Abstract
Repetitive stress negatively affects several brain functions and neuronal networks. Moreover, adult neurogenesis is consistently impaired in chronic stress models and in associated human diseases such as unipolar depression and bipolar disorder, while it is restored by effective antidepressant treatments. The adult neurogenic niche contains neural progenitor cells in addition to amplifying progenitors, neuroblasts, immature and mature neurons, pericytes, astrocytes, and microglial cells. Because of their particular and crucial position, with their end feet enwrapping endothelial cells and their close communication with the cells of the niche, astrocytes might constitute a nodal point to bridge or transduce systemic stress signals from peripheral blood, such as glucocorticoids, to the cells involved in the neurogenic process. It has been proposed that communication between astrocytes and niche cells depends on direct cell-cell contacts and soluble mediators. In addition, new evidence suggests that this communication might be mediated by extracellular vesicles such as exosomes, and in particular, by their miRNA cargo. Here, we address some of the latest findings regarding the impact of stress in the biology of the neurogenic niche, and postulate how astrocytic exosomes (and miRNAs) may play a fundamental role in such phenomenon.
1. The Relevance of the Hippocampus in the Stress Response
Stressful life events are strong precipitating factors of neuropsychiatric pathologies including mood disorders such as major depression (MD) or bipolar disorder (BD) [1]. Stress can be defined as any adaptive mechanism triggered to recover the organism's homeostasis, composed of a vast array of modifications in the physiology of different organs, including the central nervous system (CNS) at different scales, that is, plastic changes which range from molecular dynamics to behavioral adaptations [2].
The proper adaptive response to stressors is known as “stress resilience” and the multiple biological processes underlying resilience are collectively termed allostasis [3]. Nevertheless, plastic changes can be deleterious to cerebral and overall body health under prolonged stress (reviewed in [4]). Furthermore, increasing evidence shows that stress impacts the induction not only of psychiatric but also systemic pathologies such as cardiovascular diseases, cancer, and inflammation-related diseases [5–7].
The mechanisms that participate in the stress response involve the CNS, where the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis (HPA) has a central role. HPA activation leads to an increase in the systemic levels of glucocorticoids (GCs) (cortisol in humans and corticosterone in rodents) in concomitance with changes in the activity of the autonomic system, with norepinephrine and epinephrine as final products [2]. GCs are key hormones of the stress response that are able to cross the blood-brain barrier due to their lipophilic nature. Receptors in target cells include the high-affinity mineralocorticoid receptor [8] or the low-affinity glucocorticoid receptors [9]. In the brain, both receptors are mainly occupied by GCs and translocate to the nucleus after binding to their ligand, where they modify the expression of different genes that govern the stress response. The brain area profoundly affected during chronic stress is the hippocampus. The human and rodent hippocampi correspond to a CNS region where glucocorticoid receptors (GRs) are expressed in neurons, astrocytes as well as in some neural stem cells [10–12], conferring a high sensitivity of this forebrain structure to changes in glucocorticoids levels [13]. A negative feedback loop mediated by cortisol regulates the activity of the HPA by targeting structures such as the paraventricular nucleus and the hippocampus. In the latter, synaptic inputs can directly exert an overall inhibitory effect on the activity of the HPA [14]. Stress triggers molecular and structural changes in the hippocampus, including dendritic and spine atrophy that is concomitant to downregulation of specific synaptic protein [15, 16]. Many of these glucocorticoid-mediated changes can be mimicked by exogenous application of these corticosteroids (extensively reviewed by [13]).
Intriguingly, the hippocampus harbors one of the two identified brain structures in mammals that retains the capacity to generate new neurons in adulthood, that is, the neurogenic niche of the subgranular zone (SGZ) in the dentate gyrus (DG). The process by which new neurons are continuously generated in the SGZ of adults is known as adult neurogenesis and implies the self-renewal, proliferation/activation of neural stem/precursor cells, their differentiation into neurons, as well as their migration, maturation, and even their integration into the hippocampal functional circuits [17–19]. Any modification in one of these stages can influence (positively or negatively) the generation of new neurons, and diverse pathological conditions including chronic stress have been described to decrease adult hippocampal neurogenesis [20]. Conversely, antidepressant interventions show an increase in the number of neural stem/precursor cells in the DG. In fact, some antidepressant drugs depend on neurogenesis to induce recovery from depressive symptoms [21–24].
Hippocampal newborn neurons are essential for the proper endocrine and behavioral adaptation to stress [25], and SGZ neurogenesis contributes to the negative feedback on the HPA axis, as its disruption induces a larger response to a mild stressor [26]. Consistently, it has been described that altered neurogenesis leads to a slower recovery of GC levels after stress [27], suggesting a cross talk between hippocampal neurogenesis and the HPA axis. Likewise, reduced neurogenesis is associated with impaired responsiveness of the HPA axis in the dexamethasone suppression test [28]. Thus, any process that restores hippocampal neurogenic activity might contribute to better cope with stress. This could take place at the various stages involved in this process, from cell proliferation to the generation of mature DG neurons.
2. The Adult Hippocampal Neural Stem/Precursor Cells
Seri and coworkers [29] observed for the first time that neural stem cells that undergo proliferation in the SGZ display radial glia characteristics expressing the glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), in addition to markers of undifferentiated cells such as vimentin, SOX2, and Nestin. SGZ stem cells are called type 1 cells (reviewed by Ming and Song [30]). These give rise, through asymmetric division, to highly proliferative intermediate progenitors known as type 2a (positive for Nestin and PSA-NCAM and negative for GFAP) and 2b cells (positive for Tbr2 and PSA-NCAM). The latter cells give rise to neuroblasts or type 3 cells (positive for doublecortin, PSA-NCAM, and NeuN) that migrate into the inner granular layer. Within days, type 3 cells will become immature neurons that, after about 4 weeks, extend dendrites towards the molecular layer and project axons through the hilus toward the CA3 (reviewed by Zhao et al., Covic et al., and Bonaguidi et al. [17, 31, 32]). In summary, both neural stem and progenitor cells coexist in the SGZ and can generate new granule neurons [33, 34]. In the present review, we will use the acronym NSPCs to describe both neural stem cells and precursor cells.
3. Magnitude of Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis
It has been estimated that in the rat hippocampus 9000 new cells are generated every 25 hours [35]. In mice, on the other hand, the number is much lower: only 2700 new cells per day are generated [36]. After 30 days, ~30% of new cells survive and differentiate into mature neurons with complex dendritic and axonal structure. In humans, direct evidence of adult neurogenesis has been provided first by the use of the synthetic analog BrdU (bromodeoxyuridine, 5-bromo-2′-deoxyuridine) [37] and later on by an elegant publication which presented an integrated model of cell turnover dynamics in the hippocampus by measuring the concentration of nuclear bomb test-derived 14C in hippocampal cells. This work shows that one-third of human hippocampal neurons are exchanged throughout life and that 700 new neurons are added per day. The authors calculated a turnover of 1.75% newborn neurons per year that decreased modestly during aging. Taken together, this data indicates that adult hippocampal neurogenesis is not a minor process and may contribute significantly to human brain function during physiology and disease [38].
4. Adult-Born Hippocampal Neurons and the Impact of Stress
After stressful experiences, the activation of the HPA axis and the elevation of systemic GC levels lead to the impairment of NSPC proliferation in the SGZ both in developmental stages as well as in adulthood [39, 40].
Consistently, adrenalectomy increases the formation of new neurons in young and aged rodents [41–43]. Furthermore, the hyporesponsive stress period in rats (from 2 days after birth to 2 weeks old), characterized by low basal levels of GCs and a diminished response to stress [44], is associated with the maximal neurogenesis period in the SGZ [45, 46]. Likewise, adrenalectomy prevents the suppression of neurogenesis induced by stress [47, 48]. The effect of GCs on the neurogenic potential has shown to be dose-dependent in a human hippocampal progenitor cell line. Interestingly, low concentrations of cortisol stimulate proliferation and gliogenesis and decrease neurogenesis by signaling through mineralocorticoid receptors. On the other hand, high doses of cortisol decreased proliferation through glucocorticoid receptor signaling, with no effect on gliogenesis [49]. Similarly, decreased neurogenesis has been observed in different stress models, including chronic and acute stress, for example, subordination stress [50], resident-intruder stress [51], footshock [52], restraint stress [53, 54], or stress-induced by isolation [55] and predator odor [56]. It is worth remarking that stress has been shown to affect neurogenesis in a reduced window of time. Tanapat et al. observed that animals may experience a rebound in cell proliferation after the initial stress-induced suppression to compensate the alteration [47]. These results agree with several publications in which acute stressful experiences increases neurogenesis [57–60].
