Abstract
Background
Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC), including E. coli O157:H7, are responsible for numerous foodborne outbreaks annually worldwide. E. coli O157:H7, as well as pathogenic non-O157:H7 STECs, can cause life-threating complications, such as bloody diarrhea (hemolytic colitis) and hemolytic-uremic syndrome (HUS). Previously, we developed a real-time PCR assay to detect E. coli O157:H7 in foods by targeting a unique putative fimbriae protein Z3276. To extend the detection spectrum of the assay, we report a multiplex real-time PCR assay to specifically detect E. coli O157:H7 and screen for non-O157 STEC by targeting Z3276 and Shiga toxin genes (stx1 and stx2). Also, an internal amplification control (IAC) was incorporated into the assay to monitor the amplification efficiency.
Methods
The multiplex real-time PCR assay was developed using the Life Technology ABI 7500 System platform and the standard chemistry. The optimal amplification mixture of the assay contains 12.5 μl of 2 × Universal Master Mix (Life Technology), 200 nM forward and reverse primers, appropriate concentrations of four probes [(Z3276 (80 nM), stx1 (80 nM), stx2 (20 nM), and IAC (40 nM)], 2 μl of template DNA, and water (to make up to 25 μl in total volume). The amplification conditions of the assay were set as follows: activation of TaqMan at 95 °C for 10 min, then 40 cycles of denaturation at 95 °C for 10 s and annealing/extension at 60 °C for 60 s.
Results
The multiplex assay was optimized for amplification conditions. The limit of detection (LOD) for the multiplex assay was determined to be 200 fg of bacterial DNA, which is equivalent to 40 CFU per reaction which is similar to the LOD generated in single targeted PCRs. Inclusivity and exclusivity determinants were performed with 196 bacterial strains. All E. coli O157:H7 (n = 135) were detected as positive and all STEC strains (n = 33) were positive for stx1, or stx2, or stx1 and stx2 (Table 1). No cross reactivity was detected with Salmonella enterica, Shigella strains, or any other pathogenic strains tested.
Conclusions
A multiplex real-time PCR assay that can rapidly and simultaneously detect E. coli O157:H7 and screen for non-O157 STEC strains has been developed and assessed for efficacy. The inclusivity and exclusivity tests demonstrated high sensitivity and specificity of the multiplex real-time PCR assay. In addition, this multiplex assay was shown to be effective for the detection of E. coli O157:H7 from two common food matrices, beef and spinach, and may be applied for detection of E. coli O157:H7 and screening for non-O157 STEC strains from other food matrices as well.
Keywords: Multiplex real-time PCR; Escherichia coli O157:H7; Shiga toxins (stx1, stx2); Shiga toxin-producing E. col (STEC); non-O157; Limit of detection (LOD); Pathogen detection; Sensitivity
Background
Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC), including E. coli O157:H7, is a heterogeneous group of enteric pathogens responsible for numerous sporadic infections and large outbreaks annually worldwide [1]. Besides E. coli O157:H7, non-O157 STEC strains are important foodborne pathogens estimated to cause over 112,752 cases illnesses each year in the United States [2]. Shiga toxin (Stx) production, especially Stx2, has been implicated as an important factor in causing severe disease and hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) [3–5].
E. coli serotype O157:H7 was first recognized as a causative agent of food contamination outbreaks in 1982 in Oregon and Michigan [6]. Since then, numerous E. coli O157:H7 outbreaks have been reported worldwide [7]. In the United States alone during 2003 - 2012, 390 outbreaks of E. coli O157:H7 infections were documented, which resulted in 4,928 illnesses, 1,272 hospitalizations, and 33 deaths [8]. The typical symptoms caused by E. coli O157:H7 include abdominal pain, watery diarrhea and potential progression to bloody diarrhea (hemorrhagic colitis) [9]. The pathological features of hemorrhagic colitis are attributed to the production of Shiga like cytotoxins (Stx1 and Stx2), which consists of a 32-kDa A subunit and five identical 7.7 kDa B subunits. These toxins can bind to receptors located on membranes of eukaryotic cell and cause tissue damage resulting in pathological outcomes [4, 5, 10, 11]. Non-O157 STEC strains are foodborne pathogens and have been responsible for sporadic cases of infections and outbreaks. Although O157:H7 has garnered more attention, primarily based on historical record, recent attention has recognized the significance of non-O157 STEC strains as a pathogen [9, 12–20]. Considerable attention is now drawn to non-O157 STEC strains particularly after the occurrence of a severe foodborne outbreak happened in 2011 in Germany caused by consumption of sprouts contaminated by STEC O104:H4 [21].
The clinical significance and economic burden associated with outbreaks caused by E. coli O157:H7 and non-O157 STEC have led to development of a variety of detection methods. These include the application of conventional bacteriological methods using selective media or chromogenic agar, which usually take several days to complete [1, 9, 22], and molecular-based assays such as PCR-based methods [23–25], microarray [25–27], and whole genomic sequencing (WGS) [25, 28, 29]. Of these molecular methods, real-time PCR is a commonly used method [9]. More importantly, real-time PCR enables detection to be coincided with the amplification process by the introduction of fluorogenic probes [23], and multiplex real-time PCR allows multiple genes to be simultaneously amplified either from one template [9] or multiple templates by using different primer pairs [24].
Multiplex real-time PCR has gained more acceptance and use due to its ability to its differentiation potential and reliability [11, 30]. Various target genes have been used in PCR detection scheme for E.coli O157:H7, including the Shiga toxin genes (stx1 and stx2) [9, 12, 13], eae [31, 32], fimA [33], rfbE [34], uidA [24, 35], and Z3276 [23, 36, 37]. Of the target genes, uidA is most commonly used. Specificity with this gene is based on a highly conserved point mutation at position 93 of the β-glucuronidase gene [38, 39]. However, when a uidA-based commercial kit was used for identification of a large number of E. coli O157:H7 isolates (n = 391), numerus strains (n = 21) did not generate an amplified product. This prompted us to search for a more specific and reliable gene target for detection of E. coli O157:H7 [23]. As a result, a real-time PCR-based on Z3276 gene, a putative unique fimbriae gene in E. coli O157:H7 [40], was developed. All the 391 isolates, including the 21 strains that were “negative” by the uidA-based commercial kit, that were tested were positively identified [23]. The primary focus of our previous study was to search for a unique genetic marker and the development of a real-time PCR assay for the detection of E.coli O157:H7, and the Shiga toxin genes were not included in that assay [23]. Since the annual number of episodes of domestically acquired foodborne illnesses caused by non-O157 STEC (112,752) is almost doubled that of E. coli O157:H7 (63,153) in the United States [2], the inclusion of the stx genes can be used as the primary characteristic for STEC detection within the heterogeneous STEC group [41]. Thus, in the present study, we incorporated in a multiplex real-time PCR assay the Z3276, stx1, and stx2 genes, as well as an internal amplification control to for detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and screening for non-O157 STEC. In addition, the assay was assessed with two common food matrices, beef and spinach, for specific detection of E. coli O157:H7 and non-O157 STEC strains.
