Abstract
Thermotoga sp. strain RQ7 is a member of the family Thermotogaceae in the order Thermotogales. It is a Gram negative, hyperthermophilic, and strictly anaerobic bacterium. It grows on diverse simple and complex carbohydrates and can use protons as the final electron acceptor. Its complete genome is composed of a chromosome of 1,851,618 bp and a plasmid of 846 bp. The chromosome contains 1906 putative genes, including 1853 protein coding genes and 53 RNA genes. The genetic features pertaining to various lateral gene transfer mechanisms are analyzed. The genome carries a complete set of putative competence genes, 8 loci of CRISPRs, and a deletion of a well-conserved Type II R-M system.
Keywords: Thermotoga, T. sp. strain RQ7, Natural competence, CRISPR, Restriction-modification system, TneDI, CP007633
Background
10.1601/nm.459 species are a group of thermophilic or hyperthermophilic bacteria that can ferment a wide range of carbohydrates and produce hydrogen gas as one of the major final products [1, 2]. Their hydrogen yield from glucose can reach the theoretical maximum: 4 mol of H2 from each mole of glucose [2, 3], which makes them ideal candidates for biofuel production. Meanwhile, because their enzymes are thermostable by nature, they also hold great prospect in the biocatalyst sector. 16S rRNA gene sequence analyses place 10.1601/nm.459 at a deep branch in the tree of life, and genomic studies also reveal extensive horizontal gene transfer events between 10.1601/nm.457 and other groups, particularly Archaea and 10.1601/nm.3874 [4]. Controversy over the phylogenetic significance of 10.1601/nm.459 has triggered a prolonged debate on the concepts of species and biogeography, etc. [5].
We have been interested in the genetics of 10.1601/nm.459 over the years and have developed the earliest set of tools to genetically modify these bacteria [6–8]. Strain RQ7 plays an essential role in these studies. This strain possesses the smallest known plasmid, pRQ7 (846 bp) [9], that is absent from most 10.1601/nm.459 strains and serves as the base vector for all Thermotoga-E. coli shuttle vectors developed so far. T. sp. strain RQ7 is also the first 10.1601/nm.459 strain in which natural competence was discovered [7]. To gain insights into the genetic and genomic features of the strain and to facilitate the continuing effort on developing genetic tools for 10.1601/nm.459, we set out to sequence the whole genome of T. sp. strain RQ7.
Organism information
Classification and features
T. sp. strain RQ7 was isolated from marine sediments of Ribeira Quente, Azores [1]. The strain is a member of the genus 10.1601/nm.459 , the family 10.1601/nm.458, and the order 10.1601/nm.457 (Table 1). Based on 16S rRNA gene sequences, the closest relative of T. sp. strain RQ7 is 10.1601/nm.465 10.1601/strainfinder?urlappend=%3Fid%3DDSM+4359 , and these two strains cluster with 10.1601/nm.460 MSB8 and T. sp. strain RQ2 (Fig. 1). The results are in agreement with previous reports [10].
Table 1.
Classification and general features of Thermotoga sp. strain RQ7 according to the MIGS recommendations [36]
| MIGS ID | Property | Term | Evidence codea |
|---|---|---|---|
| Classification | Domain Bacteria | TAS [37] | |
| Phylum Thermotogae | TAS [38, 39] | ||
| Class Thermotogae | TAS [39, 40] | ||
| Order Thermotogales | TAS [39, 41] | ||
| Family Thermotogaceae | TAS [39, 42] | ||
| Genus Thermotoga | TAS [1, 43, 44] | ||
| Species T. neapolitana | IGC, TSA [45, 46] | ||
| strain: RQ7 | TAS [1] | ||
| Gram stain | Negative | TAS [1] | |
| Cell shape | Rod | IDA, TAS [1] | |
| Motility | Motile | IDA, TAS [1] | |
| Sporulation | Not reported | ||
| Temperature range | 55–90 °C | TAS [1] | |
| Optimum temperature | Around 80 °C | TAS [1] | |
| pH range; Optimum | 5.5–9; 6.5 | IDA, TAS [1] | |
| Carbon source | Mono- and polysaccharides | IDA, TAS [1, 47, 48] | |
| MIGS-6 | Habitat | Geothermally heated sediments | TAS [1] |
| MIGS-6.3 | Salinity | 0.25–3.75% NaCl (w/v) | IDA, TAS [1] |
| MIGS-22 | Oxygen requirement | Anaerobic | IDA, TAS [1] |
| MIGS-15 | Biotic relationship | Free-living | IDA, TAS [1] |
| MIGS-14 | Pathogenicity | Non-pathogen | IDA, TAS [1] |
| MIGS-4 | Geographic location | Azores, Sao Miguel, Ribeira Quente | TAS [1] |
| MIGS-5 | Sample collection | 1985 | NAS |
| MIGS-4.1 | Latitude | Not reported | |
| MIGS-4.2 | Longitude | Not reported | |
| MIGS-4.4 | Altitude | About sea level | NAS |
aEvidence codes - IDA Inferred from Direct Assay, TAS Traceable Author Statement (i.e., a direct report exists in the literature), NAS Non-traceable Author Statement (i.e., not directly observed for the living, isolated sample, but based on a generally accepted property for the species, or anecdotal evidence), IGC Inferred from Genomic Content (i.e., average nucleotide identity, syntenic regions). These evidence codes are from the Gene Ontology project [49]
Fig. 1.

Phylogenetic tree showing the position of T. sp. strain RQ7 relative to other species within the order Thermotogales. Only species with complete genome sequences are included. The tree was built with 16S rRNA gene sequences, using the Neighbor-Joining method with MEGA7 [50]. Fervidobacterium nodosum serves as the outgroup
Like its close relatives 10.1601/nm.465 10.1601/strainfinder?urlappend=%3Fid%3DDSM+4359 and 10.1601/nm.460 MSB8, T. sp. strain RQ7 is a strict anaerobe, growing best around 80 °C, utilizing both simple and complex sugars, and producing hydrogen gas. These bacteria grow in both rich and defined media, are free living and non-pathogenic to humans, animals, or plants. Cells are rod-shaped, about 0.5 to 2 μm in length and 0.4 to 0.5 μm in diameter (Fig. 2). The most distinctive feature of 10.1601/nm.459 cells is the “toga” structure that balloons out from both ends of the rod [1, 11], an extension of their outer membrane [12].