Despite significant advances in the field of neurogenesis and stress over the past two decades, detailed mechanisms underlying the inhibition of cell proliferation under stress conditions and its adaptations remain unknown.
5. Astrocytes Are Key Players in Adult Neurogenic Niche
Neurogenesis is regulated through its specialized microenvironment, the neurogenic niche. In adult mammals, including humans, neurogenic niches are concentrated in restricted areas; the most commonly described are the subventricular zone (SVZ) of the lateral ventricles and, mentioned above, the SGZ of hippocampal DG [61, 62]. The regulation of neurogenesis in the neurogenic niche is such that NSPCs obtained from exogenous SVZ and grafted into another SVZ host are able to generate new neurons; but NSPCs from the SVZ grafted into nonneurogenic brain regions show a scarce neurogenic potential, suggesting that here, a very particular cellular and molecular context accounts for the control of neurogenesis [63, 64].
Any cellular type within the niche can influence the neurogenic process by diffusible signals or by cell-cell interactions. In the SGZ, the main cellular components are astrocytes, endothelial cells, pericytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia, different types of neurons present in the DG, and the aforementioned NSPCs [65]. Although each cell type may have a significant contribution to the neurogenic process, in the present review, we will focus on the role of astrocytes as key elements in the control of the neurogenic process under stress.
Astrocytes subserve a myriad of functions that have been described both in vitro and in vivo (extensively reviewed by Khakh and Sofroniew [66]). In the hippocampus, protoplasmic astrocytes extend their processes radially and some of them contact blood vessels to form perivascular end feet of the blood-brain barrier (BBB), while others may contact neurons (e.g., tripartite synapse) or be coupled to oligodendrocytes through connexins [67]. In addition, astrocytes may connect with other astrocytes through connexins, generating a sort of functional syncytium able to signal by propagating calcium waves along several distant cells in vivo [68]. It is therefore not surprising that they are thought to have a central role in the functional output of the neurogenic process [69]. For example, astrocytes negatively influence the differentiation of NSPCs after the activation of jagged1-mediated Notch pathway by cell-cell contact [70] or by the secretion of growth factors such as insulin-like growth factor binding protein 6 (IGFBP6) and decorin [71]. On the contrary, released factors such as Wnt3a, neurogenesin-1, and different interleukins such as IL-1β and IL-6 or cell-to-cell contact mediated by ephirn-B2 signaling positively regulate neurogenesis [29, 71–74]. Thus, it is possible that, depending on the physiological and anatomical context, the astrocyte secretome has distinct effects on the neurogenic process [71]. In this line, hippocampal astrocytes are more efficient than cortical astrocytes in promoting neuronal differentiation of NSPCs [75].
The secretory activity of astrocytes in the DG mediates the synaptic and network integration of newborn neurons in vivo, highlighting their role as key mediators of the functional output of neurogenesis [76]. Previous data supports this view, as astrocytes promote the differentiation of progenitor cells and control the maturation and synaptic integration of newborn neurons in vitro [77, 78].
6. Stress, Astrocyte Plasticity, and Neurogenesis
A wide body of evidence has shown that acute and/or chronic stress can alter the morphology and functionality of different glial cell types in the brain, such as microglia [79, 80], oligodendroglia [81], and astrocytes [82].
Czéh et al. observe that tree shrews subjected to 5 weeks of psychosocial stress showed a 25% reduction in the intermediate filament protein of astrocytes GFAP, as well as a 25% reduction in the somatic volume of hippocampal astrocytes [83]. In the past few years, several publications using other stress protocols have led to similar observations [84–86]. Nevertheless, some publications using the chronic restraint model have reported an increase in GFAP positive cell number and in the protein level in the hippocampus [87, 88].
Other proteins expressed by astrocytes such as connexin 30 and 43 (gap junction proteins), the water channel aquaporin-4 (AQP4), the calcium-binding protein S100β and the amino acid transporters 1 and 2 (EAAT1, EAAT2), and glutamine synthetase have altered expression levels in both animals models of stress and in human brain samples analyzed postmortem compared with controls (reviewed in [89]). Despite the importance of some of these proteins in calcium homeostasis, there is a lack of studies showing how astrocytic calcium metabolism is regulated under stress conditions.
Moreover, a recent publication by Zhao et al. has shown that a decrease in glycogen content is associated with chronic stress, being one of the main mechanism in astrocytes capable of inducing their structural and molecular alterations. This result may be of importance as it moves away from the GC-centered theory of stress [90].
On the other hand, different publications have reported that when astrocytes are exposed to high levels of GCs, GC bound to GRs translocates to the nucleus and enhances the expression of genes related with neurogenesis, one example is the Fgf2 gene [91]. FGF2, the protein encoded by Fgf2, is a potent and necessary proliferative factor in adult NSPCs [92]. Nevertheless, other different effects mediated by astrocytes over the adult neurogenesis after a stressful condition have not been fully unveiled. In Table 1, we resume the main effects described for this issue, both in vivo and in vitro.
Table 1.
Effect of stress over neurogenesis mediated by astrocytes.
| Type of stress | Type of study | Cellular effect | Molecular mechanism | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acute and chronic induced by dexamethasone | In vivo | Growth inhibition of astrocytes | After inducing cell cycle exit by reduction of cyclin D1 and increase of p27 | [128] |
| In vitro | Inhibition of NSPC proliferation (cultured with CM of stressed astrocytes) | By altered expression of neurotrophic factors (BDNF, NGF) and mitogenic factors (BFGF, VEGF) and death-inducing factors (FasL, Trail, Tweak, and TNFα) | ||
| Acute induced by dexamethasone or corticosterone | In vitro | Inhibition of astrocytes proliferation | By inducing reduction of GR expression | [129] |
| Chronic induced by administration of ACTH | In vivo | Inhibition of astrocytes proliferation | By inducing reduction of GR expression | |
| Acute and chronic | In vivo | Regulation of mRNAs in a cell type-dependent fashion | By glucocorticoids receptors | [130] |
| Acute | In vivo | Increase hippocampus cellular proliferation | Increase of astrocytes FGF2 expression | [131] |
7. Exosomes Biogenesis and the Relevance of Their Content in Controlling Cellular Function
In addition to soluble components (see Section 5), the astrocyte secretome contains extracellular vesicles (EVs) such as exosomes [93] that represent a different source of cell-cell communication [94, 95]. Exosomes are generated in the endocytic pathway after the invagination and subsequent fission of a domain in the endosomal membrane that give rise to an exosome precursor called intraluminal vesicle (ILV) of the multivesicular body (MVB). After the fusion with the plasma membrane, the ILVs are released into the extracellular space as spherical vesicles of 40–100 nm, called exosomes [96]. The biogenesis of exosomes requires different molecular components including the mechanisms dependent of the ESCRT (endosomal sorting complex required for transport) machinery [97, 98] and lipid-dependent mechanisms [99, 100]. Proteins that participate in their biogenesis are frequently used as positive markers of exosomes, as well as proteins associated with lipid rafts and tetraspanins such as Alix, flotillin, TSG101, and CD63 [101].
Exosomes contain a complex molecular cargo that include proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids that may be biologically active on recipient cells [102]. The protein composition is diverse and depends on the cellular type and the physiological context; nevertheless, as they originate in the endocytic pathway, the most common proteins independent of the cell type of origin are related to vesicular transport and fusion (Rab GTPasas, SNAREs, annexins, and flotillin), different integrins and tetraspanins (CD63, CD9, CD81, and CD82), and heat shock proteins (Hsc/Hsp 70 and 90) and proteins implicated in the biogenesis of MVB (Alix and TSG 101) [103]. Regarding their lipidic content, one characteristic of the exosomes is their enrichment in lipid rafts including cholesterol, sphingolipids (such as ceramide), and glycerophospholipids with long and saturated fatty acyl chains [101]. Finally, among the most relevant biologically active molecules present in exosomes are nucleic acids, particularly small noncoding RNAs such as miRNAs (see below).
