Abstract
Introduction
Sex differences in cognition of HIV positive (HIV+) patients are controversial. We aimed to investigate the relationship between cognition, HIV status, and sex, in a highly homogenous cohort of young Romanians parenterally infected during early childhood.
Methods
250 HIV+ participants were compared to age-matched HIV negative (HIV−) controls (n=72) in a cross-sectional study. After standardized neurocognitive, psychological testing and medical evaluation, linear regression was used to assess the effect of sex and HIV on neurocognitive outcomes.
Results
Study participants were on average 23 years old with balanced sex distribution (% female = 52% vs 43%). HIV− were more educated (12.7 vs 11.6 years, p=0.002).
Positive HIV status was associated with a lower global performance (Beta=−0.22, p<0.001), after controlling for age and education. HIV+ females had better previous and current HIV-associated markers.
The effect of HIV on global cognition did not differ between sexes in most cognitive domains (Beta=0.07, p=0.14). An interaction between sex, HIV status, and cognitive functioning was found in the Psychomotor domain. HIV+ females had worse Motor skills than HIV− females (Beta=−0.32, p<0.001) suggesting a specific effect of HIV on motor functioning in females only. Moreover, current CD4< 200 cells/mm3 (p=0.013) and longer time lived with CD4< 200 cells/mm3 (p=0.023) were negatively correlated with the Motor scaled score in females (Beta=−0.22, p=0.034).
Conclusion
Despite less advanced disease in women, long term HIV infection has an equally detrimental effect on cognitive performances of both sexes, in all cognitive domains, except the psychomotor domain where women are preferentially affected.
Keywords: HIV infection, HIV women, young adults, neurocognitive impairment, sex differences
INTRODUCTION
Sex differences in cognition are controversial. Poorer neurological outcomes in HIV infected (HIV+) women compared to men have been reported in several cohorts [1] [2]. HIV+ women have a higher prevalence of neuropsychological impairment compared to HIV negative (HIV−) women regardless of symptom status and AIDS diagnosis [3] [4], with impairment in psychomotor tasks being particularly noted [3].
Many studies examining the relationships between sex, cognition, and HIV have utilized limited cohorts with numerous confounders, often comparing HIV+ men to HIV+ women, or HIV+ women to HIV− women, but rarely all four groups of interest.
We investigated the relationship between cognition according to HIV status and sex, and determinants of cognition in a highly homogenous HIV infected young cohort. We also aimed to describe the pattern and magnitude of impairment evaluated in different cognitive domains according to HIV status, viral and immunological characteristics and sex.
METHODS
Study population
All 322 participants were evaluated at “Dr. Victor Babes” Hospital for Infectious and Tropical Diseases (VBH), a reference center in Bucharest, Romania. The study was approved by the institutional review boards of VBH and the University of California at San Diego. All participants provided written informed consent to participate. HIV+ (n=250) participants in this study are representative of the Romanian cohort of nosocomial HIV infected children in their first years of life in the late 1980s, with HIV clade F [5].
The exclusion criteria have previously been described [6].
Age-matched HIV− participants (n=72) with similar socioeconomic backgrounds were recruited. These participants were siblings (n=14) or partners (n=10) of HIV+ patients, or peers from school or work.
Neurocognitive assessment
All participants completed tests assessing 7 ability domains (Verbal Fluency, Speed of Information Processing, Attention/Working Memory, Executive Function, Learning and Memory, and Motor) and underwent medical evaluations as previously described [6].
Scores of the HIV− controls were used to convert raw scores to normally distributed scaled scores with a mean of 10 and a standard deviation (SD) of 3, such that higher values represent a better performance for all measures. The conversion formulas were then applied to HIV+ participants. For each participant, scaled scores were averaged to calculate the domain summary scaled score, which were then averaged to obtain the global scaled score.
Current and past alcohol and substance use were determined using a substance use history questionnaire and the MINI-International Neuropsychiatric Interview (MINI-Plus). Depression was evaluated with Beck Depression Inventory II [7].
In order to evaluate the impact of neurocognitive impairment on day to day functioning, the Patient’s Assessment of Own Functioning Inventory (PAOFI) [8], was administered.
Neuromedical evaluation
The neuromedical (NM) examination included (1) a review of medical files for medical and neurological histories, current or past antiretroviral medications, and (2) a brief medical and neurological examination. Current CD4 and HIV RNA were measured with an HIV RNA detection limit of 50 copies/ml.
For each participant, the “first visit” was considered the first visit where a CD4 count was determined; an “interim visit” was considered any visit after the first visit and before the current study visit; the “last visit” was considered the study visit. The total days lived with CD4<200 cells/mm3 was obtained by summing up estimates from individual visits where CD4 was below 200 cells/mm3, as follows: if 1st visit: the number of days from the visit to ½-way to the next visit, if that visit was CD4>200; if interim visit: the number of days from ½-way between the previous visit and the visit added to the number of days from the visit to ½-way to the next visit; if last visit: the number of days from ½-way since the previous visit to the visit. For any participant with CD4≥200 at all times, this estimated variable would be zero. For the analyses, days were converted to years. The approach for calculating total time lived with detectable RNA was similar.
All control participants had negative HIV serology.
For all participants, standard laboratory testing was performed in order to assess for co-infections (HBV, HCV, and syphilis), renal, liver insufficiency, severe anemia, and thrombocytopenia.
Statistical analysis
Demographic and clinical characteristics were compared between HIV status and sex, and their 4 combinations, using independent samples t-test and Chi-square test (or Fisher’s exact test where more appropriate) for numeric and categorical variables, respectively. P-values from the tests of differences between 4 HIV by sex groups were adjusted for multiple comparisons using false discovery rate method [9].