Fig. 2.

Scanning electron micrograph of T. sp. strain RQ7 cells after 12 h of growth. Bar, 0.5 μm
Genome sequencing information
Genome project history
The project started in June 2011, and the genome was sequenced by BGI Americas (Cambridge, MA) using the Illumina technology. A total of 400 Mb of clean data were generated, which covered the genome more than 200 fold. The assembled scaffold covers 97.7% of the chromosome. PCR and Sanger sequencing were later used for gap filling. The assembly was finalized in February 2014, and the complete sequence was submitted to the GenBank in April 2014. The sequence was annotated with the NCBI Prokaryotic Genome Annotation Pipeline [13] and the DOE-JGI Microbial Genome Annotation Pipeline (MGAP v.4) [14]. The project information is summarized in Table 2.
Table 2.
Project information
| MIGS ID | Property | Term |
|---|---|---|
| MIGS 31 | Finishing quality | Complete |
| MIGS-28 | Libraries used | Three Illumina paired-end libraries in sizes of 500, 2000, and 5000 bp |
| MIGS 29 | Sequencing platforms | Illumina and Sanger |
| MIGS 31.2 | Fold coverage | > 200× |
| MIGS 30 | Assemblers | SOAPdenovo [17], SOAPaligner [18], CLC Workbench 5.1 [19], and GapFish [20] |
| MIGS 32 | Gene calling method | GeneMarkS+ [51], Prodigal [52] |
| Locus Tag | TRQ7 in GenBank; Ga0077854 in JGI-IMG | |
| GenBank ID | CP007633, KF798180 | |
| GenBank Date of Release | February 4, 2015 | |
| GOLD ID | Gp0117593 | |
| BIOPROJECT | PRJNA246218 | |
| MIGS 13 | Source Material Identifier | Personal culture collection (Dr. Harald Huber) |
| Project relevance | Bioenergy, biotechnology, evolution |
Growth conditions and genomic DNA preparation
T. sp. strain RQ7 was kindly provided by Drs. Harald Huber and Robert Huber at the University of Regensburg, Germany. It was cultivated in SVO medium [15] at 77 °C, and its genomic DNA was extracted with standard phenol extraction method [16]. Briefly, cells from 250 ml of overnight culture were collected by centrifugation and resuspended in 10 ml of STE solution (10 mM Tris-HCl, 1 mM EDTA, 100 mM NaCl, pH 8.0). SDS and proteinase K were added to a final concentration of 1% (w/v) and 20 μg/ml. The mixture was incubated at 50 °C for 6 h followed by the addition of an equal volume of phenol/chloroform/isoamyl alcohol (25:24:1, v/v/v). After gentle mixing, the mixture was centrifuged at 12,000 g at 4 °C for 15 min. The upper aqueous layer was transferred to a clean tube and mixed with 1/10 volume of 3 M sodium acetate (pH 5.5) and 2 volumes of ice cold 95% (v/v) ethanol. The DNA was spooled out by a glass rod, washed with 70% (v/v) ethanol, air dried, dissolved in 2 ml of TE buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl, 1 mM EDTA, pH 8.0) containing 20 μg/ml RNase A, and stored at −20 °C.
Genome sequencing and assembly
The genome of T. sp. strain RQ7 was mainly sequenced by BGI Americas using Illumina HiSeq 2000 sequencing platform. Three paired-end libraries, in size of 500, 2000, and 5000 kb, were constructed. The raw data were filtered by a quality control step and generated 400 Mb of clean data, which indicated a coverage of more than 200-fold. The reads were assembled by SOAPdenovo [17] and polished by SOAPaligner [18]. This resulted in a single scaffold of 1,822,593 bp that covered 97.7% of the genome and contained 28 gaps. The gap filling efforts included the integration of the current scaffold with contigs generated by the CLC Genomics Workbench [19] and a small amount of public sequences in GenBank. GapFish [20] was then used to solve a dozen ambiguous regions. Finally, PCR and primer walking were performed to close the remaining gaps, resulting a final assembly of 1,851,618 bp. The entire assembling process integrated wet lab methods with in silico approaches, and the programs used included public software (SOAPdenovo and SOAPaligner [17, 18]), a commercial product (CLC Genomics Workbench [19]), and an in-house program GapFish [20]. Details of the assembling process are described in our previous report [20].
Genome annotation
The genome was independently annotated by two pipelines, the NCBI Prokaryotic Genome Annotation Pipeline [13] and the DOE-JGI Microbial Genome Annotation Pipeline (MGAP v.4) [14]. Both pipelines combine a gene-calling algorithm with a similarity-based gene detection approach, even though the algorithms and databases they use are different. For example, PGAAP uses GeneMarkS+ for de novo gene prediction, while MGAP uses Prodigal. Consequently, the two pipelines produced slightly different annotation results. The analyses in this report took into consideration of the results from both pipelines and are assisted with manual curation.
Genome properties
The genome of T. sp. strain RQ7 is composed of a circular chromosome of 1,851,618 bp with a GC content of 47.05% and a single mini-plasmid of 846 bp with a GC percentage of 39.95 (Fig. 3; Table 3). The plasmid pRQ7 has been characterized [9] and sequenced [6, 21] before. According to the annotation of MGAP, the chromosome carries 1906 putative genes, of which, 1853 are protein coding genes and 53 are RNA genes (Table 4). Among all the genes that are assigned to a COG category (Table 5), a significant portion (~12%, 191 genes) are devoted to carbohydrate utilization, which is typical to 10.1601/nm.459 strains and accords with their versatile use of carbon and energy sources.
Fig. 3.

Chromosomal map of T. sp. strain RQ7. From outside to the center: genes on forward strand (color by COG categories), genes on reverse strand (color by COG categories), RNA genes (tRNAs: green, rRNAs: red, other RNAs: black), GC content (black), GC skew (olive/purple)
Table 3.