Exosomes play a significant role in the secretome of a given cell, subserving functions in the communication between cells [104]. Furthermore, virtually all eukaryotic cells release exosomes and are capable of taking them up [105, 106]. Regarding the CNS, oligodendrocytes, neurons, astrocytes, and microglia are capable of releasing exosomes with functional consequence on neuronal physiology [107]. Actually, exosomes have been proposed to be key players in the pathogenesis of different CNS diseases, including neurodegenerative diseases, infectious diseases, neuroinflammation, and even psychiatric disorders such as depression [108, 109]. Considering the high molecular diversity and complexity of their cargo, a fundamental question to understand the biological relevance of astrocytic exosomes in neurogenesis is a critical analysis of the relevant molecular cargo that could potentially control the fate of NSPCs and the neurogenic process.
So far, the functional transfer/interaction of exosomes to target cells has been shown mostly in vitro, but there is increasing data being obtained in vivo. Analysis of in vivo evidence is crucial as it settles the basis to propose that astrocytes within the neurogenic niche might be able to modify NSPCs' physiology through functional transfer of exosomal cargo in physiological conditions and during diseases. In this regard, an outstanding result came from the work of Zhang et al. where they found in vivo that tumor cells lose the expression of the tumor suppressor protein phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) after incorporating astrocytic exosomes, due to the presence of a microRNA (miRNA) that targets PTEN [110].
Thus, although still speculative, we discuss a putative scenario where astrocytes in the neurogenic niche modulate the cellular behavior of NSPCs on the virtue of exosome transfer. It is important to notice that, in the literature, several of the functional effects described for exosomes are attributed to mRNA or miRNA transfer rather than proteins or lipids (as an example see [111]), though there is a growing interest to examine the relevance of these molecules in the exosomal cargo.
8. miRNAs in Astrocyte-Derived Exosomes as Modulators of Adult Neurogenesis and Stress Response
miRNAs are small noncoding RNAs (20–22 nucleotides) that cause deadenylation as well as translational repression of mRNAs by binding to their 3′ untranslated region (3′UTR). They have been proposed to be integral regulatory molecules in both physiological conditions and in disease states, because a single miRNA molecule can repress several hundreds (and even thousands) of mRNA molecules [112, 113]. Furthermore, the targeting of a single mRNA by a miRNA can potentially modulate the transcription of a vast array of proteins [114].
miRNAs are known to be a key element for neuronal differentiation; for example, Kawase-Koga et al. observed that NSPCs undergo cell death and affecting also the neuronal differentiation and their maturation after conditionally deleting the expression of the RNAse III enzyme DICER, an enzyme that processed miRNA precursor into mature miRNAs in specific stages of mice development [115]. Another miRNA that has also proved to modulate neuronal differentiation is miR-124, which contributes to the downregulation of Ezh2, a histone H3 Lys-27 histone methyltransferase that governs the transcription of several neuron-specific genes, diminishing the differentiation of mouse embryonic NSPCs as a final outcome [116, 117].
On the other hand, an increase in the expression of miR-9 in neurogenic regions leads to a reduction of NSPC proliferation and accelerated neural differentiation due to its modulation of TLX, a key regulator of NSPCs self-renewal, whereas the knock-in of miR-9 leads to increased proliferation of NSPCs [118]. Other miRNAs such as miR-128 and miR-137 promote differentiation of NSPCs, while their knockdown compromises their self-renewal [119].
Recently, Han et al. have shown that miRNA-19 (a member of polycistronic miRNA genes critical for brain development) is enriched in NSPCs and decreases during neuronal development. They found that this miRNA controls the maturation and positioning of newborn neurons in the granular cell layer of the DG by suppressing Rap guanine nucleotide exchange factor 2 (Rapgef2) [120]. In another study, the authors found that miR-20 downregulates the transcriptional repressor gene REST, inhibiting the differentiation of NSPCs [121]. Other miRNAs controlling both proliferation and differentiation of adult NSPCs are miR-137 [122] and rno-miR-592 [123]. Taken together, these data indicate an important participation of miRNAs in adult neurogenesis.
Multiple evidence has shown a relationship between miRNAs and stress, both in animal models of stress and in human patients with depression. Furthermore, some miRNAs have been postulated as potential biomarkers of stress/depression (extensively reviewed by Dwivedi and Brites and Fernandes [124, 125]). miRNAs also may play important roles in the mechanism of action of antidepressants: for example, in early-life stress models, the downregulation of miR-451 was reversed after antidepressant treatment [126].
Regarding astrocytes, although the information available about the differential cargo of astrocyte-derived exosomes after stressful conditions is scarce, it is worth pointing out that several miRNAs that are up or downregulated in stress conditions are contained in exosomes secreted by astrocytes. These miRNAs have also been described to play a role in the neurogenic process (Tables 2 and 3). Interestingly, miRNAs contained in astrocyte-derived exosomes are differentially enriched as compared to their levels in astrocytes [127], suggestive of their unique role in cellular communication. Moreover, many of the miRNAs contained in astrocytes can be modulated by different stimuli (see Table 4). All these data lead us to postulate astrocyte-derived exosomes as potential modulators of proliferation, migration, and/or differentiation of NSPCs within the neurogenic niche, and that changes in exosomal release as well as in their miRNA cargo can play a role in neurogenesis under stress conditions, in a similar fashion as it has been described for other CNS pathologies.
Table 2.
miRNA associated with neurogenesis present in astrocytes- and astrocytes-derived exosomes.
| miRNA | Expression level | Cellular process | Molecular target | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-9 | Overexpression | Reduces axonal branching and neurite outgrowth | MAP1b | [132] |
| miR-9 | Upregulation/overexpression | Promotes neuronal differentiation | Notch signaling, several targets | [133] |
| miR-9 | Upregulation/overexpression | Promotes neuronal differentiation and dendritic branching, inhibits migration | TLX, REST, Rap2a, and stathmin | [134] |
| miR-9 | Upregulation/overexpression | Suppresses astrogliogenesis | Lifr-beta, Il6st (gp130), and Jak1 (jack/stat pathway) | [135] |
| miR-9 | Upregulation/overexpression | Promotes neuronal differentiation and migration | TLX/Nre1, Foxg1, REST/NRSF, CoREST, Meis2, Gsh2, Islet1, Id4, and stathmin | [136] |
| miR-9 | Overexpression | Mediates neural differentiation of ES cell | STAT3 | [137] |
| miR-9 | Overexpression | Promotes neuronal differentiation | Foxg1, Gsh2, SIRT1, and REST/NRSF | [138] |
| miR-9 | Overexpression | Inhibits NSPC proliferation and facilitates NSPC differentiation | TLX | [118] |
| miR-9 | Overexpression | Inhibits NSPC proliferation and facilitates NSPC differentiation | Hes1 (notch signaling) | [139] |
| miR-26a | Upregulation | Inhibits spine enlargement | RSK3 | [140] |
| miR-26a | Downregulation | Prevents axonal regeneration | GSK3β | [141] |
| miR-26b | Upregulation | Promotes neuronal differentiation | Ctdsp2 | [142] |
| miR-29a | Upregulation | Increase axonal branching | DCX | [143] |
| miR-34a | Upregulation | Promotes neural differentiation and synaptogenesis | TAp73, synaptotagmin-1, and sintaxin-1A | [144] |
| miR-34a | Upregulation | Inhibits neuronal differentiation, promotes proliferation | Numbl, NeuroD1, and Mash1 | [134] |
| miR-34a | Upregulation | Promotes apoptosis, inhibits cell cycle progression and synaptic development | BCL-2, Cdk-4 Cyclin D2 synaptotagmin syntaxin-1A | [134] |
| miR-34a | Upregulation | Negatively regulate neurite outgrowth and dendritic branching | [134] | |
| miR-125b | Upregulation | Promotes neuronal differentiation | BMP/TGFβ signaling | [133] |
| miR-125b | Upregulation | Promotes neuronal differentiation | Nestin | [145] |
| miR-125b | Upregulation | Inhibits NSPC proliferation and promotes differentiation | Musashi1 | [146] |
| miR-129 | Upregulation | Determination of the bipolar cell identity in retina | Xotx2, Xvsv1 | [147] |
| miR-135b | Upregulation/Overexpression | Promotes neuronal induction | BMP/TGFβ signaling | [148] |
| miR-145 | Upregulation | Promotes neuronal differentiation | OCT4, SOX2, and KLF4 | [149] |
| miR-145 | Upregulation | Promotes neuronal differentiation | SOX2, Lin28/let7 | [150] |
| miR-221 | Downregulated | Neurite guidance | [151] | |
| Let-7 family | Upregulation | Pluripotency inhibitor promoting neural lineage, promotes neuronal differentiation | Lin28 | [133] |
| Let-7 family | Upregulation | Promotes NSPCs differentiation | c-Myc, Lin28 | [136] |
| Let-7b | Upregulation | Inhibits proliferation and promotes the differentiation of NSPCs | TLX, Cyclin D1 | [152] |
| miR-543 | Upregulation | Promotes neural stem cell differentiation and neuronal migration | N-Cadherin, TrappC8 | [153] |
Table 3.