The primary analysis used global and domain summary scaled scores as the outcomes, followed by the secondary analysis of the scaled scores for each test. In separate models for each primary and secondary measure, linear regressions assessed effect of sex and HIV on these outcomes, adjusting for demographic covariates (age and education) that may affect cognition. Interactions between HIV and sex were explored; only significant interactions were kept in the models.
For the HIV+ subset, in multivariable analyses, global and domain scaled scores were regressed on sex, controlling for age, education, and those HIV disease covariates that either differed between sexes or showed an association with a specific scaled score in a univariable analyses with a significance level of 0.15. The HIV covariates were kept in the multivariable model only if their p-value was below 0.05, after adjusting for other predictors.
Of particular interest, interactions between sex and the following HIV covariates were investigated in multivariable models for global and domain scaled scores: time lived with CD4<200 cells/mm3, current CD4 (<200 cells/mm3 vs ≥200 cells/mm3), detectable plasma HIV viral load (HIV ARN>50 copies/ml), and AIDS. Select interactions between these HIV covariates were also examined. All models controlled for age and education.
The effect size for the strength of associations between the outcomes and predictors in linear regressions was estimated with the standardized beta (hereafter Beta). Negative and positive values of Beta, respectively, represent an association with a worse and a better cognitive outcome.
RESULTS
Sample characteristics
The cohort consisted of 322 participants, 250 (78%) of whom were HIV+. Participants were on average 23 years old and half were female (N=160, 50%). The distribution of sexes was not statistically different between HIV+ and HIV− groups (% female = 52% vs 43%, p=0.25). HIV− participants were on average more educated (12.7 vs 11.6 years, p=0.002) and more likely to be employed or in school (72% vs 48%, p=0.001). However, controlling for these variables in the models did not significantly change the effects of HIV status on cognitive scaled scores. Table 1 lists demographic and psychological characteristics of the participants by HIV/sex groups. There were no differences between HIV+ and HIV− groups and males and females regarding drug use, hepatitis C co-infection (<2.4%) and PAOFI complains. Overall, the HIV+ group had more depressive symptoms, but this did not change the effects of HIV status when controlled for statistically. Males had a slightly higher proportion of alcohol use than females (7.4% vs 0.8%, p=0.01), but no effect of lifetime cumulative alcohol abuse was found on cognition (data not shown).
Table 1.
Demographic and HIV disease characteristics of the participants, N=322.
| HIV+ | HIV− | Significant comparisons* | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. Female N=129 |
B. Male N=121 |
C. Female N=31 |
D. Male N=41 |
||
| Age (years) a | 22.9 (2.7) | 23.0 (2.5) | 22.3 (3.1) | 23.1 (3.4) | - |
| Education (years) a | 11.6 (3.0) | 11.5 (2.6) | 12.8 (2.6) | 12.7 (2.3) | A,B < C,D; HIV+ < HIV− |
| Employed/in school b | 43% | 54% | 74% | 71% | A < C,D; HIV+ < HIV− |
| PAOFI: >3 complaints b | 20% | 17% | 10% | 10% | - |
| Beck depression score >13 b | 16.3% | 15.9% | 6.5% | 0% | HIV+>HIV− |
| AIDS b | 39% | 37% | - | - | - |
| Estimated years with HIV from the date of infection a | 21.7 (3.6) | 22.1 (3.6) | - | - | - |
| Estimated years with HIV from the date of 1st positive test a | 12.7 (5.8) | 13.1 (6.4) | - | - | - |
| CD4 Nadir c | 98 (36–206) | 74 (19–180) | - | - | - |
| Estimated years lived with CD4< 200 cells/mm3 c | 1.7 (2.1) | 2.2 (2.8) | - | - | - |
| CD4 current c | 516 (348–743) | 458 (234–667) | - | - | A > B |
| CD8 c | 716 (522–992) | 888 (675–1159) | - | - | A < B |
| CD4/CD8 c | 0.72 (0.43–1.10) | 0.49 (0.20–0.70) | - | - | A > B |
| Detectable HIV viral load in plasma b | 29% | 47% | - | - | A < B |
| Estimated years with detectable HIV viral load c | 4.0 (3.6) | 5.2 (4.0) | - | - | A < B |
| Months on current ART regimen c | 24 (12–46) | 29 (10–50) | - | - | - |
| Months of exposure to all ARV medications c | 120 (71–164) | 123 (74–166) | - | - | - |
Notes: Groups are A = HIV+ female, B = HIV+ male, C = HIV− female, D = HIV− male. Values represent a mean (standard deviation), b percent (%), c median (interquartile range).
Only significant comparisons are shown (p<0.05).
Characteristics were compared by HIV status, by sex, and by HIV/sex groups. For the latter, p-values were adjusted for multiple group comparisons by false discovery rate (FDR) method. AIDS = acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, ART = antiretroviral therapy, ARV = antiretroviral, FrSBe = frontal systems behavior scale, HIV = human immunodeficiency virus, PAOFI = patient assessment of own functioning inventory.
In the HIV+ group, there were no statistical sex differences in proportions of patients with AIDS, nadir CD4 levels, cumulative time lived with CD4<200 cells/mm3, estimated durations of HIV infection or exposure to antiretroviral treatments. Males had a lower current CD4 count, lower CD4/CD8 ratio, a greater proportion of patients with detectable HIV viral load, and spent a longer cumulative time with detectable HIV viral load (Table 1).
