Abstract
Lead (Pb) is a known nephrotoxic element. Recently we have proved that subcellular Ca2+ redistribution is involved in Pb-induced apoptosis in primary cultures of rat proximal tubular (rPT) cells, but the underlying mechanism remains to be elucidated. Firstly, data showed that Pb triggers endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress response in rPT cells, as evidenced by the elevations of ER stress markers. Moreover, pharmacological modulation of Ca2+ mobilization in ER and cytoplasm with three chemicals (2-APB or TG or BAPTA-AM) can effectively increase or decrease the protein expression of ER stress markers in Pb-exposed rPT cells, demonstrating that Pb-induced ER stress is Ca2+-dependent. We found that Pb stimulates phosphorylation of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) to activate its activity. Meanwhile, inhibition of CaMKII with KN93 or KN62 attenuated Pb-activated caspase-12 and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein homologous protein (CHOP) in rPT cells, demonstrating that CaMKII activation promoted ER stress in rPT cells. Likewise, Pb-induced apoptosis can be effectively inhibited by CaMKII inhibitor KN93 or KN62. Furthermore, co-treatment with KN93 or KN62 significantly reversed Pb-induced ER Ca2+ release and concomitant intracellular Ca2+ overload in rPT cells. In summary, these results expound the mechanisms involving in ER stress, Ca2+ dyshomeostasis and activated CaMKII, which all contribute to Pb-induced apoptosis. CaMKII acts as a critical mediator of ER stress and associated apoptosis via regulating intracellular Ca2+ mobilization from ER to cytoplasm.
Keywords: lead, calcium, proximal tubular cells, CaMKII, endoplasmic reticulum stress
INTRODUCTION
Lead (Pb) is a nonessential toxic heavy metal and one of the most widely used metals in industries. Globally, Pb exposure is ubiquitous and routes of its exposure to animals and human beings include inhalation of Pb-contaminated dust particles or aerosols, and ingestion of Pb-contaminated food or water [1]. The persistence of Pb in humans and its associated health risks are a matter of serious concern and a global issue. As a multi-organ toxicant, Pb exerts potent toxic effects on different tissues [2–7]. Kidney is one of the most sensitive targets organs for Pb toxicity, and the proximal tubule is the major site of Pb-induced renal injury [2, 4, 7]. Primary cultures possess more advantages compared to permanent cell lines in the toxicological research [8], thus primary rat proximal tubular (rPT) cells were established to elucidate low-level Pb-induced nephrotoxicity in this study.
Our research group have recently found that the apoptotic death triggered by subcellular Ca2+ redistribution played a chief role in low-dose (0–1.0 µM) Pb-induced nephrotoxicity in rPT cells [9]. Ca2+ ion is the most commonly employed signal transduction element in the process of apoptosis. Ca2+ is neither synthesized nor metabolized as other intracellular messengers, and its storage and mobilization is controlled by calcium channels, pumps and exchangers [10]. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is an essential intracellular organelle, responsible for intracellular Ca2+ homeostasis and protein folding and processing [11]. Dysfunction of Ca2+ homeostasis in the ER leads to the accumulation of unfolded proteins and activates the ER stress-induced apoptosis pathway [12]. Based on our previous results [9], we intend to investigate the correlation between Ca2+ dyshomeostasis and ER stress-mediated apoptosis in Pb-exposed rPT cells.
Moreover, Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII), a Ca2+-dependent protein kinase, is a key modulator of Ca2+ homeostasis [13]. CaMKII is characterized by its unique ability to decode and integrate oscillatory Ca2+ signals into specific outcomes through regulation of intracellular Ca2+ stores [14]. Sustained, excessive CaMKII activation is an upstream signaling event for promoting ER-Ca2+ release, while CaMKII inhibition markedly accelerates and amplifies ER Ca2+ stores [14]. Also, CaMKII is emerging as a critical mediator of ER stress and oxidative damage, while both pharmacological inhibition and genetic deletion of CaMKII have been shown to be protective against ER stress-induced apoptosis [15]. Our previous study has demonstrated that Pb disrupted the intracellular Ca2+ homeostasis in rPT cells [9], but the role of ER stress and CaMKII modulation in this process were not defined. This study will offer further evidences to clarify this question and investigate the role of CaMKII in Ca2+ mobilization, ER stress and apoptosis in Pb-exposed rPT cells.
RESULTS
Pb triggers ER stress response in rPT cells
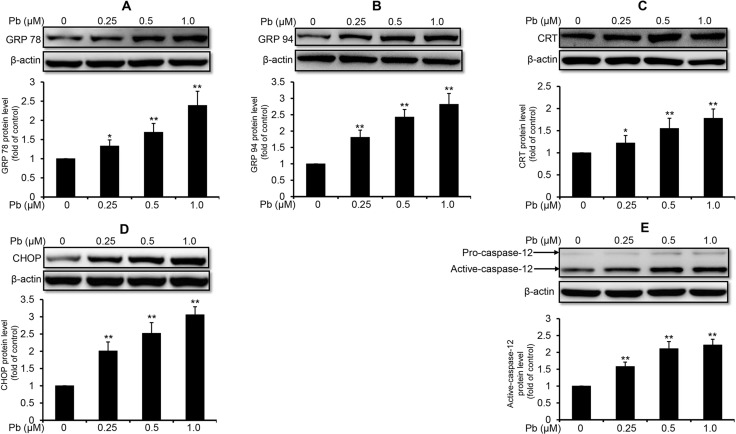
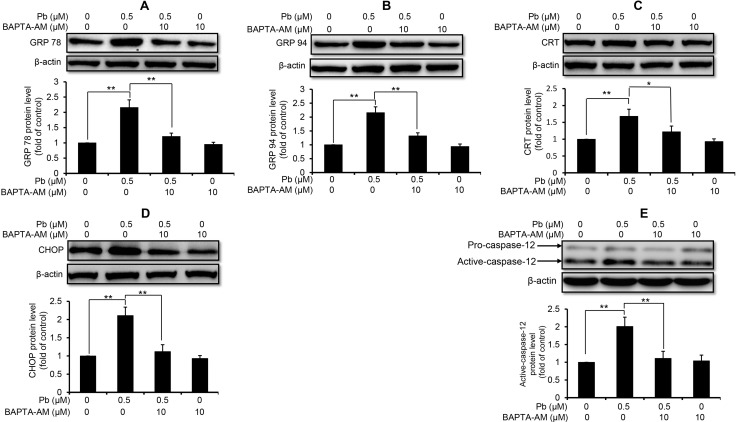
To investigate whether Pb induced ER stress in rPT cells, protein levels of several markers relevant to ER stress response were determined in this study. As shown in Figure 1, 12 h-Pb treatment caused a significant increase in the protein levels of glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78) (A), glucose-regulated protein 94 (GRP94) (B), calreticulin (CRT) (C), CHOP (D) and active caspase-12 (E) in rPT cells (P < 0.05), following by a dose-dependent manner, suggesting that Pb exposure induced the ER stress in rPT cells.