miRNA associated with neurogenesis enriched in astrocytes derived exosomes.
| miRNA | Expression level | Cellular process | Molecular target | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-25b | Overexpression | Promotes proliferation and differentiation of NSPCs | IGF signaling | [154] |
| miR-17-92 | Overexpression | Increase axonal outgrowth | PTEN | [123] |
| miR-92a | Upregulation/overexpression | Inhibits the transition from radial glial cells to intermediate progenitors | Tbr2 | [155] |
| miR-184 | Upregulation | Inhibits differentiation and promotes proliferation of NSPCs | Numbl | [156] |
| miR-302 | Upregulation | Block neural progenitor induction | BMP/TGFβ, NR2F2 | [157] |
| miR-96 | Upregulation | Block neural progenitor induction | PAX6 | [158] |
Table 4.
miRNA associated with neurogenesis modified after different stimulus.
| miRNA | Expression level | Cellular process | Molecular target | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-181a | Upregulated by morphine | Promote astrocyte-preferential differentiation of NSPCs | Prox1/Notch2 | [159] |
| miR-23b | Upregulated by morphine | Adult neurogenesis | Morphine receptor expression (MOR1) | [160] |
| miR-190 | Downregulated by fentanyl | Adult neurogenesis | NeuroD | [161] |
| miR-143 | Upregulation by IGF-1 | Promotes proliferation, neural differentiation, and cell survival | PDGFRA, PRKCE, MAPK7, DSSP, DMP-1, KRAS, and BCL-2 | [162] |
| miR-181c | Upregulation by IGF1/LIF | Enhanced self-renewal of NSPCs | PTPN11, PTPN22, PTEN, Dusp6, PBX3, ZEB2, and IRF8 | [162] |
9. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
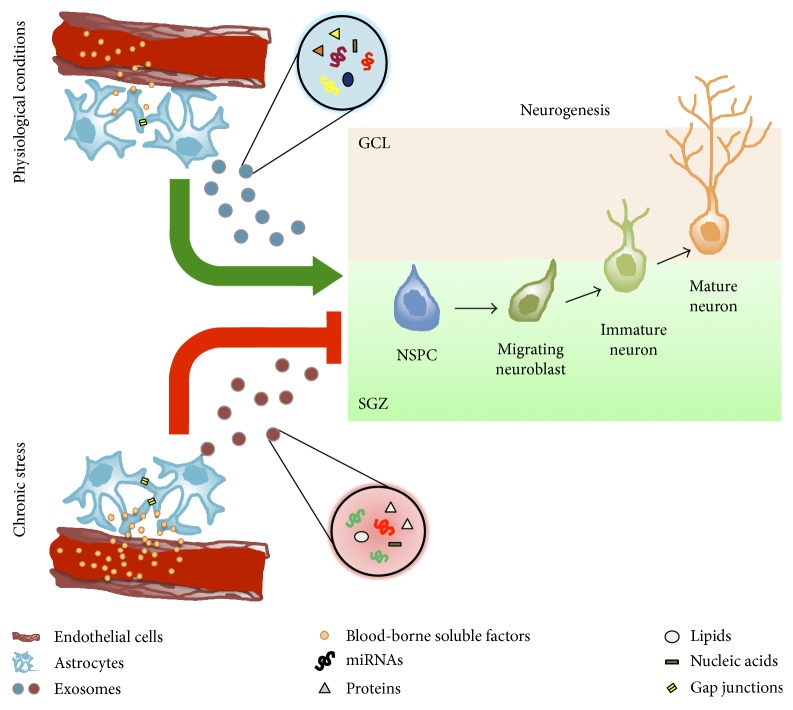
The production and proliferation of neural lineages (neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes) are a complex phenomenon tightly regulated by a multiplicity of factors. This regulation is susceptible to profound modifications when the homeostasis of the environment changes due to acute or chronic disorders. In the case of chronic stress, the observed modifications in the neurogenic niche (i.e., a decrease in NSPC proliferation/differentiation) lack a solid molecular explanation. Astrocytes may be key players to further understand on how and why the neurogenic niche responds the way it does in physiological and pathophysiological conditions. This is especially true in the case of the SGZ, where, due to their proximity with the vasculature, astrocytes may respond to factors in circulation (e.g., corticosteroids) to influence the behavior of the neurogenic niche [18]. We propose that a putative mechanism by which astrocytes exert their influence is through exosomal delivery of specific miRNAs. This could provide a finely tuned regulatory system, acting through two mechanisms: the first one is related to the unique membrane protein footprint that would enable astrocyte-derived exosomes to target specifically some, but not all, cell types of the neurogenic niche, and the second one is related with the miRNA cargo that most probably is unique under certain conditions. This could provide an exquisite temporal and spatial regulation for every single cell type implicated during the whole process of neurogenesis (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Blood-borne soluble factors reach astrocytes in the neurogenic niche, thus triggering the release of exosomes. In physiological conditions, the content of their cargo may exert a positive modulatory effect over one or more neurogenic stages (e.g., enhancing proliferation, and differentiation). During pathological conditions such as chronic stress, astrocytes respond to blood-borne soluble factors (e.g., corticosteroids and cytokines) by releasing exosomes with a cargo that may have a negative modulatory influence over one or more neurogenic stages. Astrocytes may in turn communicate with each other through gap junctions and/or by exosomal release. This may partly explain the decrease in differentiation and proliferation observed under such conditions. Note that the exosomal content under pathological or physiological conditions may differ in terms of the identity of the molecules (e.g., different types of miRNAs or proteins) and/or in their overall quantity. GCL: granule cell layer; SGZ: subgranular zone; NPSC: neural stem/precursor cell.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by CONICYT (FONDECYT Program 3170887 (Alejandro Luarte), FONDECYT Program 1140108 (Ursula Wyneken), and FONDECYT Program 1141015 (Luis Federico Batiz)) and by the Universidad de los Andes Fondo de Ayuda a la Investigación (FAI Carlos Lafourcade and FAI Roberto Henzi).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
References
- 1.Hammen C. Stress and depression. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology. 2005;1(1):293–319. doi: 10.1146/annurev.clinpsy.1.102803.143938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chrousos G. P. Stress and disorders of the stress system. Nature Reviews Endocrinology. 2009;5(7):374–381. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2009.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.McEwen B. S. Plasticity of the hippocampus: adaptation to chronic stress and allostatic load. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 2006;933(1):265–277. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2001.tb05830.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Sapolsky R. M. Stress, glucocorticoids, and damage to the nervous system: the current state of confusion. Stress. 1996;1(1):1–19. doi: 10.3109/10253899609001092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Reiche E. M., Nunes S. O., Morimoto H. K. Stress, depression, the immune system, and cancer. Lancet Oncology. 2004;5(10):617–625. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(04)01597-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sorrells S. F., Caso J. R., Munhoz C. D., Sapolsky R. M. The stressed CNS: when glucocorticoids aggravate inflammation. Neuron. 2009;64(1):33–39. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.09.032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Tawakol A., Ishai A., Takx R. A., et al. Relation between resting amygdalar activity and cardiovascular events: a longitudinal and cohort study. Lancet. 2017;389(10071):834–845. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31714-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Arriza J., Weinberger C., Cerelli G., et al. Cloning of human mineralocorticoid receptor complementary DNA: structural and functional kinship with the glucocorticoid receptor. Science. 1987;237(4812):268–275. doi: 10.1126/science.3037703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hollenberg S., Weinberger C., Ong E., et al. Primary structure and expression of a functional human glucocorticoid receptor cDNA. Nature. 1985;318(6047):452–457. doi: 10.1038/318635a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Joëls M. Role of corticosteroid hormones in the dentate gyrus. Progress in Brain Research. 2007;163:355–370. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(07)63021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wang Q., Van Heerikhuize J., Aronica E., et al. Glucocorticoid receptor protein expression in human hippocampus; stability with age. Neurobiology of Aging. 2013;34(6):1662–1673. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2012.11.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Garcia A., Steiner B., Kronenberg G., Bick-sander A., Kempermann G. Age-dependent expression of glucocorticoid- and mineralocorticoid receptors on neural precursor cell populations in the adult murine hippocampus. Aging Cell. 2004;3(6):363–371. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9728.2004.00130.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Conrad C. D. Chronic stress-induced hippocampal vulnerability: the glucocorticoid vulnerability hypothesis. Reviews in the Neurosciences. 2008;19(6):395–411. doi: 10.1515/revneuro.2008.19.6.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Herman J. P., Figueiredo H., Mueller N. K., et al. Central mechanisms of stress integration: hierarchical circuitry controlling hypothalamo–pituitary–adrenocortical responsiveness. Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology. 2003;24(3):151–180. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2003.07.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Popoli M., Yan Z., McEwen B. S., Sanacora G. The stressed synapse: the impact of stress and glucocorticoids on glutamate transmission. Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 2012;13(1):22–37. doi: 10.1038/nrn3138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.McEwen B. S., Bowles N. P., Gray J. D., et al. Mechanisms of stress in the brain. Nature Neuroscience. 2015;18(10):1353–1363. doi: 10.1038/nn.4086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Zhao C., Deng W., Gage F. H. Mechanisms and functional implications of adult neurogenesis. Cell. 2008;132(4):645–660. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.01.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ming G. L., Song H. Adult neurogenesis in the mammalian brain: significant answers and significant questions. Neuron. 2011;70(4):687–702. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.05.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.GonÇalves J. T., Schafer S. T., Gage F. H. Adult neurogenesis in the hippocampus: from stem cells to behavior. Cell. 2016;167(4):897–914. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.10.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lucassen P. J., Oomen C. A. Stress, hippocampal neurogenesis and cognition: functional correlations. Frontiers in Biology. 2016;11(3):182–192. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Malberg J. E., Eisch A. J., Nestler E. J., Duman R. S. Chronic antidepressant treatment increases neurogenesis in adult rat hippocampus. The Journal of Neuroscience. 2000;20(24):9104–9110. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-24-09104.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Madsen T. M., Treschow A., Bengzon J., Bolwig T. G., Lindvall O., Tingstrom A. Increased neurogenesis in a model of electroconvulsive therapy. Biological Psychiatry. 2000;47(12):1043–1049. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3223(00)00228-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Sairanen M. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and antidepressant drugs have different but coordinated effects on neuronal turnover, proliferation, and survival in the adult dentate gyrus. The Journal of Neuroscience. 2005;25(5):1089–1094. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3741-04.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Perera T. D., Coplan J. D., Lisanby S. H., et al. Antidepressant-induced neurogenesis in the hippocampus of adult nonhuman primates. The Journal of Neuroscience. 2007;27(18):4894–4901. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0237-07.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kino T. Stress, glucocorticoid hormones, and hippocampal neural progenitor cells: implications to mood disorders. Frontiers in Physiology. 2015;6:p. 230. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2015.00230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Schloesser R. J., Manji H. K., Martinowich K. Suppression of adult neurogenesis leads to an increased hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis response. Neuroreport. 2009;20(6):553–557. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0b013e3283293e59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Snyder J. S., Soumier A., Brewer M., Pickel J., Cameron H. A. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis buffers stress responses and depressive behaviour. Nature. 2011;476(7361):458–461. doi: 10.1038/nature10287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Schoenfeld T. J., Gould E. Stress, stress hormones, and adult neurogenesis. Experimental Neurology. 2012;233(1):12–21. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2011.01.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Seri B., Garcı J. M., Mcewen B. S., Alvarez-buylla A. Astrocytes give rise to new neurons in the adult mammalian hippocampus. The Journal of Neuroscience. 2001;21(18):7153–7160. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-18-07153.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ming G., Song H. Adult neurogenesis in the mammalian brain: significant answers and significant questions. Neuron. 2012;70(4):687–702. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.05.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Covic M., Karaca E., Lie D. C. Epigenetic regulation of neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus. Heredity (Edinburg) 2010;105(1):122–134. doi: 10.1038/hdy.2010.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Bonaguidi M. A., Song J., Ming G., Song H. A unifying hypothesis on mammalian neural stem cell properties in the adult hippocampus. Current Opinion in Neurobiology. 2012;22(5):754–761. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2012.03.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Bonaguidi M. A., Wheeler M. A., Shapiro J. S., et al. In vivo clonal analysis reveals self-renewing and multipotent adult neural stem cell characteristics. Cell. 2011;145(7):1142–1155. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.05.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Braun S. M. G., Jessberger S. Adult neurogenesis: mechanisms and functional significance. Development. 2014;141(10):1983–1986. doi: 10.1242/dev.104596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Cameron H. A., Mckay R. D. G. Adult neurogenesis produces a large pool of new granule cells in the dentate gyrus. The Journal of Comparative Neurology. 2001;435(4):406–417. doi: 10.1002/cne.1040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Snyder J. S., Choe J. S., Clifford M. A., et al. Adult-born hippocampal neurons are more numerous, faster maturing, and more involved in behavior in rats than in mice. The Journal of Neuroscience. 2009;29(46):14484–14495. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1768-09.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Eriksson P. S., Perfilieva E., Björk-Eriksson T., et al. Neurogenesis in the adult human hippocampus. Nature Medicine. 1998;4(11):1313–1317. doi: 10.1038/3305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Spalding K. L., Bergmann O., Alkass K., et al. Dynamics of hippocampal neurogenesis in adult humans. Cell. 2013;153(6):1219–1227. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Gould E., Cameron H. A. Regulation of neuronal birth, migration and death in the rat dentate gyrus. Developmental Neuroscience. 1996;18:22–35. doi: 10.1159/000111392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Mirescu C., Gould E. Stress and adult neurogenesis. Hippocampus. 2006;16(3):233–238. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Gould E., Cameron H. A., Daniels D. C., Woolley C. S., McEwen B. S. Adrenal hormones suppress cell division in the adult rat dentate gyrus. The Journal of Neuroscience. 1992;12(9):3642–3650. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-09-03642.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Cameron H. A., Gould E. Adult neurogenesis is regulated by adrenal-steroids in the dentate gyrus. Neuroscience. 1994;61(2):203–209. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(94)90224-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Cameron H. A., McKay R. D. Restoring production of hippocampal neurons in old age. Nature Neuroscience. 1999;2(10):894–897. doi: 10.1038/13197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Sapolsky R. M., Meaney M. Maturation of the adrenocortical stress response: neuroendocrine control mechanisms and the stress hyporesponsive period. Brain Research. 1986;396(1):64–76. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(86)80190-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Altman J., Bayer S. A. Migration and distribution of two populations of hippocampal granule cell precursors during the perinatal and postnatal periods. The Journal of Comparative Neurology. 1990;301(3):365–381. doi: 10.1002/cne.903010304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Tanapat P., Galea L. A., Gould E. Stress inhibits the proliferation of granule cell precursors in the developing dentate gyrus. Internation of Journal Developmental Neuroscience. 1998;16(3-4):235–239. doi: 10.1016/s0736-5748(98)00029-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Tanapat P., Hastings N. B., Rydel T. A., Galea L. A. M., Gould E. Exposure to fox odor inhibits cell proliferation in the hippocampus of adult rats via an adrenal hormone-dependent mechanism. The Journal of Comparative Neurology. 2001;437(4):496–504. doi: 10.1002/cne.1297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Mirescu C., Peters J. D., Gould E. Early life experience alters response of adult neurogenesis to stress. Nature Neuroscience. 2004;7(8):841–846. doi: 10.1038/nn1290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Anacker C., Cattaneo A., Luoni A., et al. Glucocorticoid-related molecular signaling pathways regulating hippocampal neurogenesis. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013;38(5):872–883. doi: 10.1038/npp.2012.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Gould E., McEwen B. S. S., Tanapat P., Galea L. A., Fuchs E. Neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of the adult tree shrew is regulated by psychosocial stress and NMDA receptor activation. The Journal of Neuroscience. 1997;17(7):2492–2498. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-07-02492.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Gould E., Tanapat P., Mcewen B. S., Flgge G., Fuchs E. Proliferation of granule cell precursors in the dentate gyrus of adult monkeys is diminished by stress. Neurobiology. 1998;95(6):3168–3171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.6.3168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Malberg J. E., Duman R. S. Cell proliferation in adult hippocampus is decreased by inescapable stress: reversal by fluoxetine treatment. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2003;28(9):1562–1571. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Pham K., Nacher J., Hof P. R., McEwen B. S. Repeated restraint stress suppresses neurogenesis and induces biphasic PSA-NCAM expression in the adult rat dentate gyrus. The European Journal of Neuroscience. 2003;17(4):879–886. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2003.02513.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Bain M. J., Dwyer S. M., Rusak B. Restraint stress affects hippocampal cell proliferation differently in rats and mice. Neuroscience Letters. 2004;368(1):7–10. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2004.04.096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Heine V. M., Maslam S., Joëls M., Lucassen P. J. Increased P27KIP1 protein expression in the dentate gyrus of chronically stressed rats indicates G 1 arrest involvement. Neuroscience. 2004;129(3):593–601. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.07.048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Falconer E. M., Galea L. A. M. Sex differences in cell proliferation, cell death and defensive behavior following acute predator odor stress in adult rats. Brain Research. 