Sex differences in cognitive outcomes
Table 2 shows the results of multivariable analyses by cognitive domain. On average, regardless of HIV status, males performed significantly better than females in Working Memory (Beta=0.21, p<0.001) and Executive Functioning (Beta=0.12, p=0.01) domains. There was no statistical difference in global scaled scores between sexes (Beta=0.07, p=0.14).
Table 2.
Multivariable models investigating effects of HIV and sex on neurocognitive test, domain, and global scaled scores, adjusted for age and education. The values shown in the table represent standardized betas (Betas) from the multivariable models, such that a larger absolute value represents a stronger predictor, and positive values are associated with a better test performance.
| Domain: Test | Model Terms | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIV Status (ref = HIV−) | Male Sex (ref = Female) | Age | Education | Male×HIV+ | |
| Global | −0.22** | 0.07 | −0.02 | 0.47** | - |
| Verbal | −0.08 | 0.08 | −0.04 | 0.50** | - |
| COWA Test - FAS | −0.12* | −0.01 | −0.02 | 0.48** | - |
| Animal Fluency | 0.01 | 0.13* | 0.005 | 0.40** | - |
| Action Fluency | −0.09 | 0.08 | −0.07 | 0.37** | - |
| SIP | −0.17** | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.44** | - |
| WAIS-III Digit Symbol | −0.20** | −0.11* | −0.08 | 0.46** | - |
| WAIS-III Symbol Search | −0.11* | 0.09 | −0.06 | 0.42** | |
| Trail Making Test A | −0.11* | 0.14** | 0.09 | 0.29** | - |
| Color Trail Test 1 | −0.12* | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.28** | - |
| Stroop Test - Word | −0.11* | −0.01 | −0.005 | 0.36** | - |
| Stroop Test - Color | −0.16** | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.23** | - |
| Working Memory | −0.18** | 0.21** | −0.12* | 0.33** | - |
| PASAT-50 | −0.21** | 0.20** | −0.02 | 0.35** | - |
| WMS-III Spatial Span | −0.12* | 0.19** | −0.17** | 0.23** | - |
| Executive Function | −0.21** | 0.12* | 0.03 | 0.41** | - |
| Category Test | −0.19** | 0.19** | 0.08 | 0.33** | - |
| WCST Total Errors | −0.14* | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.25** | - |
| Stroop Incongruent Condition | −0.18** | 0.03 | −0.01 | 0.30** | - |
| Color Trails Test 2 | −0.14* | 0.06 | −0.05 | 0.35** | - |
| Learning | −0.19** | −0.01 | −0.12* | 0.40** | - |
| HVLT-R Learning | −0.16** | 0.004 | −0.08 | 0.39** | - |
| BVMT-R Learning | −0.16** | −0.02 | −0.12* | 0.29** | - |
| Memory | −0.19** | 0.01 | −0.07 | 0.32** | - |
| HVLT-R Delayed Recall | −0.16** | 0.05 | −0.06 | 0.33** | - |
| BVMT-R Delayed Recall | −0.16** | −0.03 | −0.05 | 0.23** | − |
| Motor | −0.32** | −0.28* | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.25* |
| Grooved Pegboard – DH | −0.23** | −0.10 | 0.11* | 0.10 | - |
| Grooved Pegboard - NDH | −0.26** | −0.26* | 0.04 | 0.10 | 0.28* |
Notes:
p<0.05,
p<0.01.
ref = reference group, Male×HIV+ = interaction term between sex and HIV status. SIP = speed of information processing. BVMT-R = Brief Visuospatial Memory Test-Revised; COWA = Controlled Oral Word Association; DH = dominant hand; NDH = non-dominant hand; HVLT-R = Hopkins Verbal Learning Test-Revised; PASAT-50 = Paced Auditory Serial Addition Test-50 item; SIP = speed of information processing; WAIS-III = Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale-III; WCST-III = Wisconsin Card Sorting Test-III, WMS-III = Wechester Memory Scale-III Test.
When assessed separately within the HIV+ and HIV− groups, and controlling for age and education, males outperformed women in Working Memory in HIV+ group (Beta=0.23, p<0.001), but not in the HIV− group (Beta=0.19, p=0.10). For the Executive Function domain, the male sex effect was found to be significant only in the HIV− group (Beta=0.22, p=0.048), consistent with the overall model. Results of these subgroup analyses are shown in Table 3. The results of multivariable models regressing individual scaled scores for each test on HIV status and sex, controlling for age and education, are shown in Table 2.
Table 3.
Multivariable models investigating effects of sex on domain and global scaled scores, adjusted for age and education, in HIV+, and separately, in HIV− groups. The values shown in the table represent standardized betas (Betas) from the multivariable models, such that a larger absolute value represents a stronger predictor, and positive values are associated with a better test performance.
| Group: HIV+ | Model Terms | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Male Sex (ref = Female) | Age | Education | |
| Global | 0.09 | 0.02 | 0.48** |
| Verbal | 0.08 | 0.03 | 0.48** |
| SIP | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.44** |
| Working Memory | 0.23** | −0.09 | 0.32** |
| Executive Function | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.41** |
| Learning | −0.01 | −0.12 | 0.42** |
| Memory | 0.04 | −0.07 | 0.34** |
| Motor | −0.02 | 0.16* | 0.11 |
| Group: HIV− | |||
| Global | 0.03 | −0.14 | 0.51** |
| Verbal | 0.09 | −0.18 | 0.57** |
| SIP | 0.001 | −0.03 | 0.45** |
| Working Memory | 0.19 | −0.21 | 0.37** |
| Executive Function | 0.22* | −0.14 | 0.44** |
| Learning | −0.03 | −0.14 | 0.37** |
| Memory | −0.11 | −0.04 | 0.32** |
| Motor | −0.28* | −0.09 | 0.07 |
Notes:
p<0.05,
p<0.01.
ref = reference group; SIP = speed of information processing.