Figure 1. Pb elevated the protein levels of ER stress markers in rPT cells.
Cells were treated with Pb(NO3)2 (0.25, 0.5 and 1 µM) for 12 h, then collected to assess the protein levels of GRP78 (A), GRP94 (B), CRT (C), CHOP (D) and caspase-12 (E) using western-blot analysis. Upper panel representative western blot image; lower panel quantitative analysis (mean ± SEM, n = 4). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.
Effects of 2-APB, TG and BAPTA-AM on the modulation of [Ca2+]c and [Ca2+]ER
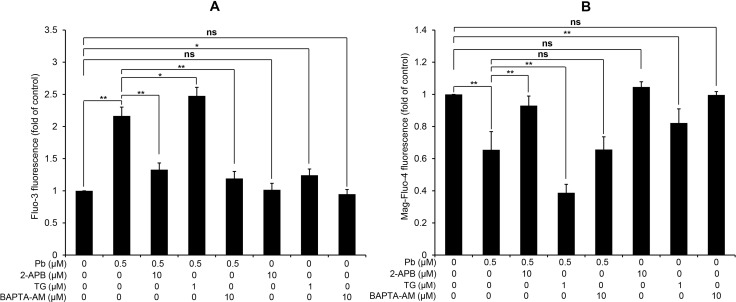
Next, we aim to confirm the effects of three Ca2+ modulators (2-APB, TG and BAPTA-AM) on the [Ca2+]c and [Ca2+]ER in Pb-exposed rPT cells. 2-APB is a specific inhibitor of inositol 1, 4, 5-trisphosphate receptor (IP3R) that functions to release Ca2+ from ER stores [16]. TG raises cytosolic calcium concentration by inhibiting the ER-Ca2+-ATPase [17], while BAPTA-AM is an intracellular Ca2+ chelator to attenuate the elevation of [Ca2+]c [18]. Data in Figure 2A showed that treatment with 2-APB or BAPTA-AM significantly suppressed Pb-induced [Ca2+]c elevation, respectively; 2-APB or BAPTA-AM treatment alone has no obvious effect on [Ca2+]c in rPT cells. However, treatment with TG further aggravated Pb-mediated cytosolic Ca2+ overload and TG treatment only caused significant cytosolic Ca2+ elevation in rPT cells. As shown in Figure 2B, treatment with 2-APB significantly inhibited Pb-induced [Ca2+]ER depletion while TG treatment further aggravated Pb-mediated ER Ca2+ release. Treatment with BAPTA-AM has no effect on Pb-induced [Ca2+]ER. Neither 2-APB nor BAPTA-AM treatment only has no obvious effect on [Ca2+]ER in rPT cells, and TG treatment alone caused significant ER Ca2+ release in rPT cells. Data in Figure 2 give us a solid evidence that these three chemicals can efficiently regulate Pb-induced [Ca2+]c elevation and [Ca2+]ER depletion.
Figure 2. Modulation of [Ca2+]c and [Ca2+]ER by three regulators of Ca2+ signaling in rPT cells.
Cells were treated with 0.5 µM Pb for 12 h in the presence or absence of 10 µM 2-APB (co-incubation for the entire course), 1 µM TG (co-incubation for the entire course) and 10 µM BAPTA-AM (30 min pre-incubation before Pb treatment) to assess the changes of [Ca2+]c and [Ca2+]ER, assessed by flow cytometry. Values of fluorescence intensity of Fluo-3 (A) and Mag-Fluo-4 (B) are quantified in a relative way to its respective control, whose value is set at one. Data represent mean ± SEM (n = 6). ns not significant, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.
Pb-mediated ER stress is Ca2+-dependent
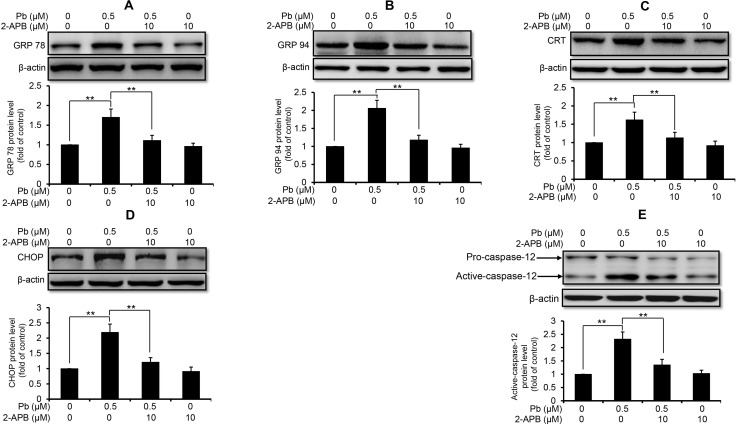
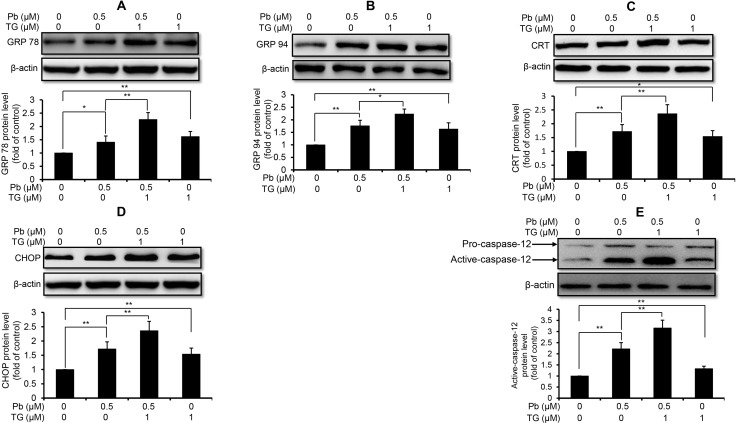
Next, we used these three intracellular Ca2+ modulators to explore the role of Ca2+ signaling in Pb-induced ER stress in rPT cells. As shown in Figure 3, inhibition of ER Ca2+ release with 2-APB markedly diminished the protein levels of GRP78 (A), GRP94 (B), CRT (C), CHOP (D) and active caspaes-12 (E) in Pb-exposed rPT cells. In contrast, induction of ER Ca2+ release with TG significantly aggravated the protein levels of GRP78 (A), GRP94 (B), CRT (C), CHOP (D) and active caspaes-12 (E) in Pb-exposed rPT cells (Figure 4). Data in Figure 3 and Figure 4 clearly indicated that the ER Ca2+ release plays a crucial role in Pb-mediated ER stress in rPT cells. Additionally, data in Figure 5 showed that chelation of cytosolic Ca2+ with BAPTA-AM significantly suppressed the elevation of these five ER stress marker protein levels in Pb-exposed rPT cells. Based on the changes of [Ca2+]c regulated by three Ca2+ modulators, these data sufficiently demonstrated the regulatory effect of elevated cytosolic Ca2+ on Pb-induced ER stress in rPT cells. Collectively, Pb-induced ER stress in rPT cells is Ca2+ dependent.