2003;975(1-2):22–36. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(03)02542-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Thomas R. M., Urban J. H., Peterson D. A. Acute exposure to predator odor elicits a robust increase in corticosterone and a decrease in activity without altering proliferation in the adult rat hippocampus. Experimental Neurology. 2006;201(2):308–315. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2006.04.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Thomas R. M., Hotsenpiller G., Peterson D. A. Acute psychosocial stress reduces cell survival in adult hippocampal neurogenesis without altering proliferation. The Journal of Neuroscience. 2007;27(11):2734–2743. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3849-06.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Dagyte G., Van der Zee E. A., Postema F., et al. Chronic but not acute foot-shock stress leads to temporary suppression of cell proliferation in rat hippocampus. Neuroscience. 2009;162(4):904–913. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.05.053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Hanson N. D., Owens M. J., Boss-Williams K. A., Weiss J. M., Nemeroff C. B. Several stressors fail to reduce adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2011;36(10):1520–1529. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2011.04.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Alvarez-Buylla A., Lim D. A. For the long run: maintaining germinal niches in the adult brain. Neuron. 2004;41(5):683–686. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(04)00111-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Bonaguidi M. A., Peng C.-Y., McGuire T., et al. Noggin expands neural stem cells in the adult hippocampus. The Journal of Neuroscience. 2008;28(37):9194–9204. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3314-07.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Gage F. H. Mammalian neural stem cells. Science. 2000;287(5457):1433–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.287.5457.1433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Lim D. A., Tramontin A. D., Trevejo J. M., Herrera D. G., García-Verdugo J. M., Alvarez-Buylla A. Noggin antagonizes BMP signaling to create a niche for adult neurogenesis. Neuron. 2000;28(3):713–726. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)00148-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Bátiz L. F., Castro M. A., Burgos P. V., et al. Exosomes as novel regulators of adult neurogenic niches. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience. 2016;9:1–28. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2015.00501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Khakh B. S., Sofroniew M. V. Diversity of astrocyte functions and phenotypes in neural circuits. Nature Neuroscience. 2015;18(7):942–952. doi: 10.1038/nn.4043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Orthmann-Murphy J. L., Abrams C. K., Scherer S. S. Gap junctions couple astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience. 2008;35(1):101–116. doi: 10.1007/s12031-007-9027-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Kuga N., Sasaki T., Takahara Y., Matsuki N., Ikegaya Y. Large-scale calcium waves traveling through astrocytic networks in vivo. The Journal of Neuroscience. 2011;31(7):2607–2614. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5319-10.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Kempermann G. Astrocytes, makers of new neurons. Neuron. 2015;88(5):850–851. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.11.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Wilhelmsson U., Faiz M., De Pablo Y., et al. Astrocytes negatively regulate neurogenesis through the jagged1-mediated notch pathway. Stem Cells. 2012;30(10):2320–2329. doi: 10.1002/stem.1196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Barkho B. Z., Song H., Aimone J. B., et al. Identification of astrocyte-expressed factors that modulate neural stem/progenitor cell differentiation. Stem Cells and Development. 2006;15(3):407–421. doi: 10.1089/scd.2006.15.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Ueki T., Tanaka M., Yamashita K., et al. A novel secretory factor, neurogenesin-1, provides neurogenic environmental cues for neural stem cells in the adult hippocampus. The Journal of Neuroscience. 2003;23(37):11732–11740. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-37-11732.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Lu Z., Kipnis J. Thrombospondin 1—a key astrocyte-derived neurogenic factor. The FASEB Journal. 2010;24(6):1925–1934. doi: 10.1096/fj.09-150573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Ashton R. S., Conway A., Pangarkar C., et al. Astrocytes regulate adult hippocampal neurogenesis through ephrin-B signaling. Nature Neuroscience. 2012;15(10):1399–1406. doi: 10.1038/nn.3212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Oh J., McCloskey M. A., Blong C. C., Bendickson L., Nilsen-Hamilton M., Sakaguchi D. S. Astrocyte-derived interleukin-6 promotes specific neuronal differentiation of neural progenitor cells from adult hippocampus. Journal of Neuroscience Research. 2010;88(13):2798–2809. doi: 10.1002/jnr.22447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Sultan S., Li L., Moss J., et al. Synaptic integration of adult-born hippocampal neurons is locally controlled by astrocytes. Neuron. 2015;88(5):957–972. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.10.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Song H., Stevens C. F., Gage F. H. Astroglia induce neurogenesis from adult neural stem cells. Nature. 2002;417(6884):39–44. doi: 10.1038/417039a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Lim D. A., Alvarez-Buylla A. Interaction between astrocytes and adult subventricular zone precursors stimulates neurogenesis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1999;96(13):7526–7531. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.13.7526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Walker F., Nilsson M., Jones K. Acute and chronic stress-induced disturbances of microglial plasticity, phenotype and function. Current Drug Targets. 2013;14(11):1262–1276. doi: 10.2174/13894501113149990208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Delpech J. C., Madore C., Nadjar A., Joffre C., Wohleb E. S., Layé S. Microglia in neuronal plasticity: influence of stress. Neuropharmacology. 2015;96(Part A):19–28. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.12.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Edgar N., Sibille E. A putative functional role for oligodendrocytes in mood regulation. Translational Psychiatry. 2012;2(5, article e109) doi: 10.1038/tp.2012.34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Pearson-leary J., Osborne D. M., Mcnay E. C. Role of glia in stress-induced enhancement and impairment of memory. 2016;9(63):1–14. doi: 10.3389/fnint.2015.00063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Czéh B., Simon M., Schmelting B., Hiemke C., Fuchs E. Astroglial plasticity in the hippocampus is affected by chronic psychosocial stress and concomitant fluoxetine treatment. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006;31(8):1616–1626. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Ye Y., Wang G., Wang H., Wang X. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) infusion restored astrocytic plasticity in the hippocampus of a rat model of depression. Neuroscience Letters. 2011;503(1):15–19. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2011.07.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Sun J.-D., Liu Y., Yuan Y.-H., Li J., Chen N.-H. Gap junction dysfunction in the prefrontal cortex induces depressive-like behaviors in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012;37(5):1305–1320. doi: 10.1038/npp.2011.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Tynan R. J., Beynon S. B., Hinwood M., et al. Chronic stress-induced disruption of the astrocyte network is driven by structural atrophy and not loss of astrocytes. Acta Neuropathologica. 2013;126(1):75–91. doi: 10.1007/s00401-013-1102-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Jang S., Suh S. H., Yoo H. S., Lee Y. M., Oh S. Changes in iNOS, GFAP and NR1 expression in various brain regions and elevation of sphingosine-1-phosphate in serum after immobilized stress. Neurochemical Research. 2008;33(5):842–851. doi: 10.1007/s11064-007-9523-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Kwon M. S., Seo Y. J., Lee J. K., et al. The repeated immobilization stress increases IL-1B immunoreactivities in only neuron, but not astrocyte or microglia in hippocampal CA1 region, striatum and paraventricular nucleus. Neuroscience Letters. 2008;430(3):258–263. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2007.11.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Rajkowska G., Stockmeier C. A. Astrocyte pathology in major depressive disorder: insights from human postmortem brain tissue. Current Drug Targets. 2013;14(11):1225–1236. doi: 10.2174/13894501113149990156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Zhao Y., Zhang Q., Shao X., et al. Decreased glycogen content might contribute to chronic stress-induced atrophy of hippocampal astrocyte volume and depression- like behavior in rats. Scientific Reports. 2017;7:1–14. doi: 10.1038/srep43192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Gubba E. M., Fawcett J. W., Herbert J. The effects of corticosterone and dehydroepiandrosterone on neurotrophic factor mRNA expression in primary hippocampal and astrocyte cultures. Molecular Brain Research. 2004;127(1-2):48–59. doi: 10.1016/j.molbrainres.2004.05.