Summary of genome: one chromosome and one plasmid
| Label | Size (bp) | Topology | INSDC identifier | RefSeq ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chromosome | 1,851,618 | Circular | CP007633 | NZ_CP007633 |
| pRQ7 | 846 | Circular | KF798180 | NC_023152 |
Table 4.
Genome statistics according to the MGAP pipeline annotation (chromosome only)
| Attribute | Value | % of total |
|---|---|---|
| Genome size (bp) | 1,851,618 | 100.00 |
| DNA coding (bp) | 1,768,561 | 95.51 |
| DNA G + C (bp) | 871,250 | 47.05 |
| DNA scaffolds | 1 | |
| Total genes | 1906 | 100.00 |
| Protein coding genes | 1853 | 97.22 |
| RNA genes | 53 | 2.78 |
| Pseudo genes | – | – |
| Genes in internal clusters | 110 | 5.77 |
| Genes with function prediction | 1522 | 79.85 |
| Genes assigned to COGs | 1453 | 76.23 |
| Genes with Pfam domains | 1629 | 85.47 |
| Genes with signal peptides | 35 | 1.84 |
| Genes with transmembrane helices | 462 | 24.24 |
| CRISPR repeats | 8 |
Table 5.
Number of genes associated with general COG functional categories
| Code | Value | %age | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| J | 165 | 10.17 | Translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis |
| A | – | – | RNA processing and modification |
| K | 75 | 4.62 | Transcription |
| L | 53 | 3.27 | Replication, recombination and repair |
| B | 1 | 0.06 | Chromatin structure and dynamics |
| D | 19 | 1.17 | Cell cycle control, Cell division, chromosome partitioning |
| V | 34 | 2.09 | Defense mechanisms |
| T | 57 | 3.51 | Signal transduction mechanisms |
| M | 74 | 4.56 | Cell wall/membrane biogenesis |
| N | 55 | 3.39 | Cell motility |
| U | 21 | 1.29 | Intracellular trafficking and secretion |
| O | 66 | 4.07 | Posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones |
| C | 104 | 6.41 | Energy production and conversion |
| G | 191 | 11.77 | Carbohydrate transport and metabolism |
| E | 169 | 10.41 | Amino acid transport and metabolism |
| F | 65 | 4 | Nucleotide transport and metabolism |
| H | 73 | 4.5 | Coenzyme transport and metabolism |
| I | 42 | 2.59 | Lipid transport and metabolism |
| P | 103 | 6.35 | Inorganic ion transport and metabolism |
| Q | 18 | 1.11 | Secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism |
| R | 156 | 9.61 | General function prediction only |
| S | 75 | 4.62 | Function unknown |
| – | 453 | 23.77 | Not in COGs |
The total is based on the total number of protein coding genes in the genome as annotated by MGAP v.4 [14]
Insights from the genome sequence
The chromosomal sequence of T. sp. strain RQ7 was compared to those of 10.1601/nm.460 MSB8, 10.1601/nm.465 10.1601/strainfinder?urlappend=%3Fid%3DDSM+4359 , and T. sp. strain RQ2, with emphases on the genetic elements that have the highest impacts on genetic engineering attempts, such as natural competence genes, CRISPRs, and R-M systems.
Full genome comparison
The alignment of the complete genomic sequence of the four 10.1601/nm.459 strains (Fig. 4) revealed high levels of synteny among their genomes, particularly within the pairs of T. sp. strain RQ7−T. neapolitana 10.1601/strainfinder?urlappend=%3Fid%3DDSM+4359 and T. sp. strain RQ2−T. maritima MSB8. This is in agreement with their placements in the phylogenetic tree (Fig. 1). The average nucleotide identity between T. sp. strain RQ7 and the type strain 10.1601/nm.465 10.1601/strainfinder?urlappend=%3Fid%3DDSM+4359 is 98.49%, which is higher than the conventional cutoff of 95% for species delineation [22]. Therefore, T. sp. strain RQ7 should be considered as a strain of 10.1601/nm.465, same as T. sp. strain RQ2 to 10.1601/nm.460 [23].
Fig. 4.

Full genome alignment of the four Thermotoga strains using Mauve [53]. Each horizontal panel represents one genome sequence, from top to bottom: T. neapolitana DSM 4359, T. sp. strain RQ7, T. sp. strain RQ2, and T. maritima MSB8. The sequences were downloaded from GenBank, and genomes of T. neapolitana DSM 4359 and T. maritima MSB8 were re-linearized at the dnaA gene. Blocks with the same color represent homologous regions. Blocks below the center lines are inversed regions. Inside of each block, the height of the similarity profile corresponds to the average level of conservation of the local area
A detailed comparison of T. sp. strain RQ7 and 10.1601/nm.465 10.1601/strainfinder?urlappend=%3Fid%3DDSM+4359 found 100 genes belonging only to the former and 120 genes only to the latter. Some of these genes became unique because their counterparts in the other genome have mutated to a pseudogene. However, many of the unique genes seem to have been acquired via recent lateral gene transfer events. The putative functions of these genes are mainly associated to transportation and utilization of carbohydrates and nucleotides. The most notable gene clusters include TRQ7_01555-01655 (nucleotide metabolism), TRQ7_02675-02725 (carbohydrate metabolism), TRQ7_03440-03490 (arabinose metabolism), CTN_0026-0038 (synthesis of antibiotics), CTN_0236-0245 (carbohydrate metabolism), CTN_0355-0373 (ribose metabolism), CTN_1540-1554 (carbohydrate metabolism), and CTN_1602-1627 (ribose metabolism). Follow-up functional genomics studies are needed to validate the predictions on these gene functions and metabolic pathways.
Natural competence
10.1601/nm.459 species are known to undergo lateral gene transfer events. One of the ways this could happen is via natural transformation. Natural competence has been established in T. sp. strain RQ7 [7] and T. sp. strain RQ2 [8]. Using experimentally characterized competence genes as references, we are able to identify the genes that might play a role in natural competence in 10.1601/nm.459 (Table 6). These genes are widely spread among bacterial genomes, and none of them are clustered into operons. This might imply a primitive form of natural competence that is shared by most, if not all, bacteria. Perhaps, most free-living bacteria are more or less naturally competent during some points of their life. The trick is to identify the right conditions under which the natural competence will be allowed to develop.
Table 6.