Figure 3. 2-APB inhibited the protein expression of ER stress markers in Pb-exposed cells.
Cells were co-treated with 10 µM 2-APB and/or 0.5 µM Pb for 12 h, then harvested to measure the protein levels of GRP78 (A), GRP94 (B), CRT (C), CHOP (D) and caspase-12 (E). Upper panel representative western blot image; lower panel quantitative analysis (mean ± SEM, n = 4). **P < 0.01.
Figure 4. TG aggravated Pb-elevated protein levels of ER stress markers in rPT cells.
Cells were co-incubated with 1 µM TG and/or 0.5 µM Pb for 12 h to detect the protein levels of GRP78 (A), GRP94 (B), CRT (C), CHOP (D) and caspase-12 (E). Upper panel representative western blot image; lower panel quantitative analysis (mean ± SEM, n = 4). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.
Figure 5. Effect of BAPTA-AM on Pb-induced protein levels of ER stress markers in rPT cells.
Cells were pretreated with 10 µM BAPTA-AM for 30 min, then exposed to 0.5 µM Pb for another 12 h to measure the protein levels of GRP78 (A), GRP94 (B), CRT (C), CHOP (D) and caspase-12 (E). Upper panel representative western blot image; lower panel quantitative analysis (mean ± SEM, n = 4). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.
CaMKII activation is involved in Pb-exposed rPT cells
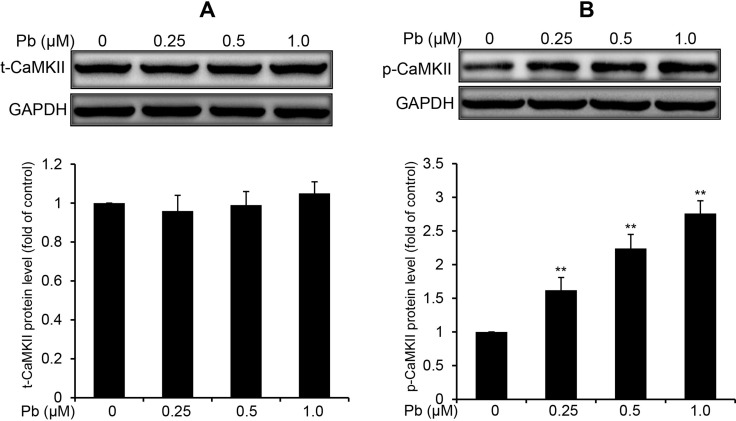
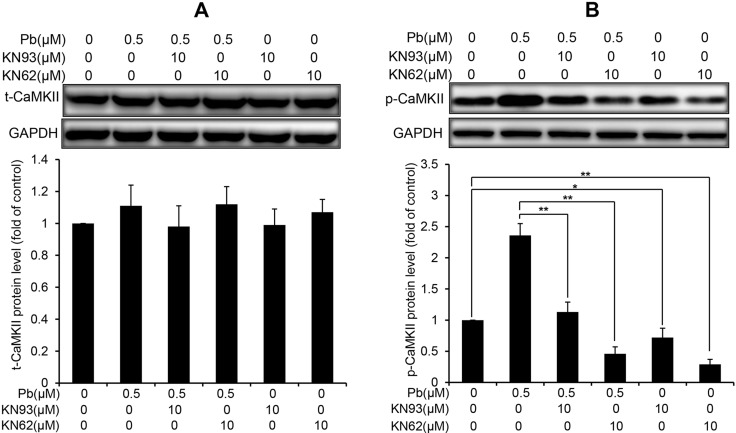
CaMKII is an important mediator of Ca2+ signaling in cells, and canonically activated by the elevation of intracellular Ca2+ [19]. Thus, we examined the CaMKII protein expression and phospho-activation in Pb-treated rPT cells. Western blot analysis showed that the total CaMKII protein levels were not affected by Pb treatment compared to control cells (Figure 6A). In contrast, CaMKII kinase activation, as indicated by CaMKII phosphorylation (p-CaMKII expression), was revealed in Pb-exposed rPT cells (Figure 6B). Simultaneously, two classical CaMKII inhibitors KN62 and KN93 were applied to validate the CaMKII activation in Pb-exposed cells (Figure 7). As expected, pre-treatment with KN62 or KN93 had no effect on total CaMKII expression in Pb-exposed rPT cells. However, Pb-elevated p-CaMKII level was blocked by pre-treatment with KN62 or KN93, respectively. Given these results, CaMKII activation is involved in Pb-exposed rPT cells.
Figure 6. Pb elevated the phosphorylation of CaMKII in rPT cells.
Cells were treated with Pb(NO3)2 (0.25, 0.5 and 1 µM) for 12 h, then collected to analyze the protein levels of t-CaMKII (A) and p-CaMKII (B). Upper panel representative western blot image; lower panel quantitative analysis (mean ± SEM, n = 4). **P < 0.01.
Figure 7. Effects of two CaMKII inhibitors (KN93, KN62) on the protein levels of t-CaMKII and p-CaMKII in Pb-exposed cells.
Cells were pre-incubated with 10 µM KN93 or 10 µM KN62 for 2 h, then exposed to 0.5 µM Pb for another 12 h to measure the protein levels of t-CaMKII (A) and p-CaMKII (B), respectively. Upper panel representative western blot image; lower panel quantitative analysis (mean ± SEM, n = 4). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.