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Chipperfield H., Bedi K. S., Cool S. M., Nurcombe V. Heparan sulfates isolated from adult neural progenitor cells can direct phenotypic maturation. The International Journal of Developmental Biology. 2002;46(4):661–670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Verkhratsky A., Matteoli M., Parpura V., Mothet J.-P., Zorec R. Astrocytes as secretory cells of the central nervous system: idiosyncrasies of vesicular secretion. The EMBO Journal. 2016;35(3):239–257. doi: 10.15252/embj.201592705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Harding C., Heuser J., Stahl P. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of transferrin and recycling of the transferrin receptor in rat reticulocytes. The Journal of Cell Biology. 1983;97(2):329–339. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.2.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Théry C. Exosomes: secreted vesicles and intercellular communications. F1000 Biology Reports. 2011;3:p. 15. doi: 10.3410/B3-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.van Niel G., Porto-Carreiro I., Simoes S., Raposo G. Exosomes: a common pathway for a specialized function. Journal of Biochemistry. 2006;140(1):13–21. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvj128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Hurley J. H. ESCRT complexes and the biogenesis of multivesicular bodies. Current Opinion in Cell Biology. 2008;20(1):4–11. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2007.12.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Henne W. M., Stenmark H., Emr S. D. Molecular mechanisms of the membrane sculpting ESCRT pathway. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine. 2013;3(10):1–12. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a016766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Trajkovic K., Hsu C., Chiantia S., et al. Ceramide triggers budding of exosome vesicles into multivesicular endosomes. Science. 2008;319(5867):1244–1247. doi: 10.1126/science.1153124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Bianco F., Perrotta C., Novellino L., et al. Acid sphingomyelinase activity triggers microparticle release from glial cells. The EMBO Journal. 2009;28(8):1043–1054. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2009.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Raposo G., Stoorvogel W. Extracellular vesicles: exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. The Journal of Cell Biology. 2013;200(4):373–383. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201211138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.O’Driscoll L. Expanding on exosomes and ectosomes in cancer. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2015;372(24):2359–2362. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcibr1503100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Simons M., Raposo G. Exosomes – vesicular carriers for intercellular communication. Current Opinion in Cell Biology. 2009;21(4):575–581. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2009.03.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Colombo M., Raposo G., Théry C. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology. 2014;30:255–289. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-101512-122326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Lopez-Verrilli M. A., Court F. A. Exosomes: mediators of communication in eukaryotes. Biological Research. 2013;46(1):5–11. doi: 10.4067/S0716-97602013000100001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Luarte A., Bátiz L. F., Wyneken U., Lafourcade C. Potential therapies by stem cell-derived exosomes in CNS diseases: focusing on the neurogenic niche. Stem Cells International. 2016;2016:16. doi: 10.1155/2016/5736059.5736059 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Budnik V., Ruiz-Cañada C., Wendler F. Extracellular vesicles round off communication in the nervous system. Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 2016;17(3):160–172. doi: 10.1038/nrn.2015.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Pegtel D. M., Peferoen L., Amor S. Extracellular vesicles as modulators of cell-to-cell communication in the healthy and diseased brain. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, Series B: Biological Sciences. 2014;369(1652) doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Brites D., Fernandes A. Neuroinflammation and depression: microglia activation, extracellular microvesicles and microRNA dysregulation. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience. 2015;9:p. 476. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2015.00476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Zhang L., Zhang S., Yao J., et al. Microenvironment-induced PTEN loss by exosomal microRNA primes brain metastasis outgrowth. Nature. 2015;527(7576):100–104. doi: 10.1038/nature15376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Katsuda T., Ochiya T. Molecular signatures of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicle-mediated tissue repair. Stem Cell Research & Therapy. 2015;6:p. 212. doi: 10.1186/s13287-015-0214-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Guo H., Ignolia N., Wiessman J., Bartel D. Mammalian microRNAs predominantly act to decrease target mRNA levels. Lung. 2011;466(7308):835–840. doi: 10.1038/nature09267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Gao W., Lu X., Liu L., Xu J., Feng D., Shu Y. MiRNA-21: a biomarker predictive for platinum-based adjuvant chemotherapy response in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Biology & Therapy. 2012;13(5):330–340. doi: 10.4161/cbt.19073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Hausser J., Zavolan M. Identification and consequences of miRNA-target interactions—beyond repression of gene expression. Nature Reviews Genetics. 2014;15(9):599–612. doi: 10.1038/nrg3765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Kawase-Koga Y., Otaegi G., Sun T. Different timings of Dicer deletion affect neurogenesis and gliogenesis in the developing mouse central nervous system. Developmental Dynamics. 2009;238(11):2800–2812. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.22109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Neo W. H., Yap K., Lee S. H., et al. MicroRNA miR-124 controls the choice between neuronal and astrocyte differentiation by fine-tuning Ezh2. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology. 2014;289(30):20788–20801. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.525493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Akerblom M., Sachdeva R., Barde I., et al. MicroRNA-124 is a subventricular zone neuronal fate determinant. The Journal of Neuroscience. 2012;32(26):8879–8889. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0558-12.2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Zhao C., Sun G., Li S., Shi Y., Discovery D. A feedback regulatory loop involving microRNA-9 and nuclear receptor TLX in neural stem cell fate determination. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology. 2009;16(4):365–371. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Santos M. C., Tegge A. N., Correa B. R., Mahesula S., Kohnke L. O. miR-124, −128, and −137 orchestrate neural differentiation by acting on overlapping gene sets containing a highly connected transcription factor network. Stem Cells. 2016;34(1):220–232. doi: 10.1002/stem.2204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Han J., Kim H. J., Schafer S. T., et al. Functional implications of miR-19 in the migration of newborn neurons in the adult brain article functional implications of miR-19 in the migration of newborn neurons in the adult brain. Neuron. 2016;91(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.05.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Cui Y., Han J., Xiao Z., et al. The miR-20-Rest-Wnt signaling axis regulates neural progenitor cell differentiation. Scientific Reports. 2016;6, article 23300 doi: 10.1038/srep23300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Szulwach K. E., Li X., Smrt R. D., et al. Cross talk between microRNA and epigenetic regulation in adult neurogenesis. The Journal of Cell Biology. 2010;189(1):127–141. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200908151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Zhang Y., Ueno Y., Liu X. S., et al. The MicroRNA-17-92 cluster enhances axonal outgrowth in embryonic cortical neurons. The Journal of Neuroscience. 2013;33(16):6885–6894. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5180-12.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Dwivedi Y. Emerging role of microRNAs in major depressive disorder: diagnosis and therapeutic implications. Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience. 2014;16(1):43–61. doi: 10.31887/DCNS.2014.16.1/ydwivedi. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Brites D., Fernandes A. Neuroinflammation and depression: microglia activation, extracellular microvesicles and microRNA dysregulation. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience. 2015;9(476):1–20. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2015.00476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Connor R. M. O., Grenham S., Dinan T. G., Cryan J. F. microRNAs as novel antidepressant targets: converging effects of ketamine and electroconvulsive shock therapy in the rat hippocampus. The International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013;16(8):1885–1892. doi: 10.1017/S1461145713000448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Jovičić A., Gitler A. D. Distinct repertoires of microRNAs present in mouse astrocytes compared to astrocyte-secreted exosomes. PLoS One. 2017;12(2, article e0171418) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0171418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Yu S., Yang S., Holsboer F., Sousa N., Almeida O. F. X. Glucocorticoid regulation of astrocytic fate and function. PLoS One. 2011;6(7, article e22419) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Unemura K., Kume T., Kondo M., Maeda Y., Izumi Y., Akaike A. Glucocorticoids decrease astrocyte numbers by reducing glucocorticoid receptor expression in vitro and in vivo. Journal of Pharmacological Sciences. 