Manually curated competence genes
| RQ7 | Gene namea | Putative function | Tn | Tm | RQ2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNA uptake and translocation | |||||
| TRQ7_00110 | pilZ (Pa, Vc) | Type IV pilus biogenesis and twitching motility [54–56] | CTN_1670 | TM0905 | TRQ2_0022 |
| TRQ7_00455 | pilB (Pa, Vc) | Type II secretion system (T2SS), Type IV fimbrial assembly NTPase [57–59] | CTN_1739 | TM0837 | TRQ2_0090 |
| TRQ7_01410 TRQ7_04530 TRQ7_08710 |
pilQ (Nm, Tt) | Secretin, forms gated channel for extrusion of assembled pilin [60–62] | CTN_1450 CTN_1933 CTN_0604 |
TM1117 TM0088 |
TRQ2_1699 TRQ2_0859 |
| TRQ7_04500 | pilC (Ps, Ng) | Type II secretory pathway, component PulF / Type IV fimbrial assembly protein [63, 64] | CTN_0598 | TM_0094 | TRQ2_0853 |
| TRQ7_05855 | pilD (Vv,Ng) | Type IV prepilin peptidase, processes N-terminal leader peptides for prepilins [65–67] | CTN_0883 | TM1696 | TRQ2_1138 |
| TRQ7_06260 | comEC (Bs) | Putative channel protein, Transports DNA across the cell membrane [68, 69] | CTN_0965 | TM1775 | TRQ2_1049 |
| TRQ7_07315 | comF (Hi) | Phosphoribosyltransferase [70, 71] | CTN_1168 | TM1584 | TRQ2_1247 |
| TRQ7_07650 | pilT (Ng) | Motility protein [72] | CTN_1229 | TM1362 | TRQ2_1467 |
| TRQ7_07980 | pilE (Ng, Pa) | Type IV pilin; major structural component of Type IV pilus [73, 74] | CTN_1301 | TM1271 | TRQ2_1548 |
| TRQ7_09065 | comEA (Bs) | High affinity DNA-binding periplasmic protein [75–78] | CTN_1515 | TM1052 | TRQ2_1756 |
| Post-translocation | |||||
| TRQ7_02260 | comM (Hi) | Promotes the recombination of the donor DNA into the chromosome [79] | CTN_0158 | TM0513 | TRQ2_0424 |
| TRQ7_03645 | dprA (Hi) | DNA protecting protein [80, 81] | CTN_0436 | TM0250 | TRQ2_0698 |
aGene names are given after the experimentally characterized genes of the species in parentheses. Pa Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Vc Vibrio cholerae, Nm Neisseria meningitidis, Tt Thermus thermophilus, Ps Pseudomonas stutzeri, Ng Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Vv Vibrio vulnificus, Bs Bacillus subtilis, Hi influenza, RQ7 T. sp. strain RQ7, Tn T. neapolitana DSM 4359, Tm T. maritima MSB8, RQ2 T. sp. strain RQ2
CRISPRs
CRISPRs provide prokaryotes a form of adaptive immunity against invading phages and plasmids in a sequence specific manner [24, 25]. The system utilizes non-coding CRISPR RNA and a set of CRISPR-associated proteins to target invading nucleic acid, including both DNA and RNA. CRISPRs have been reported to prevent natural transformation [26, 27]. They have been noticed before in 10.1601/nm.459 and are credited for large scale chromosomal recombination events in these species [28, 29]. NCBI’s PGAAP pipeline identified 6 loci of CRISPR arrays in T. sp. strain RQ7, whereas JGI-IMG’s MGAP pipeline and a manual analysis using CRISPRFinder [30] recognized a total of 8 loci (Table 7). Among these eight CRISPR loci, #1 and #3 are the ones not considered by PGAAP. Two clusters of cas genes are also found. The cas6-cas2 cassette is sandwiched between loci #3 and #4, and the cas6-csm1 cassette is located 2285 bp upstream of locus #3 (Fig. 5, Table 7).
Table 7.
Summary of CRISPR loci in T. sp. strain RQ7
| Locus | Repeats | Coordinatesa | No. of spacers | Cas genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GTTTCAATCCTTCCTTAGAGGTATGGAAACA GTTTCAATACTTCCTTAGAGGTATGGAAACA GTTTCAATACTTCCTTTGAGGTATGAAAACA |
553,849-554,014 | 2 | No |
| 2 | TTTCCTATACCTCTAAGAAAGGATTGAAAC GTTTCCATACCTCTAAGGAAGTATTGAAAC |
594,500-594,927 | 6 | No |
| 3 | GTTTCAATACTTCCTTTGAGGTATGGAAA GTTTCAATACTTCCTTAGAGGTATGGAAA GTTTCAATACATCCTCAGAGGTATGATTT |
975,191-975,420 | 3 | Yes |
| 4 | GTTTTTATCTTCCTAAGAGGAATATGAAC GTTTTTATCTTCCTAAGAGGAATATAGTA |
983,596-986,955 | 51 | Yes |
| 5 | GTTTCAATACTTCCTTTGAGGTATGGAAAC GTTTCAATATTTCCTTATAGGTACAAACCC |
1,011,410-1,012,101 | 10 | No |
| 6 | GTTTCAATACTTCCTTAGAGGTATGGAAAC | 1,090,312-1,090,681 | 5 | No |
| 7 | GTTTCCATACCTCTAAGGAAGTATTGAAAC | 1,233,649-1,233,878 | 3 | No |
| 8 | GTTTCAATACTTCCTTTGAGGTATGGAAAC | 1,422,811-1,423,509 | 10 | No |
aCoordinates as documented in JGI-IMG. The start coordinates in GenBank are 20 bp smaller because the chromosome is linearized at a site 20 bp downstream of what JGI-IMG uses
Fig. 5.