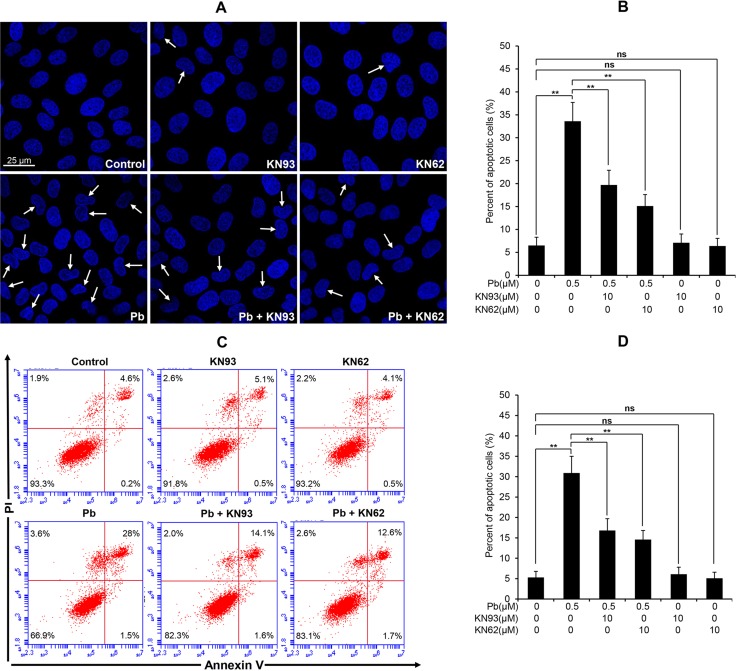
CaMKII inhibition blocks Pb-induced ER stress and apoptosis in rPT cells
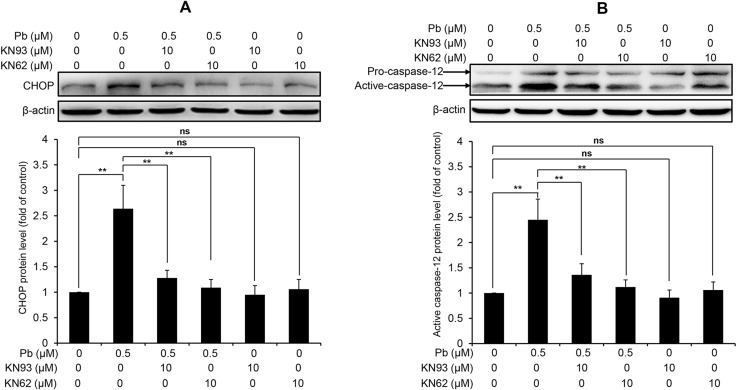
CaMKII is a well-known mediator of apoptosis, while activated CaMKII can result in ER stress-induced apoptosis [15]. CHOP and active caspase-12 are two important mediators in ER stress-induced apoptosis. Firstly, we performed immunoblots to verify the effect of pharmacologic inhibition of CaMKII on the changes of two ER stress markers in Pb-exposed cells. Data in Figure 8 showed that Pb-elevated CHOP and active caspase-12 protein levels were significantly blunted with CaKMII inhibitor KN62 or KN93, respectively. To further assess whether CaMKII activation contributes to Pb-induced apoptosis, two CaMKII inhibitors (KN93 and KN62) were applied to prove this issue. As shown in Figure 9, Pb-induced apoptosis was significantly inhibited by specific CaMKII inhibitor KN93 or KN62, respectively. Neither KN93 nor KN62 treatment alone affected apoptosis in rPT cells. Collectively, it is reasonable to suggest that CaMKII activation promotes ER stress-induced apoptosis in Pb-exposed rPT cells.
Figure 8. CaMKII inhibition blocks the activation of CHOP and caspase-12 in Pb-exposed rPT cells.
Cells were pre-incubated with 10 µM KN93 or 10 µM KN62 for 2 h, then exposed to 0.5 µM Pb for another 12 h to measure the protein levels of CHOP (A) and caspase-12 (B), respectively. Upper panel representative western blot image; lower panel quantitative analysis (mean ± SEM, n = 4). ns not significant; **P < 0.01.
Figure 9. Effects of two CaMKII inhibitors (KN93, KN62) on Pb-induced apoptosis in rPT cells.
(A, B) Cells grown on coverslips were pre-incubated with 10 µM KN93 or 10 µM KN62 for 2 h, then exposed to 0.5 µM Pb for another 12 h to assess the apoptosis using Hoechst 33258 staining. Representative morphological changes of apoptosis are present in (A), and its statistical result of apoptotic rates (B) are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 9). (C, D) Cells were pre-treated with 10 µM KN93 or 10 µM KN62 for 2 h, then exposed to 0.5 µM Pb for 12 h to assess the apoptosis using flow cytometry. Data in (D) are mean ± SEM of three separate experiments, and each one performed in triplicate (n = 9). ns not significant; ** P < 0.01.
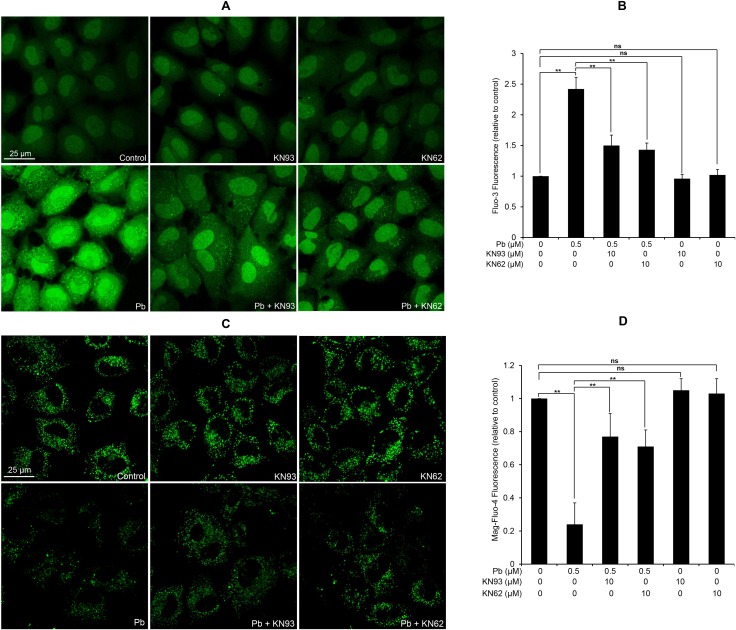
CaMKII controls intracellular Ca2+ level and ER Ca2+ release in Pb-exposed rPT cells
Since activated CaMKII promotes apoptosis partly through regulation of ER Ca2+ uptake and CaMKII inhibition significantly reduced ER Ca2+ levels [20], we next assessed whether there is a link between CaMKII activation and subcellular Ca2+ redistribution in Pb-exposed rPT cells. As shown in Figure 10, 10 µM KN93 or 10 µM KN62 treatment alone has no obvious effect on the changes of [Ca2+]c and [Ca2+]ER in rPT cells, compared with the control group. Pb exposure resulted in a robust increase in [Ca2+]c and decrease in [Ca2+]ER, while co-treatment with KN93 or KN62 significantly reversed the Pb-induced subcellular Ca2+ redistribution. These findings were confirmed in separate experiments by confocal microscopy with the fluorescent dye Fluo-3 and Mag-Fluo-4. Our data demonstrate that CaMKII activation is required for Pb-induced subcellular calcium redistribution (ER Ca2+ release and concomitant intracellular Ca2+ overload) in rPT cells.