2012;119(1):30–39. doi: 10.1254/jphs.12047fp. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Carter B. S., Hamilton D. E., Thompson R. C. Acute and chronic glucocorticoid treatments regulate astrocyte-enriched mRNAs in multiple brain regions in vivo. Frontiers in Neuroscience. 2013;7(7):p. 139. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2013.00139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Kirby E. D., Muroy S. E., Sun W. G., et al. Acute stress enhances adult rat hippocampal neurogenesis and activation of newborn neurons via secreted astrocytic FGF2. eLife. 2013;2, article e00362 doi: 10.7554/eLife.00362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Dajas-bailador F., Bonev B., Garcez P., Stanley P., Guillemot F., Papalopulu N. microRNA-9 regulates axon extension and branching by targeting Map1b in mouse cortical neurons. Nature Neuroscience. 2012;15(5):697–699. doi: 10.1038/nn.3082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Stappert L., Roese-koerner B., Brüstle O. The role of microRNAs in human neural stem cells, neuronal differentiation and subtype specification. Cell and Tissue Research. 2015;359(1):47–64. doi: 10.1007/s00441-014-1981-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Bielefield P., Mooney C., Henshall D., Fitzsimons C. miRNA-mediated regulation of adult hippocampal neurogenesis; implications for epilepsy. Brain Plasticity. 2016:1–17. doi: 10.3233/BPL-160036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Zhao J., Lin Q., Kim K. J., Dardashti F. D., Kim J. Ngn1 inhibits astrogliogenesis through induction of miR-9 during neuronal fate specification. eLife. 2015;4, article e06885 doi: 10.7554/eLife.06885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Kawahara H., Imai T., Okano H. MicroRNAs in neural stem cells and neurogenesis. Frontiers in Neuroscience. 2012;6(30):1–13. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2012.00030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Krichevsky A. M., Sonntag K.-C., Isacson O., Kosik K. S. Specific microRNAs modulate embryonic stem cell-derived neurogenesis. Stem Cells. 2006;24(4):857–864. doi: 10.1634/stemcells.2005-0441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Wakabayashi T., Hidaka R., Fujimaki S. MicroRNAs and epigenetics in adult neurogenesis. Advances in Genetics. 2014;86:27–44. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800222-3.00002-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Bonev B., Stanley P., Papalopulu N. MicroRNA-9 modulates Hes1 ultradian oscillations by forming a double-negative feedback loop. Cell Reports. 2012;2(1):10–18. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2012.05.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Gu Q.-H., Yu D., Hu Z., et al. miR-26a and miR-384-5p are required for LTP maintenance and spine enlargement. Nature Communications. 2015;6:p. 6789. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Jiang J.-J., Liu C.-M., Zhang B.-Y., et al. MicroRNA-26a supports mammalian axon regeneration in vivo by suppressing GSK3β expression. Cell Death & Disease. 2015;6(8, article e1865) doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Dill H., Linder B., Fehr A. Intronic miR-26b controls neuronal differentiation by repressing its host transcript, ctdsp2. Genes & Development. 2012;26(1):25–30. doi: 10.1101/gad.177774.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Li H., Mao S., Wang H., Zen K., Zhang C., Li L. MicroRNA-29a modulates axon branching by targeting doublecortin in primary neurons. Protein & Cell. 2014;5(2):160–169. doi: 10.1007/s13238-014-0022-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Agostini M., Tucci P., Killick R., et al. Neuronal differentiation by TAp73 is mediated by microRNA-34a regulation of synaptic protein targets. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2011;108(52):21093–21098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1112061109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Cui Y., Xiao Z., Han J., et al. MiR-125b orchestrates cell proliferation, differentiation and migration in neural stem/progenitor cells by targeting Nestin. BMC Neuroscience. 2012;13(1):p. 116. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-13-116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Gioia U., Di Carlo V., Caramanica P., et al. Mir-23a and mir-125b regulate neural stem/progenitor cell proliferation by targeting Musashi1. RNA Biology. 2014;11(9):1105–1112. doi: 10.4161/rna.35508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Decembrini S., Bressan D., Vignali R., et al. MicroRNAs couple cell fate and developmental timing in retina. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2009;106(50):21179–21184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0909167106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Bhinge A., Poschmann J., Namboori S. C., et al. MiR-135b is a direct PAX6 target and specifies human neuroectoderm by inhibiting TGF- b/BMP signaling. The EMBO Journal. 2014;33(11):1271–1283. doi: 10.1002/embj.201387215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Xu N., Papagiannakopoulos T., Pan G., Thomson J. A., Kosik K. S. MicroRNA-145 regulates OCT4, SOX2, and KLF4 and represses pluripotency in human embryonic stem cells. Cell. 2009;137(4):647–658. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.02.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Morgado A. L., Rodrigues M., Solá S. MicroRNA-145 regulates neural stem cell differentiation through the Sox2-Lin28/let-7 signaling pathway. Stem Cells. 2016;34(5):1386–1395. doi: 10.1002/stem.2309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Cheng H., Zhou L., Li B., Zhu M. Nano-topology guided neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells is mediated by miRNAs. Nanomedicine Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine. 2014;10(8):1871–1875. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2014.07.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Zhao C., Sun G., Li S., et al. MicroRNA let-7b regulates neural stem cell proliferation and differentiation by targeting nuclear receptor TLX signaling. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2010;107(5):1876–1881. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0908750107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Rago L., Beattie R., Taylor V., Winter J. miR 379 – 410 cluster miRNAs regulate neurogenesis and neuronal migration by fine-tuning N-cadherin. The EMBO Journal. 2014;33(8):906–920. doi: 10.1002/embj.201386591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Brett J. O., Renault V. M., Rafalski V. A., Webb A. E., Brunet A., Program N. The MicroRNA cluster miR-106b ~ 25 regulates adult neural stem/progenitor cell proliferation and neuronal differentiation. Aging (Albany NY) 2011;3(2):108–124. doi: 10.18632/aging.100285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Nowakowski T. J., Fotaki V., Pollock A., Sun T., Pratt T., Price D. J. MicroRNA-92b regulates the development of intermediate cortical progenitors in embryonic mouse brain. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2013;110(17):7056–7061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1219385110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Liu C., Teng Z.-Q., Santistevan N. J., et al. Epigenetic regulation of miR-184 by MBD1 governs neural stem cell proliferation and differentiation. Cell Stem Cell. 2010;6(5):433–444. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2010.02.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Lipchina I., Elkabetz Y., Hafner M., et al. Genome-wide identification of microRNA targets in human ES cells reveals a role for miR-302 in modulating BMP response. Genes & Development. 2011;25(20):2173–2186. doi: 10.1101/gad.17221311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Du Z., Ma L., Phillips C., Zhang S. miR-200 and miR-96 families repress neural induction from human embryonic stem cells. Development. 2013;140(12):2611–2618. doi: 10.1242/dev.092809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Xu C., Zhang Y., Zheng H., Loh H., Law P. Morphine modulates mouse hippocampal progenitor cell lineages by up-regulating miR-181a level. Stem Cells. 2014;32(11):2961–2972. doi: 10.1002/stem.1774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Wu Q., Zhang L., Law P., Wei L., Loh H. H. Long-term morphine treatment decreases the association of μ-opioid receptor (MOR1) mRNA with polysomes through miRNA23b. Molecular Pharmacology. 2009;75(4):744–750. doi: 10.1124/mol.108.053462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Zheng H., Zeng Y., Zhang X., Chu J., Loh H. H., Law P. μ -Opioid receptor agonists differentially regulate the expression of miR-190 and NeuroD. Molecular Pharmacology. 2010;77(1):102–109. doi: 10.1124/mol.109.060848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Pati S., Supeno N. E., Muthuraju S., et al. MicroRNA profiling reveals unique miRNA signatures in IGF-1 treated embryonic striatal stem cell fate decisions in striatal neurogenesis in vitro. BioMed Research International. 2014;2014:14. doi: 10.1155/2014/503162.503162 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]