Methods
Bacterial strains and growth conditions
All the E. coli O157:H7 and non-O157 STEC strains used in this study are listed in Table 1. EDL933 (ATCC 43985) was used as the E. coli O157:H7 reference strain. Strains of E. coli O157:H7 (n = 135) and non-O157 STEC (n = 33) were used for inclusivity determination. Salmonella enterica strains, Shigella strains and other pathogenic strains were used for the exclusivity test (Table 2). These strains are all from the strain collections of Division of Molecular Biology, Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Table 1.
Results of E. coli O157:H7 and non-O157 STEC strains detected by the multiplex real-time PCR assay
| Strain | Serotype | Source | Target gene | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z3276 | stx1 | stx2 | |||
| EC1275 | O157:H7 | CDC EDL933, hamburger meat | + | + | + |
| EC1225 | O157:H7 | WA, 1993 | + | + | + |
| EC1759 | O157:H7 | USA (MI), 2003 | + | + | + |
| EC1429 | O157:H7 | Denmark, 1987 | + | - | + |
| EC4420 | O157:H7 | NY, 12/2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4421 | O157:H7 | White Onions, NY, 12/2006 | + | + | + |
| EC4422 | O157:H7 | White Onions, NY, 12/2006 | + | + | + |
| EC4504 | O157:H7 | MN, 12/2006 | + | + | + |
| EC1428 | O157:H7 | Argentina, 1977 | + | - | + |
| EC1738 | O157:H7 | Food isolate | + | - | + |
| EC1530 | O157:H7 | Thailand, 1994 | + | - | + |
| EC4440 | O157:H7 | CDC | + | + | + |
| EC4163 | O157:H7 | USA (IL) | + | - | + |
| EC4438 | O157:H7 | CDC | + | - | + |
| EC4431 | O157:H7 | NY, 12/2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4452 | O157:H7 | USA (NJ), 2006 | + | - | + |
| EC1709 | O157:H7 | USA (MI), 2002 | + | - | + |
| EC1760 | O157:H7 | USA (MI), 2004 | + | - | + |
| EC1431 | O157:H7 | Japan, 1987 | + | - | + |
| EC4115 | O157:H7 | Sep-06 | + | - | + |
| EC1734 | O157:H7 | MA, 2009 | + | - | + |
| EC4302 | O157:H7 | NY, 12/2006 | + | + | + |
| EC4301 | O157:H7 | NY, 12/2006 | + | + | + |
| EC4429 | O157:H7 | NY, 12/2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4428 | O157:H7 | NY, 12/2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4437 | O157:H7 | NJ, 12/2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4436 | O157:H7 | NJ, 12/2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4434 | O157:H7 | NY, 12/2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4433 | O157:H7 | NY, 12/2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4432 | O157:H7 | NY, 12/2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4449 | O157:H7 | NJ, 12/2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4448 | O157:H7 | WI, 12/2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4447 | O157:H7 | CA, 12/2006 | + | + | + |
| EC4201 | O157:H7 | USA (CA), 2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4456 | O157:H7 | USA (NJ),2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4461 | O157:H7 | USA (NJ),2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4502 | O157:H7 | USA (NJ),2006 | + | + | + |
| EC4503 | O157:H7 | USA (NJ),2006 | + | + | + |
| EC4505 | O157:H7 | USA (NJ),2006 | + | + | + |
| EC4511 | O157:H7 | USA (NJ),2006 | + | + | + |
| EC4200 | O157:H7 | USA (CA), 2006 | + | - | + |
| EC1267 | O157:H7 | USA, (NH), 1991 | + | + | + |
| EC1268 | O157:H7 | USA (MT), 1991 | + | + | + |
| EC4194 | O157:H7 | USA (CA), 2006 | + | - | + |
| EC1590 | O157:H7 | USA (WA) | + | + | + |
| EC4458 | O157:H7 | USA (NJ),2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4197 | O157:H7 | USA (CA), 2006 | + | - | + |
| EC1231 | O157:H7 | USA (WA), 1995 | + | + | + |
| EC4470 | O157:H7 | USA (NJ),2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4471 | O157:H7 | USA (NJ),2006 | + | - | + |
| EC1244 | O157:H7 | USA (GA), 1992 | + | + | + |
| EC4199 | O157:H7 | USA (CA), 2006 | + | - | + |
| EC1260 | O157:H7 | USA (GA),1993 | + | - | + |
| EC4167 | O157:H7 | USA (WI), 2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4168 | O157:H7 | USA (WI), 2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4193 | O157:H7 | USA (OH), 2006 | + | - | + |
| EC1265 | O157:H7 | USA (CA), 1993 | + | + | + |
| EC4184 | O157:H7 | USA (IL), 2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4204 | O157:H7 | USA (CA), 2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4171 | O157:H7 | USA (WI), 2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4205 | O157:H7 | USA (CA), 2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4206 | O157:H7 | USA (CA), 2006 | + | - | + |
| EC1593 | O157:H7 | USA (MI), 2003 | + | + | + |
| EC1239 | O157:H7 | USA (NE), 1993 | + | - | + |
| EC4174 | O157:H7 | USA (IL), 2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4187 | O157:H7 | USA (CT), 2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4188 | O157:H7 | USA (CT), 2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4191 | O157:H7 | Spinach, USA (IL), 2006 | + | - | + |
| EC1276 | O157:H7 | Japan, 1996 | + | + | + |
| EC4501 | O157:H7 | MN, 12/2006 | + | + | + |
| EC558 | O157:H7 | Patient raw milk | + | + | + |
| EC867 | O157:H7 | USDA-FSIS-380-94 | + | + | + |
| EC874 | O157:H7 | Apple cider | + | + | + |
| EC4162 | O157:H7 | Feces (New Jersey) | + | - | + |
| EC506 | O157:H7 | Feces | + | - | + |
| EC507 | O157:H7 | Feces | + | + | + |
| EC4443 | O157:H7 | CDC | + | + | + |
| EC4442 | O157:H7 | CDC | + | + | + |
| EC4441 | O157:H7 | CDC | + | + | + |
| EC4451 | O157:H7 | NJ, 12/2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4445 | O157:H7 | NJ, 12/2006 | + | + | + |
| EC4446 | O157:H7 | NJ, 12/2006 | + | + | + |
| EC1601 | O157:H7 | USA (MI), 2002 | + | + | + |
| EC1727 | O157:H7 | MI, 2002 | + | + | + |
| EC1426 | O157:H7 | Canada, 1988 | + | - | + |
| EC4419 | O157:H7 | NY, 12/2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4418 | O157:H7 | NY, 12/2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4417 | O157:H7 | NY, 12/2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4416 | O157:H7 | NY, 12/2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4423 | O157:H7 | NY, 12/2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4424 | O157:H7 | NY, 12/2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4427 | O157:H7 | NY, 12/2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4426 | O157:H7 | NY, 12/2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4435 | O157:H7 | NY, 12/2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4425 | O157:H7 | NY, 12/2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4164 | O157:H7 | USA (WI), 2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4439 | O157:H7 | MS, 12/2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4450 | O157:H7 | NJ, 12/2006 | + | - | + |
| EC1217 | O157:H7 | 2003 | + | + | + |
| EC1577 | O157:H7 | USA (WA), 1995 | + | + | + |
| EC4201 | O157:H7 | USA (CA), 2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4207 | O157:H7 | USA (IL), 2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4208 | O157:H7 | Spinach, USA (IL), 2006 | + | - | + |
| EC1245 | O157:H7 | USA (GA), 1995 | + | + | + |
| EC4506 | O157:H7 | USA (MN), 2006 | + | + | + |
| EC4507 | O157:H7 | USA (MN), 2006 | + | + | + |
| EC4508 | O157:H7 | USA (MN), 2006 | + | + | + |