Figure 10. Modulation of [Ca2+]c and [Ca2+]ER by two CaMKII inhibitors in Pb-exposed rPT cells.
Cells were pre-treated with 10 µM KN93 or 10 µM KN62 for 2 h, then exposed to 0.5 µM Pb for another 12 h to measure the changes of [Ca2+]c and [Ca2+]ER using confocal microscopy, respectively. (A, C) Representative confocal images. (B, D) Quantification of fluorescence intensity from two Ca2+ indicators. The values of Fluo-3 fluorescence (B) and Mag-Fluo-4 fluorescence (D) are quantified in a relative way to its respective control group, whose value is set at “1”. Data represent mean ± SEM of three separate experiments and each one performed in duplicate (n = 6). ns not significant; ** P < 0.01.
DISCUSSION
Lead is a well-known nephrotoxicant, of which proximal tubular epithelium is the main site of Pb-induced nephrotoxicity [21, 22]. It has been previously revealed that Pb induces apoptosis in rPT cells by triggering ER-Ca2+ release and cytosolic Ca2+ overload [9], but the detailed mechanism underlying Ca2+ dyshomeostasis-associated apoptosis remains to be elucidated. Herein, the present experiments provide evidences to demonstrate the effect of disturbed Ca2+ signaling on ER stress, and address the role of CaMKII in ER stress, subcellular Ca2+ redistribution and apoptosis in Pb-exposed rPT cells.
ER performs crucial cellular functions and acts as the largest dynamic intracellular Ca2+-storage organelle. ER dysfunction can lead to an imbalance between protein-folding capacity and protein-folding load as well as Ca2+ dyshomeostasis, which in turn leads to ER stress [23]. Adaptive ER stress is initially aimed at ensuring cell survival by activating the transcription of ER chaperones, such as GRP78, GRP94 and CRT [23]. If the ER stress is too severe or prolonged to repair, the stressed cell will initiate apoptotic cell death through several signaling cascades, such as caspase-12 and CHOP [24]. Caspase-12, predominantly localized on the cytoplasmic side of the ER, is a regulator specific to ER stress-induced apoptosis [25]. Activation of caspase-12 (active caspase-12) from procaspase-12 is specifically induced by excessive or prolonged ER stress, which initiates the apoptotic death cascades [26]. CHOP is a transcription factor to induce several proapoptotic factors, which has been identified as one of the most important mediators in ER stress-induced apoptosis [27]. Noteworthy, ER stress has been described as a contributing factor to tubular damage in kidney diseases because tubular cells are particularly sensitive to ER stress [28]. However, the role of ER stress in Pb-induced nephrotoxicity has not yet been reported in previous studies. In this study, elevated protein levels of GRP78, GRP94 and CRT as well as activation of CHOP and caspase-12 were revealed in Pb-exposed rPT cells (Figure 1), indicating that ER stress and ER stress-mediated apoptosis are involved in Pb-induced nephrotoxicity.
It is important to note that ER-Ca2+ homeostasis is crucial to ensure the proper protein-folding, while ER Ca2+ imbalance can greatly impact the folding capacity and induce ER stress-mediated apoptosis [29–31]. Our previous studies have demonstrated that Pb causes Ca2+ dysregulation in rPT cells [9], which arises our interest to investigate the correlation between ER stress and Ca2+ dyshomeostasis in Pb-exposed rPT cells. Hereby, 2-APB (the blocker of ER Ca2+ release channel-IP3R), TG (an ER Ca2+ pump inhibitor) and BAPTA-AM (cytosolic Ca2+ chelator) was chosen to modulate the changes of [Ca2+]c and [Ca2+]ER in this study, respectively. As expected, three modulators of Ca2+ signaling can potently regulate the oscillations of [Ca2+]c and [Ca2+]ER in Pb-treated rPT cells (Figure 2). Next, we assessed the effects of three Ca2+ modulators on protein levels of five ER stress markers in Pb-treated rPT cells. Data from this study (Figures 3–5) give us a solid conclusion that subcellular calcium redistribution acts as an important pathological mediator of ER stress in Pb-exposed rPT cells, i.e., Pb-induced ER stress is Ca2+-dependent.
Calcium requires a variety of effectors to sustain signaling events. CaMKII has emerged as a key effector of Ca2+ signaling, which is involved in the regulation of Ca2+ mobilization [32, 33]. CaMKII is a multifunctional serine/threonine protein kinase present in many tissues, which activates several signaling cascades involved in cell survival or cell death [33]. Emerging evidence suggests CaMKII evoked apoptotic cell death, is one of the key underlying mechanisms for the detrimental effect of sustained CaMKII activation [34]. While CaMKII function is well defined in cardiac myocytes and neurons [30], the role of CaMKII in Pb-induced nephrotoxicity has not been reported up to date. Data in Figure 6 verified the activation of CaMKII in Pb-exposed rPT cells, which gave us a hint that activated CaMKII may be related to Pb-induced apoptosis in rPT cells.
Moreover, CaMKII is emerging as a central signaling effector involved in the amplification of oxidative stress initiated by the CHOP-mediated maladaptive ER stress response pathway to promote apoptosis [15]. Also, activated CaMKII can result in ER stress-induced apoptosis through activation of caspase-12 pathway [30]. Next, we used two CaMKII inhibitors, i.e., KN93 and KN62, which can potently block CaMKII activation (Figure 7), to investigate the role of CaMKII activation in Pb-induced ER stress and associated apoptosis in rPT cells. Firstly, western-blot analysis results (Figure 8) showed that Pb-induced activation of CHOP and caspase-12 was effectively blocked by KN93 or KN62, verifying the promoting effect of CaMKII activation in Pb-induced ER stress in rPT cells. Secondly, Pb-induced apoptosis (Figure 9), assessed by two methods, can be significantly inhibited by the co-treatment of KN93 or KN62, demonstrating the regulatory role of CaMKII activation in Pb-induced apoptosis. Collectively, it can be concluded that CaMKII is an important mediator in ER stress and associated apoptosis in Pb-exposed rPT cells.