Cognitive outcomes between HIV positive versus HIV negative groups
Multivariable analysis of the global scaled score showed that HIV status was associated with lower neurocognitive performance (Beta=−0.22, p<0.001) with a significant effect of HIV infection on summary scaled scores seen in most domains (Beta range=−0.17 to −0.21, ps<0.001), except Verbal Fluency (Beta=−0.08, p=0.11), when controlling for age and education (Table 2).
Interaction effect of sex and HIV status on cognitive outcomes
For outcomes presented in Table 2, interactions between sex and HIV status were investigated for all measures. The interaction was not statistically significant for the global scaled score (p=0.54) and most domain scaled scores (ps>0.05), suggesting that the effect of HIV on those measures does not differ statistically between females and males.
The exception was within the Motor domain, for which the interaction between sex and HIV status was significant (p=0.045, Figure 1). Specifically, after controlling for age and education, HIV+ females had worse Motor skills than HIV− females (Beta=−0.32, p<0.001), but there was no difference in mean Motor scaled scores between HIV+ and HIV− males (Beta=−0.10, p=0.17), suggesting a specific effect of HIV on motor functioning in HIV+ females only. These results are consistent with the subset analyses presented above.
Figure 1.
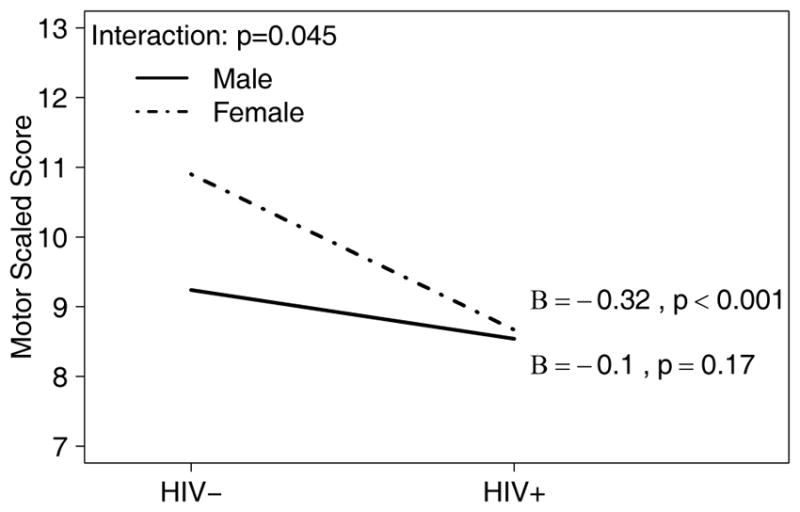
Visual representation of the sex x HIV interaction effect on the scaled score for the motor domain.
Note: Effect size Beta (B) and p-value are shown for the effect of HIV status (on the x-axis), separately for each sex (represented by lines).
When looking at individual test scores, the interaction between sex and HIV status was significant only in the analysis of the Grooved Pegboard Test for non-dominant hand (p=0.03), showing that HIV seropositivity was associated with a worse outcome in females (Beta=−0.26, p=0.002), but not in males (Beta=−0.02, p=0.83)(Table 2).
HIV positive group analysis
When looking at the subset of HIV+ participants, the effects of most HIV characteristics listed in Table 1 on scaled scores were not significant in presence of age, education, and sex in multivariable models (models are not shown).
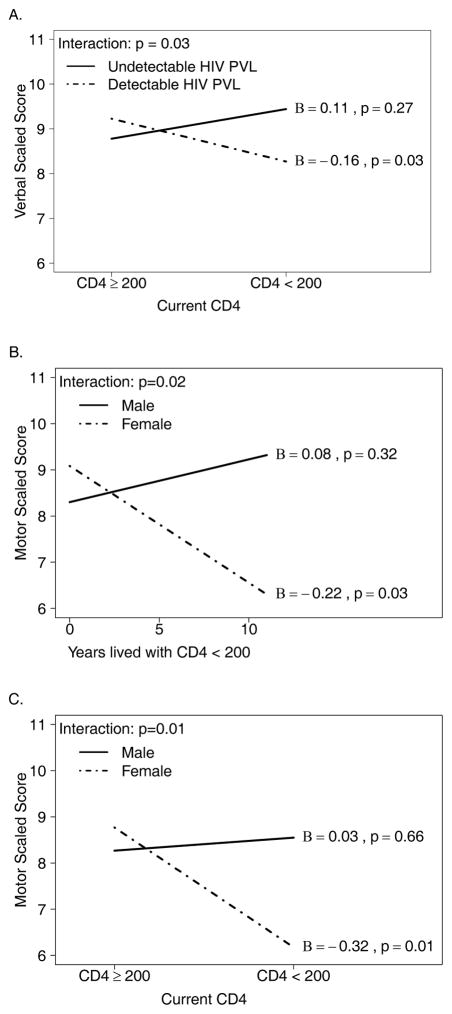
In the analysis of the Verbal scaled score, a significant interaction was observed between low CD4 count and detectable plasma HIV viral load (p=0.03, Figure 2A). Specifically, among participants with a detectable plasma HIV viral load, those with CD4<200 cells/mm3 had a significantly lower Verbal scaled score compared to participants with CD4≥200 cells/mm3 (Beta=−0.16, p=0.03). This effect was not observed in the group with undetectable plasma HIV viral load (Beta=0.11, p=0.27).