Diagrammatic representation of CRISPR/Cas systems in T. sp. strain RQ7. a Positions of the 8 regions of CRISPR arrays; drawn in scale using Clone Manager Professional Suite v.8 [82]. b Positions of the cas genes (open boxed) relative to the CRISPR arrays (filled boxes); not in scale
Although analysis with CRISPRFinder revealed the same number of CRISPR loci in the four close relatives, i.e. T. sp. strain RQ7, 10.1601/nm.465 10.1601/strainfinder?urlappend=%3Fid%3DDSM+4359 , 10.1601/nm.460 MSB8, and T. sp. strain RQ2, the total number of spacers they carry vary dramatically, as 95, 60, 106, and 129 spacers are found respectively. 10.1601/nm.460 MSB8 and T. sp. strain RQ2 also harbor RNA-targetting cmr genes in addition to DNA-targetting cas genes [31]. These differences may affect the efficiency of lateral gene transfer events among the strains.
Type II R-M system TneDI
R-M systems are other defense mechanisms that prokaryotes have developed to protect the integrity of their genetic materials. The Type II R-M system TneDI has been characterized in 10.1601/nm.465 10.1601/strainfinder?urlappend=%3Fid%3DDSM+4359 and overexpressed in 10.1601/nm.3093 [32, 33]. The nuclease R.TneDI cleaves at the center of the recognition site (CG↓CG), and the methylase M.TneDI modifies one of the cytosines. The TneDI system has been found in many members of the 10.1601/nm.458 family, including 10.1601/nm.460 MSB8 and T. sp. strain RQ2 [32]. However, it is absent from T. sp. strain RQ7, although the neighborhood is still highly conserved (Fig. 6). To exclude the possibility of an assembling error, primers spanning the region in question were designed, and the PCR results confirmed the deletion (Fig. 7). The absence of the TneDI system makes the DNA of T. sp. strain RQ7 susceptible to R.TneDI, and in vitro treatment with M.TneDI provides complete protection to its genomic DNA (Fig. 8).
Fig. 6.

Deletion of the TneDI system in T. sp. RQ7. The neighborhoods of the deletion site were compared (color by COG categories). The big rectangle box highlights the R-M system that is absent in T. sp. strain RQ7 (show as RQ7 in the diagram). The numerical values are genome coordinates as documented in JGI-IMG. RQ2, T. sp. strain RQ2; Tm, T. maritima MSB8; Tn, T. neapolitana DSM 4359
Fig. 7.

Experimental confirmation of the deletion of the TneDI system in T. sp. strain RQ7. T. neapolitana DSM 4359 (Tn) was used as the positive control. The expected sizes are 1831 bp in T. neapolitana DSM 4359 and 503 bp in T. sp. strain RQ7
Fig. 8.

Digestion of the genomic DNA of T. neapolitana DSM 4359 (Tn), T. sp. strain RQ2 (RQ2), T. maritima MSB8 (Tm), and T. sp. strain RQ7 (RQ7) with R.TneDI. -, negative control, no R.TneDI; +, digestion with R.TneDI; m_+, DNA was treated with M.TneDI prior to being digested by R.TneDI
M.TneDI has been predicted to be a m4C methylase based on sequence analysis [32]. It has also been noticed that m4C methylation is more common than m5C in thermophiles, probably due to a reduced risk of deamination [34]. The speculation of M.TneDI being a m4C methylase is further supported by the observation that the genomic DNA of TneDI-bearing species is still suspetible to BstUI (Fig. 9), which is an isoschizomer of R.TneDI and known to be blocked by m5C methylation [35].
Fig. 9.
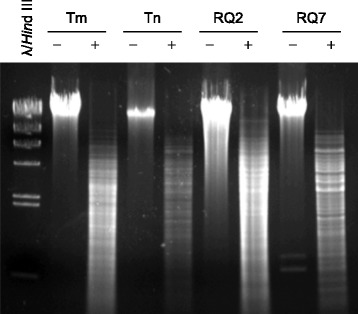
Digestion of genomic DNA of T. maritima MSB8 (Tm), T. neapolitana DSM 4359 (Tn), T. sp. strain RQ2 (RQ2), and T. sp. strain RQ7 by BstUI. -, negative control, no BstUI; +, treated with BstUI
Conclusions
The genome of T. sp. strain RQ7 shares large regions of synteny with those of its close relatives, namely, 10.1601/nm.465 10.1601/strainfinder?urlappend=%3Fid%3DDSM+4359 , 10.1601/nm.460 MSB8, and T. sp. strain RQ2. They all have a complete set of putative competence genes, although natural transformation has yet to be established in 10.1601/nm.465 10.1601/strainfinder?urlappend=%3Fid%3DDSM+4359 and 10.1601/nm.460 MSB8. The same number of CRISPR loci are found in all four genomes, even though the number of spacers vary. The most noticeable difference among the strains is the absence of the TneDI R-M system in T. sp. strain RQ7, which partially explains why this strain is more amenable to genetic modifications than others. In general, this work sheds light on the genetic features of T. sp. strain RQ7, promoting genetic and genomic studies of 10.1601/nm.459 spp.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Drs. Harald Huber and Robert Huber at the University of Regensburg, Germany, for kindly providing T. sp. strain RQ7.
Funding
This work was supported by the BGSU Commercialization Catalyst Award and the BGSU Building Strength Award to ZX. BGSU plays no role in designing or conducting the study, collecting or analysing the data, or writing the manuscript.