Additionally, CaMKII activation is an upstream signaling event for promoting ER-Ca2+ release [14]. Given the regulatory role of CaMKII activation in ER stress-induced apoptosis, we hypothesized that there is a certain relationship between CaMKII activation and subcellular calcium redistribution in Pb-exposed rPT cells. As expected, Pb-induced subcellular calcium redistribution, i.e., increase in [Ca2+]c and concomitant decrease in [Ca2+]ER, was effectively blocked by CaMKII antagonist KN93 or KN62 (Figure 10), indicating the controller role of CaMKII in this process. However, the detailed mechanism underlying CaMKII regulates intracellular Ca2+ dynamics in Pb-exposed rPT cells remains to be further clarified.
In summary, Pb induced ER stress in rPT cells, which is dependent on Ca2+ signaling. Our findings demonstrated an essential role of CaMKII in Pb-induced nephrotoxicity. Activated CaMKII acts as an important intermediate in Pb-induced ER stress and associated apoptosis in rPT cells, mainly through promoting subcellular calcium redistribution.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Chemicals and antibodies
All chemicals were of the highest grade purity available. Lead nitrate, collagenase IV, trypsin, Thapsigargin (TG), DMEM-F12 (1:1), Hoechst 33258 solution and all other chemicals were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. A phosphatase inhibitor (04906845001) was obtained from Roche Applied Science. Pluronic F-127 and Fluo-3-AM were obtained from Dojindo Laboratories (Tokyo, Japan). Mag-Fluo-4-AM and N, N, N′, N′-tetrakis-(2-pyridylmethyl) ethylenediamine (TPEN) were purchased from Molecular Probes (Eugene, OR, USA). KN62 and KN93 were purchased from Selleck (Houston, Texas, USA). 2-Aminoethoxydiphenyl borate (2-APB) and 1, 2-Bis (2-aminophenoxy) ethane-N, N, N’, N’-tetraacetic acid acetoxymethyl ester (BAPTA-AM) were from Tocris Bioscience (Bristol, UK). Annexin V-FITC apoptosis detection kit was from Pharmingen (Becton Dickinson Company, USA). BCA protein assay kit and enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) kit were obtained from Thermo Fisher Scientific Pierce. The following primary antibodies were used: GRP78 (cat No. 3183), GRP94 (cat No. 2104), Calreticulin (CRT, cat No. 12238), phospho-CaMKII (p-CaMKII, cat No. 12716), β-actin (cat No. 3700) and GAPDH (cat No. 5174) were purchased from Cell Signaling Technology. CHOP (cat No. ab11419), Caspase-12 (cat No. ab62484) and total-CaMKII (t-CaMKII, cat No. ab52476) were obtained from Abcam. Secondary antibodies were conjugated to horseradish peroxidase (Jackson Immuno Research, cat No. 705-505-303 and cat No. 111-006-062).
Cell culture and treatment
All procedures followed the ethics guidelines and were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Shandong Agricultural University (SDAUA-2017-003). Isolation, identification and culture of Sprague-Dawley rat proximal tubular (rPT) cells were as previously described [35]. BAPTA-AM, TG, 2-APB, KN93 and KN62 were dissolved in DMSO to make the stock solutions, filtered and stored at −20°C, then diluted to work solution prior to use. The final concentration of DMSO was less than 0.1% and 0.1% DMSO has no effect on Ca2+ signaling and cell viability [36]. Meanwhile, 2-APB, BAPTA-AM, KN93 and KN62 have no significant toxic effects on cells, as confirmed in this study (data not shown). Based on the doses of Pb in our previous study [37], cell cultures were incubated in the presence of 0, 0.25, 0.5, and 1 µM Pb. Primarily, events of Pb exposure over a 12-h period were chosen to investigate the Pb-induced cytotoxicity.
Flow cytometric measurement of cytosolic Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]c)
Three chemicals, i.e., BAPTA-AM (cytosolic Ca2+ chelator), 2-APB {an inhibitor of inositol 1, 4, 5-trisphosphate receptor (IP3R)} and TG (a potent ER Ca2+ pump inhibitor) were chosen to investigate the changes of [Ca2+]c in this study. rPT cells were pretreated with 10 µM BAPTA-AM for 30 min, followed by incubation with 0.5 µM Pb for another 12 h. Also, cells were co-incubated with 10 µM 2-APB and 2.5 µM Cd or 1 µM TG and 2.5 µM Cd for 12 h. After the treatment, harvested cells were incubated with 0.5 mM of TPEN at 37°C for 10 min, loaded with 1 µM Fluo-3-AM (containing 0.02% Pluronic F-127) for 30 min in dark at 37°C, and then washed with D-Hank’s solution. Intracellular Ca2+ levels were represented with fluorescent intensity (FL-1, 530 nm) of 10,000 cells on flow cytometer. This assay was replicated six different times using different batches of cells.
Flow cytometric analysis of endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ levels ([Ca2+]ER)
It has been verified that Mag-Fluo-4-AM was selectively labelled on ER, making its specificity for measuring [Ca2+]ER [9]. After corresponding treatment, cells were incubated with 2 µM Mag-Fluo-4-AM and 0.02% (w/v) Pluronic F-127 for 30 min at 37°C in dark. Pb was removed by treatment of TPEN as described above. 488-nm laser was used to excite Mag-Fluo-4 fluorescence and [Ca2+]ER was calculated by the fluorescence intensity (FL-1, 530 nm) of 10,000 cells on flow cytometer.
Western blot analysis
Cells subjected to desired treatments were lysed in ice-cold RIPA buffer supplemented with protease inhibitor (Merck Millipore) and phosphatase inhibitor (Roche) to prepare the total cell lysates. After protein quantification with BCA method, samples were subjected to SDS-PAGE gels and transferred to PVDF membranes. After blocking with 5% skim milk for 1 h at room temperature, membranes were incubated overnight at 4°C with the following primary antibodies: GRP78 (diluted 1:1000), GRP94 (diluted 1:1000), CRT (diluted 1:1000), CHOP (diluted 1:1000), Caspase-12 (diluted 1:1000), t-CaMKII (diluted 1:1250), p-CaMKII (diluted 1:1000), β-actin (diluted 1:1000) and GAPDH (diluted 1:1000). After several washes with TBST, the membranes were incubated with appropriate secondary antibodies (1:5000 dilution) for 50 min at room temperature. Finally, each protein was detected on a Chemidoc XRS (Bio-Rad, Marnes-La-Coquette, France) by using the ECL kit. Proteins levels were determined by computer-assisted densitometric analysis (Densitometer, GS-800, BioRad Quantity One). The density of each band was normalized to its respective loading control (β-actin or GAPDH). Data obtained were expressed as the ratio of intensity of the protein in chemical-treated cells to that of the corresponding protein in control cells. Each test was performed in four experiments with different batches of cells.