Figure 2.
Multivariable linear regression models were used to assess effect of HIV disease covariates on scaled scores and their moderating effect on association between scaled scores and sex, adjusting for age and education.
Note: Three significant interactions were detected (A) between HIV plasma viral load (PVL, detectable vs. undetectable) and current CD4 count on Verbal scaled score; (B) between sex and cumulative years spent with CD4< 200 cells/mm3 on Motor scaled scores; and (C) between sex and current CD4 count on Motor scaled scores. Effect size Beta (B) and p-value are shown for the effect of the covariate on the x-axis, separately for each group of the covariate represented by lines.
For the Learning and Memory domains, while the mean scaled scores for all HIV+ participants were below the mean scaled scores for the HIV− participants, the multivariable regression analysis within HIV+ group showed that participants with AIDS had a higher mean Memory scaled score than participants without AIDS (Beta=0.12, p=0.047).
In the analysis of the Motor domain, a significant interaction of sex with time lived with CD4<200 cells/mm3 (p=0.023, Figure 2B) showed that longer duration of low CD4 was negatively correlated with the Motor scaled score in females (Beta=−0.22, p=0.03), but not in males (Beta=0.08, p=0.32). In a separate model, a similar association was found between the Motor scaled score and the current CD4<200 cells/mm3 (interaction with sex p=0.01, Figure 2C). For females, the association was significant (Beta=−0.32, p=0.007).
DISCUSSION
Our study is unique in that it addresses sex differences on neurocognition in young adults with lifelong HIV infection acquired in early childhood. The HIV+ group has approximately 25 years of chronic HIV infection, a balanced sex distribution, about 15 years of exposure to cART, and no significant medical, psychiatric or behavioral confounding conditions.
In this highly homogenous group, when controlling for age and education, we show a significant effect of HIV+ status on neurocognition. The effect of HIV does not differ between females and males on global cognition and most cognitive domains with the remarkable exception of the psychomotor domain, where an effect of HIV status on cognitive functioning is present only in women, suggesting a gender effect.
These findings are particularly interesting since HIV+ females have better HIV-associated overall status (higher levels of current CD4 count, higher CD4/CD8 ratio, lower proportion with detectable HIV viral load and shorter cumulative estimated time spent with detectable HIV viral load).
Since the study group is young and has no other known neurocognitive morbidity except HIV infection, we can postulate that the neurocognitive alterations seen are mainly linked to HIV itself and its impact on the developing brain.
Consistent with previous research examining sex and cognition, sex differences were found irrespective of HIV-status. In our study, males performed significantly better than females in working memory and executive functioning domains, but females outperformed males in the motor domain, which is also consistent with previous reports [10] [11] [12] [13]. Although it has been hypothesized that differences in male/female finger sizes [14] [15] might account for performance differences, studies using the small pegboard for the Grooved Pegboard Test (GPT) and accounting for finger size have found that females still do better than males [16], contradicting some previous reports [17]. Regardless, in our study females outperformed males in the motor domain in HIV− group, but within the HIV+ group no differences were found.
Cognition and HIV serostatus
In our cohort, HIV+ status was associated with worse performance, compared to HIV− group, on all but the verbal fluency tests. Several possible factors could have contributed to lower performances, namely uncontrolled HIV infection and low nadir CD4 count. Indeed, all our HIV+ participants had a history of at least 8–10 years of chronic untreated HIV infection.
Uncontrolled HIV replication in the CNS has previously been linked to cognitive deficits [18,19]. Most of the HIV+ participants in the present study had a low nadir CD4 count, which may allow greater virus access to the CNS [20] and lead to higher risk of neurocognitive impairment in both adults [21,22] and children [23].
Although verbal fluency performances were not significantly different between HIV+ and HIV− participants, those with advanced HIV disease (detectable plasma HIV viral load and current CD4<200 cells/mm3) achieved a significantly lower verbal scaled score compared to participants with better HIV infection markers as previously described in HIV+ individuals in the pre-ART period [24].
HIV+ participants scored below HIV− participants in Learning and Memory domains. However, within the HIV+ group, participants without AIDS had slightly lower mean Memory scaled scores than those with AIDS (Beta=0.12, p=0.047). The factors leading to this are not clear, but were not related to other variables collected in the present study. Several other factors, such as quality of education and better retention in care might have contributed to the differences. Children with AIDS spent more time hospitalized and were more closely monitored after discharge. During these periods, according to their health state, they attended the on-site provided schooling. Indeed, schooling with a normal schedule has been available in our pediatric clinic for all hospitalized HIV infected children and patients with AIDS attended it for prolonged periods of time. Conversely, the educational opportunities for non-hospitalized children was variable.
Unfortunately, it is impossible for us to evaluate the extent and impact of these periods of time on their neurocognitive performance, but we hypothesize that it may have favorably influenced their learning and memory abilities as compared to patients who haven’t attended the same courses. We acknowledge, however, that this is a hypothesis that we are unable to resolve.
Effects of HIV on Cognition in Males and Females
Within the HIV+ group, females had less advanced HIV disease compared to men, but performed significantly worse in the working memory domain. Other studies, examining individuals infected in adulthood, have reported lower performances in HIV+ women compared to HIV+ men [25], [26], [27], [28], [29], [30]. Two other studies using a similar testing battery, found that despite better HIV indicators, women had poorer cognitive performances compared to males [25], [26]. It has been speculated that immunogenic responses, which might be influenced by hormonal patterns, impact the size of the viral reservoir [31], including in the CNS.