| EC4509 | O157:H7 | USA (MN), 2006 | + | + | + |
| EC4510 | O157:H7 | USA (MN), 2006 | + | + | + |
| EC1590 | O157:H7 | USA (WA) | + | + | + |
| EC1597 | O157:H7 | USA (CT), 1996 | + | + | + |
| EC1225 | O157:H7 | USA (WA), 1993 | + | + | + |
| EC1236 | O157:H7 | Food, USA (CA), 1993 | + | + | + |
| EC1240 | O157:H7 | USA (OH), 1993 | + | + | + |
| EC1241 | O157:H7 | Food, USA (OR), 1995 | + | + | + |
| EC4472 | O157:H7 | USA, (NJ), 2006 | + | - | + |
| EC1242 | O157:H7 | USA (GA), 1992 | + | - | + |
| EC1243 | O157:H7 | USA (GA), 1992 | + | + | + |
| EC4463 | O157:H7 | USA (NJ), 2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4165 | O157:H7 | USA (WI), 2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4166 | O157:H7 | USA (WI), 2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4195 | O157:H7 | Spinach, USA (OH), 2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4192 | O157:H7 | USA (CA), 2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4182 | O157:H7 | USA (IL), 2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4469 | O157:H7 | USA (NJ), 2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4465 | O157:H7 | USA (NJ), 2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4170 | O157:H7 | USA (WI), 2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4183 | O157:H7 | USA (IL), 2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4186 | O157:H7 | USA (IL), 2006 | + | - | + |
| Ec4169 | O157:H7 | USA (WI), 2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4189 | O157:H7 | USA (CT), 2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4175 | O157:H7 | USA (IL), 2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4176 | O157:H7 | USA (IL), 2006 | + | - | + |
| EC4444 | O157:H7 | USA, NJ, 2006 | + | + | + |
| EC4173 | O157:H7 | USA (IL), 2006 | + | - | + |
| EC1892 | O104:H4 | STEC, Republic of Georgia, 2011 | - | - | + |
| EC1893 | O104:H4 | STEC, Republic of Georgia, 2011 | - | - | + |
| EC1891 | O104:H4 | STEC, Germany, 2011 | - | - | + |
| EC1894 | O104:H4 | STEC, Germany, 2011 | - | - | + |
| EC1769 | O26 | STEC | - | + | - |
| EC1770 | O26 | STEC | - | + | + |
| EC1771 | O26 | STEC | - | + | - |
| EC1773 | O26:H11 | STEC | - | + | - |
| EC1775 | O26:H11 | STEC | - | + | - |
| EC1768 | O26:H2 | STEC | - | + | - |
| EC1786 | O111:NM | STEC | - | + | + |
| EC1787 | O111:H8 | STEC | - | + | + |
| EC1788 | O111:NM | STEC | - | + | - |
| EC1791 | O145:H25 | STEC | - | - | + |
| EC1794 | O145:NM | STEC | - | + | + |
| EC1801 | O103:H2 | STEC | - | + | - |
| EC1802 | O103:H25 | STEC | - | + | - |
| EC1803 | O103:H11 | STEC | - | + | + |
| EC1806 | O121:H19 | STEC | - | - | + |
| EC1807 | O121:H19 | STEC | - | - | + |
| EC1808 | O121:H19 | STEC | - | + | + |
| EC331 | O26 | STEC | - | + | + |
| EC400 | O26:H11 | STEC | - | + | + |
| EC521 | O26:H11 | STEC | - | + | + |
| EC540 | O26:H- | STEC | - | + | + |
| EC550 | O26:H- | STEC | - | + | + |
| EC1232 | O55:H7 | STEC | - | + | + |
| EC1235 | O55:H7 | STEC | - | + | + |
| EC1668 | O111:H8 | STEC | - | + | - |
| EC1669 | O118:H16 | STEC | - | - | + |
| EC1631 | O111:H8 | STEC | - | + | - |
| EC1655 | O111:H8 | STEC | - | + | - |
| K12 | Negative E. coli strain control | - | - | - | |
| NTC | - | - | - | ||
Table 2.
Detection results of the exclusivity test with different bacterial strains by the multiplex real-time PCR assay
| Target gene | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Pathotype | Strain name/Serotype | Z3276 | stx1 | stx2 |
| Escherichia | coli | EHEC | EDL933/O157:H7 | + | + | + |
| Escherichia | coli | ETEC | EC1775/O26:H11 | _ | + | _ |
| Escherichia | coli | STEC | EC1803/O103:H11 | _ | + | + |
| Escherichia | coli | STEC | EC1807/O121:H19 | _ | _ | + |
| Escherichia | coli | ETEC | EC1801 | _ | + | _ |
| Escherichia | coli | EPEC | EC1501 | _ | _ | _ |
| Escherichia | coli | EIEC | EC1513 | _ | _ | _ |
| Escherichia | coli | EDC | DEC5A | _ | _ | _ |
| Escherichia | coli | K12/MG1655 | _ | _ | _ | |
| _ | _ | _ | ||||
| Salmonella | enterica | SL192/Typhi | _ | _ | _ | |
| Salmonella | enterica | SL317/Newport | _ | _ | _ | |
| Salmonella | enterica | SL535/Typhimurim | _ | _ | _ | |
| _ | _ | _ | ||||
| Shigella | sonnei | SH20145 | _ | _ | _ | |
| Shigella | dysenteriae | SH20152 | _ | _ | _ | |
| Shigella | flexneri | SH20155 | _ | _ | _ | |
| Shigella | boydii | SH20140 | _ | _ | _ | |
| _ | _ | _ | ||||
| Staphylococcus | aureus | ATCC25923 | _ | _ | _ | |
| Staphylococcus | epidermidis | ATCC12228 | _ | _ | _ | |
| Staphylococcus | pyogenes | ATCC19615 | _ | _ | _ | |
| _ | _ | _ | ||||
| Vibrio | alginolytica | ATCC17749 | _ | _ | _ | |
| Vibrio | parahemolyticus | ATCC17802 | _ | _ | _ | |
| Vibrio | vulasfians | ATCC27562 | _ | _ | _ | |
| _ | _ | _ | ||||
| Enterobacter | cloacae | ATTCC23355 | _ | _ | _ | |
| Enterobacter | cloacae | ATCC13047 | _ | _ | _ | |
| Enterobacter | cloacae | ATCC13048 | _ | _ | _ | |
| _ | _ | _ | ||||
| Citrobacter | freundii | ATCC8090 | _ | _ | _ | |
| _ | _ | _ | ||||
| Klebsiella | pneumoniae | ATCC13883 | _ | _ | _ | |
| _ | _ | _ | ||||
| Pseudomonas | aeruginosa | ATCC27853 | _ | _ | _ | |
Bacterial DNA preparation
Bacteria were grown at 37 °C in Luria-Bertani (LB) broth with agitation at 180 rpm, or on LB agar placed in a gravity convection incubator. Bacterial growth was measured by monitoring the turbidity at 600 nm (OD600) using a DU530 spectrophotometer (Beckman, CA). To enumerate bacterial cells, cultures were diluted serially in 10-fold increments with medium and plated on LB agar plates at 37 °C overnight. DNA preparation from bacterial cultures was made with a Puregene cell and tissue kit (Gentra, Minneapolis, MN) as described previously [23]. Briefly, cell pellets from 1 ml of overnight culture were suspended in 3 ml of cell lysis solution and heated to 80 °C for 5 min, followed by addition of 15 μl of RNase A and incubation at 37 °C for 60 min. To remove protein and cell debris, the cell lysate was further mixed with 1 ml of protein precipitation solution, vortexed and centrifuged at 3000 × g. DNA in the supernatant was precipitated by the addition of 2-propanol, centrifuged as above, washed with 70% ethanol, and dissolved in 500 μl of rehydration solution. The concentration of DNA extraction was determined by measuring the optical density (OD260) using a NanoDrop spectrophotometer (NanoDrop Technology, Wilmington, DE)
Primers and probes for the multiplex real-time PCR assay
All the primers, probes, and sequence information are listed in Table 3. The primers and labeled TaqMan probes in this study were designed using Primer Express 3.0 software (Life Technology, Foster City, CA) and synthesized by Life Technology. The primers and probe for E. coli O157:H7 specific gene open reading frame (ORF) ORFZ3276 were described previously [23], the primers and probes for stx1, and stx2 were designed in this study, and the primers and probe for internal amplification control (IAC) were selected based on the DNA sequence of plasmid pUC19 as previously reported [42]. The IAC was incorporated into the multiplex real-time PCR assay to ensure the amplification is free of inhibitory factors from examined food samples.