Abbreviations
- Cas
CRISPR associated
- CRISPR
Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats
- R-M
Restriction-modification
Authors’ contributions
ZX conceived and coordinated the study, participated in all aspects of data analysis and drafted the manuscript. RP participated in most parts of the work and helped in writing the manuscript. JX produced the SEM photo and the phylogenetic tree. HX contributed to the R-M study. DH initiated the sequencing project and the R-M study. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Huber R, Langworthy TA, Konig H, Thomm M, Woese CR, Sleytr UB, Stetter KO. Thermotoga maritima sp. nov. represents a new genus of unique extremely thermophilic eubacteria growing up to 90 degrees C. Arch Microbiol. 1986;144(4):324–333. doi: 10.1007/BF00409880. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Schroder C, Selig M, Schonheit P. Glucose Fermentation to Acetate, CO2 and H2 in the Anaerobic Hyperthermophilic Eubacterium Thermotoga Maritima: Involvement of the Embden-Meyerhof Pathway. Arch Microbiol. 1994;161(6):460–470. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Takahata Y, Nishijima M, Hoaki T, petrophila MTT. sp. nov. and Thermotoga naphthophila sp. nov., two hyperthermophilic bacteria from the Kubiki oil reservoir in Niigata, Japan. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2001;51:1901–1909. doi: 10.1099/00207713-51-5-1901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Zhaxybayeva O, Swithers KS, Lapierre P, Fournier GP, Bickhart DM, DeBoy RT, Nelson KE, Nesbo CL, Doolittle WF, Gogarten JP, et al. On the chimeric nature, thermophilic origin, and phylogenetic placement of the Thermotogales. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(14):5865–5870. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0901260106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Nesbo CL, Dlutek M, Doolittle WF. Recombination in thermotoga: Implications for species concepts and biogeography. Genetics. 2006;172(2):759–769. doi: 10.1534/genetics.105.049312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Han D, Norris SM, Xu Z. Construction and transformation of a Thermotoga-E. coli shuttle vector. BMC Biotechnol. 2012;12:2. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-12-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Han D, Xu H, Puranik R, Xu Z. Natural transformation of Thermotoga sp. strain RQ7. BMC Biotechnol. 2014;14:39. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-14-39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Xu H, Han D, Xu Z. Expression of Heterologous Cellulases in Thermotoga sp. Strain RQ2. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:304523. doi: 10.1155/2015/304523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Harriott OT, Huber R, Stetter KO, Betts PW, Noll KM. A Cryptic Miniplasmid from the Hyperthermophilic Bacterium Thermotoga Sp Strain Rq7. J Bacteriol. 1994;176(9):2759–2762. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.9.2759-2762.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Frock AD, Notey JS, Kelly RM. The genus Thermotoga: recent developments. Environ Technol. 2010;31(10):1169–1181. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2010.484076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Windberger E, Huber R, Trincone A, Fricke H, Stetter KO. Thermotoga thermarum sp. nov. and Thermotoga neapolitana occurring in African continental solfataric springs. Arch Microbiol. 1989;151(6):506–512. doi: 10.1007/BF00454866. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Rachel R, Engel AM, Huber R, Stetter KO, Baumeister W. A Porin-Type Protein Is the Main Constituent of the Cell-Envelope of the Ancestral Eubacterium Thermotoga-Maritima. FEBS Lett. 1990;262(1):64–68. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80155-C. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Angiuoli SV, Gussman A, Klimke W, Cochrane G, Field D, Garrity G, Kodira CD, Kyrpides N, Madupu R, Markowitz V, et al. Toward an online repository of Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) for (meta)genomic annotation. OMICS. 2008;12(2):137–141. doi: 10.1089/omi.2008.0017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Huntemann M, Ivanova NN, Mavromatis K, Tripp HJ, Paez-Espino D, Palaniappan K, Szeto E, Pillay M, Chen IM, Pati A, et al. The standard operating procedure of the DOE-JGI Microbial Genome Annotation Pipeline (MGAP v.4) Stand Genomic Sci. 2015;10:86. doi: 10.1186/s40793-015-0077-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Van Ooteghem SA, Beer SK, Yue PC. Hydrogen production by the thermophilic bacterium Thermotoga neapolitana. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2002;98:177–189. doi: 10.1385/ABAB:98-100:1-9:177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sambrook J, Russell DW. The Condensed Protocols from Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 2006.
- 17.Li R, Zhu H, Ruan J, Qian W, Fang X, Shi Z, Li Y, Li S, Shan G, Kristiansen K, et al. De novo assembly of human genomes with massively parallel short read sequencing. Genome Res. 2010;20(2):265–272. doi: 10.1101/gr.097261.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.SOAPaligner [http://soap.genomics.org.cn/soapaligner.html].
- 19.CLC Genomics Workbench [https://www.qiagenbioinformatics.com/products/clc-genomics-workbench/].
- 20.Puranik R, Quan G, Werner J, Zhou R, Xu Z. A pipeline for completing bacterial genomes using in silico and wet lab approaches. BMC Genomics. 2015;16(Suppl 3):S7. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-16-S3-S7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Yu JS, Noll KM. Plasmid pRQ7 from the hyperthermophilic bacterium Thermotoga species strain RQ7 replicates by the rolling-circle mechanism. J Bacteriol. 1997;179(22):7161–7164. doi: 10.1128/jb.179.22.7161-7164.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Goris J, Konstantinidis KT, Klappenbach JA, Coenye T, Vandamme P, Tiedje JM. DNA-DNA hybridization values and their relationship to whole-genome sequence similarities. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2007;57(Pt 1):81–91. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.64483-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Swithers KS, DiPippo JL, Bruce DC, Detter C, Tapia R, Han S, Saunders E, Goodwin LA, Han J, Woyke T, et al. Genome sequence of Thermotoga sp. strain RQ2, a hyperthermophilic bacterium isolated from a geothermally heated region of the seafloor near Ribeira Quente, the Azores. J Bacteriol. 2011;193(20):5869–5870. doi: 10.1128/JB.05923-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sorek R, Kunin V, Hugenholtz P. CRISPR--a widespread system that provides acquired resistance against phages in bacteria and archaea. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2008;6(3):181–186. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Garneau JE, Dupuis ME, Villion M, Romero DA, Barrangou R, Boyaval P, Fremaux C, Horvath P, Magadan AH, Moineau S. The CRISPR/Cas bacterial immune system cleaves bacteriophage and plasmid DNA. Nature. 2010;468(7320):67–71. doi: 10.1038/nature09523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Jorth P, Whiteley M. An evolutionary link between natural transformation and CRISPRadaptive immunity. MBio. 2012;3(5):e00309-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 27.Bikard D, Hatoum-Aslan A, Mucida D, Marraffini LA. CRISPR interference can prevent natural transformation and virulence acquisition during in vivo bacterial infection. Cell Host Microbe. 2012;12(2):177–186. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2012.06.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Mongodin EF, Hance IR, DeBoy RT, Gill SR, Daugherty S, Huber R, Fraser CM, Stetter K, Nelson KE. Gene transfer and genome plasticity in Thermotoga maritima, a model hyperthermophilic species. J Bacteriol. 