Previously, different patterns of cognitive impairment have been described in HIV+ men and women [32], [25], [26]. Among the HIV+ group, Zambian females had worse performances in memory and learning domains compared to males [25], while Nigerian HIV+ women had worse performance compared to HIV+ males in speed of information processing, verbal fluency, learning and memory domains [33].
Conversely, in a prospective study on a US HIV infected cohort, no evidence of differential declines regarding neuropsychological functioning between HIV+ males and HIV+ females was found [34].
Notably, many of the studies above were not able to examine differences in male and female performance within both HIV+ and HIV− participants.
Differences between the effects of HIV+ status on sexes
In our study, the effect of HIV differed between females and males in the psychomotor domain. However HIV+ status has an equally detrimental effect on cognitive performances of both sexes, in all other cognitive domains.
A recent study of 1521 women from the Women’s Interagency HIV Study (WIHS) showed that the largest cognitive deficit associated with HIV infection was in the domain of verbal memory, particularly delayed verbal memory when compared to uninfected women. Secondarily, deficits were also found in speed of information processing and attention [35].
In the present study, the psychomotor domain was the only cognitive domain where a significant interaction between female sex and HIV status was found, such that HIV+ females had worse psychomotor skills than HIV− females. This was characterized by HIV− women performing better than seronegative men, but that difference disappearing within the HIV+ groups.
It has already been described that HIV+ women, especially those with AIDS diagnosis, had slower psychomotor speed when compared to HIV− women [36] and that HIV+ status was a predictor for motor slowing in females [37], but no specific interactions were described between sex and HIV status.
In our study though, a preferential, negative effect of HIV+ status on cognition was observed, only in women, despite them having better HIV overall status (higher current CD4 count and CD4/CD8 ratio, greater proportion of patients with current undetectable HIV viral load and longer cumulative time spent with undetectable HIV viral load) compared to males.
Moreover, current low CD4 count and longer time with CD4<200 cells/ml was associated with worse motor performance in HIV-infected women. The findings were driven by the Grooved Pegboard Test on the non-dominant hand.
The GPT has been one of the most sensitive psychomotor measures over the years [38] [39] [40]. Not merely a “motor” measure, the GPT involves fine motor control and dexterity, visual processing, speed, attention, and continuous coordination and monitoring of accuracy [41].
It is possible that there were hormonal influences on this finding. Estradiol acts as a protector in striatal dopamine neurons [42] where high concentrations of estrogen receptors exist [43] and in a study of males and females, better performance on the GPT was related to higher striatal specific uptake values in women, but not in men [44]. However, the linkage between the role of estrogen and Motor performance differences seen in the present report remains speculative.
Since our cohort experienced untreated HIV in the first decade of life, it is likely that damage occurred in several brain regions. We propose that the myelination process was impaired, leading to altered motor performances and connectivity between motor areas, as it has been described in the pre-cART period [45]. Although preliminary, it might be posited that HIV-related disruption of developmental, and perhaps, hormonal influences in females resulted in the preferential deficits seen in psychomotor performance.
There are several limitations to our study. On average, participants without HIV were more educated and more likely to be employed or in school, but this did not change the effect of HIV status when controlled for statistically. Also, the control group was small, but very homogenous given that the majority of the participants were friends, siblings or colleagues of HIV+ and thus had similar socioeconomic status. The design of the study was cross sectional. Future studies involving a longitudinal evaluation are necessary in order to determine if the cognitive pattern that we found is influenced by the further development of these young adults. Hormonal influences would also be interesting to follow in women versus men in this maturing cohort.
Given the unique characteristics of early childhood infection and their young age, as well as their long-term infection, these patients are a valuable model for evaluating HIV-related neurocognitive impairment. The impact of other factors known to contribute to alterations in cognition in older patients (cardiovascular disease, metabolic disorders, etc.) is low in this cohort, thus allowing a more accurate evaluation of the effects of HIV. We have shown that, although HIV has an equally detrimental effect on cognitive performances of both sexes in most cognitive domains of a developing brain, the effect of HIV on psychomotor performances in females and its long-term consequences warrants further study.
Acknowledgments
SOURCE OF FUNDING: This work was supported by 1R01MH094159 and P30 MH62512 from National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH).
Ruxandra BURLACU and Anya Umlauf report grants from National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), during the conduct of the study.
Luminita Ene reports grants from National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), during the conduct of the study; personal fees and non-financial support from Abbvie, personal fees from Johnson & Johnson, Dr. Burlacu reports grants from National Institute of Mental Health, during the conduct of the study.
Simona Ruta reports grants from National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), during the conduct of the study.
Roxana Radoi reports grants from National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), during the conduct of the study; personal fees from Abbvie, personal fees from Bristol Meyers Squibb, personal fees from Johnson & Johnson, personal fees from Merck Sharp Dohme, outside the submitted work.
Anca Luca reports grants from National Institute of Mental Health, during the conduct of the study; grants from University College Dublin, School of Medicine, Ireland, outside the submitted work.
RB contributed to the study design and conception and interpretation of the data and drafted the manuscript. LE, TM, CA, SMR contributed to the study design and conception, to the interpretation of the data and edited the manuscript. AU performed the statistical analysis, contributed to drafting and edited the manuscript. RB, LE, AL, RR contributed to patient recruitment and testing and assisted with the collection of data. SG helped with data interpretation and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
The authors thank all the participants in the study, Terence Hendrix from the HIV Neurobehavioural Research Center in San Diego for neuropsychological training and study coordination as well as Adina Bulacu-Talnariu and Adrian Luca (psychologists) for their help with neuropsychological testing.