Table 3.
Primers and probes used in the multiplex real-time PCR assay
| Target gene | Primer/Probe | Sequence (5' -- 3') | Amplicon | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| length (bp) | ||||
| Z3276 | Z3276 forward | TATTCCGCGATGCTTGTTTTT | 130 | Li and Chen. 2012 |
| Z3276 reverse | ATTATCTCACCAGCAAACTGGCGG | |||
| Z3276 probe | FAM-CCCGCAAATCTTTCCMGBNFQ | |||
| stx1 | stx1 forward | GGATTTCGTACAACACTGGATGAT | 67 | This study |
| stx1 reverse | ATCCACATCTTCAGCAGTCATTACA | |||
| stx1 probe | TAMRA-CAGTGGGCGTTCTTMGBNFQ | |||
| stx2 | stx2 forward | GGGCAGTTATTTTGCTGTGGAT | 59 | This study |
| stx2 reverse | GGTCAAAACGCGCCTGAT | |||
| stx2 probe | JOE-ACGAGGGCTTGATGTCMGBNFQ | |||
| IAC | IAC forward | CAGGATTAGCAGAGCGAGGTATG | 65 | Fricker et al. 2007 |
| IAC reverse | CGTAGTTAGGCCACCACTTCAAG | |||
| IAC probe | CY5-AGGCGGTGCTACAGAG-MGBNFQ |
Development of the multiplex real-time PCR assay
The multiplex real-time PCR assay was developed using the Life Technology ABI 7500 System platform and the standard chemistry. The concentrations of primers and probes for each target gene were adjusted to achieve optimal amplification condition. The reaction mixture contains 12.5 μl of 2 × Universal Master Mix (Life Technology), 200 nM forward and reverse primers, appropriate concentrations of four probes [(Z3276 (80 nM), stx1 (80 nM), stx2 (20 nM), and IAC (40 nM)] and 2 μl of template DNA. Water was added to make a final reaction volume of 25 μl. The amplification conditions for the multiplex assay were set as follows: activation of TaqMan at 95 °C for 10 min, then 40 cycles of denaturation at 95 °C for 10 s and annealing/extension at 60 °C for 60 s.
To compare the efficiency of the multiplex assay with simplex assay, each of the target genes Z3276, stx1, and stx2 was amplified by three individual simplex assays. For the simplex assays, three individual reaction mixtures each contains 12.5 μl of 2 × Universal Master Mix (Life Technology), corresponding forward and reverse primers (200 nM) and probe (100 nM). An equal amount of template DNA (2 μl) was used for the simplex assays, and water was added to make a final reaction volume of 25 μl. The amplification conditions for simplex assays were the same as the multiplex assay.
Sensitivity test and the limit of detection (LOD) of the multiplex qPCR assay
To determine the sensitivity of the multiplex real-time PCR, standard curves of Z3276, stx1, and stx2 in the multiplex real-time PCR were generated. A serial 10-fold dilution from 10 ng to 10 fg/μl of genomic DNA of E. coli O157:H7 strain (EDL933) was prepared and 2.0 μl of each dilution was used as template for PCR amplification. The real-time PCR assay was performed using the conditions described as above. The amplification efficiency of the assay was determined using the formula E = (10-1/slope-1)*100 [43, 44].
Inclusivity and exclusivity tests
The inclusivity test for the multiplex real-time PCR was performed with the optimized concentrations for probes Z3276, stx1 and stx2 on the genomic DNA of E. coli O157:H7 strains (n = 135) and non-O157 STEC strains (n = 21) (Table 1). The exclusivity test was performed on various pathogenic strains including strains of EIEC, EPEC, Shigella, and Salmonella (n = 27) (Table 2). DNA samples were diluted with nuclease-free water to concentration of 50 pg/μl and 2 μl of DNA dilute was used for amplification of target genes. Furthermore, 2 μl of nuclease free water was used to substitute DNA in no template control in the triplex real-time PCR.
Application of the multiplex real-time PCR assay to detect E. coli O157:H7 from spiked spinach and beef
Fresh spinach and beef were purchased from a local retail source and used as food matrices to assess the multiplex real-time PCR assay. These samples were first confirmed to be free of E. coli O157:H7 and non-O157 STEC by standard FDA BAM method [45], and subsequently used for the spiking experiments. One for beef (set 1) spinach spiking (set 2). Each set contained six replicates (25 g of beef or spinach), and were inoculated with 80 and 800 CFU/g O157:H7 (EDL933) cells, respectively. Each sample was mixed with 225 ml of LB medium and homogenized for 2 min using a stomacher (Seward, England). The samples were incubated at 37 °C with shaking at 180 rpm for 24 h.
Two ml of the enriched culture was sampled at 0, 4, 8, 12 and 24 h. At these times, the samples were centrifuged at 600 × g for 1 min to remove fat tissues (for beef) or leaf (for spinach) from the samples. The supernatants were transferred to 2-ml microtubes and centrifuged again at 3000 × g for 5 min to collect bacterial cells. The cell pellets were used for DNA extraction with PreMan Ultra Sample Preparation Reagent (Life Technologies), following the instruction of the manufacturer. Two μl of the DNA extraction was used in the multiplex real-time PCR, and roughly 200 copies of plasmid pUC19 DNA (Promega, Madison, MI) was added as template for IAC.
