duclaux I, et al. . Isolated deficient alpha6beta4 integrin expression in the gut associated with intractable diarrhea. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1999;29:395–401. 10.1097/00005176-199910000-00005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Zhang Y, Li W, Li L, et al. . Structural damage in the C. elegans epidermis causes release of STA-2 and induction of an innate immune response. Immunity 2015;42:309–20. 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.01.014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Fu J, Wei B, Wen T, et al. . Loss of intestinal core 1-derived O-glycans causes spontaneous colitis in mice. J Clin Invest 2011;121:1657–66. 10.1172/JCI45538 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Specian RD, Neutra MR. Cytoskeleton of intestinal goblet cells in rabbit and monkey. The theca. Gastroenterology 1984;87:1313–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Huber S, Gagliani N, Zenewicz LA, et al. . IL-22BP is regulated by the inflammasome and modulates tumorigenesis in the intestine. Nature 2012;491:259–63. 10.1038/nature11535 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Kirchberger S, Royston DJ, Boulard O, et al. . Innate lymphoid cells sustain colon cancer through production of interleukin-22 in a mouse model. J Exp Med 2013;210:917–31. 10.1084/jem.20122308 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Liu J, Duan Y, Cheng X, et al. . IL-17 is associated with poor prognosis and promotes angiogenesis via stimulating VEGF production of cancer cells in colorectal carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2011;407:348–54. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.03.021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Baribault H, Penner J, Iozzo RV, et al. . Colorectal hyperplasia and inflammation in keratin 8-deficient FVB/N mice. Genes Dev 1994;8:2964–73. 10.1101/gad.8.24.2964 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Habtezion A, Toivola DM, Butcher EC, et al. . Keratin-8-deficient mice develop chronic spontaneous Th2 colitis amenable to antibiotic treatment. J Cell Sci 2005;118:1971–80. 10.1242/jcs.02316 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Habtezion A, Toivola DM, Asghar MN, et al. . Absence of keratin 8 confers a paradoxical microflora-dependent resistance to apoptosis in the colon. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2011;108:1445–50. 10.1073/pnas.1010833108 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Guo W, Pylayeva Y, Pepe A, et al. . Beta 4 integrin amplifies ErbB2 signaling to promote mammary tumorigenesis. Cell 2006;126:489–502. 10.1016/j.cell.2006.05.047 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Stewart RL, O'Connor KL. Clinical significance of the integrin α6β4 in human malignancies. Lab Invest 2015;95:976–86. 10.1038/labinvest.2015.82 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Raymond K, Kreft M, Song JY, et al. . Dual Role of alpha6beta4 integrin in epidermal tumor growth: tumor-suppressive versus tumor-promoting function. Mol Biol Cell 2007;18:4210–21. 10.1091/mbc.E06-08-0720 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Zhang H, Landmann F, Zahreddine H, et al. . A tension-induced mechanotransduction pathway promotes epithelial morphogenesis. Nature 2011;471:99–103. 10.1038/nature09765 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
gutjnl-2015-310847supp001.pdf (5MB, pdf)