Assessment of apoptosis by morphological changes and flow cytometry
Cells were pre-incubated with 10 µM KN62 or 10 µM KN93 for 2 h, then treated with 0.5 µM Pb for another 12 h to assess its effect on apoptosis, respectively. Apoptosis is characterized morphologically by condensation and fragmentation of nuclei. Thus, Hoechst 33258 staining was firstly applied to assess the morphological changes of treated cells, and 200 cells were randomly selected to count those apoptotic cells within every batch of experiment, each one performed in triplicate. Another concern is the quantitative analysis of apoptosis by flow cytometry. Both of these two methods have been extensively described in our previous study [37].
Analysis of the changes of [Ca2+]c and [Ca2+]ER by confocal microscopy
Two CaMKII inhibitors, i.e., KN62 and KN93, were applied to assess its effect on the changes of [Ca2+]c and [Ca2+]ER in Pb-exposed rPT cells, respectively. Cells grown on coverslips were pre-incubated with 10 µM KN62 or 10 µM KN93 for 2 h, then exposed to 0.5 µM Pb for another 12 h. After incubated with 0.5 mM of TPEN (Pb chelator) at 37°C for 10 min, one part of slides were loaded with 2.5 µM Fluo-3-AM (containing 0.02% Pluronic F-127) in dark at 37°C for 30 min, and the other part of slides were incubated with 2.5 µM Mag-Fluo-4-AM (containing 0.02% Pluronic F-127) in dark at 37°C for 30 min. After washing with D-Hank’s solution, cells labeled with Fluo-3-AM or Mag-Fluo-4-AM were visualized by the confocal microscope (TCS SPE, Leica, Germany) to assess the changes of [Ca2+]c and [Ca2+]ER, respectively. Representative confocal images were captured. [Ca2+]c and [Ca2+]ER were quantified using the ImageJ software under identical threshold conditions.
Data presentation
Experiments were performed at least three times with similar results. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM of the indicated number of replicates. Statistical comparisons were made using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) (Scheffe’s F test) after ascertaining the homogeneity of variance between the treatments, and P < 0.05 was regarded as significant.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the national nature science foundation of China (No. 31472251), a foundation for the author of national excellent doctoral dissertation of PR China (No. 201266) and Funds of Shandong “Double Tops” Program.
Abbreviations
- 2-APB
2-Aminoethoxydiphenyl borate
- BAPTA-AM
1, 2-Bis (2-aminophenoxy) ethane-N, N, N’, N’-tetraacetic acid acetoxymethyl ester
- BCA
bicinchonininc acid
- CaMKII
Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II
- CHOP
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein homologous protein
- CRT
Calreticulin
- [Ca2+]c
free Ca2+ concentration in the cytosol
- [Ca2+]ER
free Ca2+ concentration in the ER
- ECL
enhanced chemiluminescence
- ER
endoplasmic reticulum
- GRP78
glucose-regulated protein 78
- GRP94
glucose-regulated protein 94
- IP3
inositol 1, 4, 5-trisphosphate
- IP3R
inositol 1, 4, 5-trisphosphate (IP3) receptor
- TPEN
N, N, N′, N′-tetrakis-(2-pyridylmethyl) ethylenediamine
- TG
Thapsigargin
- rPT
rat proximal tubular
- PI
propidium iodide
- PBS
phosphate buffered saline
Footnotes
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
REFERENCES
- 1.Nevin R. Understanding international crime trends: the legacy of preschool lead exposure. Environ Res. 2007;104:315–336. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2007.02.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Patrick L. Lead toxicity, a review of the literature. Part 1: Exposure, evaluation, and treatment. Altern Med Rev. 2006;11:2–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Li X, Xing M, Chen M, Zhao J, Fan RF, Zhao X, Cao C, Yang J, Zhang Z, Xu SW. Effects of selenium-lead interaction on the gene expression of inflammatory factors and selenoproteins in chicken neutrophils. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2017;139:447–453. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.02.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Jin X, Xu Z, Zhao X, Chen M, Xu SW. The antagonistic effect of selenium on lead-induced apoptosis via mitochondrial dynamics pathway in the chicken kidney. Chemosphere. 2017;180:259–266. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.03.130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zhao PP, Guo Y, Zhang W, Chai HL, Xing HJ, Xing MW. Neurotoxicity induced by arsenic in Gallus Gallus: Regulation of oxidative stress and heat shock protein response. Chemosphere. 2017;166:238–245. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.09.060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Han Y, Li C, Su M, Wang Z, Jiang N, Sun D. Antagonistic effects of selenium on lead-induced autophagy by influencing mitochondrial dynamics in the spleen of chickens. Oncotarget. 2017;8:33725–33735. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16736. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.16736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Liu B, Zhang H, Tan X, Yang D, Lv Z, Jiang H, Lu J, Baiyun R, Zhang Z. GSPE reduces lead-induced oxidative stress by activating the Nrf2 pathway and suppressing miR153 and GSK-3β in rat kidney. Oncotarget. 2017;8:42226–42237. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15033. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.15033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Follmann W, Birkner S. The use of cultured primary bovine colon epithelial cells as a screening model to detect genotoxic effects of heterocyclic aromatic amines in the comet assay. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2008;71:947–953. doi: 10.1080/15287390801988962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Wang H, Wang ZK, Jiao P, Zhou XP, Yang DB, Wang ZY, Wang L. Redistribution of subcellular calcium and its effect on apoptosis in primary cultures of rat proximal tubular cells exposed to lead. Toxicology. 2015;333:137–146. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2015.04.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lam AK, Galione A. The endoplasmic reticulum and junctional membrane communication during calcium signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1833:2542–2559. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.06.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Baumann O, Walz B. Endoplasmic reticulum of animal cells and its organization into structural and functional domains. Int Rev Cytol. 2001;205:149–214. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(01)05004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Paschen W, Mengesdorf T, Althausen S, Hotop S. Peroxidative stress selectively down-regulates the neuronal stress response activated under conditions of endoplasmic reticulum dysfunction. J Neurochem. 2001;76:1916–1924. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2001.00206.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chen S, Xu Y, Xu B, Guo M, Zhang Z, Liu L, Ma H, Chen Z, Luo Y, Huang S, Chen L. CaMKII is involved in cadmium activation of MAPK and mTOR pathways leading to neuronal cell death. J Neurochem. 2011;119:1108–1118. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07493.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Toussaint F, Charbel C, Blanchette A, Ledoux J. CaMKII regulates intracellular Ca2+ dynamics in native endothelial cells. Cell Calcium. 2015;58:275–285. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2015.06.