Results
Designation and optimization of multiplex real-time PCR
Z3276 is a unique target gene that was used as the basis for a multiplex real-time PCR assay for the detection of E. coli O157:H7. In addition to the Z3276 marker, three additional targets stx1, stx2, and IAC, were optimized for amplification and detection (data not shown). In order to minimize the interference among probes during the amplification process, the concentration of each probe was titrated and tested with a fixed amount of DNA (1 ng/reaction). The optimal concentrations for probes Z3276, stx1, stx2, IAC were determined as 80 nM, 80 nM, 20 nM, and 40 nM, respectively.
We further assessed whether the sensitivity of the probes was affected in the multiplex real-time PCR by comparing with those from the corresponding simplex assays. The C T values for the target genes Z3276, stx1, and stx2 were determined to be 23.86, 22.23, and 21.22, respectively in the multiplex real-time PCR (Fig. 1a), whereas the C T values for Z3276, stx1, and stx2 were 21.62, 21.38, and 20.63, respectively in simplex real-time PCR (Fig. 1b). These results demonstrated that at a specified amount of target DNA, the sensitivity of the multiplex PCR assay is comparable with that of each respective simplex assay.
Fig. 1.
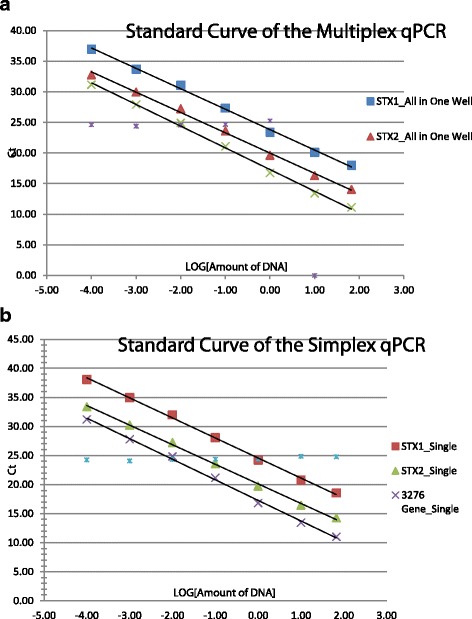
Comparison of the sensitivity of simultaneously detecting the targeting genes Z3276, stx1, and stx2 in E. coli O157:H7 by the multiplex real-time PCR assay. The standard curves of Z3276, stx1, and stx2 created by the multiplex real-time PCR assay (a); the standard curves of Z3276, stx1, and stx2 generated by three individual simplex real-time PCR assays (b). The C T values represent the average of six replicates from two independent tests ±SD
Comparison of sensitivity and specificity of the multiplex and simplex real-time PCR assays
Using a serial 10-fold dilution of genomic DNA from E. coli O157:H7 (EDL933) as template, the limit of detection (LOD) in the multiplex real-time PCR was determined to be 200 fg of DNA per reaction with average C T values of 38.63, 36.21, and 34.04 for Z3276, stx1, and stx2, respectively. The value of 200 fg of DNA per reaction is equivalent to 40 CFU of DNA. Three standard curves with slopes of -3.60, -3.49, and -3.36, for the target genes Z3276, for stx1, and stx2, respectively, were generated and the amplification efficiencies for the three target genes differed slightly ranging from 90% - 98% (Fig. 1). These data indicated the sensitivity of the multiplex real-time PCR was robust and reliable.
Inclusivity and exclusivity of the multiplex real-time PCR
The multiplex real-time PCR positively identified all the E. coli O157:H7 strains (n = 135) (Table 1). This collection of 135 positively identified E. coli O157:H7 strains included the 21 strains that were not amplified in a real-time PCR assay targeting the uidA gene [23]. The Shiga toxin profiles (stx1 and stx2) of these strains were also found to be perfectly matched with those previously determined by conventional PCR and uidA-based real-time PCR methods. No cross-reaction was observed from the E. coli O157:H7 specific probe Z3276 on all the non-O157 STEC strains, Salmonella strains, Shigella strains, and other pathogenic strains; while the stx probes positively identified the non-O157 STEC strains with presence of either stx1 or stx2, or both (Table 1).
Detection of E. coli O157:H7 from spiked food matrices by the multiplex real-time PCR assay
Beef and spinach samples were initially inoculated with 80 CFU/g E. coli O157:H7 cells. At 0 h, none of the three detection target genes (Z3276, stx1, and stx2) were detected by multiplex real-time PCR assay, but the IAC was positive. However, after 4-h enrichment, all the three detection target genes (Z3276, stx1, and stx2) from both food matrices were amplified in the multiplex real-time PCR assay (Table 4).
Table 4.
Detection results of the multiplex real-time PCR on the spiked food samples that inoculated with different concentations of E. coli O157:H7 and enriched with different incubation time
| Target gene | Food matrice | Incubation time (h) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CFU/gram | 0 | 4 | 8 | 12 | 24 | |||||
| Beef | CT a | ±SD | CT | ±SD | CT | ±SD | CT | ±SD | ||
| Z3276 | 80 | UDb | 34.50 | 0.29 | 28.43 | 0.07 | 27.98 | 0.10 | 27.98 | 0.10 |
| 800 | UD | 30.51 | 0.38 | 24.54 | 0.10 | 24.00 | 0.04 | 24.00 | 0.04 | |
| stx1 | 80 | UD | 27.54 | 0.19 | 21.73 | 0.22 | 20.84 | 0.25 | 19.06 | 0.36 |
| 800 | UD | 24.45 | 0.22 | 18.51 | 0.14 | 17.46 | 0.03 | 18.48 | 0.02 | |
| stx2 | 80 | UD | 31.34 | 0.10 | 25.47 | 0.02 | 25.03 | 0.04 | 23.63 | 0.02 |
| 800 | UD | 27.93 | 0.34 | 21.68 | 0.03 | 21.33 | 0.06 | 22.52 | 0.05 | |
| IAC | 200 copiesc | 28.88 | 27.72 | 21.96 | 21.09 | 19.59 | ||||
| Spinach | CT | ±SD | CT | ±SD | CT | ±SD | CT | ±SD | ||
| Z3276 | 80 | UD | 33.92 | 0.04 | 24.32 | 0.26 | 22.86 | 0.15 | 24.26 | 0.09 |
| 800 | UD | 30.91 | 0.05 | 23.04 | 0.11 | 23.08 | 0.08 | 23.12 | 0.07 | |
| stx1 | 80 | UD | 27.63 | 0.16 | 17.32 | 0.15 | 15.74 | 0.13 | 16.87 | 0.11 |
| 800 | UD | 25.04 | 0.06 | 16.57 | 0.12 | 16.25 | 0.15 | 16.37 | 0.10 | |
| stx2 | 80 | UD | 30.88 | 0.06 | 21.21 | 0.07 | 20.10 | 0.06 | 21.64 | 0.07 |
| 800 | UD | 28.19 | 0.14 | 20.05 | 0.15 | 20.58 | 0.05 | 20.74 | 0.04 | |
| IAC | 200 copies | 24.94 | 23.82 | 24.77 | 23.83 | 23.69 | ||||
aData were shown as average of two independent experiment
bUD refers to "Underdetermined", a negative detection result
cAbout 200 copies of pUC19 plasmid DNA was added as template for IAC to each multiplex real-time PCR reaction
Discussion
PCR technology is widely used for pathogen detection from clinical, food, and environment samples. Real-time PCR methods are used for their enhanced sensitivity and specificity. Several PCR-based methods are available for the detection of E. coli O157:H7 and non-O157 STEC (4, 7, 9, 10) by amplifying various target genes [23]. Target genes such as stx [9, 12–20], eae [31, 32], fimA [33], rfbE [34] have been used in various assays for detection of for E. coli O157:H7, however, most of those genes are not unique genetic markers for this pathogen [23]. This inadequate discriminatory power of those target genes calls for selection of more genetic markers for E. coli O157:H7. Consequently, we identified Z3276 as a unique genetic marker for detection of E. coli O157:H7 [23, 36], and confirmed by other scientific groups [37, 46].