2005;187(14):4935–4944. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.14.4935-4944.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.DeBoy RT, Mongodin EF, Emerson JB, Nelson KE. Chromosome evolution in the Thermotogales: Large-scale inversions and strain diversification of CRISPR sequences. J Bacteriol. 2006;188(7):2364–2374. doi: 10.1128/JB.188.7.2364-2374.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Grissa I, Vergnaud G, Pourcel C. CRISPRFinder: a web tool to identify clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(Web Server issue):W52–W57. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Haft DH, Selengut J, Mongodin EF, Nelson KE. A guild of 45 CRISPR-associated (Cas) protein families and multiple CRISPR/Cas subtypes exist in prokaryotic genomes. PLoS Comput Biol. 2005;1(6):e60. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.0010060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Xu Z, Han D, Cao J, Saini U. Cloning and characterization of the TneDI restriction: modification system of Thermotoga neapolitana. Extremophiles. 2011;15(6):665–672. doi: 10.1007/s00792-011-0397-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Xu H, Han D, Xu Z. Overexpression of a lethal methylase, M.TneDI, in E. coli BL21(DE3) Biotechnol Lett. 2014;36(9):1853–1859. doi: 10.1007/s10529-014-1552-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Ehrlich M, Gama-Sosa MA, Carreira LH, Ljungdahl LG, Kuo KC, Gehrke CW. DNA methylation in thermophilic bacteria: N4-methylcytosine, 5-methylcytosine, and N6-methyladenine. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985;13(4):1399–1412. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Jin SG, Kadam S, Pfeifer GP. Examination of the specificity of DNA methylation profiling techniques towards 5-methylcytosine and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38(11):e125. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Field D, Garrity G, Gray T, Morrison N, Selengut J, Sterk P, Tatusova T, Thomson N, Allen MJ, Angiuoli SV, et al. The minimum information about a genome sequence (MIGS) specification. Nat Biotechnol. 2008;26(5):541–547. doi: 10.1038/nbt1360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Woese CR, Kandler O, Wheelis ML. Towards a natural system of organisms: proposal for the domains Archaea, Bacteria, and Eucarya. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990;87(12):4576–4579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Reysenbach A-L, BII P. Thermotogae phy.nov. In: Garrity GM, Boone DR, Castenholz RW, editors. Bergey's manual of systematic bacteriology. 2. New York: Springer; 2001. pp. 369–387. [Google Scholar]
- 39.List Editor Validation of the Publication of New Names and New Combinations Previously Effectively Published Outside the IJSB. List No. 85. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 2002;52(3):685–690. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Reysenbach A-L, Class I. Thermotogae class. nov. In: Garrity GM, Boone DR, Castenholz RW, editors. Bergey's manual of systematic bacteriology. 2. New York: Springer; 2001. pp. 369–387. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Reysenbach A-L, Order I. Thermotogales ord. nov. Huber and Stetter 1992c, 3809. In: Garrity GM, Boone DR, Castenholz RW, editors. Bergey's manual of systematic bacteriology. 2. New York: Springer; 2001. pp. 369–387. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Reysenbach A-L, Family I. Thermotogaceae fam. nov. In: Garrity GM, Boone DR, Castenholz RW, editors. Bergey's manual of systematic bacteriology. 2. New York: Springer; 2001. pp. 370–387. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Bhandari V, Gupta RS. Molecular signatures for the phylum (class) Thermotogae and a proposal for its division into three orders (Thermotogales, Kosmotogales ord. nov. and Petrotogales ord. nov.) containing four families (Thermotogaceae, Fervidobacteriaceae fam. nov., Kosmotogaceae fam. nov. and Petrotogaceae fam. nov.) and a new genus Pseudothermotoga gen. nov. with five new combinations. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2014;105(1):143–168. doi: 10.1007/s10482-013-0062-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.List Editor Validation of the Publication of New Names and New Combinations Previously Effectively Published Outside the IJSB. List No. 22. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1986;36(4):573–576. doi: 10.1099/00207713-36-4-573. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Jannasch HW, Huber R, Belkin S, Stetter, KO. Thermotoga neapolitana sp. nov. of the extremely thermophilic, eubacterial genus Thermotoga. Arch Microbiol. 1988;150(1):103-4
- 46.List Editor Validation of the Publication of New Names and New Combinations Previously Effectively Published Outside the IJSB. List No. 28. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1989;39(1):93–94. doi: 10.1099/00207713-39-1-93. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Chhabra SR, Shockley KR, Conners SB, Scott KL, Wolfinger RD, Kelly RM. Carbohydrate-induced differential gene expression patterns in the hyperthermophilic bacterium Thermotoga maritima. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(9):7540–7552. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M211748200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Yu X, Drapcho CM. Hydrogen production by the hyperthermophilic bacterium Thermotoga neapolitana using agricultural-based carbon and nitrogen sources. Biol Eng Trans. 2011;4(2):101–112. doi: 10.13031/2013.38506. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT, et al. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet. 2000;25(1):25–29. doi: 10.1038/75556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol Biol Evol. 2016;33(7):1870–1874. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msw054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Besemer J, Lomsadze A, Borodovsky M. GeneMarkS: a self-training method for prediction of gene starts in microbial genomes. Implications for finding sequence motifs in regulatory regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001;29(12):2607–2618. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.12.2607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Hyatt D, Chen GL, Locascio PF, Land ML, Larimer FW, Hauser LJ. Prodigal: prokaryotic gene recognition and translation initiation site identification. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010;11:119. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Darling AC, Mau B, Blattner FR, Perna NT. Mauve: multiple alignment of conserved genomic sequence with rearrangements. Genome Res. 2004;14(7):1394–1403. doi: 10.1101/gr.2289704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Alm RA, Bodero AJ, Free PD, Mattick JS. Identification of a novel gene, pilZ, essential for type 4 fimbrial biogenesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1996;178(1):46–53. doi: 10.1128/jb.178.1.46-53.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.van Schaik EJ, Giltner CL, Audette GF, Keizer DW, Bautista DL, Slupsky CM, Sykes BD, Irvin RT. DNA binding: a novel function of Pseudomonas aeruginosa type IV pili. J Bacteriol. 2005;187(4):1455–1464. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.4.1455-1464.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Pratt JT, Tamayo R, Tischler AD, Camilli A. PilZ domain proteins bind cyclic diguanylate and regulate diverse processes in Vibrio cholerae. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(17):12860–12870. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M611593200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Chiang P, Sampaleanu LM, Ayers M, Pahuta M, Howell PL, Burrows LL. Functional role of conserved residues in the characteristic secretion NTPase motifs of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa type IV pilus motor proteins PilB, PilT and PilU. Microbiology. 