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bracken C, Beauverger P, Duclos O, Russo RJ, Rogers KA, Husson H, Natoli TA, Ledbetter SR, Janiak P, Ibraghimov-Beskrovnaya O, Bukanov NO. CaMKII as a pathological mediator of ER stress, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial dysfunction in a murine model of nephronophthisis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016;310:F1414–1422. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00426.2015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Yoon MJ, Lee AR, Jeong SA, Kim YS, Kim JY, Kwon YJ, Choi KS. Release of Ca2+ from the endoplasmic reticulum and its subsequent influx into mitochondria trigger celastrol-induced paraptosis in cancer cells. Oncotarget. 2014;5:6816–6831. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2256. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.2256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Abdoul-Azize S, Dubus I, Vannier JP. Improvement of dexamethasone sensitivity by chelation of intracellular Ca2+ in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells through the prosurvival kinase ERK1/2 deactivation. Oncotarget. 2017;8:27339–27352. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16039. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.16039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Liu C, Ye Y, Zhou Q, Zhang R, Zhang H, Liu W, Xu C, Liu L, Huang S, Chen L. Crosstalk between Ca2+ signaling and mitochondrial H2O2 is required for rotenone inhibition of mTOR signaling pathway leading to neuronal apoptosis. Oncotarget. 2016;7:7534–7549. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7183. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.7183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Dupont G, Houart G, De Koninck P. Sensitivity of CaM kinase II to the frequency of Ca2+ oscillations: a simple model. Cell Calcium. 2003;34:485–497. doi: 10.1016/s0143-4160(03)00152-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Winters CJ, Koval O, Murthy S, Allamargot C, Sebag SC, Paschke JD, Jaffer OA, Carter AB, Grumbach IM. CaMKII inhibition in type II pneumocytes protects from bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by preventing Ca2+-dependent apoptosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2016;310:L86–L94. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00132.2015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ekong EB, Jaar BG, Weaver VM. Lead-related nephrotoxicity: a review of the epidemiologic evidence. Kidney Int. 2006;70:2074–2084. doi: 10.1038/sj.ki.5001809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Song XB, Liu G, Liu F, Yan ZG, Wang ZY, Liu ZP, Wang L. Autophagy blockade and lysosomal membrane permeabilization contribute to lead-induced nephrotoxicity in primary rat proximal tubular cells. Cell Death Dis. 2017;8:e2863. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Inagi R. Endoplasmic reticulum stress as a progression factor for kidney injury. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2010;10:156–165. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2009.11.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sun X, Liao W, Wang J, Wang P, Gao H, Wang M, Xu C, Zhong Y, Ding Y. CSTMP induces apoptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction in human myeloma RPMI8226 cells via CHOP-dependent endoplasmic reticulum stress. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016;83:776–784. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.07.045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Morishima N, Nakanishi K, Takenouchi H, Shibata T, Yasuhiko Y. An endoplasmic reticulum stress-specific caspase cascade in apoptosis. Cytochrome c-independent activation of caspase-9 by caspase-12. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:34287–34294. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M204973200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kim EM, Shin EJ, Choi JH, Son HJ, Park IS, Joh TH, Hwang O. Matrix Metalloproteinase-3 is increased and participates in neuronal apoptotic signaling downstream of caspase-12 during endoplasmic reticulum stress. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:16444–16452. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.093799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ma J, Yang YR, Chen W, Chen MH, Wang H, Wang XD, Sun LL, Wang FZ, Wang DC. Fluoxetine synergizes with temozolomide to induce the CHOP-dependent endoplasmic reticulum stress-related apoptosis pathway in glioma cells. Oncol Rep. 2016;36:676–684. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.4860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kitamura M. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in the kidney. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2008;12:317–325. doi: 10.1007/s10157-008-0060-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Giorgi C, Romagnoli A, Pinton P, Rizzuto R. Ca2+ signaling, mitochondria and cell death. Curr Mol Med. 2008;8:119–130. doi: 10.2174/156652408783769571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Luciani DS, Gwiazda KS, Yang TL, Kalynyak TB, Bychkivska Y, Frey MH, Jeffrey KD, Sampaio AV, Underhill TM, Johnson JD. Roles of IP3R and RyR Ca2+ channels in endoplasmic reticulum stress and beta-cell death. Diabetes. 2009;58:422–432. doi: 10.2337/db07-1762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Bahar E, Kim H, Yoon H. ER Stress-mediated signaling: action potential and Ca2+ as key players. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17:E1558. doi: 10.3390/ijms17091558. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17091558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Choong G, Liu Y, Templeton DM. Interplay of calcium and cadmium in mediating cadmium toxicity. Chem Biol Interact. 2014;211:54–65. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2014.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Mustroph J, Neef S, Maier LS. CaMKII as a target for arrhythmia suppression. Pharmacol. 2016 doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.10.006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.10.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Feng N, Anderson ME. CaMKII is a nodal signal for multiple programmed cell death pathways in heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2017;103:102–109. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2016.12.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Liu G, Wang ZK, Wang ZY, Yang DB, Liu ZP, Wang L. Mitochondrial permeability transition and its regulatory components are implicated in apoptosis of primary cultures of rat proximal tubular cells exposed to lead. Arch Toxicol. 2016;90:1193–1209. doi: 10.1007/s00204-015-1547-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Takenouchi T, Ogihara K, Sato M, Kitani H. Inhibitory effects of U73122 and U73343 on Ca2+ influx and pore formation induced by the activation of P2X7 nucleotide receptors in mouse microglial cell line. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005;1726:177–186. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2005.08.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Wang L, Wang H, Hu MZ, Cao J, Chen DW, Liu ZP. Oxidative stress and apoptotic changes in primary cultures of rat proximal tubular cells exposed to lead. Arch Toxicol. 2009;83:417–427. doi: 10.1007/s00204-009-0425-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]