Selection of Z3276 as a unique genetic marker for detection of E. coli O157:H7 was the basis for the development of a multiplex PCR assay. Simultaneous detection of multiple genes in a single reaction may increase specificity and reliability for the detection of E. coli O157:H7, since the amplification of different target genes can corroborate the final conclusion. More importantly, the inclusion of the Shiga toxin genes enables the assay to detect not only E. coli O157:H7, but also screen for non-O157 STEC strains, the latter often underestimated [47–53].
Multiplex real-time PCR can provide better detection efficiency. However, interference among probes and competition among primers for supplies during amplification may compromise the sensitivity and increase the background. Therefore, it is necessary to fine tune the parameters of the multiplex reaction to achieve the optimal conditions for each target gene. In this study, by optimizing the concentration of each probe in the assay (Z3276, stx1, and stx2), we were able to achieve robust sensitivity in the multiplex assay, and positively identified all the E. coli O157:H7 strains (n = 135), demonstrating the multiplex assay is compatible to the simplex assays.
Nowadays, WGS has been explored for a more efficient and more comprehensive approach for STEC detection. Although WGS potential with STEC characterization and surveillance is apparent, STEC detection will likely continue to rely on a combination of culture and non-culture methods, the latter including real-time PCR [49]. The multiplex real-time PCR developed in this study not only can detect E. coli O157:H7 and its profile of the Shiga toxin genes, but also detect non-O157 STEC strains. The capability for simultaneous detection of the Shiga toxin genes and the differentiation of E. coli O157:H7 from non-O157 STEC strains offers several advantages: i) determination of the presence or absence of Shiga toxin genes can be used to verify the detection results of E. coli O157:H7, because almost all E. coli O157:H7 strains possess stx1 and/or stx2 gene(s); ii) profile of the Shiga toxin genes of E. coli O157:H7 provides genetic markers for differentiating isolates from outbreaks; iii) differentiation of stx1 and stx2 harboring E. coli O157:H7 strains may help health care providers manage HUS patients caused by E. coli O157:H7 [49]; and iv) identification of stx gene harboring isolates can serve as a useful clue for detection of STEC, and then more comprehensive and sophistical analytical analyses, such as cultural biological tests, toxin detection, serotyping, genotyping, and WGS, can be performed to confirm the final detection result.
Multiplex real-time PCR targeting uidA, stx1, and stx2 genes for detection of E. coli O157:H7 and non-O157 STECs has become a routine test for preliminary screening in clinical laboratories as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommended [54]. Although WGS is not yet a routine testing, future prediction would include this technology as a means to track the mobility of pathogenic microbes as the food market has become global. The multiplex real-time PCR developed in this study has been demonstrated to be a reliable, efficient, and sensitive assay, and may serve as a useful method for the detection of E. coli O157:H7 and non-O157 STEC in epidemiological surveillance programs as well as in food analytical laboratories. The multiplex real-time PCR assay was successfully tested in this study for the detection of E. coli O157:H7 from spiked food matrices, i.e., beef and spinach, and more than likely applicable to other food matrices.
It is worth noting that on the one hand, in the development of the multiplex real-time PCR assay, great efforts were made toward getting high sensitivity and specificity by optimizing the amplification conditions and by minimizing the interferences among probes, primers, and target genes to reduce the false negative rate in detection; on the other hand, in the use of the assay, precaution is needed in interpretation of the positive results from certain strains that free phages might harbor stx gene [55–57] or even some Shigella strains acquired stx genes [58–61].
Conclusions
A multiplex real-time PCR assay that can rapidly and simultaneously detect E. coli O157:H7 and screen for non-O157 STEC strains has been developed and assessed for efficacy. The inclusivity and exclusivity tests demonstrated high sensitivity and specificity of the multiplex real-time PCR assay. In addition, this multiplex assay was shown to be effective for the detection of E. coli O157:H7 from two common food matrices, beef and spinach, and may be applied for detection of E. coli O157:H7 and screening for non-O157 STEC strains from other food matrices as well.
Acknowledgments
WW was supported by a fellowship appointment administered by Oak Ridge Institute for Science and Education.
Funding
This research project including the design of the study, collection, analysis, and interpretation of data, and writing the manuscript was all funded by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- HUS
hemolytic-uremic syndrome
- IAC
internal amplification control
- ORF
open reading frame
- STEC
Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli
Authors’ contributions
BL conceived the project. BL and HL designed the study. BL, HL, and WW performed the experiments and analyzed the results. BL and HL wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent for participation
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Contributor Information
Baoguang Li, Phone: (240) 402-3620, Email: baoguang.li@fda.hhs.gov.
Huanli Liu, Email: Huanli.Liu@fda.hhs.gov.
Weimin Wang, Email: Weimin.wang@fda.hhs.gov.