2008;154(Pt 1):114–126. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2007/011320-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Nunn D, Bergman S, Lory S. Products of three accessory genes, pilB, pilC, and pilD, are required for biogenesis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa pili. J Bacteriol. 1990;172(6):2911–2919. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.2911-2919.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Seitz P, Blokesch M. DNA-uptake machinery of naturally competent Vibrio cholerae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(44):17987–17992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1315647110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Assalkhou R, Balasingham S, Collins RF, Frye SA, Davidsen T, Benam AV, Bjoras M, Derrick JP, Tonjum T. The outer membrane secretin PilQ from Neisseria meningitidis binds DNA. Microbiology. 2007;153(Pt 5):1593–1603. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2006/004200-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Burkhardt J, Vonck J, Averhoff B. Structure and function of PilQ, a secretin of the DNA transporter from the thermophilic bacterium Thermus thermophilus HB27. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(12):9977–9984. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.212688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Collins RF, Davidsen L, Derrick JP, Ford RC, Tonjum T. Analysis of the PilQ secretin from Neisseria meningitidis by transmission electron microscopy reveals a dodecameric quaternary structure. J Bacteriol. 2001;183(13):3825–3832. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.13.3825-3832.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Graupner S, Frey V, Hashemi R, Lorenz MG, Brandes G, Wackernagel W. Type IV pilus genes pilA and pilC of Pseudomonas stutzeri are required for natural genetic transformation, and pilA can be replaced by corresponding genes from nontransformable species. J Bacteriol. 2000;182(8):2184–2190. doi: 10.1128/JB.182.8.2184-2190.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Rudel T, Facius D, Barten R, Scheuerpflug I, Nonnenmacher E, Meyer TF. Role of pili and the phase-variable PilC protein in natural competence for transformation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995;92(17):7986–7990. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.17.7986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Nunn DN, Lory S. Product of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa gene pilD is a prepilin leader peptidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991;88(8):3281–3285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Freitag NE, Seifert HS, Koomey M. Characterization of the pilF-pilD pilus-assembly locus of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Mol Microbiol. 1995;16(3):575–586. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.tb02420.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Paranjpye RN, Lara JC, Pepe JC, Pepe CM, Strom MS. The type IV leader peptidase/N-methyltransferase of Vibrio vulnificus controls factors required for adherence to HEp-2 cells and virulence in iron-overloaded mice. Infect Immun. 1998;66(12):5659–5668. doi: 10.1128/iai.66.12.5659-5668.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Hahn J, Inamine G, Kozlov Y, Dubnau D. Characterization of comE, a late competence operon of Bacillus subtilis required for the binding and uptake of transforming DNA. Mol Microbiol. 1993;10(1):99–111. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb00907.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Draskovic I, Dubnau D. Biogenesis of a putative channel protein, ComEC, required for DNA uptake: membrane topology, oligomerization and formation of disulphide bonds. Mol Microbiol. 2005;55(3):881–896. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04430.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Bakaletz LO, Baker BD, Jurcisek JA, Harrison A, Novotny LA, Bookwalter JE, Mungur R, Munson RS., Jr Demonstration of Type IV pilus expression and a twitching phenotype by Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 2005;73(3):1635–1643. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.3.1635-1643.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Larson TG, Goodgal SH. Sequence and transcriptional regulation of com101A, a locus required for genetic transformation in Haemophilus influenzae. J Bacteriol. 1991;173(15):4683–4691. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.15.4683-4691.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Wolfgang M, Lauer P, Park HS, Brossay L, Hebert J, Koomey M. PilT mutations lead to simultaneous defects in competence for natural transformation and twitching motility in piliated Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Mol Microbiol. 1998;29(1):321–330. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1998.00935.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Kline KA, Criss AK, Wallace A, Seifert HS. Transposon mutagenesis identifies sites upstream of the Neisseria gonorrhoeae pilE gene that modulate pilin antigenic variation. J Bacteriol. 2007;189(9):3462–3470. doi: 10.1128/JB.01911-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Russell MA, Darzins A. The pilE gene product of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, required for pilus biogenesis, shares amino acid sequence identity with the N-termini of type 4 prepilin proteins. Mol Microbiol. 1994;13(6):973–985. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00489.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Provvedi R, Dubnau D. ComEA is a DNA receptor for transformation of competent Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol. 1999;31(1):271–280. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01170.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Inamine GS, Dubnau D. ComEA, a Bacillus subtilis integral membrane protein required for genetic transformation, is needed for both DNA binding and transport. J Bacteriol. 1995;177(11):3045–3051. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.11.3045-3051.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Chen I, Gotschlich EC. ComE, a competence protein from Neisseria gonorrhoeae with DNA-binding activity. J Bacteriol. 2001;183(10):3160–3168. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.10.3160-3168.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Takeno M, Taguchi H, Akamatsu T. Role of ComEA in DNA uptake during transformation of competent Bacillus subtilis. J Biosci Bioeng. 2012;113(6):689–693. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2012.02.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Gwinn ML, Ramanathan R, Smith HO, Tomb JF. A new transformation-deficient mutant of Haemophilus influenzae Rd with normal DNA uptake. J Bacteriol. 1998;180(3):746–748. doi: 10.1128/jb.180.3.746-748.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Mortier-Barriere I, Velten M, Dupaigne P, Mirouze N, Pietrement O, McGovern S, Fichant G, Martin B, Noirot P, Le Cam E, et al. A key presynaptic role in transformation for a widespread bacterial protein: DprA conveys incoming ssDNA to RecA. Cell. 2007;130(5):824–836. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.07.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Karudapuram S, Zhao X, Barcak GJ. DNA sequence and characterization of Haemophilus influenzae dprA+, a gene required for chromosomal but not plasmid DNA transformation. J Bacteriol. 1995;177(11):3235–3240. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.11.3235-3240.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Clone Manager [http://www.scied.com/index.htm].