Footnotes
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
Thomas Marcotte, Sara Gianella and Cristian Achim have nothing to disclose.
References
- 1.Morlat P, Parneix P, Douard D, Lacoste D, Dupon M, Chêne G, et al. Women and HIV infection: a cohort study of 483 HIV-infected women in Bordeaux, France, 1985–1991. The Groupe d’Epidémiologie Clinique du SIDA en Aquitaine. AIDS Lond Engl. 1992;6:1187–1193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Robertson K, Fiscus S, Wilkins J, van der Horst C, Hall C. Viral Load and Neuropsychological Functioning in HIV Seropositive Individuals:A Preliminary Descriptive Study. J Neuro-AIDS. 1996;1:7–15. doi: 10.1300/j128v01n04_02. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Richardson JL, Martin EM, Jimenez N, Danley K, Cohen M, Carson VL, et al. Neuropsychological functioning in a cohort of HIV infected women: importance of antiretroviral therapy. J Int Neuropsychol Soc JINS. 2002;8:781–793. doi: 10.1017/s1355617702860064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Stern RA, Arruda JE, Somerville JA, Cohen RA, Boland RJ, Stein MD, et al. Neurobehavioral functioning in asymptomatic HIV-1 infected women. J Int Neuropsychol Soc JINS. 1998;4:172–178. doi: 10.1017/s1355617798001726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Patrascu IV, Dumitrescu O. The epidemic of human immunodeficiency virus infection in Romanian children. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1993;9:99–104. doi: 10.1089/aid.1993.9.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ene L, Franklin DR, Burlacu R, Luca AE, Blaglosov AG, Ellis RJ, et al. Neurocognitive functioning in a Romanian cohort of young adults with parenterally-acquired HIV-infection during childhood. J Neurovirol. doi: 10.1007/s13365-014-0275-1. Published Online First: 4 September 2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Beck A, Steer R. Beck depression inventory manual. Psychological Corporation. San Antonio: 1993. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chelune R, Heaton R, Lehman R. Neuropsychological and personality correlates of patient’s complaints of disability. 1986. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J R Stat Soc Ser B Methodol. 1995;57:289–300. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Torres A, Gómez-Gil E, Vidal A, Puig O, Boget T, Salamero M. Gender differences in cognitive functions and influence of sex hormones. Actas Esp Psiquiatr. 2006;34:408–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ruff RM, Parker SB. Gender- and Age-Specific Changes in Motor Speed and Eye-Hand Coordination in Adults: Normative Values for the Finger Tapping and Grooved Pegboard Tests. Percept Mot Skills. 1993;76:1219–1230. doi: 10.2466/pms.1993.76.3c.1219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Schmidt SL, Oliveira RM, Rocha FR, Abreu-Villaca Y. Influences of Handedness and Gender on the Grooved Pegboard Test. Brain Cogn. 2000;44:445–454. doi: 10.1006/brcg.1999.1204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Bryden PJ, Roy EA. Preferential reaching across regions of hemispace in adults and children. Dev Psychobiol. 2006;48:121–132. doi: 10.1002/dev.20120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Peters M, Campagnaro P. Do women really excel over men in manual dexterity? J Exp Psychol Hum Percept Perform. 1996;22:1107–1112. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kilshaw D, Annett M. Right- and left-hand skill I: Effects of age, sex and hand preference showing superior skill in left-handers. Br J Psychol. 1983;74:253–268. doi: 10.1111/j.2044-8295.1983.tb01861.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sivagnanasunderam M, Gonzalez DA, Bryden PJ, Young G, Forsyth A, Roy EA. Handedness throughout the lifespan: cross-sectional view on sex differences as asymmetries change. Front Psychol. 2015:5. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2014.01556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Peters M, Servos P, Day R. Marked sex differences on a fine motor skill task disappear when finger size is used as covariate. Journal of Applied Psychology. 75(1):87–90. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.75.1.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Pratt RD, Nichols S, McKinney N, Kwok S, Dankner WM, Spector SA. Virologic markers of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in cerebrospinal fluid of infected children. J Infect Dis. 1996;174:288–293. doi: 10.1093/infdis/174.2.288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Reger M, Welsh R, Razani J, Martin DJ, Boone KB. A meta-analysis of the neuropsychological sequelae of HIV infection. J Int Neuropsychol Soc JINS. 2002;8:410–424. doi: 10.1017/s1355617702813212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Brew BJ, Pemberton L, Ray J. Can the peripheral blood monocyte count be used as a marker of CSF resistance to antiretroviral drugs? J Neurovirol. 2004;10(Suppl 1):38–43. doi: 10.1080/753312751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ellis RJ, Badiee J, Vaida F, Letendre S, Heaton RK, Clifford D, et al. CD4 nadir is a predictor of HIV neurocognitive impairment in the era of combination antiretroviral therapy. AIDS Lond Engl. 2011;25:1747–1751. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e32834a40cd. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Heaton RK, Clifford DB, Franklin DR, Woods SP, Ake C, Vaida F, et al. HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders persist in the era of potent antiretroviral therapy: CHARTER Study. Neurology. 2010;75:2087–2096. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e318200d727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Foster CJ, Biggs RL, Melvin D, Walters MDS, Tudor-Williams G, Lyall EGH. Neurodevelopmental outcomes in children with HIV infection under 3 years of age. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2006;48:677–682. doi: 10.1017/S0012162206001423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Heaton RK, Franklin DR, Ellis RJ, McCutchan JA, Letendre SL, Leblanc S, et al. HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders before and during the era of combination antiretroviral therapy: differences in rates, nature, and predictors. J Neurovirol. 