References
- 1.Parsons BD, Zelyas N, Berenger BM, Chui L. Detection, Characterization, and Typing of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli. Frontiers in Microbiology. 2016;7(478) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 2.Scallan E, Griffin PM, Angulo FJ, Tauxe RV, Hoekstra RM. Foodborne illness acquired in the United States--unspecified agents. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011;17(1):16–22. doi: 10.3201/eid1701.P21101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Schimmer B, Nygard K, Eriksen HM, Lassen J, Lindstedt BA, Brandal LT, Kapperud G, Aavitsland P. Outbreak of haemolytic uraemic syndrome in Norway caused by stx2-positive Escherichia coli O103:H25 traced to cured mutton sausages. BMC Infect Dis. 2008;8:41. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-8-41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lee JE, Reed J, Shields MS, Spiegel KM, Farrell LD, Sheridan PP. Phylogenetic analysis of Shiga toxin 1 and Shiga toxin 2 genes associated with disease outbreaks. BMC Microbiol. 2007;7:109. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-7-109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Paton JC, Paton AW. Pathogenesis and diagnosis of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli infections. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1998;11(3):450–479. doi: 10.1128/cmr.11.3.450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Riley LW, Remis RS, Helgerson SD, McGee HB, Wells JG, Davis BR, Hebert RJ, Olcott ES, Johnson LM, Hargrett NT, et al. Hemorrhagic colitis associated with a rare Escherichia coli serotype. N Engl J Med. 1983;308(12):681–685. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303243081203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Mead PS, Slutsker L, Dietz V, McCaig LF, Bresee JS, Shapiro C, Griffin PM, Tauxe RV. Food-related illness and death in the United States. Emerg Infect Dis. 1999;5(5):607–625. doi: 10.3201/eid0505.990502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Heiman KE, Mody RK, Johnson SD, Griffin PM, Gould LH. Escherichia coli O157 Outbreaks in the United States, 2003-2012. Emerg Infect Dis. 2015;21(8):1293–1301. doi: 10.3201/eid2108.141364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Deisingh AK, Thompson M. Strategies for the detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in foods. J Appl Microbiol. 2004;96(3):419–429. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2003.02170.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.DeGrandis S, Law H, Brunton J, Gyles C, Lingwood CA. Globotetraosylceramide is recognized by the pig edema disease toxin. J Biol Chem. 1989;264(21):12520–12525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Jinneman KC, Yoshitomi KJ, Weagant SD. Multiplex real-time PCR method to identify Shiga toxin genes stx1 and stx2 and Escherichia coli O157:H7/H- serotype. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003;69(10):6327–6333. doi: 10.1128/AEM.69.10.6327-6333.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Gannon VP, King RK, Kim JY, Thomas EJ. Rapid and sensitive method for detection of Shiga-like toxin-producing Escherichia coli in ground beef using the polymerase chain reaction. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992;58(12):3809–3815. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.12.3809-3815.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lefterova MI, Slater KA, Budvytiene I, Dadone PA, Banaei N. A sensitive multiplex, real-time PCR assay for prospective detection of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli from stool samples reveals similar incidences but variable severities of non-O157 and O157 infections in northern California. J Clin Microbiol. 2013;51(9):3000–3005. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00991-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hara-Kudo Y, Konishi N, Ohtsuka K, Iwabuchi K, Kikuchi R, Isobe J, Yamazaki T, Suzuki F, Nagai Y, Yamada H, et al. An interlaboratory study on efficient detection of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O26, O103, O111, O121, O145, and O157 in food using real-time PCR assay and chromogenic agar. International Journal of Food Microbiology. 2016;230:81–88. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2016.03.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Verhaegen B, Van Damme I, Heyndrickx M, Botteldoorn N, Elhadidy M, Verstraete K, Dierick K, Denayer S, De Zutter L, De Reu K. Evaluation of detection methods for non-O157 Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli from food. International Journal of Food Microbiology. 2016;219:64–70. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2015.12.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Brusa V, Galli L, Linares LH, Ortega EE, Lirón JP, Leotta GA. Development and validation of two SYBR green PCR assays and a multiplex real-time PCR for the detection of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in meat. Journal of Microbiological Methods. 2015;119:10–17. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2015.09.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Harada T, Iguchi A, Iyoda S, Seto K, Taguchi M, Kumeda Y. Multiplex Real-Time PCR Assays for Screening of Shiga Toxin 1 and 2 Genes, Including All Known Subtypes, and Escherichia coli O26-, O111-, and O157-Specific Genes in Beef and Sprout Enrichment Cultures. J Food Prot. 2015;78(10):1800–1811. doi: 10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-15-050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Tunsjø HS, Kvissel AK, Follin-Arbelet B, Brotnov BM, Ranheim TE, Leegaard TM. Suitability of stx-PCR directly from fecal samples in clinical diagnostics of STEC. APMIS. 2015;123(10):872–878. doi: 10.1111/apm.12428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.de Boer RF, Ferdous M, Ott A, Scheper HR, Wisselink GJ, Heck ME, Rossen JW, Kooistra-Smid AM. Assessing the public health risk of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli by use of a rapid diagnostic screening algorithm. J Clin Microbiol. 2015;53(5):1588–1598. doi: 10.1128/JCM.03590-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Baliere C, Rince A, Thevenot D, Gourmelon M. Successful detection of pathogenic Shiga-toxin-producing Escherichia coli in shellfish, environmental waters and sediment using the ISO/TS-13136 method. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2015;60(4):315–320. doi: 10.1111/lam.12386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Frank C, Werber D, Cramer JP, Askar M, Faber M, an der Heiden M, Bernard H, Fruth A, Prager R, Spode A et al: Epidemic Profile of Shiga-Toxin–Producing Escherichia coli O104:H4 Outbreak in Germany. New England Journal of Medicine 2011, 365(19):1771-1780. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 22.March SB, Ratnam S. Sorbitol-MacConkey medium for detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 associated with hemorrhagic colitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1986;23(5):869–872. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.5.869-872.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Li B, Chen JQ. Real-time PCR methodology for selective detection of viable Escherichia coli O157:H7 cells by targeting Z3276 as a genetic marker. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012;78(15):5297–5304. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00794-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Cebula TA, Payne WL, Feng P. Simultaneous identification of strains of Escherichia coli serotype O157:H7 and their Shiga-like toxin type by mismatch amplification mutation assay-multiplex PCR. J Clin Microbiol. 1995;33(1):248–250. doi: 10.1128/jcm.33.1.248-250.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Fratamico PM, DebRoy C, Liu Y, Needleman DS, Baranzoni GM, Feng P. Advances in Molecular Serotyping and Subtyping of Escherichia coli†. Frontiers in Microbiology. 2016;7(644) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 26.Jackson SA, Kotewicz ML, Patel IR, Lacher DW, Gangiredla J, Elkins CA. Rapid genomic-scale analysis of Escherichia coli O104:H4 by using high-resolution alternative methods to next-generation sequencing. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012;78(5):1601–1605. doi: 10.1128/AEM.07464-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Patel IR, Gangiredla J, Lacher DW, Mammel MK, Jackson SA, Lampel KA, Elkins CA. FDA Escherichia coli Identification (FDA-ECID) Microarray: a Pangenome Molecular Toolbox for Serotyping, Virulence Profiling, Molecular Epidemiology, and Phylogeny. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2016;82(11):3384–3394. doi: 10.1128/AEM.04077-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lindsey RL, Pouseele H, Chen JC, Strockbine NA, Carleton HA. Implementation of Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS) for Identification and Characterization of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli (STEC) in the United States. Frontiers in Microbiology. 2016;7(766) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 29.Leonard SR, Mammel MK, Lacher DW, Elkins CA. Strain-Level Discrimination of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli in Spinach Using Metagenomic Sequencing. PLoS One. 2016;11(12):e0167870. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Elizaquivel P, Aznar R. A multiplex RTi-PCR reaction for simultaneous detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella spp. and Staphylococcus aureus on fresh, minimally processed vegetables. Food Microbiol. 2008;25(5):705–713. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2008.03.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Barletta F, Ochoa TJ, Ecker L, Gil AI, Lanata CF, Cleary TG. Validation of five-colony pool analysis using multiplex real-time PCR for detection of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 2009;47(6):1915–1917. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00608-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Schmidt H, Plaschke B, Franke S, Russmann H, Schwarzkopf A, Heesemann J, Karch H. Differentiation in virulence patterns of Escherichia coli possessing eae genes. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1994;183(1):23–31. doi: 10.1007/BF00193628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Li B, Koch WH, Cebula TA. Detection and characterization of the fimA gene of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Mol Cell Probes. 1997;11(6):397–406. doi: 10.1006/mcpr.1997.0132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Desmarchelier PM, Bilge SS, Fegan N, Mills L, Vary JC, Jr., Tarr PI: A PCR specific for Escherichia coli O157 based on the rfb locus encoding O157 lipopolysaccharide. J Clin Microbiol 1998, 36(6):1801-1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 35.Fields PI, Blom K, Hughes HJ, Helsel LO, Feng P, Swaminathan B. Molecular characterization of the gene encoding H antigen in Escherichia coli and development of a PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism test for identification of E. coli O157:H7 and O157:NM. J Clin Microbiol. 1997;35(5):1066–1070. doi: 10.1128/jcm.35.5.1066-1070.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Li B, Hu Z, Elkins CA. Detection of live Escherichia coli O157:H7 cells by PMA-qPCR. J Vis Exp. 2014;84:e50967. doi: 10.3791/50967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ravan H, Amandadi M, Sanadgol N. A highly specific and sensitive loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for the detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Microb Pathog. 2016;91:161–165. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2015.12.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Feng P, Lampel KA. Genetic analysis of uidA expression in enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli serotype O157:H7. Microbiology. 1994;140(Pt 8):2101–2107. doi: 10.1099/13500872-140-8-2101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Monday SR, Whittam TS, Feng PC. Genetic and evolutionary analysis of mutations in the gusA gene that cause the absence of beta-glucuronidase activity in Escherichia coli O157:H7. J Infect Dis. 2001;184(7):918–921. doi: 10.1086/323154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Perna NT, Plunkett G, 3rd, Burland V, Mau B, Glasner JD, Rose DJ, Mayhew GF, Evans PS, Gregor J, Kirkpatrick HA et al: Genome sequence of enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7. Nature 2001, 409(6819):529-533. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 41.Fratamico PM, Wasilenko JL, Garman B, Demarco DR, Varkey S, Jensen M, Rhoden K, Tice G. Evaluation of a multiplex real-time PCR method for detecting shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in beef and comparison to the U.S. Department of Agriculture Food Safety and Inspection Service Microbiology laboratory guidebook method. J Food Prot. 2014;77(2):180–188. doi: 10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-13-248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Fricker M, Messelhausser U, Busch U, Scherer S, Ehling-Schulz M. Diagnostic real-time PCR assays for the detection of emetic Bacillus cereus strains in foods and recent food-borne outbreaks. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007;73(6):1892–1898. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02219-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Pfaffl MW. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001;29(9):e45. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.9.e45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Pfaffl MW, Horgan GW, Dempfle L. Relative expression software tool (REST) for group-wise comparison and statistical analysis of relative expression results in real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002;30(9):e36. doi: 10.1093/nar/30.9.e36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Administration FD. Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli. Bacteriological Analytical Manual. Gaithersburg, MD USA; 2011.
- 46.Ravan H, Amandadi M. Analysis of yeh Fimbrial Gene Cluster in Escherichia coli O157:H7 in Order to Find a Genetic Marker for this Serotype. Curr Microbiol. 2015;71(2):274–282. doi: 10.1007/s00284-015-0842-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Chui L, Lee M-C, Allen R, Bryks A, Haines L, Boras V. Comparison between ImmunoCard STAT!® and real-time PCR as screening tools for both O157:H7 and non-O157 Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in Southern Alberta, Canada. Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Disease. 2013;77(1):8–13. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2013.05.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Gould LH, Walsh KA, Vieira AR, Herman K, Williams IT, Hall AJ, Cole D, Centers for Disease C, Prevention: Surveillance for foodborne disease outbreaks - United States, 1998-2008. MMWR Surveill Summ 2013, 62(2):1-34. [PubMed]
- 49.Parsons BD, Zelyas N, Berenger BM, Chui L. Detection, Characterization, and Typing of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli. Front Microbiol. 2016;7:478. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Fratamico PM, Briggs CE, Needle D, Chen CY, DebRoy C. Sequence of the Escherichia coli O121 O-antigen gene cluster and detection of enterohemorrhagic E. coli O121 by PCR amplification of the wzx and wzy genes. J Clin Microbiol. 2003;41(7):3379–3383. doi: 10.1128/JCM.41.7.3379-3383.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Wickham ME, Lupp C, Mascarenhas M, Vazquez A, Coombes BK, Brown NF, Coburn BA, Deng W, Puente JL, Karmali MA, et al. Bacterial genetic determinants of non-O157 STEC outbreaks and hemolytic-uremic syndrome after infection. J Infect Dis. 2006;194(6):819–827. doi: 10.1086/506620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Kuehne A, Bouwknegt M, Havelaar A, Gilsdorf A, Hoyer P, Stark K, Werber D, and the HUSasnG: Estimating true incidence of O157 and non-O157 Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli illness in Germany based on notification data of haemolytic uraemic syndrome. Epidemiol Infect 2016, 144(15):3305-3315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 53.Mora A, Blanco M, Blanco JE, Dahbi G, Lopez C, Justel P, Alonso MP, Echeita A, Bernardez MI, Gonzalez EA, et al. Serotypes, virulence genes and intimin types of Shiga toxin (verocytotoxin)-producing Escherichia coli isolates from minced beef in Lugo (Spain) from 1995 through 2003. BMC Microbiol. 2007;7:13. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-7-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Gould MS, Marrocco FA, Hoagwood K, Kleinman M, Amakawa L, Altschuler E. Service use by at-risk youths after school-based suicide screening. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2009;48(12):1193–1201. doi: 10.1097/CHI.0b013e3181bef6d5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Monday SR, Beisaw A, Feng PC. Identification of Shiga toxigenic Escherichia coli seropathotypes A and B by multiplex PCR. Mol Cell Probes. 2007;21(4):308–311. doi: 10.1016/j.mcp.2007.02.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Martinez-Castillo A, Muniesa M. Implications of free Shiga toxin-converting bacteriophages occurring outside bacteria for the evolution and the detection of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014;4:46. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Grys TE, Sloan LM, Rosenblatt JE, Patel R. Rapid and sensitive detection of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli from nonenriched stool specimens by real-time PCR in comparison to enzyme immunoassay and culture. J Clin Microbiol. 2009;47(7):2008–2012. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02013-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Strauch E, Lurz R, Beutin L. Characterization of a Shiga toxin-encoding temperate bacteriophage of Shigella sonnei. Infect Immun. 2001;69(12):7588–7595. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.12.7588-7595.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Gray MD, Lampel KA, Strockbine NA, Fernandez RE, Melton-Celsa AR, Maurelli AT. Clinical isolates of Shiga toxin 1a-producing Shigella flexneri with an epidemiological link to recent travel to Hispaniola. Emerg Infect Dis. 2014;20(10):1669–1677. doi: 10.3201/eid2010.140292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Carter CC, Fierer J, Chiu WW, Looney DJ, Strain M, Mehta SR: A Novel Shiga Toxin 1a-Converting Bacteriophage of Shigella sonnei With Close Relationship to Shiga Toxin 2-Converting Pages of Escherichia coli. Open Forum Infect Dis 2016, 3(2):ofw079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 61.Kozyreva VK, Jospin G, Greninger AL, Watt JP, Eisen JA, Chaturvedi V. Recent Outbreaks of Shigellosis in California Caused by Two Distinct Populations of Shigella sonnei with either Increased Virulence or Fluoroquinolone Resistance. mSphere. 2016;1(6) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.