2011;17:3–16. doi: 10.1007/s13365-010-0006-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kabuba N, Menon JA, Franklin DR, Heaton RK, Hestad KA. HIV− and AIDS-associated neurocognitive functioning in Zambia - a perspective based on differences between the genders. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2016;12:2021–2028. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S105481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Royal W, Cherner M, Burdo TH, Umlauf A, Letendre SL, Jumare J, et al. Associations between Cognition, Gender and Monocyte Activation among HIV Infected Individuals in Nigeria. PloS One. 2016;11:e0147182. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bacon MC, von Wyl V, Alden C, Sharp G, Robison E, Hessol N, et al. The Women’s Interagency HIV Study: an observational cohort brings clinical sciences to the bench. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2005;12:1013–1019. doi: 10.1128/CDLI.12.9.1013-1019.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Holguin A, Banda M, Willen EJ, Malama C, Chiyenu KO, Mudenda VC, et al. HIV-1 effects on neuropsychological performance in a resource-limited country, Zambia. AIDS Behav. 2011;15:1895–1901. doi: 10.1007/s10461-011-9988-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Manly JJ, Smith C, Crystal HA, Richardson J, Golub ET, Greenblatt R, et al. Relationship of ethnicity, age, education, and reading level to speed and executive function among HIV+ and HIV− women: the Women’s Interagency HIV Study (WIHS) Neurocognitive Substudy. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 2011;33:853–863. doi: 10.1080/13803395.2010.547662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Hestad KA, Menon JA, Silalukey-Ngoma M, Franklin DR, Imasiku ML, Kalima K, et al. Sex differences in neuropsychological performance as an effect of human immunodeficiency virus infection: a pilot study in Zambia, Africa. J Nerv Ment Dis. 2012;200:336–342. doi: 10.1097/NMD.0b013e31824cc225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Hagen S, Altfeld M. The X awakens: multifactorial ramifications of sex-specific differences in HIV-1 infection. J Virus Erad. 2016;2:78–81. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Faílde-Garrido JM, Alvarez MR, Simón-López MA. Neuropsychological impairment and gender differences in HIV-1 infection. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2008;62:494–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1819.2008.01841.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Royal W, Cherner M, Burdo TH, Umlauf A, Letendre SL, Jumare J, et al. Associations between Cognition, Gender and Monocyte Activation among HIV Infected Individuals in Nigeria. PloS One. 2016;11:e0147182. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Robertson KR, Kapoor C, Robertson WT, Fiscus S, Ford S, Hall CD. No gender differences in the progression of nervous system disease in HIV infection. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 1999. 2004;36:817–822. doi: 10.1097/00126334-200407010-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Maki PM, Rubin LH, Valcour V, Martin E, Crystal H, Young M, et al. Cognitive function in women with HIV: findings from the Women’s Interagency HIV Study. Neurology. 2015;84:231–240. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000001151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Maki PM, Martin-Thormeyer E. HIV, cognition and women. Neuropsychol Rev. 2009;19:204–214. doi: 10.1007/s11065-009-9093-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Durvasula RS, Miller EN, Myers HF, Wyatt GE. Predictors of neuropsychological performance in HIV positive women. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 2001;23:149–163. doi: 10.1076/jcen.23.2.149.1211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Sacktor NC, Lyles RH, Skolasky RL, Anderson DE, McArthur JC, McFarlane G, et al. Combination antiretroviral therapy improves psychomotor speed performance in HIV-seropositive homosexual men. Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study (MACS) Neurology. 1999;52:1640–1647. doi: 10.1212/wnl.52.8.1640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Ashendorf L, Vanderslice-Barr JL, McCaffrey RJ. Motor tests and cognition in healthy older adults. Appl Neuropsychol. 2009;16:171–176. doi: 10.1080/09084280903098562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Selnes OA, Galai N, McArthur JC, Cohn S, Royal W, Esposito D, et al. HIV infection and cognition in intravenous drug users: long-term follow-up. Neurology. 1997;48:223–230. doi: 10.1212/wnl.48.1.223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lezak MDHD, Bigler ED, Tranel D. Neuropsychological Assessment. Oxford University Press; 2012. [accessed 9 Oct2016]. https://global.oup.com/academic/product/neuropsychological-assessment-9780195395525. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Dluzen DE. Neuroprotective effects of estrogen upon the nigrostriatal dopaminergic system. J Neurocytol. 2000;29:387–399. doi: 10.1023/a:1007117424491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Donahue JE, Stopa EG, Chorsky RL, King JC, Schipper HM, Tobet SA, et al. Cells containing immunoreactive estrogen receptor-alpha in the human basal forebrain. Brain Res. 2000;856:142–151. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(99)02413-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Mozley LH, Gur RC, Mozley PD, Gur RE. Striatal dopamine transporters and cognitive functioning in healthy men and women. Am J Psychiatry. 2001;158:1492–1499. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.158.9.1492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Sacktor N, Nakasujja N, Skolasky R, Robertson K, Wong M, Musisi S, et al. Antiretroviral therapy improves cognitive impairment in HIV+ individuals in sub-Saharan Africa. Neurology. 2006;67:311–314. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000225183.74521.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]